Abstract
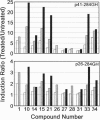
Inductions of detoxication (phase 2) enzymes, such as glutathione transferases and NAD(P)H:(quinone-acceptor) oxidoreductase, are a major mechanism for protecting animals and their cells against the toxic and neoplastic effects of carcinogens. These inductions result from enhanced transcription, and they are evoked by diverse chemical agents: oxidizable diphenols and phenylenediamines; Michael reaction acceptors; organic isothiocyanates; other electrophiles--e.g., alkyl and aryl halides; metal ions--e.g., HgCl2 and CdCl2; trivalent arsenic derivatives; vicinal dimercaptans; organic hydroperoxides and hydrogen peroxide; and 1,2-dithiole-3-thiones. The molecular mechanisms of these inductions were analyzed with the help of a construct containing a 41-bp enhancer element derived from the 5' upstream region of the mouse liver glutathione transferase Ya subunit gene ligated to the 5' end of the isolated promoter region of this gene, and inserted into a plasmid containing a human growth hormone reporter gene. When this construct was transfected into Hep G2 human hepatoma cells, the concentrations of 28 compounds (from the above classes) required to double growth hormone production, and the concentrations required to double quinone reductase specific activities in Hepa 1c1c7 cells, spanned a range of four orders of magnitude but were closely linearly correlated. Six compounds tested were inactive in both systems. A 26-bp subregion of the above enhancer oligonucleotide (containing the two tandem "AP-1-like" sites but lacking the preceding ETS protein binding sequence) was considerably less responsive to the same inducers. We conclude that the 41-bp enhancer element mediates most, if not all, of the phase 2 enzyme inducer activity of all of these widely different classes of compounds.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abate C., Patel L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Curran T. Redox regulation of fos and jun DNA-binding activity in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 7;249(4973):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.2118682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannai S. Induction of cystine and glutamate transport activity in human fibroblasts by diethyl maleate and other electrophilic agents. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2435–2440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannai S., Sato H., Ishii T., Taketani S. Enhancement of glutathione levels in mouse peritoneal macrophages by sodium arsenite, cadmium chloride and glucose/glucose oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 17;1092(2):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90153-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batzinger R. P., Ou S. Y., Bueding E. Antimutagenic effects of 2(3)-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole and of antimicrobial agents. Cancer Res. 1978 Dec;38(12):4478–4485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson A. M., Cha Y. N., Bueding E., Heine H. S., Talalay P. Elevation of extrahepatic glutathione S-transferase and epoxide hydratase activities by 2(3)-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole. Cancer Res. 1979 Aug;39(8):2971–2977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel V., Sharon R., Bensimon A. Regulatory elements controlling the basal and drug-inducible expression of glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene. DNA. 1989 Jul-Aug;8(6):399–408. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel V., Sharon R., Tichauer Y., Sarid S. Mouse glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit: gene structure and sequence. DNA. 1987 Aug;6(4):317–324. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Long M. J., Dolan P., Santamaria A. B., Bueding E. 1,2-Dithiol-3-thione analogs: effects on NAD(P)H:quinone reductase and glutathione levels in murine hepatoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 1986 Jun;7(6):977–980. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.6.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favreau L. V., Pickett C. B. Transcriptional regulation of the rat NAD(P)H:quinone reductase gene. Identification of regulatory elements controlling basal level expression and inducible expression by planar aromatic compounds and phenolic antioxidants. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4556–4561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friling R. S., Bensimon A., Tichauer Y., Daniel V. Xenobiotic-inducible expression of murine glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene is controlled by an electrophile-responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6258–6262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friling R. S., Bergelson S., Daniel V. Two adjacent AP-1-like binding sites form the electrophile-responsive element of the murine glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):668–672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal A. K. Human NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase (NQO1) gene structure and induction by dioxin. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 5;30(44):10647–10653. doi: 10.1021/bi00108a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakoby W. B., Ziegler D. M. The enzymes of detoxication. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20715–20718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Jaiswal A. K. Regulation of human NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase gene. Role of AP1 binding site contained within human antioxidant response element. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15097–15104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod K., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The ets gene family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jul;17(7):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90404-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochaska H. J., De Long M. J., Talalay P. On the mechanisms of induction of cancer-protective enzymes: a unifying proposal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8232–8236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochaska H. J., Santamaria A. B. Direct measurement of NAD(P)H:quinone reductase from cells cultured in microtiter wells: a screening assay for anticarcinogenic enzyme inducers. Anal Biochem. 1988 Mar;169(2):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochaska H. J., Santamaria A. B., Talalay P. Rapid detection of inducers of enzymes that protect against carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2394–2398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochaska H. J., Talalay P. Regulatory mechanisms of monofunctional and bifunctional anticarcinogenic enzyme inducers in murine liver. Cancer Res. 1988 Sep 1;48(17):4776–4782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore T. H., King R. G., Paulson K. E., Pickett C. B. Regulation of glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene expression: identification of a unique xenobiotic-responsive element controlling inducible expression by planar aromatic compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3826–3830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore T. H., Morton M. R., Pickett C. B. The antioxidant responsive element. Activation by oxidative stress and identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for functional activity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11632–11639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore T. H., Pickett C. B. Transcriptional regulation of the rat glutathione S-transferase Ya subunit gene. Characterization of a xenobiotic-responsive element controlling inducible expression by phenolic antioxidants. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14648–14653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R. F., Howie K. B., Rowe M. E., Goodman H. M., Moore D. D. Human growth hormone as a reporter gene in regulation studies employing transient gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3173–3179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer S. R., Xue L. A., Klenz E. M., Talalay P. The potency of inducers of NAD(P)H:(quinone-acceptor) oxidoreductase parallels their efficiency as substrates for glutathione transferases. Structural and electronic correlations. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):711–717. doi: 10.1042/bj2730711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talalay P., De Long M. J., Prochaska H. J. Identification of a common chemical signal regulating the induction of enzymes that protect against chemical carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8261–8265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Curran T. Identification and characterization of Ref-1, a nuclear protein that facilitates AP-1 DNA-binding activity. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):653–665. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Miao G., Wang F., Pan Y. C., Curran T. Redox activation of Fos-Jun DNA binding activity is mediated by a DNA repair enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3323–3335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05411.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Talalay P., Cho C. G., Posner G. H. A major inducer of anticarcinogenic protective enzymes from broccoli: isolation and elucidation of structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2399–2403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]