Cisplatin is an essential part of testicular cancer treatment. We investigated whether long-term exposure to circulating platinum (Pt) plays a role in the development of late effects in survivors. We assessed Pt decay in samples collected 1–13 years after chemotherapy. Renal function is a strong determinant of exposure to Pt. Higher exposure to Pt is associated with an increased prevalence of adverse effects hypogonadism and hypertension.
Keywords: germ cell cancer, platinum, nephrotoxicity, long-term toxicity, BEP
Abstract
Background
The success of cisplatin-based (Platinol, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, New York, NY, USA) chemotherapy for testicular cancer comes at the price of long-term and late effects related to healthy tissue damage. We assessed and modelled serum platinum (Pt) decay after chemotherapy and determined relationships between long-term circulating Pt levels and known late effects.
Patients and methods
In 99 testicular cancer survivors, treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy, serum and 24-h urine samples were collected during follow-up (1–13 years after treatment). To build a population pharmacokinetic model, measured Pt data were simultaneously analysed, together with cisplatin dose, age, weight and height using the NONMEM software. Based on this model, area under the curve between 1 and 3 years after treatment (Pt AUC1–3 years) was calculated for each patient. Predicted long-term Pt exposure was related to renal function and to late effects of treatment assessed median 9 (3–15) years after chemotherapy.
Results
Decay of Pt was best described by a two-compartment model. Mean terminal T1/2 was 3.7 (range 2.5–5.2) years. Pt AUC1–3 years correlated with cumulative cisplatin dose, and creatinine clearance before and 1 year after treatment. Patients with paraesthesia had higher Pt AUC1–3 years (30.9 versus 27.0 µg/l month) compared with those without paraesthesia (P = 0.021). Patients with hypogonadism, elevated LDL-cholesterol levels or hypertension also had higher Pt AUC1–3 years.
Conclusions
Renal function before and after cisplatin treatment is an important determinant of long-term Pt exposure. Known long-term effects of testicular cancer treatment, such as paraesthesia, hypogonadism, hypercholesterolaemia and hypertension, are associated with long-term circulating Pt exposure.
introduction
Since the introduction of platinum (Pt)-based chemotherapy, metastatic testicular cancer has become a curable disease with an excellent prognosis. However, late effects of the treatment may compromise the quality of life after treatment [1]. Several studies have shown that testicular cancer survivors are prone to develop cardiovascular morbidity and experience metabolic changes [2, 3]. Cardiovascular risk factors, in particular clustered in the metabolic syndrome, are more prevalent in testicular cancer survivors compared with age-matched controls. Already during the first years after chemotherapy, a subgroup of testicular cancer survivors appears to develop an adverse cardiovascular risk profile [4]. The underlying mechanisms have not yet been elucidated.
A decade ago, Gietema et al. [5] found that long-term circulating Pt levels remained detectable up to 20 years after cisplatin combination chemotherapy. Other studies have confirmed the presence of circulating Pt residuals in serum after Pt-based treatment [6, 7]. The role of long-term exposure to circulating Pt in the development of cardiovascular disease in testicular cancer survivors is not clear. Moreover, the pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic characteristics of long-term decay of Pt are also largely unknown.
We hypothesised that higher exposure to circulating Pt during follow-up is associated with a higher prevalence of late adverse effects of treatment. The primary aim of our study was to develop a population PK model to characterise the long-term decay of Pt. This population PK model is based on individual cisplatin dose, age, weight, height and body surface area at the start of treatment combined with measured Pt concentrations in samples collected at various time-points during follow-up after cisplatin-based chemotherapy for testicular cancer. The second aim was to use the PK model to determine the influence of various treatment-related factors on the modelled decay of Pt concentrations from individual patients and to determine the association between estimated Pt exposure and known long-term effects of cisplatin-based chemotherapy.
methods
study population and design
Non-seminomatous testicular cancer patients treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy at the University Medical Centre Groningen between 1988 and 2000 were eligible. Refractory or recurrent disease, radiotherapy, a history of cardiovascular events before diagnosis and psychosocial issues were exclusion criteria (supplementary Figure S1, available at Annals of Oncology online). The Medical Ethics Committee of the hospital approved the study protocol and all patients gave their written informed consent.
Between 1997 and 2002, serum and 24-h urine samples were collected at regular follow-up visits, starting at least 1 year after treatment. The timing of collection was diverse in order to obtain data in different phases of Pt decay. One of the serum samples was taken simultaneously with a 24-h urine sample. In total, 240 serum samples from 98 patients (one to three samples per patient) were collected and analysed. Median interval between the start of chemotherapy and the date of sample was 5.0 (range 0.9–13.2) years. A single 24-h urine sample was collected from 91 patients, with a median interval of 6.6 (range 2.8–13.2) years after chemotherapy.
Serum creatinine levels were measured before chemotherapy and 1 year after the start of chemotherapy. Creatinine clearance (CRCL), an indicator of renal function, was calculated using the Cockcroft-Gault formula.
At median 9 (range 3–15) years after chemotherapy, a follow-up assessment was carried out at the outpatient clinic in 96 patients to assess known late effects of treatment, such as an adverse metabolic profile, presence of paraesthesia and Raynaud's phenomenon [2, 4].
quantification of Pt concentration in serum and urine
Serum and 24-h urine samples were stored at −20°C until Pt measurement. Pt concentrations were measured in serum and urine samples by a sensitive procedure during which high-pressure decomposition of samples is followed by an adsorptive voltammetric measurement. The lower limit of quantification of Pt was 6 pg/g serum. Measurements were done in duplicate; the coefficient of variation and day-to-day variation were 6% and 5%, respectively [5].
population PK analysis
The measured serum Pt concentrations and 24-h urinary excretion rates were simultaneously analysed by non-linear mixed-effects modelling (NONMEM software, Version VI, ICON Development Solutions, Hanover, MD, USA) using a one- or two-compartment model. We assumed that the treatment period (9–12 weeks) was negligible compared with the duration of follow-up. Since a major fraction of the dose was excreted in the urine before the first measurement, the PK analysis was restricted to the fraction remaining in the body after the pre-measurement phase. An apparent bioavailability factor F1 was therefore added as a parameter in the model. We assumed that Pt was cleared solely via urinary excretion, so the urinary excretion rate was estimated from clearance multiplied by the estimated serum concentration. The first-order conditional estimation method was used throughout. PLT Tools (PLTsoft, San Francisco, CA, USA) were used as a graphical user interface. To evaluate the final model, a bootstrap analysis was carried out, based on 1000 sets of 99 patients each, randomly selected from the available 99 patients, and non-parametric 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were obtained.
assessment of cardiometabolic status during follow-up
Patients were asked about the presence or absence of paraesthesia and Raynaud's phenomenon. Paraesthesia was scored as the presence or absence of grade I sensory neuropathy according to Common Toxicity Criteria 2.0. It was defined as the presence of abnormal cutaneous sensations of tingling, numbness, pressure, cold and warmth that are experienced in the absence of a stimulus. The development of Raynaud's phenomenon after chemotherapy was defined as occurrence of peripheral discomfort and at least biphasic skin colour change in fingers or hands (or toes or feet) after cold exposition, since start of treatment.
Body weight and height, waist and hip circumference, and blood pressure were measured during a physical examination at the outpatient clinic. Lipids, testosterone, luteinizing hormone (LH) and von Willebrand factor (vWF) were measured in blood samples. All blood samples were drawn in the morning after an overnight fast.
Hypogonadism was defined as serum testosterone <10 nmol/l or LH >10 U/l or use of testosterone suppletion (with exclusion of patients using suppletion because of bilateral orchidectomy). Increased low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol was defined as LDL-cholesterol >4.1 mmol/l or use of statins (National Cholesterol Education Program—Adult Treatment Panel III, NCEP-ATP III) [8]. Hypertension was defined as newly diagnosed, i.e. after chemotherapy, blood pressure ≥130/85 mmHg or use of antihypertensive medication (metabolic syndrome criteria, American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute) [9].
statistical analysis
Continuous variables were described with median and range. Categorical variables were described with counts and proportions. Levels of lipids, insulin, glucose, testosterone and vWF were non-normally distributed and were log-transformed for statistical analysis. Univariate analysis was carried out with the Student's t-test. Associations between two continuous variables were assessed by the Pearson's correlation coefficient. Linear-by-linear association χ2 test was used to test categorical distributions. Multiple logistic regression analyses on the presence of paraesthesia, Raynaud's phenomenon, hypogonadism, increased LDL-cholesterol and increased blood pressure were carried out to assess the effect of long-term Pt exposure and adjust for age, body mass index (BMI) and renal function. All tests were carried out two-sided and conducted at the 0.05 significance level. Statistical analyses were carried out using IBM SPSS version 20 (IBM, Chicago, IL, USA).
results
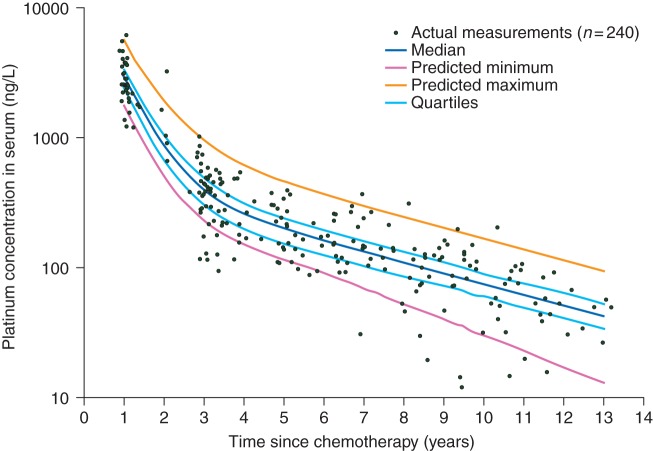
Characteristics of the study population are summarised in Table 1. The median cumulative dose of cisplatin was 809 (range 554–1713) mg. Measured serum Pt concentrations are shown in Figure 1. Circulating Pt levels declined rapidly between 1 and 3 years after treatment.
Table 1.
Demographic, diagnostic, treatment-related and follow-up characteristics of study participants
| Study population characteristics | n/median | %/range |
|---|---|---|
| Cohort size | 96 | |
| Age at start chemotherapy (years) | 29 | 17–53 |
| Age at follow-up (years) | 39 | 23–64 |
| Year of treatment | 1988–2000 | |
| Disease stage (Royal Marsden Classification) | ||
| II | 51 | 53 |
| III | 5 | 5 |
| IV | 40 | 42 |
| IGCCCG risk group | ||
| Good | 54 | 56 |
| Intermediate | 33 | 34 |
| Poor | 9 | 9 |
| Chemotherapeutic regimen | ||
| 4× BEP | 32 | 33 |
| 4× EP | 8 | 8 |
| 3× BEP/1× EP | 50 | 52 |
| Other cisplatin-based regimen | 6 | 6 |
| Cumulative cisplatin dose (mg) | 809 | 554–1713 |
| Cumulative cisplatin dose (mg/m2) | 400 | 275–800 |
| Prevalence of late effects of treatment | n | a |
| Persisting paraesthesia | 33 | 35 |
| Raynaud's phenomenon | 23 | 25 |
| Hypogonadism (T < 10 nmol/l or LH >10 U/l or suppletion) | 19 | 20 |
| Hypercholesterolaemia (≥6.5 mmol/l or statin) | 23 | 25 |
| Increased LDL-cholesterol (≥4.1 mmol/l or statin) | 37 | 40 |
| Increased blood pressure (≥130/85 mmHg or antihypertensive) | 63 | 68 |
BEP: bleomycin, etoposide and cisplatin; EP: etoposide and cisplatin; IGCCCG: International Germ Cell Cancer Collaborative Group Classification; T: testosterone; LH: luteinizing hormone, LDL: low-density lipoprotein.
aPercentages for individual characteristics calculated on total number of participants on whom information was available.
Figure 1.
Circulating serum platinum measurements (n = 240) and predicted curves 1–13 years after chemotherapy according to the population pharmacokinetic model. Predicted maximum and minimum are curves of the highest and lowest predicted decay based on the model.
population PK model
In addition to the measured serum Pt concentrations and urinary excretion rates, administered cumulative cisplatin dose (mg/m², converted to amount Pt in mg), age at the start of chemotherapy (years), body surface area (m²), height (m) and weight (kg) were included in the population PK analysis. The observed decay in Pt levels was best described by a two-compartment model with log-normally distributed interindividual variability in CL (clearance), V2 (volume of peripheral compartment) and F1 (apparent bioavailability). Interindividual variability in V1 (volume of central compartment) and Q (intercompartmental clearance), or inclusion of demographic covariates (including age, weight and height), did not result in significant improvement of the objective function value. Proportional residual error in the final model was 34%, which is acceptable and comparable with other long-term PK models [10]. Mean terminal T1/2 was 3.7 (range 2.5–5.2) years. The final population PK model is summarised in supplementary Table S1, available at Annals of Oncology online.
Based on the model, the individual Pt concentration curve for each patient was calculated using the two-compartment model equation , where C1, C2, λ1 and λ2 are the fractional coefficients and exponents of the corresponding bi-exponential equation. The median curve for the total study population is depicted in Figure 1. Subsequently, based on the model equation, individual Pt concentrations were calculated for every patient at different moments in time (supplementary Table S2, available at Annals of Oncology online). The area under the curve (AUC, µg/l months) between 1 and 3 years after chemotherapy (Pt AUC1–3 years) was calculated and used as an estimate of long-term exposure to Pt.
treatment and renal function as determinants of long-term Pt exposure
The total administered dose cisplatin (mg) correlated significantly with long-term Pt AUC1–3 years (r = 0.517, P < 0.001; supplementary Table S3, available at Annals of Oncology online). Age at the start of chemotherapy correlated with long-term Pt AUC, but this correlation disappeared after adjusting for renal function. No correlation was found between Pt AUC1–3 years and weight, BMI and body surface area at the start of chemotherapy.
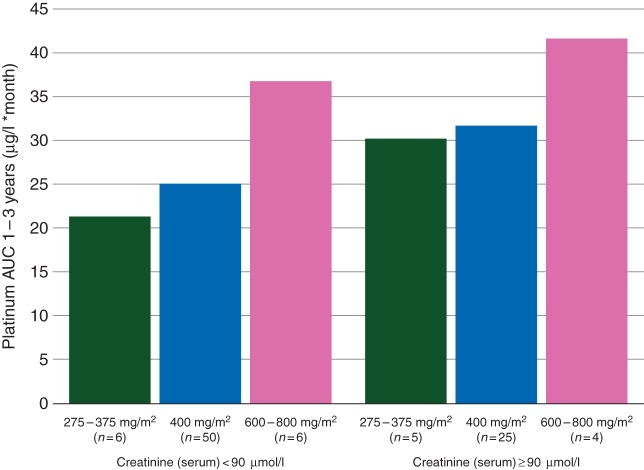
Median serum creatinine level before chemotherapy was significantly lower than 1 year after chemotherapy (74 versus 86 µmol/l, P < 0.001). At the follow-up visit median 9 (range 3–15) years after treatment, median serum creatinine was 88 µmol/l. Pt AUC1–3 years was negatively correlated with CRCL before chemotherapy (r = −0.213, P = 0.040). Also, Pt AUC1–3 years correlated negatively with CRCL 1 year after chemotherapy (r = −0.272, P = 0.008) and at follow-up (r = −0.276, P = 0.007). AUC values in different groups based on renal function and cumulative cisplatin dose are visualised in Figure 2.
Figure 2.
Platinum area under the curve (AUC1–3 years) after chemotherapy in different groups based on renal function and cumulative administered cisplatin dose.
Patients were divided into quartiles based on change in serum creatinine 1 year after start in comparison with pre-chemotherapy. Patients in the highest quartile, corresponding with the highest increase in serum creatinine, had a higher Pt AUC1–3 years (P = 0.037; supplementary Table S3, available at Annals of Oncology online). Seventy-one patients had retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) as part of their treatment. Kidney function and long-term Pt levels were comparable between the groups with and without RPLND (data not shown).
late toxicity and long-term Pt exposure
paraesthesia and Raynaud's phenomenon
The presence of paraesthesia and Raynaud's phenomenon stratified by quartiles of Pt AUC1–3 years is depicted in supplementary Figure S2, available at Annals of Oncology online. Patients who reported persisting paraesthesia at follow-up had a higher Pt AUC1–3 years (supplementary Table S4, available at Annals of Oncology online). In a multivariate model including age and BMI at follow-up and renal function after 1 year, a higher Pt AUC1–3 years was associated with an increased risk for persisting paraesthesia [odds ratio (OR) = 1.07 (95% CI 1.00–1.13), P = 0.043; supplementary Table S5, available at Annals of Oncology online]. Pt AUC1–3 years was not associated with the presence of Raynaud's phenomenon.
hypogonadism
Patients with hypogonadism at follow-up had a higher Pt AUC1–3 years (supplementary Table S4, available at Annals of Oncology online). In the multivariate logistic regression model, long-term exposure to Pt was significantly associated with hypogonadism [OR 1.10 (95% CI 1.02–1.18), P = 0.016; supplementary Table S5, available at Annals of Oncology online].
hypercholesterolaemia
Long-term Pt exposure was higher in patients with increased LDL-cholesterol (supplementary Table S4, available at Annals on Oncology online). Pt AUC1–3 years correlated with total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol in univariate analysis (r = 0.229, P = 0.038 and r = 0.249, P = 0.022, respectively; supplementary Table S6, available at Annals of Oncology online). In the multiple logistic regression model, a higher long-term exposure to Pt remained significantly associated with an increased LDL-cholesterol [OR 1.07 (95% CI 1.00–1.13), P = 0.040; supplementary Table S5, available at Annals of Oncology online].
blood pressure
Pt AUC1–3 years was higher in patients with newly diagnosed, i.e. post-chemotherapy, hypertension (supplementary Table S4, available at Annals of Oncology online). Systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure correlated with Pt AUC1–3 years (r = 0.307, P = 0.007, respectively, r = 0.237, P = 0.038; supplementary Table S6, available at Annals on Oncology online). In the multiple logistic regression analysis on hypertension, the association between Pt AUC1–3 years and hypertension remained significant [OR = 1.10 (95% CI 1.01–1.18), P = 0.027].
discussion
In this study, we found that circulating Pt levels after cisplatin-based chemotherapy for testicular cancer correlate strongly with the cumulative administered cisplatin dose and renal function before and after chemotherapy. We found a clear relationship between long-term circulating Pt levels and well-known long-term and late effects, such as paraesthesia, hypogonadism, higher LDL-cholesterol levels and hypertension.
With data from this cohort, we built a population PK model to generate new insights into the long-term decay of Pt after cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Decay of Pt was modelled using sequential measurements of Pt levels in serum and urine combined with the administered dose of cisplatin, age, weight and height at the start of chemotherapy. The population modelling approach allows the prediction of serum Pt concentrations at any time-point and AUC over any time-period for each individual patient, as used in the statistical analysis, irrespective of the actual time-points of blood and urine sampling. This allowed us to quantify the relationship between estimated exposure to Pt, renal function and known late effects of treatment.
Previously, Gietema et al. [5] detected circulating Pt in serum of patients up to 20 years after chemotherapy. Concentrations of Pt correlated with cisplatin dose and CRCL before chemotherapy. Brouwers et al. [6] reported comparable findings in patients with diverse tumour types, 0.7–6 years after chemotherapy with cisplatin or oxaliplatin. Sprauten et al. [7] quantified Pt in serum in a cross-sectional study in 169 testicular cancer patients 4–19 years after treatment. These data indicate an association between long-term circulating Pt levels and severity of observed neurotoxicity in testicular cancer survivors.
Based on our PK model, we conclude that renal function, both before and shortly after treatment, is a strong determinant of long-term exposure to circulating Pt. In addition, patients with a stronger increase in serum creatinine levels 1 year after treatment compared with baseline had higher Pt AUCs during follow-up. The relationship between circulating Pt and renal function may act both ways: patients with higher Pt levels have relatively more renal damage, which in turn decreases clearance. Loss of renal function can persist after treatment of years [11]. Recently, Lauritsen et al. [12] concluded that renal function after treatment is closely related to the number of cycles of BEP (bleomycin, etoposide and cisplatin). These findings underscore the importance of optimising renal function before treatment, preserving it during treatment and preventing decline in renal function after completion of cisplatin treatment.
Patients reporting persisting paraesthesia median 9 years after treatment had a higher Pt AUC than those without paraesthesia. In our study, the collection of sequential serum and urine samples enabled us to model exposure to circulating Pt, which is an advantage in comparison with the cross-sectional study of Sprauten et al. The exact pathogenesis of long-term neuropathy is unknown, but relatively high Pt levels have been found in the dorsal root in post-mortem studies [13]. To which extent levels of circulating Pt correspond with levels in the dorsal root is unknown. We did not find a relationship between Pt levels and the presence of Raynaud's phenomenon. Bleomycin is probably a more important causative agent in the pathogenesis of Raynaud [14].
Hypogonadism and hyperlipidaemia are frequently observed in testicular cancer survivors [15, 16], and are especially prevalent in patients treated with cisplatin-containing chemotherapy (17%–21%) [2, 4]. The higher Pt levels observed in patients with hypogonadism and hyperlipidaemia could point to long-term toxicity on healthy tissue involved in androgen- and lipid metabolism due to Pt residuals. From post-mortem studies in cisplatin-treated patients, it is known that Pt residuals can be found in fat tissue, bone and a range of organs such as liver, kidney and lungs [17].
Direct toxic effects of circulating Pt on blood vessels might result in endothelial activation, an inflammatory response or accelerated atherosclerosis. Testicular cancer survivors show signs of endothelial damage, such as microalbuminuria, increased plasma levels of endothelial and inflammatory marker proteins and increased levels of circulating endothelial cells [18, 19]. In vitro experiments demonstrate that cisplatin induces alterations in the function of endothelial cells regarding proliferation, inflammation and fibrinolysis upon exposure to Pt [20]. The association we found between blood pressure and Pt exposure indicates that circulating Pt might indeed have a long-term toxic effect on endothelial tissue.
Another serious long-term toxic effect of Pt-based chemotherapy is secondary malignancies. It is conceivable that long-term Pt contributes significantly to the development of secondary malignancies, such as urothelial cell cancer, but the limited size of our study population does not allow us to draw conclusions on this issue [21].
Strong points of this study are the sequential collection of serum and urine samples per individual patient, the long-term follow-up and the well-defined phenotype. An inherent limitation of our study is that the Pt AUC values are model-predicted values.
Cisplatin-based chemotherapy is an essential part of the successful treatment of testicular cancer and is also used as curative treatment in other tumour types, such as head and neck cancer and cervical cancer. Treatment-related late effects are inevitable, but the treatment strategy should minimise the risk of late morbidity. In cases where cisplatin is administered in an adjuvant setting, clinicians should take into account that Pt residuals may result in long-term side-effects. Owing to the potential beneficial effect on Pt levels and the association with lower long-term Pt exposure, optimal preservation of renal function—before, during and after treatment—should be a priority.
In conclusion, we found a relationship between long-term Pt exposure in testicular cancer survivors and known late effects, such as persistent paraesthesia, hypogonadism, hypercholesterolaemia and increased blood pressure. This association between healthy tissue damage in cancer survivors and long-term Pt exposure should be considered during treatment decisions and follow-up care in testicular cancer patients. Hence, further research on healthy tissue damage caused by long-term Pt exposure is needed.
funding
This work was supported by the Dutch Cancer Society (grant 00-2177; 04-3157; 09-4365).
disclosure
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary Material
references
- 1.Haugnes HS, Bosl GJ, Boer H et al. Long-term and late effects of germ cell testicular cancer treatment and implications for follow-up. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 3752–3763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nuver J, Smit AJ, Wolffenbuttel BH et al. The metabolic syndrome and disturbances in hormone levels in long-term survivors of disseminated testicular cancer. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 3718–3725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Haugnes HS, Aass N, Fosså SD et al. Components of the metabolic syndrome in long-term survivors of testicular cancer. Ann Oncol 2007; 18: 241–248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.de Haas EC, Altena R, Boezen HM et al. Early development of the metabolic syndrome after chemotherapy for testicular cancer. Ann Oncol 2013; 24: 749–755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gietema JA, Meinardi MT, Messerschmidt J et al. Circulating plasma platinum more than 10 years after cisplatin treatment for testicular cancer. Lancet 2000; 355: 1075–1076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brouwers EE, Huitema AD, Beijnen JH, Schellens JH. Long-term platinum retention after treatment with cisplatin and oxaliplatin. BMC Clin Pharmacol 2008; 8: 7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sprauten M, Darrah TH, Peterson DR et al. Impact of long-term serum platinum concentrations on neuro- and ototoxicity in cisplatin-treated survivors of testicular cancer. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 300–307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CN et al. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004; 24: e149–e161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR et al. Diagnosis and management of the metabolic syndrome: an American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation 2005; 112: 2735–2752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Feng Y, Pollock BG, Ferrell RE et al. Paroxetine: population pharmacokinetic analysis in late-life depression using sparse concentration sampling. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2006; 61: 558–569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fosså SD, Aass N, Winderen M et al. Long-term renal function after treatment for malignant germ-cell tumours. Ann Oncol 2002; 13: 222–228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lauritsen J, Mortensen MS, Kier MG et al. Renal impairment and late toxicity in germ-cell cancer survivors. Ann Oncol 2015; 26: 173–178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Krarup-Hansen A, Rietz B, Krarup C et al. Histology and platinum content of sensory ganglia and sural nerves in patients treated with cisplatin and carboplatin: an autopsy study. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 1999; 25: 29–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Berger CC, Bokemeyer C, Schneider M et al. Secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon and other late vascular complications following chemotherapy for testicular cancer. Eur J Cancer 1995; 31A: 2229–2238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Huddart RA, Norman A, Moynihan C et al. Fertility, gonadal and sexual function in survivors of testicular cancer. Br J Cancer 2005; 93: 200–207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nord C, Bjøro T, Ellingsen D et al. Gonadal hormones in long-term survivors 10 years after treatment for unilateral testicular cancer. Eur Urol 2003; 44: 322–328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dikhoff TGMH, De Goeij JJM, McVie JG. Long-term body retention and tissue distribution of platinum in cisplatin treated cancer patients. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 1998; 236: 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nuver J, Smit AJ, Sleijfer DT et al. Microalbuminuria, decreased fibrinolysis, and inflammation as early signs of atherosclerosis in long-term survivors of disseminated testicular cancer. Eur J Cancer 2004; 40: 701–706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vaughn DJ, Palmer SC, Carver JR et al. Cardiovascular risk in long-term survivors of testicular cancer. Cancer 2008; 112: 1949–1953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nuver J, De Haas EC, Van Zweeden M et al. Vascular damage in testicular cancer patients: a study on endothelial activation by bleomycin and cisplatin in vitro. Oncol Rep 2010; 23: 247–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fung C, Fosså SD, Milano MT, Oldenburg J, Travis LB. Solid tumors after chemotherapy or surgery for testicular nonseminoma: a population-based study. J Clin Oncol 2013; 31: 3807–3814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.