Abstract
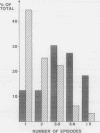
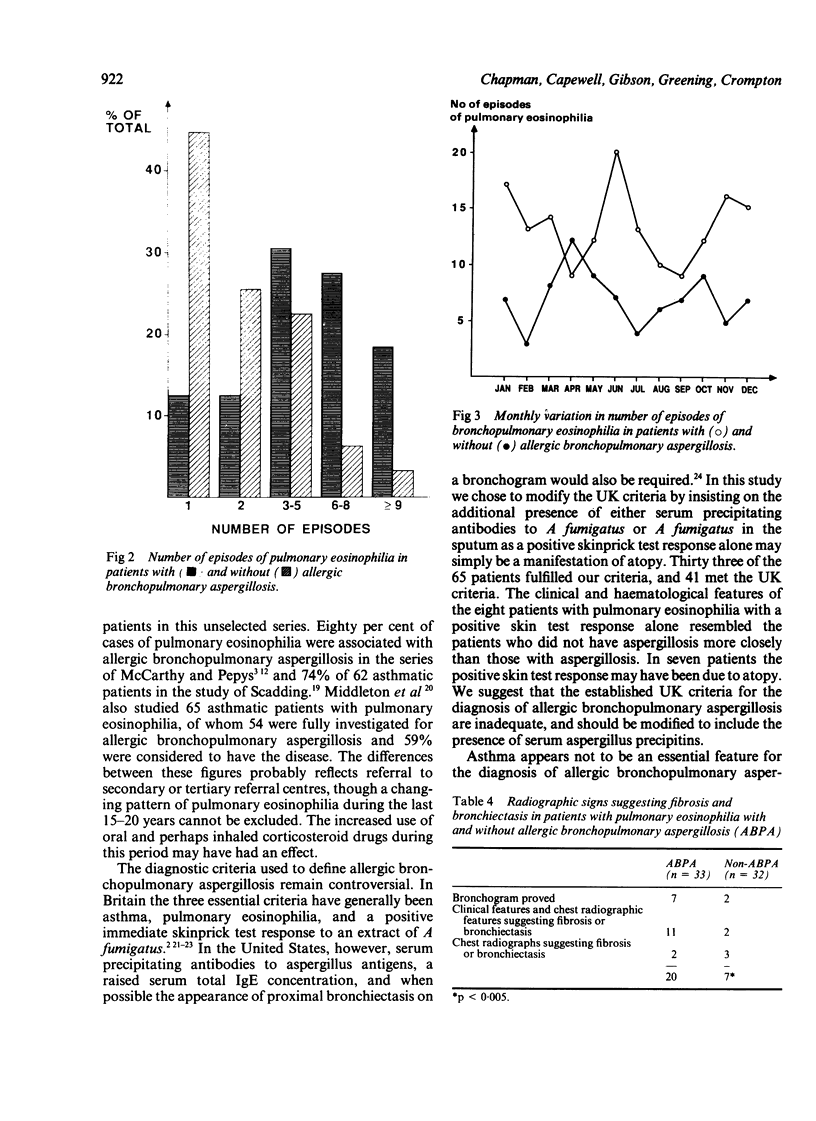
Sixty five patients with pulmonary eosinophilia attending one respiratory unit were reviewed. All had fleeting radiographic abnormalities and peripheral blood eosinophil counts greater than 500 x 10(6)/l. Eighteen had a single episode and 47 recurrent episodes during a median follow up period of 14 years. Thirty three patients had allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis on the basis of a positive skin test response to Aspergillus fumigatus, serum precipitins, or culture of A fumigatus from sputum, or a combination of these. All but seven patients had asthma, six of the seven being in the group who did not have allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. The patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis were more often male and had a greater incidence of asthma and an earlier age of onset of asthma than those without aspergillosis. The patients with aspergillosis had lower mean blood eosinophil counts and more episodes of pulmonary eosinophilia and more commonly had radiographic shadowing that suggested fibrosis or bronchiectasis (20 v 7). Pulmonary eosinophilia associated with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis appears to be a distinct clinical syndrome resulting in greater permanent radiographic abnormality despite lower peripheral blood eosinophil counts.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkin K. E., Vernon D. R., Kerr J. W. Lung collapse caused by allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in non-asthmatic patients. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Aug 21;285(6341):552–553. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6341.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHURG J., STRAUSS L. Allergic granulomatosis, allergic angiitis, and periarteritis nodosa. Am J Pathol. 1951 Mar-Apr;27(2):277–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROFTON J. W., LIVINGSTONE J. L., OSWALD N. C., ROBERTS A. T. M. Pulmonary eosinophilia. Thorax. 1952 Mar;7(1):1–35. doi: 10.1136/thx.7.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumbley L. C., Harrison E. G., Jr, DeRemee R. A. Allergic granulomatosis and angiitis (Churg-Strauss syndrome). Report and analysis of 30 cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 Aug;52(8):477–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole P. Drug-induced lung disease. Drugs. 1977 Jun;13(6):422–444. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197713060-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Harley J. B., Roberts W. C., Ferrans V. J., Gralnick H. R., Bjornson B. H. NIH conference. The idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome. Clinical, pathophysiologic, and therapeutic considerations. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jul;97(1):78–92. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-1-78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glancy J. J., Elder J. L., McAleer R. Allergic bronchopulmonary fungal disease without clinical asthma. Thorax. 1981 May;36(5):345–349. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.5.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINSON K. F. W., MOON A. J., PLUMMER N. S. Broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis; a review and a report of eight new cases. Thorax. 1952 Dec;7(4):317–333. doi: 10.1136/thx.7.4.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HYDE H. A., RICHARDS M., WILLIAMS D. A. Allergy to mould spores in Britain. Br Med J. 1956 Apr 21;1(4972):886–890. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4972.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. H. Allergic aspergillosis: review of 32 cases. Thorax. 1968 Sep;23(5):501–512. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.5.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebow A. A., Carrington C. B. The eosinophilic pneumonias. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 Jul;48(4):251–285. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196907000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo J. L., Hawkins R., Pepys J. Studies in chronic allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. 1. Clinical and physiological findings. Thorax. 1977 Jun;32(3):254–261. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.3.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. S., Pepys J. Cryptogenic pulmonary eosinophilias. Clin Allergy. 1973 Sep;3(3):339–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1973.tb01341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton W. G., Paterson I. C., Grant I. W., Douglas A. C. Asthmatic pulmonary eosinophilia: a review of 65 cases. Br J Dis Chest. 1977 Apr;71(2):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(77)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOBLE W. C., CLAYTON Y. M. FUNGI IN THE AIR OF HOSPITAL WARDS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:397–402. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R., Greenberger P. A., Halwig J. M., Liotta J. L., Roberts M. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Natural history and classification of early disease by serologic and roentgenographic studies. Arch Intern Med. 1986 May;146(5):916–918. doi: 10.1001/archinte.146.5.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radin R. C., Greenberger P. A., Patterson R., Ghory A. Mould counts and exacerbations of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Clin Allergy. 1983 May;13(3):271–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1983.tb02598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisin E., Abel R., Modan M., Silverberg D. S., Eliahou H. E., Modan B. Effect of weight loss without salt restriction on the reduction of blood pressure in overweight hypertensive patients. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 5;298(1):1–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801052980101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Patterson R., Mintzer R., Cooper B. J., Roberts M., Harris K. E. Clinical and immunologic criteria for the diagnosis of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Apr;86(4):405–414. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-4-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safirstein B. H., D'Souza M. F., Simon G., Tai E. H., Pepys J. Five-year follow-up of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Sep;108(3):450–459. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.3.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scadding J. G. Eosinophilic infiltrations of the lungs in asthmatics. Proc R Soc Med. 1971 Apr;64(4):381–392. doi: 10.1177/003591577106400419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz M., Wasserman S., Patterson R. The eosinophil and the lung. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Aug;142(8):1515–1519. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1982.00340210113021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuyler M. R. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Clin Chest Med. 1983 Jan;4(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spry C. J., Davies J., Tai P. C., Olsen E. G., Oakley C. M., Goodwin J. F. Clinical features of fifteen patients with the hypereosinophilic syndrome. Q J Med. 1983 Winter;52(205):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., Assem E. S., Lockwood M. Cryptogenic pulmonary eosinophilia. Clin Allergy. 1976 Mar;6(2):135–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01891.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]