Abstract
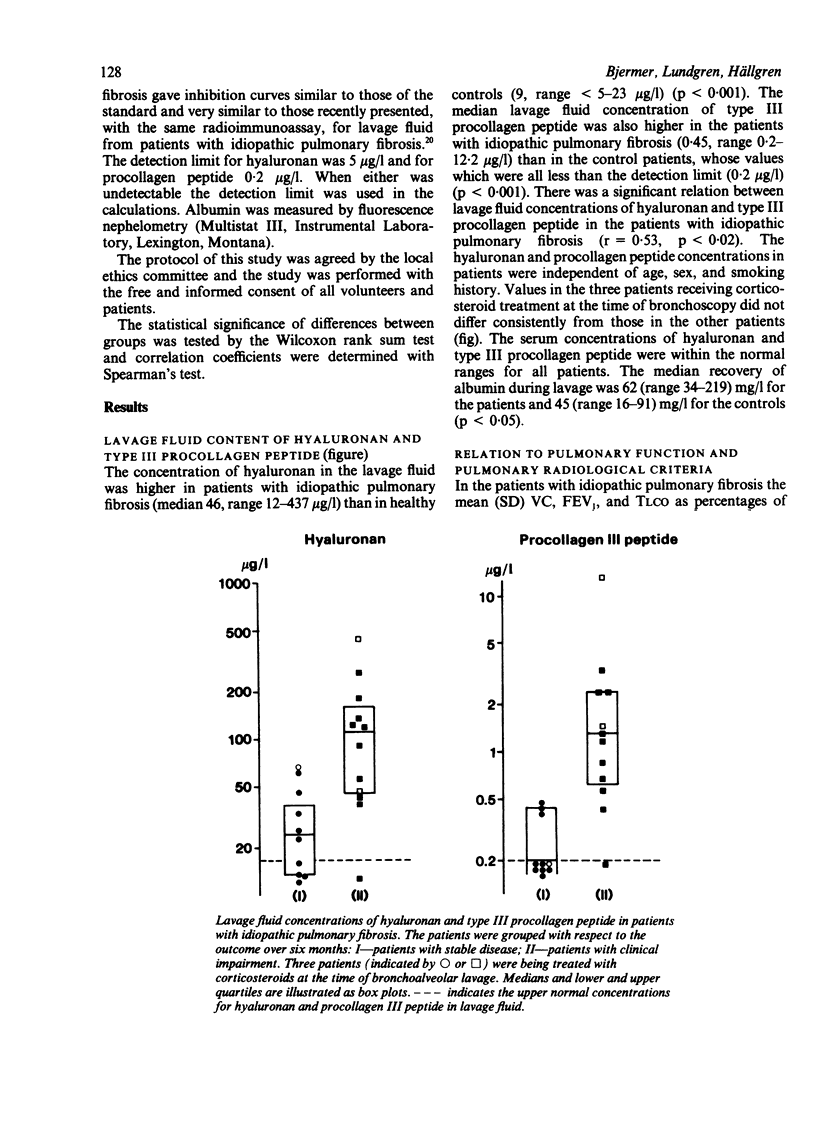
The connective tissue components hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid) and type III procollagen peptide were measured in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in 22 patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and 21 healthy control subjects. The patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis had higher concentrations of hyaluronan (median 46 micrograms/l) and type III procollagen peptide (median 0.45 micrograms/l) than the healthy controls (9 and less than 0.02 micrograms/l; p less than 0.001). The patients had normal serum concentrations of hyaluronan and of the procollagen peptide, and albumin concentrations in lavage fluid similar to those of the control subjects. Neutrophil and lymphocyte counts in lavage fluid were increased on average 10 and two fold respectively in the patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and both correlated with the amount of hyaluronan recovered (p less than 0.05). An inverse correlation was seen between the transfer factor for carbon monoxide and hyaluronan concentrations in lavage fluid in the patients (p less than 0.05). Deterioration in lung function and radiographic progression were seen over six months in 12 of the patients. These patients had higher lavage fluid concentrations of hyaluronan and type III procollagen peptide than the patients whose disease was stable (p less than 0.01). Increased synthesis of hyaluronan and type III procollagen peptide in lung parenchyma may reflect activation or proliferation (or both) of pulmonary fibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and seems to be linked to the severity and activity of the lung disease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGLUND E., BIRATH G., BJURE J., GRIMBY G., KJELLMER I., SANDQVIST L., SODERHOLM B. Spirometric studies in normal subjects. I. Forced expirograms in subjects between 7 and 70 years of age. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Feb;173:185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Hunninghake G. W., Crystal R. G. Human alveolar macrophage growth factor for fibroblasts. Regulation and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):806–822. doi: 10.1172/JCI110677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjermer L., Engström-Laurent A., Lundgren R., Rosenhall L., Hällgren R. Hyaluronate and type III procollagen peptide concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid as markers of disease activity in farmer's lung. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 Oct 3;295(6602):803–806. doi: 10.1136/bmj.295.6602.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjermer L., Engström-Laurent A., Thunell M., Hällgren R. Hyaluronic acid in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in patients with sarcoidosis: relationship to lavage mast cells. Thorax. 1987 Dec;42(12):933–938. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.12.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjermer L., Engström-Laurent A., Thunell M., Hällgren R. The mast cell and signs of pulmonary fibroblast activation in sarcoidosis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;82(3-4):298–301. doi: 10.1159/000234212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjermer L., Thunell M., Hällgren R. Procollagen III peptide in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. A potential marker of altered collagen synthesis reflecting pulmonary disease in sarcoidosis. Lab Invest. 1986 Dec;55(6):654–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantin A. M., Boileau R., Bégin R. Increased procollagen III aminoterminal peptide-related antigens and fibroblast growth signals in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Mar;137(3):572–578. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.3.572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Hance A. J., Keogh B. A. Interstitial lung diseases of unknown cause. Disorders characterized by chronic inflammation of the lower respiratory tract (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):154–166. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Fulmer J. D., Roberts W. C., Moss M. L., Line B. R., Reynolds H. Y. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinical, histologic, radiographic, physiologic, scintigraphic, cytologic, and biochemical aspects. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Dec;85(6):769–788. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-85-6-769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreisin R. B., Schwarz M. I., Theofilopoulos A. N., Stanford R. E. Circulating immune complexes in the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. N Engl J Med. 1978 Feb 16;298(7):353–357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197802162980701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström-Laurent A., Feltelius N., Hällgren R., Wasteson A. Raised serum hyaluronate levels in scleroderma: an effect of growth factor induced activation of connective tissue cells? Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Sep;44(9):614–620. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.9.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Kelman J. A., Fells G., Weinberger S. E., Horwitz A. L., Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Crystal R. G. Collagenase in the lower respiratory tract of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1979 Oct 4;301(14):737–742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197910043011401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamerman D., Wood D. D. Interleukin 1 enhances synovial cell hyaluronate synthesis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1984 Oct;177(1):205–210. doi: 10.3181/00379727-177-1-rc1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hance A. J., Crystal R. G. The connective tissue of lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Nov;112(5):657–711. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.112.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Lawley T. J., Crystal R. G. Mechanisms of neutrophil accumulation in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):259–269. doi: 10.1172/JCI110242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hällgren R., Eklund A., Engström-Laurent A., Schmekel B. Hyaluronate in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: a new marker in sarcoidosis reflecting pulmonary disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Jun 15;290(6484):1778–1781. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6484.1778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk J. M., Bateman E. D., Haslam P. L., Laurent G. J., Turner-Warwick M. Serum type III procollagen peptide concentration in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis and its clinical relevance. Thorax. 1984 Oct;39(10):726–732. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.10.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent U. B., Tengblad A. Determination of hyaluronate in biological samples by a specific radioassay technique. Anal Biochem. 1980 Dec;109(2):386–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90665-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence E. C., Martin R. R., Blaese R. M., Teague R. B., Awe R. J., Wilson R. K., Deaton W. J., Bloom K., Greenberg S. D., Stevens P. M. Increased bronchoalveolar IgG-secreting cells in interstitial lung diseases. N Engl J Med. 1980 May 22;302(21):1186–1188. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198005223022106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low R. B., Cutroneo K. R., Davis G. S., Giancola M. S. Lavage type III procollagen N-terminal peptides in human pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis. Lab Invest. 1983 Jun;48(6):755–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinet Y., Rom W. N., Grotendorst G. R., Martin G. R., Crystal R. G. Exaggerated spontaneous release of platelet-derived growth factor by alveolar macrophages from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):202–209. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLoud T. C., Carrington C. B., Gaensler E. A. Diffuse infiltrative lung disease: a new scheme for description. Radiology. 1983 Nov;149(2):353–363. doi: 10.1148/radiology.149.2.6622676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLoud T. C., Epler G. R., Gaensler E. A., Burke G. W., Carrington C. B. A radiographic classification for sarcoidosis: physiologic correlation. Invest Radiol. 1982 Mar-Apr;17(2):129–138. doi: 10.1097/00004424-198203000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Biochemical characteristics and biological significance of the genetically-distinct collagens. Mol Cell Biochem. 1976 Dec 10;13(3):165–192. doi: 10.1007/BF01731779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Hunninghake G. W., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Production of fibronectin by the human alveolar macrophage: mechanism for the recruitment of fibroblasts to sites of tissue injury in interstitial lung diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Kazmierowski J. A., Roberts W. C., Frank M. M., Crystal R. G. Analysis of cellular and protein content of broncho-alveolar lavage fluid from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):165–175. doi: 10.1172/JCI108615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohde H., Vargas L., Hahn E., Kalbfleisch H., Bruguera M., Timpl R. Radioimmunoassay for type III procollagen peptide and its application to human liver disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;9(6):451–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1979.tb00912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohde H., Vargas L., Hahn E., Kalbfleisch H., Bruguera M., Timpl R. Radioimmunoassay for type III procollagen peptide and its application to human liver disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;9(6):451–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1979.tb00912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd R. M., Haslam P. L., Turner-Warwick M. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Relationships of pulmonary physiology and bronchoalveolar lavage to response to treatment and prognosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Jul;124(1):1–8. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisson J. C., Castor C. W., Klavons J. A. Connective tissue activation. XVIII. Stimulation of hyaluronic acid synthetase activity. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Aug;96(2):189–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., Haslam P. L., Lukoszek A., Townsend P., Allan F., Du Bois R. M., Turton C. W., Collins J. V. Cells, enzymes and interstitial lung disease. The Philip Ellman Lecture. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1981 Jan;15(1):5–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watters L. C., Schwarz M. I., Cherniack R. M., Waldron J. A., Dunn T. L., Stanford R. E., King T. E. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pretreatment bronchoalveolar lavage cellular constituents and their relationships with lung histopathology and clinical response to therapy. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Mar;135(3):696–704. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.3.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaron M., Yaron I., Wiletzki C., Zor U. Interrelationship between stimulation of prostaglandin E and hyaluronate production by poly (I) . poly (C) and interferon in synovial fibroblast culture. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jul-Aug;21(6):694–698. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


