Abstract
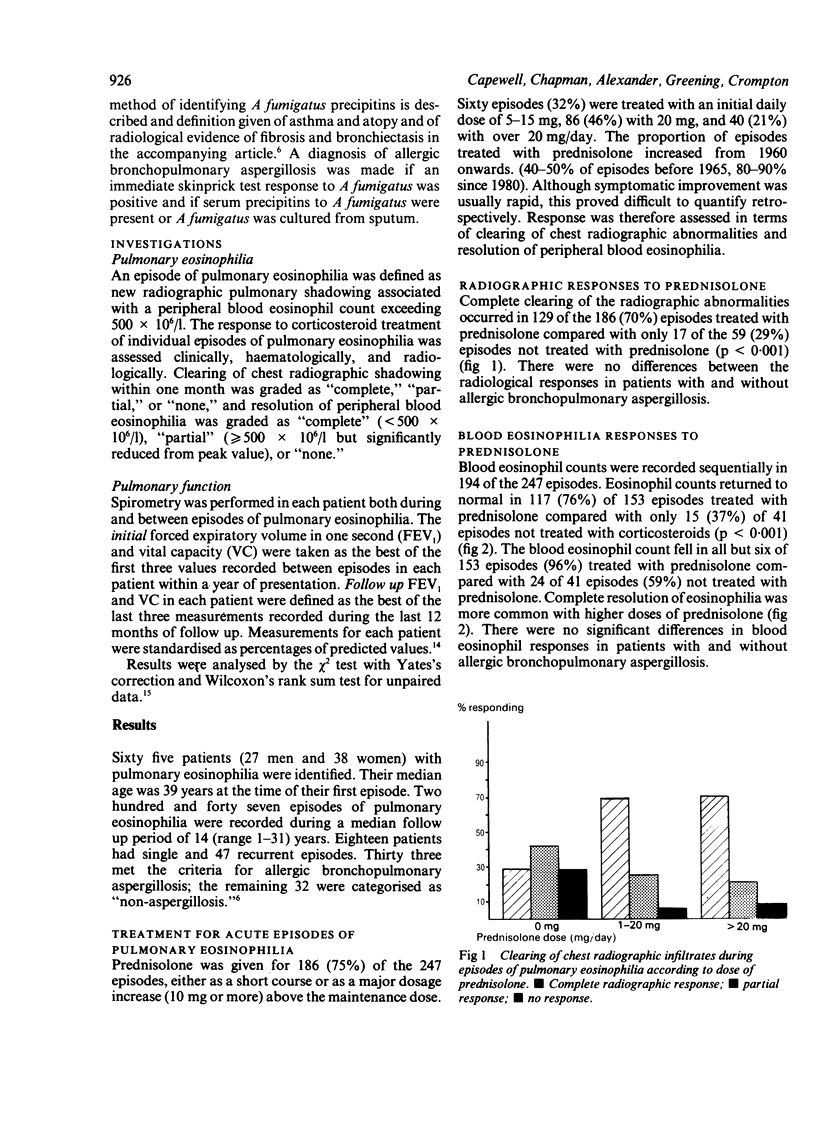
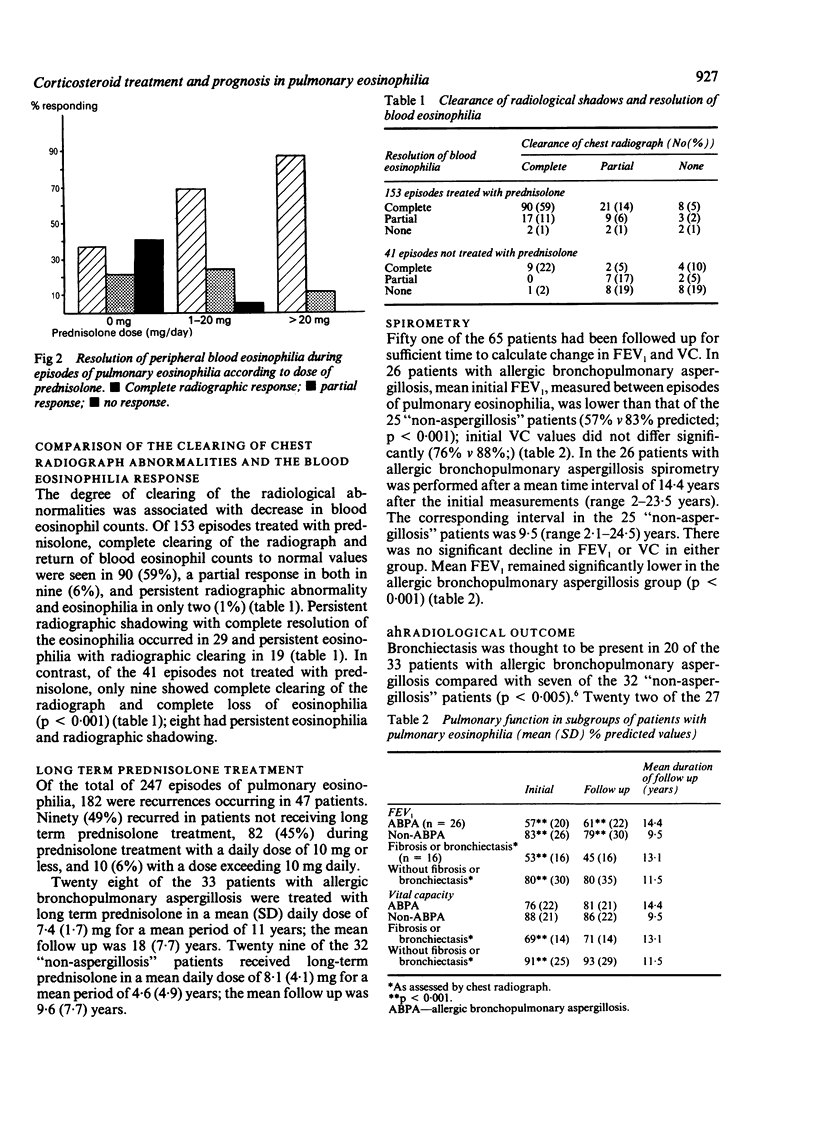
The acute and long term responses to corticosteroid treatment in 65 patients with pulmonary eosinophilia have been reviewed. Of the 247 episodes of pulmonary eosinophilia that were documented during a median follow up period of 14 years, 186 were treated with prednisolone. Complete clearing of chest radiographic infiltrates occurred in 65% of the 247 episodes, partial clearing in 25%, and no response in 9%. Blood eosinophil counts were monitored during 194 episodes and returned to normal in 72%, decreased in 19%, and remained raised in 9%. Complete radiological clearing and a reduction in blood eosinophil counts were more common in episodes treated with prednisolone. Long term prednisolone was given to 28 of the 33 patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (mean 7.4 mg/day for 11 years) and to 29 of the 32 "non-aspergillosis" patients (mean 8.1 mg/day for 4.6 years). Initial pulmonary function, measured between episodes, was worse in patients with allergic aspergillosis than in those without (mean % predicted: FEV1 57% v 83%, vital capacity (VC) 76% v 88%). During a mean follow up period of 12 years neither group displayed further decline in FEV1 or VC.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chapman B. J., Capewell S., Gibson R., Greening A. P., Crompton G. K. Pulmonary eosinophilia with and without allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Thorax. 1989 Nov;44(11):919–924. doi: 10.1136/thx.44.11.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crompton G. K., Milne L. J. Treatment of bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with clotrimazole. Br J Dis Chest. 1973 Oct;67(4):301–307. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(73)80002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay R. J. Recent advances in the management of fungal infections. Q J Med. 1987 Aug;64(244):631–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. H., Pearson J. E. Treatment of bronchopulmonary aspergillosis with observations on the use of natamycin. Thorax. 1968 Sep;23(5):519–523. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.5.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. C., Bierman C. W., VanArsdel P. P., Jr Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Report of two cases and evaluation of tests for hypersensitivity. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Oct;128(4):576–581. doi: 10.1001/archinte.128.4.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong F. K., Sue M. A., Klaustermeyer W. B. Corticosteroid complications in respiratory disease. Ann Allergy. 1987 May;58(5):326–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo J. L., Hawkins R., Pepys J. Studies in chronic allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. 1. Clinical and physiological findings. Thorax. 1977 Jun;32(3):254–261. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.3.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo J. L., Longbottom J., Mitchell J., Hawkins R., Pepys J. Studies in chronic allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. 3. Immunological findings. Thorax. 1977 Jun;32(3):269–274. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.3.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. S., Pepys J. Cryptogenic pulmonary eosinophilias. Clin Allergy. 1973 Sep;3(3):339–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1973.tb01341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. S., Simon G., Hargreave F. E. The radiological appearances in allergic broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis. Clin Radiol. 1970 Oct;21(4):366–375. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(70)80070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton W. G., Paterson I. C., Grant I. W., Douglas A. C. Asthmatic pulmonary eosinophilia: a review of 65 cases. Br J Dis Chest. 1977 Apr;71(2):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(77)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R., Greenberger P. A., Halwig J. M., Liotta J. L., Roberts M. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Natural history and classification of early disease by serologic and roentgenographic studies. Arch Intern Med. 1986 May;146(5):916–918. doi: 10.1001/archinte.146.5.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R., Greenberger P. A., Radin R. C., Roberts M. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis: staging as an aid to management. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Mar;96(3):286–291. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-3-286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Patterson R., Roberts M., Wang J. The assessment of immunologic and clinical changes occurring during corticosteroid therapy for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Am J Med. 1978 Apr;64(4):599–606. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90579-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safirstein B. H., D'Souza M. F., Simon G., Tai E. H., Pepys J. Five-year follow-up of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Sep;108(3):450–459. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.3.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scadding J. G. Eosinophilic infiltrations of the lungs in asthmatics. Proc R Soc Med. 1971 Apr;64(4):381–392. doi: 10.1177/003591577106400419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuyler M. R. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Clin Chest Med. 1983 Jan;4(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shale D. J., Faux J. A., Lane D. J. Trial of ketoconazole in non-invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Thorax. 1987 Jan;42(1):26–31. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner-Warwick M., Assem E. S., Lockwood M. Cryptogenic pulmonary eosinophilia. Clin Allergy. 1976 Mar;6(2):135–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01891.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



