Abstract
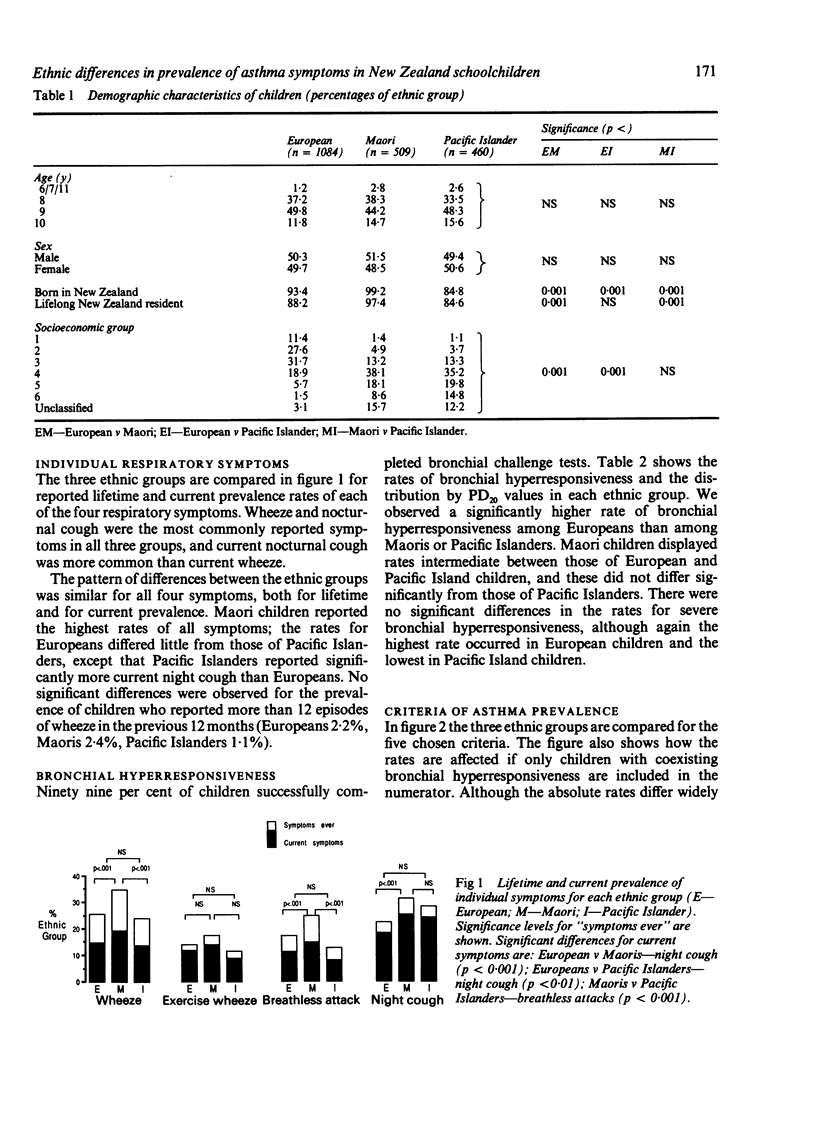
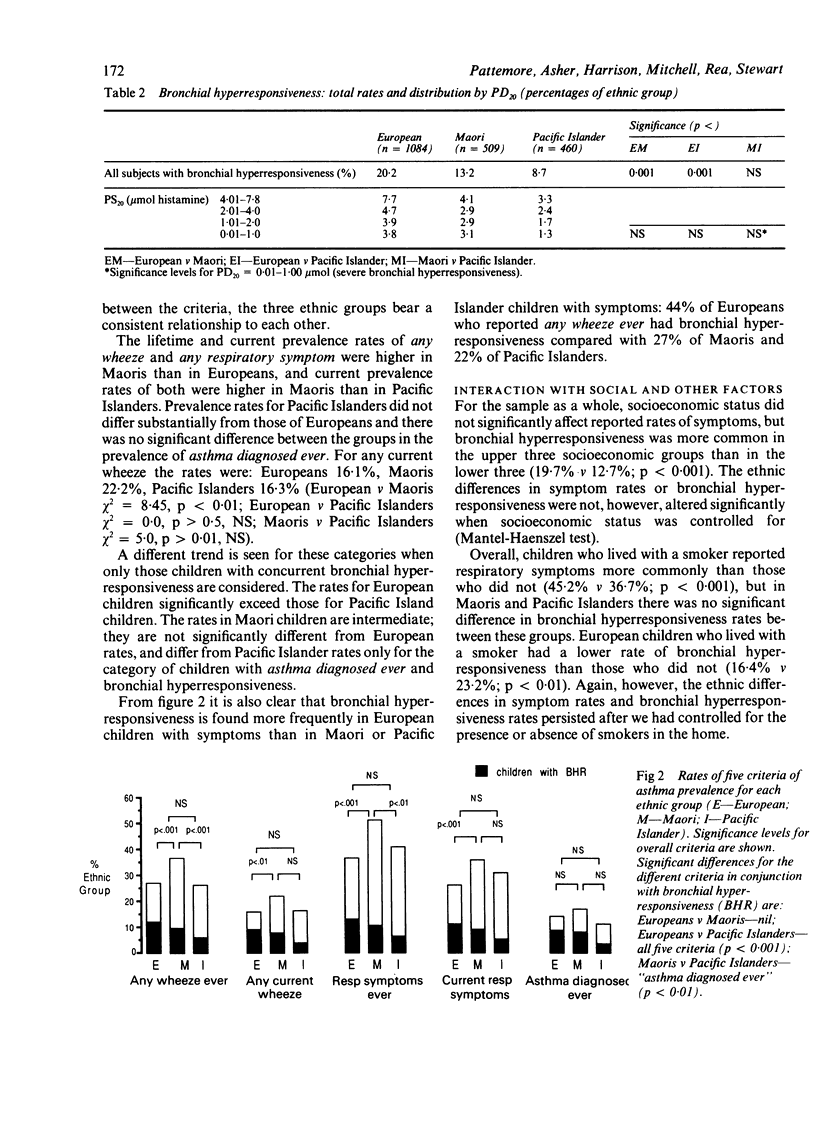
Maoris and Pacific Islanders in New Zealand have a higher asthma mortality and hospital admission rates than Europeans. To determine whether difference in asthma prevalence is the major factor underlying these differences in mortality, 2053 Auckland children aged 7-10 years (European 1084, Maori 509, Pacific Islander 460) were randomly sampled from school classes in the Auckland Urban Area, and studied by questionnaire (completed by parents) and histamine inhalation challenge to assess the provocative dose of histamine causing a 20% fall in FEV1 (PD20). Maoris had the highest prevalence rates of respiratory symptoms, and Europeans had rates similar to Pacific Islanders. For "any current wheeze" for example, the prevalence in Maoris was 22.2% compared with 16.1% and 16.3% in the Europeans and Pacific Islanders. The prevalence of diagnosed asthma was similar in the three groups. When bronchial hyperresponsiveness (defined as a PD20 less than or equal to 7.8 mumol histamine) was considered, Europeans had the highest rates (20%), followed by Maoris (13%), and then Pacific Islanders (8.7%). These differences were not accounted for by differences in socioeconomic status, rates of smoking in the home, age, gender, or height. It is concluded that differences in asthma prevalence do not satisfactorily explain the mortality and admission rate differences, although the higher symptom prevalence in the Maoris could be relevant to the higher mortality rate. Maori and Pacific Island children with symptoms of asthma were less likely to be taking prophylactic medication than European children. It is proposed that differences in management are important factors relevant to the increased mortality and morbidity from asthma in Polynesians.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asher M. I., Pattemore P. K., Harrison A. C., Mitchell E. A., Rea H. H., Stewart A. W., Woolcock A. J. International comparison of the prevalence of asthma symptoms and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Sep;138(3):524–529. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.3.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton W. J., Woolcock A. J., Peat J. K., Sedgwick C. J., Lloyd D. M., Leeder S. R. Prevalence of bronchial hyperresponsiveness in children: the relationship between asthma and skin reactivity to allergens in two communities. Int J Epidemiol. 1986 Jun;15(2):202–209. doi: 10.1093/ije/15.2.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins C. R., Breslin A. B. Upper respiratory tract infections and airway reactivity in normal and asthmatic subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Nov;130(5):879–883. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.5.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laitinen L. A., Kava T. Bronchial reactivity following uncomplicated influenza A infection in healthy subjects and in asthmatic patients. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1980;106:51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell E. A., Borman B. Demographic characteristics of asthma admissions to hospitals. N Z Med J. 1986 Aug 13;99(807):576–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell E. A., Cutler D. R. Paediatric admissions to Auckland Hospital for asthma from 1970-1980. N Z Med J. 1984 Feb 8;97(749):67–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor G. T., Weiss S. T., Tager I. B., Speizer F. E. The effect of passive smoking on pulmonary function and nonspecific bronchial responsiveness in a population-based sample of children and young adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Apr;135(4):800–804. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.4.800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomare E. W. Maori health: new concepts and initiatives. N Z Med J. 1986 Jun 11;99(803):410–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea H. H., Sears M. R., Beaglehole R., Fenwick J., Jackson R. T., Gillies A. J., O'Donnell T. V., Holst P. E., Rothwell R. P. Lessons from the national asthma mortality study: circumstances surrounding death. N Z Med J. 1987 Jan 28;100(816):10–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salome C. M., Peat J. K., Britton W. J., Woolcock A. J. Bronchial hyperresponsiveness in two populations of Australian schoolchildren. I. Relation to respiratory symptoms and diagnosed asthma. Clin Allergy. 1987 Jul;17(4):271–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1987.tb02015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenker M. B., Samet J. M., Speizer F. E. Risk factors for childhood respiratory disease. The effect of host factors and home environmental exposures. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Dec;128(6):1038–1043. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.6.1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears M. R., Jones D. T., Holdaway M. D., Hewitt C. J., Flannery E. M., Herbison G. P., Silva P. A. Prevalence of bronchial reactivity to inhaled methacholine in New Zealand children. Thorax. 1986 Apr;41(4):283–289. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears M. R., O'Donnell T. V., Rea H. H. Asthma mortality and socioeconomic status. N Z Med J. 1985 Sep 11;98(786):765–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears M. R., Rea H. H., Beaglehole R., Gillies A. J., Holst P. E., O'Donnell T. V., Rothwell R. P., Sutherland D. C. Asthma mortality in New Zealand: a two year national study. N Z Med J. 1985 Apr 24;98(777):271–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears M. R., Rea H. H., Fenwick J., Beaglehole R., Gillies A. J., Holst P. E., O'Donnell T. V., Rothwell R. P., Sutherland D. C. Deaths from asthma in New Zealand. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Jan;61(1):6–10. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. C., Beaglehole R., Fenwick J., Jackson R. T., Mullins P., Rea H. H. Death from asthma in Auckland: circumstances and validation of causes. N Z Med J. 1984 Dec 12;97(769):845–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite D. A., Eyles E. F., Tonkin S. L., O'Donnell T. V. Asthma prevalence in Tokelauan children in two environments. Clin Allergy. 1980 Jan;10(1):71–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1980.tb02082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welty C., Weiss S. T., Tager I. B., Muñoz A., Becker C., Speizer F. E., Ingram R. H., Jr The relationship of airways responsiveness to cold air, cigarette smoking, and atopy to respiratory symptoms and pulmonary function in adults. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Aug;130(2):198–203. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.2.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. R., Harris B. J. The effect of personal characteristics on response levels in a health survey. N Z Med J. 1983 Aug 24;96(738):666–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan K., Salome C., Woolcock A. J. Rapid method for measurement of bronchial responsiveness. Thorax. 1983 Oct;38(10):760–765. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.10.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



