Abstract
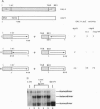
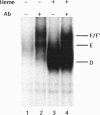
The yeast transcriptional activator HAP1 contains a DNA-binding domain homologous to the zinc finger of GAL4 and an adjacent regulatory domain that blocks DNA binding in the absence of the inducer heme. We show that short HAP1 fragments containing the zinc finger are unable to bind to DNA but can be rescued by antibody to the HAP1 zinc finger. These fragments are missing a coiled-coil sequence similar to that within the dimerization domain of GAL4 and dimerization domains of myosin heavy chain. We surmise that the antibody promotes DNA binding by bringing together two monomers. Interestingly, the antibody will also promote DNA binding of a larger HAP1 fragment containing the DNA-binding and the heme-regulatory domains. This suggests that the regulatory domain acts by preventing dimerization of HAP1 in the absence of heme. Consistent with this view is an in vivo assay that also reveals that heme promotes HAP1 dimerization in yeast cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson S. J., Stewart M. Molecular basis of myosin assembly: coiled-coil interactions and the role of charge periodicities. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1991;14:7–10. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1991.supplement_14.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum J. A., Geever R., Giles N. H. Expression of qa-1F activator protein: identification of upstream binding sites in the qa gene cluster and localization of the DNA-binding domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1256–1266. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien C. T., Bartel P. L., Sternglanz R., Fields S. The two-hybrid system: a method to identify and clone genes for proteins that interact with a protein of interest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9578–9582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawell S. E., Lees J. A., White R., Parker M. G. Characterization and colocalization of steroid binding and dimerization activities in the mouse estrogen receptor. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):953–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90343-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Ptashne M. Mutants of GAL4 protein altered in an activation function. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvorsen Y. D., Nandabalan K., Dickson R. C. Identification of base and backbone contacts used for DNA sequence recognition and high-affinity binding by LAC9, a transcription activator containing a C6 zinc finger. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1777–1784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. A model fungal gene regulatory mechanism: the GAL genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):458–476. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.458-476.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L. Protein structural domains in the Caenorhabditis elegans unc-54 myosin heavy chain gene are not separated by introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4253–4257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuragawa Y., Yanagisawa M., Inoue A., Masaki T. Two distinct nonmuscle myosin-heavy-chain mRNAs are differentially expressed in various chicken tissues. Identification of a novel gene family of vertebrate non-sarcomeric myosin heavy chains. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Oct 1;184(3):611–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketchum A. S., Stewart C. T., Stewart M., Kiehart D. P. Complete sequence of the Drosophila nonmuscle myosin heavy-chain transcript: conserved sequences in the myosin tail and differential splicing in the 5' untranslated sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6316–6320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Michels C. A. The MAL63 gene of Saccharomyces encodes a cysteine-zinc finger protein. Curr Genet. 1988 Oct;14(4):319–323. doi: 10.1007/BF00419988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Guarente L. Mutations that alter transcriptional activation but not DNA binding in the zinc finger of yeast activator HAPI. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):200–203. doi: 10.1038/342200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Pfeifer K., Powell L., Guarente L. Internal deletions in the yeast transcriptional activator HAP1 have opposite effects at two sequence elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4524–4528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb P., McKnight S. L. Diversity and specificity in transcriptional regulation: the benefits of heterotypic dimerization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90167-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. A new class of yeast transcriptional activators. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmorstein R., Carey M., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. DNA recognition by GAL4: structure of a protein-DNA complex. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):408–414. doi: 10.1038/356408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Karn J. Periodic charge distributions in the myosin rod amino acid sequence match cross-bridge spacings in muscle. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):226–231. doi: 10.1038/299226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael S. F., Kilfoil V. J., Schmidt M. H., Amann B. T., Berg J. M. Metal binding and folding properties of a minimalist Cys2His2 zinc finger peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4796–4800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Mechanism of specificity in the Fos-Jun oncoprotein heterodimer. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):699–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Arcangioli B., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator competes with the factor RC2 for binding to the upstream activation site UAS1 of the CYC1 gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90750-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Kim K. S., Kogan S., Guarente L. Functional dissection and sequence of yeast HAP1 activator. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90903-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Prezant T., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator binds to two upstream activation sites of different sequence. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90751-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorkin A., Carpenter G. Dimerization of internalized epidermal growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23453–23460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte B., Guarente L. HAP1 positive control mutants specific for one of two binding sites. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):2001–2009. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]