Abstract
High light acclimation implicates mechanisms on various molecular levels and time scales. The recently identified small transcription factor network of APETALA 2/ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR (AP2/ERF) transcription factors is triggered upon transfer of Arabidopsis to high light and depends on metabolite export and mitogen activated protein kinase activation. An experimental design was developed consisting of a low light to high light and back to low light illumination. This allowed the determination of the time point of no return post high light transfer which activates transcription of the AP2/ERF network. Within 10 seconds of high light treatment transcript levels of ERF6, ERF104, ERF105 and RRTF were triggered to increase from low to high levels within the next 10 minutes witnessing an ultrafast retrograde pathway with a very early time point of no return. This response differed profoundly from other high light-responsive transcripts such as stromal ascorbate peroxidase (sAPX) which accumulated in a dose-dependent manner or COR47.
Keywords: acclimation, chloroplast, light, photosynthesis, transcription factor
Abbreviations
- AP2/ERF
APETALA2/ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR
- A. thaliana
Arabidopsis thaliana
- H-light
High Light (800 μmol quanta m−2 s−1)
- ETC
electron transport chain
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- WWC
water-water cycle
- ABA
Abscisic Acid
- SA
Salicylic Acid
- L-light
Low Light (8 μmol quanta m−2 s−1)
- TF
Transcription Factor
- L→H
Low Light to High Light transfer
- LH→L
Low Light to High Light to Low Light transfer
- log2
logarithmic fold change to base 2
Plants are part of a complex environment where multiple chemical, physical and biotic parameters change continuously. Tailored acclimation of plants minimizes resource investments and optimizes growth. This depends on weighing and integrating multiple input signals in a timely manner. The response speed depends on stress type and intensity. Light and heat may fluctuate within short periods and require fast response.1-3 In high light (H-light) overreduction of the electron transport chain takes place which may generate reactive oxygen species (ROS).4 To reduce photooxidative damage plants activate defense mechanisms such as non-photochemical quenching or detoxify ROS via the chloroplasts water-water cycle in an ascorbate-dependent or -independent pathway involving peroxiredoxins.5-7 Since all enzymatic antioxidants are encoded in the nucleus, their transcriptional regulation depends on retrograde signaling form the chloroplast to the nucleus. This information delivery pathway allows for responses upon changing conditions e.g. under H-light. Retrograde signaling represents a multifactorial process where singlet oxygen, H2O2, metabolites, hormones and lipid derivatives form a metabolite network that tunes the appropriate expressional response.8-11 Upon shift to H-light the H2O2 concentration increases within minutes and serves as rapid retrograde signal.12 Sugars play an important role on a longer timescale.13,14 Recently, it has been shown that the predominant assimilate transporter, the triosephosphate-phosphate translocator (TPT), participates in rapid information transmission controlling transcript accumulation.15 Rapid regulation relies on existing transcription factors (TF) which conditionally adjust gene expression in response to stress stimuli.16 Downstream inducible TFs realize the acclimation response. A subgroup of the AP2/ERF TF family is transcriptionally induced within 10 min after light shift.15 Such rapid response systems serve as immediate reaction to counter the effects of fluctuating conditions and are important to allow for subsequent long term acclimation.
Deep insight into early acclimation processes requires knowledge on the chronological order of events. The identification of points of no return e.g., those that control transcript accumulation is a powerful method to pinpoint to crucial process steps. Therefore, A. thaliana (Col 0) plants were subjected to L-light to H-light transfer (L→H). This approach provides information on the time tx [min] needed to achieve a particular response strength Rx. The point of no return is the shorter HL period tx−y [min] needed to trigger the same response Rx even after transfer of the plants back to low light for ty [min]. This treatment is called L-light to H-light to L-light condition (LH→L).15 The previously identified early responding AP2/ERF-TF network with ERF6 (At4g17490), ERF104 (At5g61600), ERF105 (At5g51190) and RRTF1 (At4g34410) as elements was chosen as indicator of successful signal transmission (Fig. 1). These AP2/ERF TFs accumulate upon L→H-transfer with a maximum at 10 min.15 Here the point of no return for the reaction could be resolved in detail. The shortest time period that was tested for triggering transcript up-regulation was 10s H-light, followed by 9 min 50s of low light prior to transcript quantification. Three out of 4 AP2/ERFs were triggered to be significantly up-regulated after this short period witnessing an ultrafast retrograde pathway with a very early time point of no return. The maximal reaction of ERF6 and ERF105 depended on very short exposures to H-light. Slightly longer H-light exposure was required to for ERF104 and RRTF1.
Figure 1.
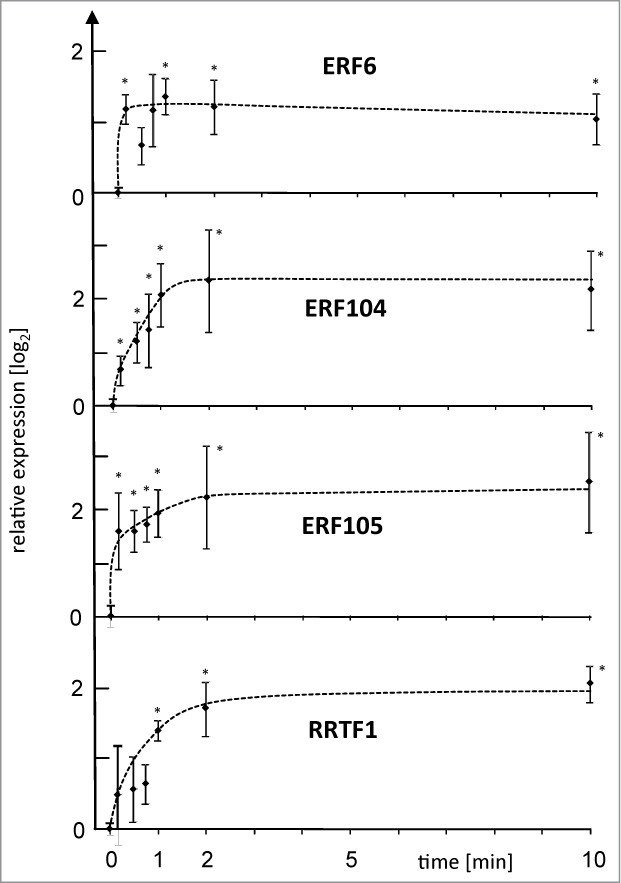
Point of no return for high light-induced transcript accumulation of 4 AP2/ERF TFs. ERF6, ERF104, ERF105 and RRTF1 mRNA levels were quantified by qPCR in wild type plants after various periods of H-light-treatment e.g. 10 s followed by 9 min 50 s of low light, or maintained in L-light (0 min). All plants were harvested after 10 min of H-light (LH→L) or transferred at indicated time points back to L-light. Thus the x-axis gives the time period in H-light. Data are means ± SE from n = 3 plus replicates (for t = 10 min n = 8) independent experiments, asterisks indicate significant difference to t = 0 min control (Student's t-test P < 0.05).
We then exemplarily explored slower response patterns in H-light acclimation (Fig. 2). To this end transcript accumulation of stromal ascorbate peroxidase (sAPX, At4g08390) as ROS marker and cold regulated and light sensitive gene (COR47, At1g20440) as ABA marker was investigated during 360 min of H-light exposure (L→H-condition) and in parallel in LH→L-treatment where plants were transferred back to low light to complete the 360 min period prior to harvest. As shown before long-term acclimation to H-light was accompanied by higher sAPX levels and decreasing COR47 amounts.17,18 ERF6 was used as reference with fast point of no return. ERF6 transcript amounts reached a maximum after 10 min and dropped to initial levels after 60 min. Significant differences between L→H- and LH→L-treatments were not seen at later time points. The sAPX level increased steadily to the maximum at 360 min in the L→H-treatment. Most importantly, transcript accumulation in the LH→L-experiment followed the same steady increase and significant differences to L→H were not established (Fig. 2B). Apparently cumulative light stress determines the reaction amplitude and the transcript level likely remains unchanged after transfer back to L-light suggesting a simple effector/dose dependency and long half life time of transcript.
Figure 2.
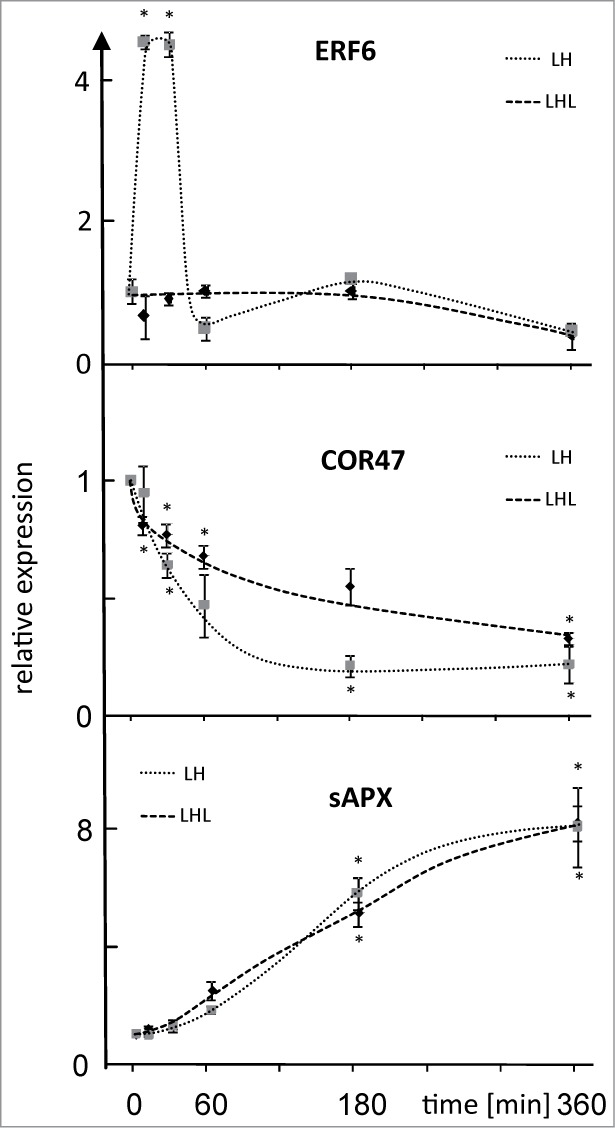
Expression level of ERF6, COR47 and sAPX after LH→L- or L→H-treatment. Transcript levels were quantified by qPCR in response to L→H shift at indicated time points. Parallel samples were transferred back to L-light after H-light-treatment and harvested at t = 360 min. Data are means ± SE of n = 3 independent experiments (with replicates), asterisks indicate significant difference to t = 0 min (Student's t-test P < 0.05).
COR47 decreased with H-light duration to the minimal level at 180 min that was maintained subsequently. COR47 levels also dropped in the LH→L-experiment but with lower amplitude (Fig. 2). This suggests cumulative suppression of COR47 transcript accumulation in H-light and significant reversal to the initial level after return to L-light. Like in the case of sAPX a point of no return was not apparent in this experiment.
A model for ultrafast retrograde signaling is suggested based on the presented and previous results15 (Fig. 3). TPT, the prime photosynthate exporter, rapidly equilibrates metabolite state of the glyceraldehde-3-phosphate reduction reaction between stroma and cytosol enabling instantaneous information exchange on the NAD(P)H and ATP system thus energization state,19 and may activate mitogen activated protein kinase 6 (MPK6).15 Especially the highly responsive AP2/ERF-TF network is regulated via this pathway. Phosphorylation of MPK6 is delayed in tpt KO mutants, but still occurs indicating the existence of TPT-independent pathways for H-light-dependent MPK6 phosphorylation. Lack of MPK6 phosphorylation excludes a function at later time points. Metabolome and transcriptome data indicate far reaching acclimation to H-light at these functional levels after 360 min.17,20 The dose-dependent and persistent increase in sAPX levels is consistent with previous results.21,22 sAPX takes part in redox homeostasis. Thus it is reasonable that they integrate the dose and thus the average stress level under fluctuating conditions.23 Other genes like cor47 are fine-tuned more slowly. The ultrarapidly responsive members of AP2/ERF-TFs are candidates as regulators of early needed downstream targets. The ‘point of no return’-experiments improve our understanding of the H-light acclimation kinetics and advance our concept of multiple pathways and time scales involved in plant acclimation to H-light.
Figure 3.
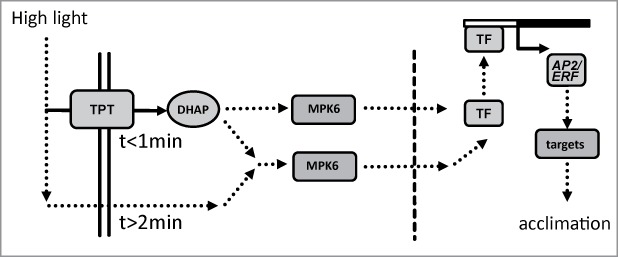
Summarizing model of signal transmission in early H-light-response. Both transport via triosephosphate/phosphate translocator (TPT) and mitogen activated protein kinases 6 (MPK6) participate in ultrafast retrograde signaling. As a consequence of increased light energy availability dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), ATP and NAD(P)H levels in the cytosol increase. The signal transmission via protein phosphorylation cascades (MPK6) to the nucleus and subsequent activation of constitutive transcription factor (TF) leads to expression of the early responsive AP2/ERF-TFs. In addition, TPT independent pathways may activate MAPK-dependent signaling pathways in a delayed manner. Additional retrograde pathways regulate nuclear gene expression on a longer time scale.
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Authors' Contribution
MM performed the experiments and wrote the paper. MOV performed the experiments and discussed the data. KJD designed, supervised and discussed the results and wrote the paper.
Funding
The Authors acknowledge support by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (FOR 804, Di 364).
References
- 01. Barnabás B, Jäger K, Fehér A. The effect of drought and heat stress on reproductive processes in cereals. Plant Cell Environ 2008; 31(1):11-38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 02. Li Z, Wakao S, Fischer BB, Niyogi KK. Sensing and responding to excess light. Annu Rev Plant Biol 2009; 60:239-260; PMID: 19575582; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1146/annurev.arplant.58.032806.103844 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 03. Mittler R, Blumwald E. Genetic engineering for modern agriculture: challenges and perspectives. Annu Rev Plant Biol 2010; 61:443-62; PMID: 20192746; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112116 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 04. Niyogi KK. Photoprotection revisited: genetic and molelcular approaches. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 1999; 50:333-359; PMID: 15012213; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.333 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 05. Ahmad P, Jaleel CA, Salem MA, Nabi G, Sharma S. Roles of enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidants in plants during abiotic stress. Crit Rev Biotechnol 2010; 30(3):161-75; PMID: 20214435; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.3109/07388550903524243 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 06. Asada K. The water-water cycle as alternative photon and electron sinks. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2000; 355(1402):1419-1431; PMID: 11127996; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1098/rstb.2000.0703 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 07. Oelze ML, Kandelbinder A, Dietz KK. Redox regulation and overreduction control in the photosynthesizing cell: complexity in redox regulatory networks. Biochim Biophy Acta 2008; 1780(11):1261-72; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.bbagen.2008.03.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 08. Baier M, Dietz KJ. Chloroplasts as source and target of cellular redox regulation: a discussion on chloroplast redox signals in the context of plant physiology. J Exp Bot 2005; 56(416):1449-62; PMID: 15863449; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/jxb/eri161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 09. Nott A, Jung HS, Koussevitzky S, Chory J. Plastid-to-nucleus retrograde signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 2006; 57:739-59; PMID: 16669780; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105310 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Park SW, Li W, Viehhauser A, Kim S, Nilsson AK, Andersson MX, Kittle JD, Ambavaram MMR, Luan S, Esker AR, et al. Cyclophilin 20-3 relays a 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid signal during stress responsive regulation of cellular redox homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110:9559-9564; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1073/pnas.1218872110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Pogson BJ, Woo NS, Foerster B, Small ID. Plastid signalling to the nucleus and beyond. Trends Plant Sci 2008; 13(11):602-9; PMID: 18838332; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.08.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Karpinski S, Reynolds H, Karpinska B, Wingsle G, Creissen G, Mullineaux P. Systemic signaling and acclimation in response to excess excitation energy in Arabidopsis. Science 1999; 284:654-657; PMID: 10213690; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1126/science.284.5414.654 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Baena-Gonzáles E, Rolland F, Thevelein JM, Sheen J. A central integrator of transcription networks in plant stress and energy signalling. Nature 2007; 448(7156):938-42; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1038/nature06069 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Hauesler RE, Heinrichs L, Schmitz J, Fluegge UI. How sugars might coordinate chloroplast and nuclear gene expression during acclimation to high light intensities. Mol Plant 2014; 7(7):1121-1137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Vogel MO, Moore M, Koenig K, Pecher P, Alsharafa K, Lee J, Dietz KJ. Fast retrograde signaling in response to high light involves metabolite export, MITOGEN-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE6 and AP2/ERF transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2014; 26:1151-1165; PMID: 24668746; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1105/tpc.113.121061 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Kadonaga JT. Regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription by sequence-specific DNA binding factors. Cell 2004; 116:247-257; PMID: 14744435; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)01078-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Oelze ML, Vogel MO, Alsharafa H, Kahmann U, Viehauser A, Maurino VG, Dietz KJ. Efficient acclimation of the chloroplast antioxidant defence of Arabidopsis thaliana leaves in response to a 10- or 100-fold light increment and the possible involvement of retrograde signals. J Exp Bot 2012; 63(3):1297-313; PMID: 22131159; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1093/jxb/err356 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Alsharafa K, Vogel MO, Oelze ML, Moore M, Stingl N, Koenig K, Friedmann H, Mueller MJ, Dietz KJ. Kinetics of retrograde signalling initiation in the high light response of Arabidopsis thaliana. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2014; 369(1640):20130424; PMID: 24591725; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1098/rstb.2013.0424 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Heber U, Neimanis S, Dietz KJ, Viil J. Assimilatory power as a driving force in photosynthesis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1986; 852: 144-155; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/0005-2728(86)90067-8 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Oelze ML, Muthuramalingam M, Vogel MO, Dietz KJ. The link between transcript regulation and de novo protein synthesis in the retrograde high light acclimation response of Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genomics 2014; 15:320; PMID: 24884362; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1186/1471-2164-15-320 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Pena-Ahumada A, Kahmann U, Dietz KJ, Baier M. Regulation of peroxiredoxin expression versus expression of Halliwell-Asada-Cycle enzymes during early seedling development of Arabidopsis thaliana. Phosynth Res 2006; 89(2-3):99-112; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1007/s11120-006-9087-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Yoshimura K, Yabuta Y, Ishikawa T, Shigeoka S. Expression of spinach ascorbate peroxidase isoenzymes in response to oxidative stresses. Plant Physiol 2000; 123(1):223-34; PMID: 10806239; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1104/pp.123.1.223 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Kangasjärvi S, Lepistö A, Hännikäinen K, Piippo M, Luomala EM, Aro EM, Rintamäki E. Diverse roles for chloroplast stromal and thylakoid-bound ascorbate peroxidases in plant stress responses. Biochem J 2008; 412(2):175-85 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


