Abstract
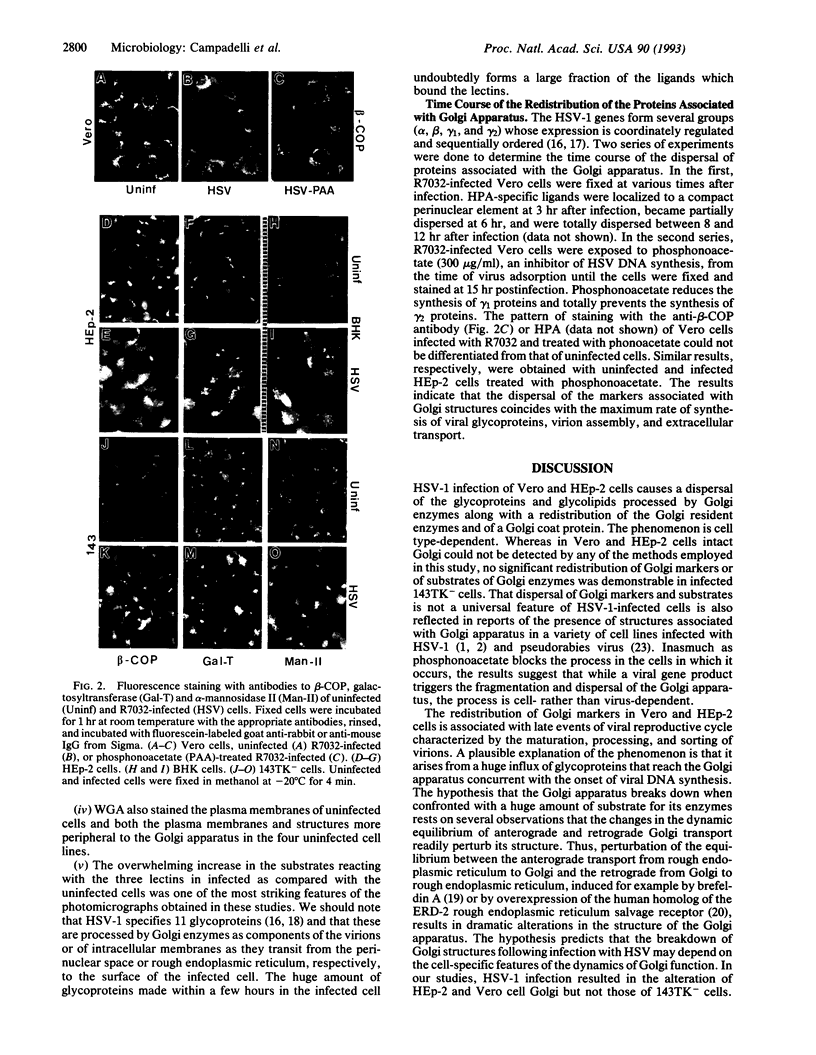
In Vero monkey cells and HEp-2 human epidermoid carcinoma cells infected with herpes simplex virus 1 the proteins beta-COP, galactosyltransferase, and alpha-mannosidase II associated with the Golgi apparatus appear to be associated with numerous smaller structures dispersed throughout the cytoplasm. Concomitantly, the intracytoplasmic ligands of lectins normally associated wholly (Helix pomatia or Ricinus communis agglutinin) or in part (wheat germ agglutinin) with the Golgi apparatus increased in amount and became dispersed. This phenomenon was seen in some of the baby hamster kidney cells analyzed but not in others and not in the human 143TK- cells. The fragmentation and dispersal of the Golgi apparatus was a late event in the reproductive cycle coinciding with virion assembly, processing of viral glycoproteins, and exocytosis from infected cells. The fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus is morphologically different from that seen with brefeldin A and may reflect disequilibration between the anterograde and retrograde Golgi transport caused by the huge influx of viral glycoproteins contained in virions and membranes flowing through the exocytic pathway.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan V. J., Kreis T. E. A microtubule-binding protein associated with membranes of the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2229–2239. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger J. U., Fiete D. Structural determinants of Ricinus communis agglutinin and toxin specificity for oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9795–9799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines J. D., Roizman B. The UL10 gene of herpes simplex virus 1 encodes a novel viral glycoprotein, gM, which is present in the virion and in the plasma membrane of infected cells. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1441–1452. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1441-1452.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. V. Identification of an Fc-binding glycoprotein. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.779-789.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. G., Thurnher M., Müller U. Galactosyltransferase and sialyltransferase are located in different subcellular compartments in HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Nov;173(1):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90352-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campadelli-Fiume G., Lombardo M. T., Foà-Tomasi L., Avitabile E., Serafini-Cessi F. Individual herpes simplex virus 1 glycoproteins display characteristic rates of maturation from precursor to mature form both in infected cells and in cells that constitutively express the glycoproteins. Virus Res. 1988 Apr;10(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campadelli-Fiume G., Poletti L., Dall'Olio F., Serafini-Cessi F. Infectivity and glycoprotein processing of herpes simplex virus type 1 grown in a ricin-resistant cell line deficient in N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase I. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1061–1071. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1061-1071.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee S., Sarkar S. Studies on endoplasmic reticulum--Golgi complex cycling pathway in herpes simplex virus-infected and brefeldin A-treated human fibroblast cells. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90195-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung P., Banfield B. W., Tufaro F. Brefeldin A arrests the maturation and egress of herpes simplex virus particles during infection. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1893–1904. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1893-1904.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dall'Olio F., Malagolini N., Speziali V., Campadelli-Fiume G., Serafini-Cessi F. Sialylated oligosaccharides O-glycosidically linked to glycoprotein C from herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):127–134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.127-134.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debray H., Decout D., Strecker G., Spik G., Montreuil J. Specificity of twelve lectins towards oligosaccharides and glycopeptides related to N-glycosylproteins. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):41–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson J. G., Lippincott-Schwartz J., Bloom G. S., Kreis T. E., Klausner R. D. Dissociation of a 110-kD peripheral membrane protein from the Golgi apparatus is an early event in brefeldin A action. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2295–2306. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duden R., Griffiths G., Frank R., Argos P., Kreis T. E. Beta-COP, a 110 kd protein associated with non-clathrin-coated vesicles and the Golgi complex, shows homology to beta-adaptin. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):649–665. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90248-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S., Murphy L. A., Goldstein I. J., Etzler M. E. Carbohydrate binding specificity of four N-acetyl-D-galactosamine- "specific" lectins: Helix pomatia A hemagglutinin, soy bean agglutinin, lima bean lectin, and Dolichos biflorus lectin. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 14;16(12):2750–2755. doi: 10.1021/bi00631a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller G., Weber K. Golgi detection in mitotic and interphase cells by antibodies to secreted galactosyltransferase. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Nov;142(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu V. W., Shah N., Klausner R. D. A brefeldin A-like phenotype is induced by the overexpression of a human ERD-2-like protein, ELP-1. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):625–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90226-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. Monensin inhibits the processing of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins, their transport to the cell surface, and the egress of virions from infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1102–1112. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1102-1112.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L. C., Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D. Rapid redistribution of Golgi proteins into the ER in cells treated with brefeldin A: evidence for membrane cycling from Golgi to ER. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90685-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low S. H., Wong S. H., Tang B. L., Tan P., Subramaniam V. N., Hong W. Inhibition by brefeldin A of protein secretion from the apical cell surface of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17729–17732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucocq J. M., Warren G. Fragmentation and partitioning of the Golgi apparatus during mitosis in HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3239–3246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02641.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meignier B., Longnecker R., Mavromara-Nazos P., Sears A. E., Roizman B. Virulence of and establishment of latency by genetically engineered deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus 1. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90417-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moremen K. W., Touster O., Robbins P. W. Novel purification of the catalytic domain of Golgi alpha-mannosidase II. Characterization and comparison with the intact enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16876–16885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Cessi F., Dall'Olio F., Scannavini M., Campadelli-Fiume G. Processing of herpes simplex virus-1 glycans in cells defective in glycosyl transferases of the Golgi system: relationship to cell fusion and virion egress. Virology. 1983 Nov;131(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90533-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini-Cessi F., Malagolini N., Dall'Olio F., Pereira L., Campadelli-Fiume G. Oligosaccharide chains of herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein gG.2. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Aug 1;240(2):866–876. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90097-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafini T., Stenbeck G., Brecht A., Lottspeich F., Orci L., Rothman J. E., Wieland F. T. A coat subunit of Golgi-derived non-clathrin-coated vesicles with homology to the clathrin-coated vesicle coat protein beta-adaptin. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):215–220. doi: 10.1038/349215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrisi M. R., Di Lazzaro C., Pavan A., Pereira L., Campadelli-Fiume G. Herpes simplex virus envelopment and maturation studied by fracture label. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):554–561. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.554-561.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whealy M. E., Card J. P., Meade R. P., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Effect of brefeldin A on alphaherpesvirus membrane protein glycosylation and virus egress. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1066–1081. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1066-1081.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]