Abstract
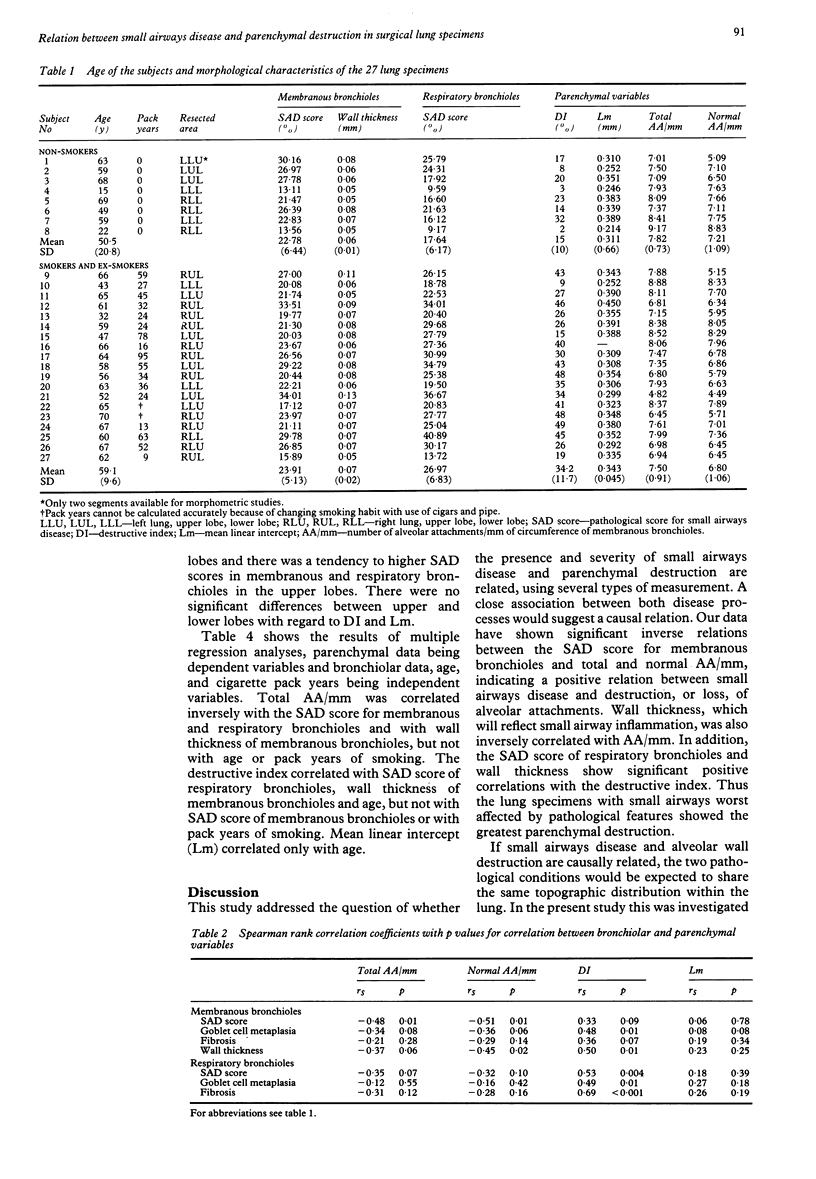
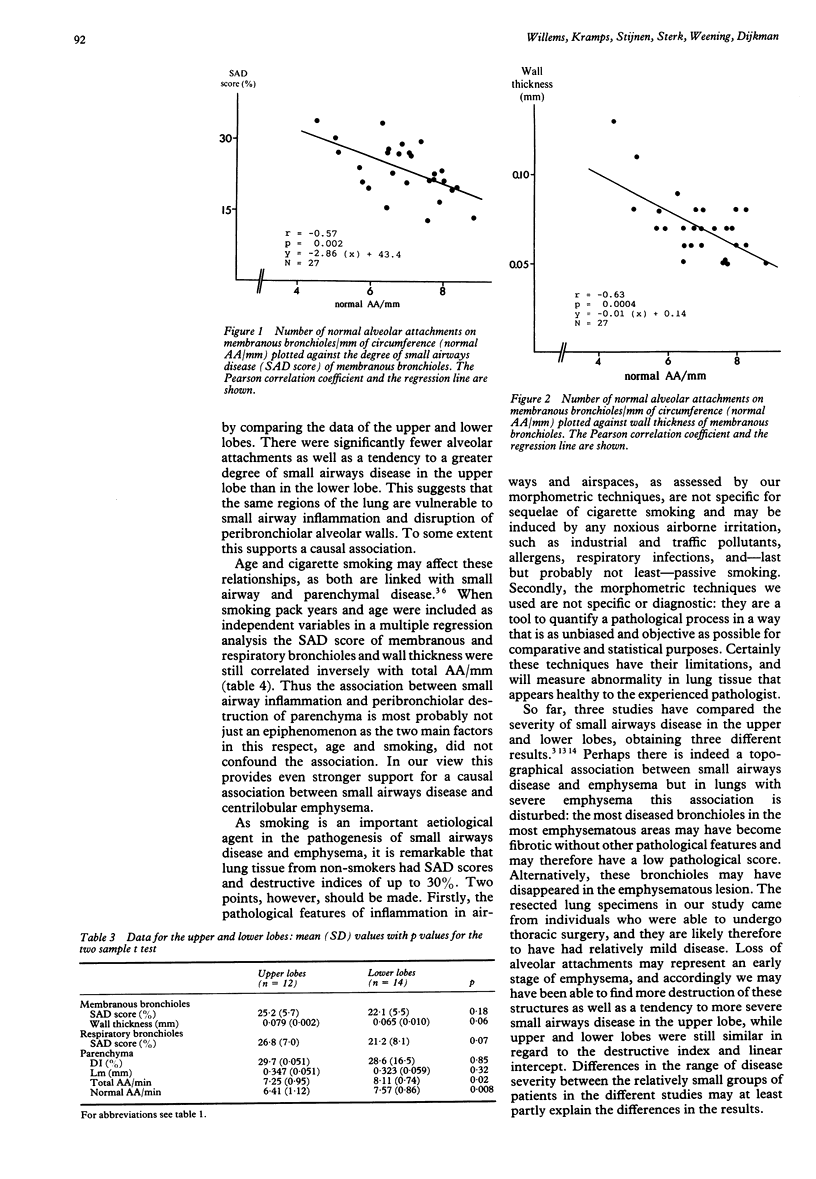
The relation between small airways disease and parenchymal destruction was investigated in lungs and lobes removed at surgery from 27 patients aged 15-70 years. Eight of the 27 patients were life-long non-smokers. The degree of small airways disease was assessed by semi-quantitative grading (SAD score) and by measuring diameter and wall thickness of membranous bronchioles. Parenchymal destruction was measured in three ways. Firstly, the number of alveolar attachments on membranous bronchioles per millimetre of circumference (AA/mm) was counted; the number of broken attachments was subtracted from the total AA/mm to give the numbers of intact attachments (normal AA/mm). Secondly, a point counting technique was used to give a destructive index (DI). Thirdly, the mean linear intercept (Lm) was determined. Total and normal AA/mm correlated negatively with the SAD score of membranous bronchioles (rs = -0.48 and -0.51) and with wall thickness (rs = -0.37 and -0.45) and DI correlated with wall thickness (rs = 0.5) and with the SAD score of respiratory bronchioles (rs = 0.53). Lm did not correlate with indices of small airway disease and total and normal AA/mm did not correlate with diameter. Multiple regression analyses showed that the correlation of total AA/mm with the SAD score of membranous and respiratory bronchioles and with wall thickness were not confounded by age or smoking. It is concluded that small airways disease is related to destruction of peribronchiolar alveoli, and it is postulated that small airways disease has a direct role in the causation of centrilobular emphysema.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON A. E., Jr, FORAKER A. G. Relative dimensions of bronchioles and parenchymal spaces in lungs from normal subjects and emphysematous patients. Am J Med. 1962 Feb;32:218–226. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(62)90291-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berend N. Lobar distribution of bronchiolar inflammation in emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Sep;124(3):218–220. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.124.3.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosio M. G., Hale K. A., Niewoehner D. E. Morphologic and morphometric effects of prolonged cigarette smoking on the small airways. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Aug;122(2):265–221. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.2.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosio M. G., Shiner R. J., Saetta M., Wang N. S., King M., Ghezzo H., Angus E. Alveolar fenestrae in smokers. Relationship with light microscopic and functional abnormalities. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jan;133(1):126–131. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.1.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosio M., Ghezzo H., Hogg J. C., Corbin R., Loveland M., Dosman J., Macklem P. T. The relations between structural changes in small airways and pulmonary-function tests. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 8;298(23):1277–1281. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806082982303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damiano V. V., Tsang A., Kucich U., Abrams W. R., Rosenbloom J., Kimbel P., Fallahnejad M., Weinbaum G. Immunolocalization of elastase in human emphysematous lungs. J Clin Invest. 1986 Aug;78(2):482–493. doi: 10.1172/JCI112600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox B., Bull T. B., Guz A., Harris E., Tetley T. D. Is neutrophil elastase associated with elastic tissue in emphysema? J Clin Pathol. 1988 Apr;41(4):435–440. doi: 10.1136/jcp.41.4.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg J. C., Macklem P. T., Thurlbeck W. M. Site and nature of airway obstruction in chronic obstructive lung disease. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jun 20;278(25):1355–1360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196806202782501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg J. C., Wright J. L., Pare P. D. Airways disease: evolution, pathology, and recognition. Med J Aust. 1985 May 27;142(11):605–607. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1985.tb113531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A. Elastases and emphysema. Current assessment of the protease-antiprotease hypothesis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Aug;132(2):417–433. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.2.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramps J. A., Te Boekhorst A. H., Fransen J. A., Ginsel L. A., Dijkman J. H. Antileukoprotease is associated with elastin fibers in the extracellular matrix of the human lung. An immunoelectron microscopic study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Aug;140(2):471–476. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.2.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEOPOLD J. G., GOUGH J. The centrilobular form of hypertrophic emphysema and its relation to chronic bronchitis. Thorax. 1957 Sep;12(3):219–235. doi: 10.1136/thx.12.3.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linhartová A., Anderson A. e., Jr, Foraker A. G. Radial traction and bronchiolar obstruction in pulmonary emphysema. Observed and theoretical aspects. Arch Pathol. 1971 Nov;92(5):384–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin R. F., Tueller E. E. Anatomic and histologic changes of early emphysema. Chest. 1971 Jun;59(6):592–599. doi: 10.1378/chest.59.6.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewoehner D. E., Kleinerman J., Rice D. B. Pathologic changes in the peripheral airways of young cigarette smokers. N Engl J Med. 1974 Oct 10;291(15):755–758. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197410102911503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty T. L., Silvers G. W., Stanford R. E. Mild emphysema is associated with reduced elastic recoil and increased lung size but not with air-flow limitation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Oct;136(4):867–871. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.4.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty T. L., Silvers G. W., Stanford R. E. Radial traction and small airways disease in excised human lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jan;133(1):132–135. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.1.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranga V., Kleinerman J. Interalveolar pores in mouse lung. Regional distribution and alterations with age. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Sep;122(3):477–481. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saetta M., Ghezzo H., Kim W. D., King M., Angus G. E., Wang N. S., Cosio M. G. Loss of alveolar attachments in smokers. A morphometric correlate of lung function impairment. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Oct;132(4):894–900. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.4.894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saetta M., Shiner R. J., Angus G. E., Kim W. D., Wang N. S., King M., Ghezzo H., Cosio M. G. Destructive index: a measurement of lung parenchymal destruction in smokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 May;131(5):764–769. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.5.764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobonya R. E., Burrows B. The epidemiology of emphysema. Clin Chest Med. 1983 Sep;4(3):351–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The definition of emphysema. Report of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Division of Lung Diseases workshop. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Jul;132(1):182–185. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.1.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurlbeck W. M. Measurement of pulmonary emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 May;95(5):752–764. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.95.5.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L. N., Kramps J. A., Stijnen T., Sterk P. J., Weening J. J., Dijkman J. H. Antileukoprotease-containing bronchiolar cells. Relationship with morphologic disease of small airways and parenchyma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 May;139(5):1244–1250. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.5.1244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L. N., Otto-Verberne C. J., Kramps J. A., ten Have-Opbroek A. A., Dijkman J. H. Detection of antileukoprotease in connective tissue of the lung. Histochemistry. 1986;86(2):165–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00493382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. L., Lawson L. M., Pare P. D., Wiggs B. J., Kennedy S., Hogg J. C. Morphology of peripheral airways in current smokers and ex-smokers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Apr;127(4):474–477. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.4.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. L., Wiggs B. J., Hogg J. C. Airway disease in upper and lower lobes in lungs of patients with and without emphysema. Thorax. 1984 Apr;39(4):282–285. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.4.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


