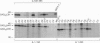Abstract
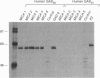
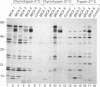
The gamma-aminobutyrate-synthesizing enzyme glutamate decarboxylase (GAD; L-glutamate 1-carboxy-lyase, EC 4.1.1.15) is a major target of autoantibodies associated with both early and late stages of pancreatic beta-cell destruction and development of type 1 diabetes. We have used five monoclonal anti-islet-cell antibodies (MICAs 1,2,3,4, and 6) derived from a newly diagnosed diabetic patient to probe the autoimmune epitopes in the enzyme. All the MICAs specifically recognized the smaller GAD protein, GAD65, and did not recognize the nonallelic GAD67 protein. A series of N-terminal, C-terminal, and internal deletion mutants, as well as protein footprinting, were used to identify the target regions in GAD65. Immunoprecipitation revealed two major native epitope areas in the GAD65 molecule. The first, defined by MICAs 1 and 3, is destroyed by deleting 41 amino acids at the C terminus but is also dependent on intact amino acids 244-295. This epitope (or epitopes) may span both middle and C-terminal domains of the protein. The second conformational epitope region, defined by MICAs 4 and 6, is dependent on intact amino acids 245-295 but is not affected by deletion of 110 amino acids at the C terminus and is therefore confined to domain(s) in the middle of the molecule. MICA 2 recognizes a linear epitope close to the C terminus. Thus, the N-terminal domain of GAD65, which differs most significantly from GAD67, does not harbor the MICA epitopes. Rather subtle amino acid differences in the middle and C-terminal domains define the GAD65-specific autoimmune epitopes. Analysis of sera from 10 type 1 diabetic patients suggests that MICAs 1, 3, 4, and 6 represent a common epitope recognition in this disease, whereas the MICA 2 epitope is rare. Furthermore, autoantibodies in some sera are restricted to the MICA 1/3 epitope, suggesting that this epitope may represent a single dominant epitope in the early phases of beta-cell autoimmunity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. A., Kaufman D. L., Campbell L., Gibbs K. A., Shah S. C., Bu D. F., Erlander M. G., Tobin A. J., Maclaren N. K. Response of peripheral-blood mononuclear cells to glutamate decarboxylase in insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1992 Feb 22;339(8791):458–459. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91061-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K., Scharp D. W., Lacy P. E., Riley W. J. 64,000 Mr autoantibodies as predictors of insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1990 Jun 9;335(8702):1357–1360. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Aanstoot H. J., Christgau S., Reetz A., Solimena M., Cascalho M., Folli F., Richter-Olesen H., De Camilli P., Camilli P. D. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):151–156. doi: 10.1038/347151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Landin M., Kristensen J. K., Srikanta S., Bruining G. J., Mandrup-Poulsen T., de Beaufort C., Soeldner J. S., Eisenbarth G., Lindgren F. Antibodies to a 64,000 Mr human islet cell antigen precede the clinical onset of insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):926–934. doi: 10.1172/JCI112903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Nielsen J. H., Marner B., Bilde T., Ludvigsson J., Lernmark A. Autoantibodies in newly diagnosed diabetic children immunoprecipitate human pancreatic islet cell proteins. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):167–169. doi: 10.1038/298167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bu D. F., Erlander M. G., Hitz B. C., Tillakaratne N. J., Kaufman D. L., Wagner-McPherson C. B., Evans G. A., Tobin A. J. Two human glutamate decarboxylases, 65-kDa GAD and 67-kDa GAD, are each encoded by a single gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2115–2119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. C., Gottlieb D. I. Characterization of the proteins purified with monoclonal antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase. J Neurosci. 1988 Jun;8(6):2123–2130. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-06-02123.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christgau S., Aanstoot H. J., Schierbeck H., Begley K., Tullin S., Hejnaes K., Baekkeskov S. Membrane anchoring of the autoantigen GAD65 to microvesicles in pancreatic beta-cells by palmitoylation in the NH2-terminal domain. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;118(2):309–320. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christgau S., Schierbeck H., Aanstoot H. J., Aagaard L., Begley K., Kofod H., Hejnaes K., Baekkeskov S. Pancreatic beta cells express two autoantigenic forms of glutamic acid decarboxylase, a 65-kDa hydrophilic form and a 64-kDa amphiphilic form which can be both membrane-bound and soluble. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21257–21264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. R., Brown T. J., Cassidy D. Binding of antibodies in sera from Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients to glutamate decarboxylase from rat tissues. Evidence for antigenic and non-antigenic forms of the enzyme. Diabetologia. 1992 Apr;35(4):380–384. doi: 10.1007/BF00401206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. R., Vohra G., Champagne P., Daneman D., Delovitch T. L. Distinct antibody specificities to a 64-kD islet cell antigen in type 1 diabetes as revealed by trypsin treatment. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):789–794. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M., Landin-Olsson M., Sundkvist G., Dahlquist G., Lernmark A., Baekkeskov S. Antibodies to a Mr-64,000 islet cell protein in Swedish children with newly diagnosed type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia. 1988 Aug;31(8):597–602. doi: 10.1007/BF00264766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke A. An overview on possible mechanisms of destruction of the insulin-producing beta cell. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;164:125–142. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75741-9_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deres K., Schild H., Wiesmüller K. H., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. In vivo priming of virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes with synthetic lipopeptide vaccine. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):561–564. doi: 10.1038/342561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz J. L., Ways J., Hammonds P. T-lymphocyte lines specific for glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) the 64K beta-cell antigen of IDDM. Diabetes. 1992 Jan;41(1):118–121. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlander M. G., Tillakaratne N. J., Feldblum S., Patel N., Tobin A. J. Two genes encode distinct glutamate decarboxylases. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90077-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb D. I., Chang Y. C., Schwob J. E. Monoclonal antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8808–8812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsen A. E., Hagopian W. A., Grubin C. E., Dube S., Disteche C. M., Adler D. A., Bärmeier H., Mathewes S., Grant F. J., Foster D. Cloning and primary structure of a human islet isoform of glutamic acid decarboxylase from chromosome 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8337–8341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsen A. E., Hagopian W. A., Petersen J. S., Boel E., Dyrberg T., Grubin C. E., Michelsen B. K., Madsen O. D., Lernmark A. Recombinant glutamic acid decarboxylase (representing the single isoform expressed in human islets) detects IDDM-associated 64,000-M(r) autoantibodies. Diabetes. 1992 Oct;41(10):1355–1359. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.10.1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann P. V., Forsthuber T., Miller A., Sercarz E. E. Spreading of T-cell autoimmunity to cryptic determinants of an autoantigen. Nature. 1992 Jul 9;358(6382):155–157. doi: 10.1038/358155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeilage L. J., Macmillan E. M., Whittingham S. F. Mapping of epitopes on the La(SS-B) autoantigen of primary Sjögren's syndrome: identification of a cross-reactive epitope. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3829–3835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter W., Endl J., Eiermann T. H., Brandt M., Kientsch-Engel R., Thivolet C., Jungfer H., Scherbaum W. A. Human monoclonal islet cell antibodies from a patient with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus reveal glutamate decarboxylase as the target antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8467–8471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. H., Case M. C., Brooks C. G. Palmitic acid conjugation of a protein antigen enhances major histocompatibility complex class II-restricted presentation to T cells. Immunology. 1992 Aug;76(4):593–598. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheshberadaran H., Payne L. G. Protein antigen-monoclonal antibody contact sites investigated by limited proteolysis of monoclonal antibody-bound antigen: protein "footprinting". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):1–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solimena M., Folli F., Aparisi R., Pozza G., De Camilli P. Autoantibodies to GABA-ergic neurons and pancreatic beta cells in stiff-man syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 31;322(22):1555–1560. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005313222202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair E. W., Burch J. A., Jr, Ward M. M., Keene J. D., Pisetsky D. S. Temporal correlation of antibody responses to different epitopes of the human La autoantigen. J Clin Invest. 1990 Feb;85(2):515–521. doi: 10.1172/JCI114467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]