Abstract
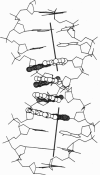
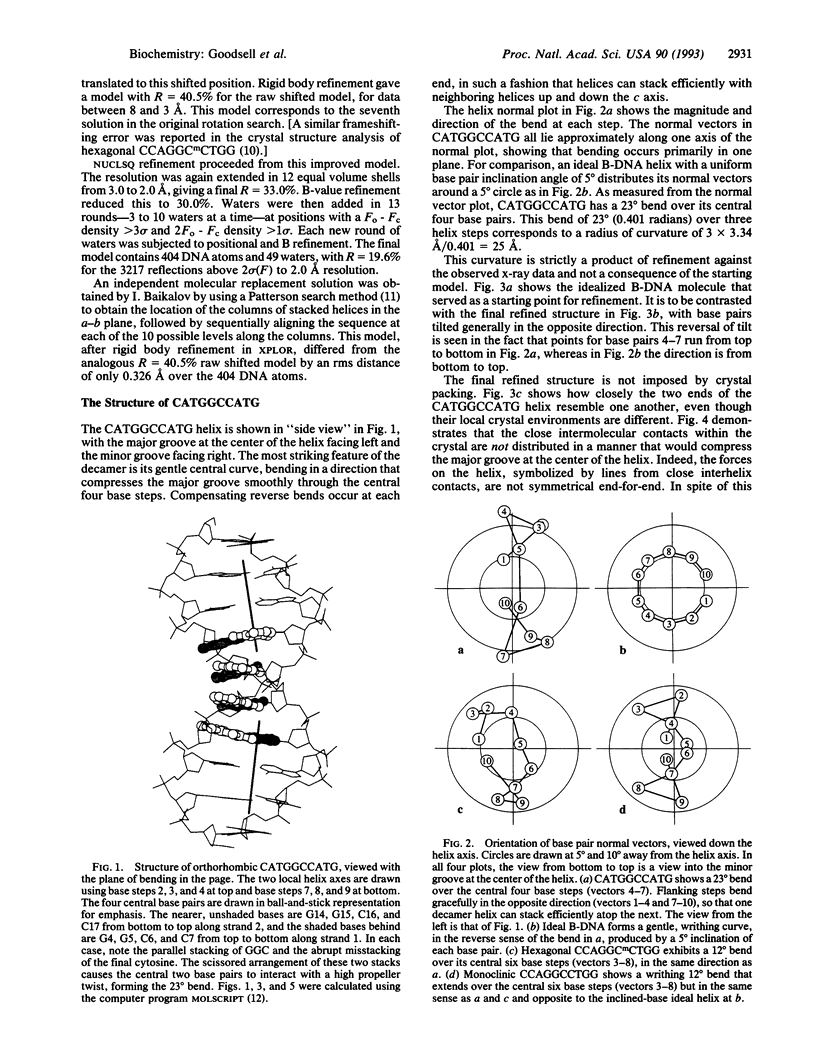
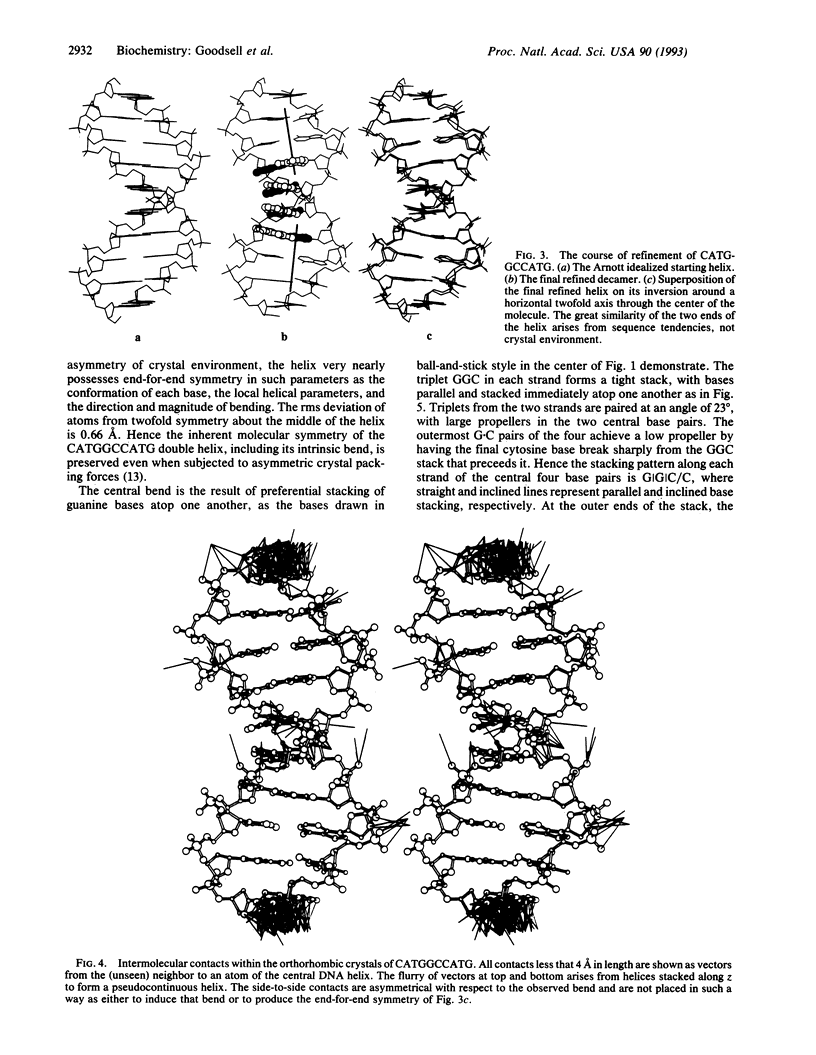
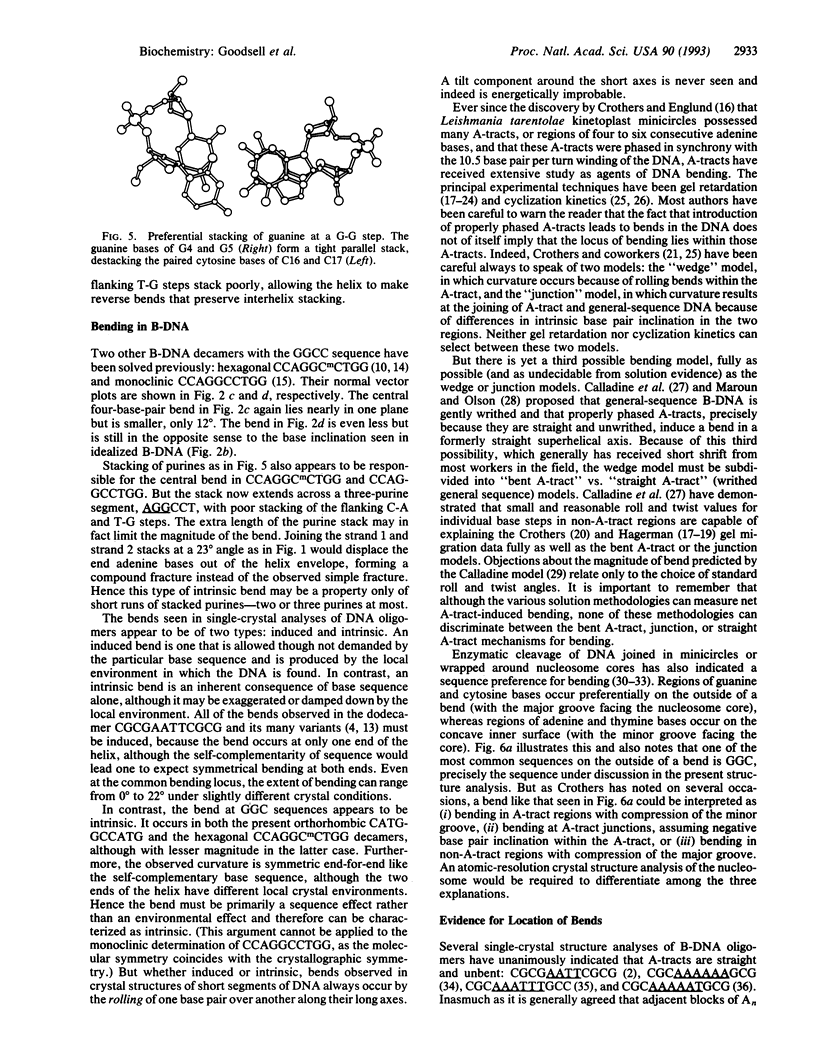
The single-crystal x-ray analysis of orthorhombic CATGGCCATG has revealed a previously unrecognized mode of intrinsic bending in DNA. The decamer shows a smooth bend of 23 degrees over the central four base pairs, caused by preferential stacking interactions at guanine bases. The bend is produced by a roll of base pairs along their long axes, in a direction that compresses the wide major groove of the double helix. This major-groove-compressing bend at GGC, plus the abundant crystallographic evidence that runs of successive adenine bases (A-tracts) are straight and unbent, requires rethinking of the models most commonly invoked to explain A-tract bending. A decade of excellent experimental work involving gel migration experiments, cyclization kinetics, and nucleosome phasing has clearly established that introduction of short A-tracts into a general DNA sequence in synchrony with the natural repeat of the helix leads to bending. But it does not logically and inevitably follow that the actual bending is to be found within these introduced A-tracts or even at junctions with general-sequence B-DNA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R., Drew H. R., McCall M. J. The intrinsic curvature of DNA in solution. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):127–137. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90444-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll M., Frederick C. A., Wang A. H., Rich A. A bifurcated hydrogen-bonded conformation in the d(A.T) base pairs of the DNA dodecamer d(CGCAAATTTGCG) and its complex with distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8385–8389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Drak J. Global features of DNA structure by comparative gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:46–71. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12005-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Drak J., Kahn J. D., Levene S. D. DNA bending, flexibility, and helical repeat by cyclization kinetics. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:3–29. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M., Haran T. E., Nadeau J. G. Intrinsically bent DNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7093–7096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiGabriele A. D., Sanderson M. R., Steitz T. A. Crystal lattice packing is important in determining the bend of a DNA dodecamer containing an adenine tract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1816–1820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Kopka M. L., Pjura P. A random-walk model for helix bending in B-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7099–7103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Kopka M. L., Pjura P. A stochastic model for helix bending in B-DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Dec;1(3):755–771. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekmann S. Analyzing DNA curvature in polyacrylamide gels. Methods Enzymol. 1992;212:30–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)12004-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA bending and its relation to nucleosome positioning. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):773–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. Synthetic DNA bending sequences increase the rate of in vitro transcription initiation at the Escherichia coli lac promoter. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):217–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90563-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzeskowiak K., Yanagi K., Privé G. G., Dickerson R. E. The structure of B-helical C-G-A-T-C-G-A-T-C-G and comparison with C-C-A-A-C-G-T-T-G-G. The effect of base pair reversals. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8861–8883. doi: 10.2210/pdb1d23/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Evidence for the existence of stable curvature of DNA in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4632–4636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Sequence dependence of the curvature of DNA: a test of the phasing hypothesis. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7033–7037. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Sequence-directed curvature of DNA. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):449–450. doi: 10.1038/321449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann U., Alings C. Crystallographic study of one turn of G/C-rich B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 20;210(2):369–381. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann U., Alings C. The conformation of a B-DNA decamer is mainly determined by its sequence and not by crystal environment. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):35–43. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07918.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann U., Hahn M. C-C-A-G-G-C-m5C-T-G-G. Helical fine structure, hydration, and comparison with C-C-A-G-G-C-C-T-G-G. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7332–7341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Drak J., Rice J. A., Crothers D. M. Determination of the extent of DNA bending by an adenine-thymine tract. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4227–4234. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M., Hartley J. A., Pon R. T., Krowicki K., Lown J. W. Sequence specific molecular recognition by a monocationic lexitropsin of the decadeoxyribonucleotide d-[CATGGCCATG]2: structural and dynamic aspects deduced from high field 1H-NMR studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):665–684. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroun R. C., Olson W. K. Base sequence effects in double-helical DNA. III. Average properties of curved DNA. Biopolymers. 1988 Apr;27(4):585–603. doi: 10.1002/bip.360270404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H. C., Finch J. T., Luisi B. F., Klug A. The structure of an oligo(dA).oligo(dT) tract and its biological implications. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):221–226. doi: 10.1038/330221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. Sequence-dependent helical periodicity of DNA. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):378–380. doi: 10.1038/292378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satchwell S. C., Drew H. R., Travers A. A. Sequence periodicities in chicken nucleosome core DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 20;191(4):659–675. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90452-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Dumas P., Moras D. Crystallographic refinement of yeast aspartic acid transfer RNA. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):119–145. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing R., Drew H., Takano T., Broka C., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. Crystal structure analysis of a complete turn of B-DNA. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):755–758. doi: 10.1038/287755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. Catabolite activator protein-induced DNA bending in transcription initiation. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):201–215. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90562-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. Comparative gel electrophoresis measurement of the DNA bend angle induced by the catabolite activator protein. Biopolymers. 1990 Jan;29(1):29–38. doi: 10.1002/bip.360290106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]