Abstract
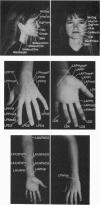
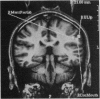
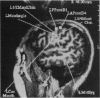
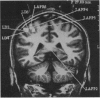
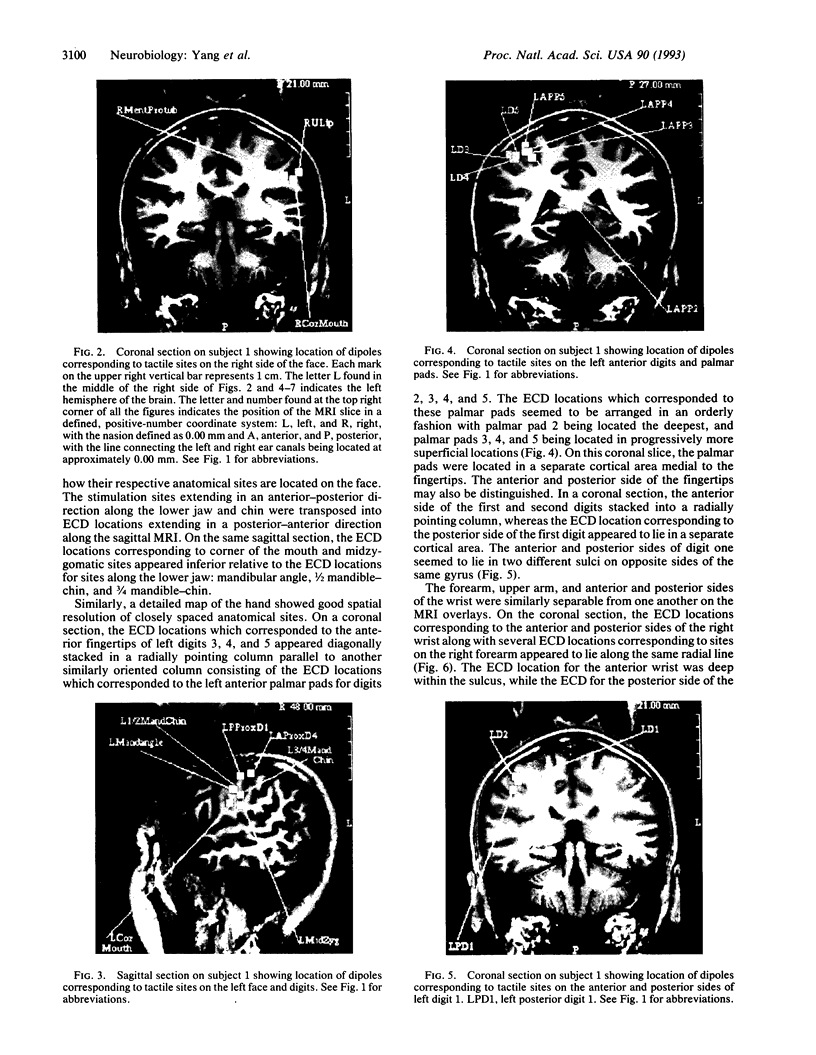
To validate the feasibility of precise noninvasive functional mapping in humans, a large-array biomagnetometer was used to map the somatosensory cortical locations corresponding to numerous distinct tactile sites on the fingers, hand, arm, and face in different subjects. Source localizations were calculated by using a single equivalent current dipole (ECD) model. Dipole localizations were transposed upon the corresponding subject's magnetic resonance image (MRI) to resolve the anatomic locus of the individual dipoles within a given subject. Biomagnetic measurements demonstrated that (i) there were distinct separations between the ECD locations representing discrete sites on the face and hand; (ii) the ECD localizations from facial sites clustered in a region inferior to ECD localizations from hand and digit sites; and (iii) there was clear spatial resolution of ECD locations representing closely spaced tactile sites on the hand and face. The ability of magnetoencephalography (MEG) to provide high-resolution spatial maps of the somatosensory system noninvasively in humans should make MEG a useful tool to define the normal or pathological organization of the human somatosensory system and should provide an approach to the rapid detection of neuroplasticity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison T. Localization of sensorimotor cortex in neurosurgery by recording of somatosensory evoked potentials. Yale J Biol Med. 1987 Mar-Apr;60(2):143–150. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner C., Barth D. S., Levesque M. F., Sutherling W. W. Functional anatomy of human hand sensorimotor cortex from spatiotemporal analysis of electrocorticography. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1991 Jan;78(1):56–65. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(91)90019-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner C., Doppelbauer A., Sutherling W. W., Zeitlhofer J., Lindinger G., Lind C., Deecke L. Human somatosensory cortical finger representation as studied by combined neuromagnetic and neuroelectric measurements. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Dec 16;134(1):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90518-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D., Lipton J., Kaufman L., Williamson S. J. Somatically evoked magnetic fields of the human brain. Science. 1978 Jan 6;199(4324):81–83. doi: 10.1126/science.199.4324.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff T. A. Topography of scalp recorded potentials evoked by stimulation of the digits. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1980 Sep;49(5-6):452–460. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(80)90388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. T., Burton H., Raichle M. E. Mapping human somatosensory cortex with positron emission tomography. J Neurosurg. 1987 Jul;67(1):34–43. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.67.1.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hari R. On brain's magnetic responses to sensory stimuli. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1991 Apr;8(2):157–169. doi: 10.1097/00004691-199104000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen J. Magnetic cortical responses evoked by tactile stimulation of the middle finger in man. Pflugers Arch. 1986 Aug;407(2):129–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00580663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämäläinen H., Kekoni J., Sams M., Reinikainen K., Nätänen R. Human somatosensory evoked potentials to mechanical pulses and vibration: contributions of SI and SII somatosensory cortices to P50 and P100 components. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1990 Feb;75(2):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(90)90148-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaukoranta E., Hämäläinen M., Sarvas J., Hari R. Mixed and sensory nerve stimulations activate different cytoarchitectonic areas in the human primary somatosensory cortex SI. Neuromagnetic recordings and statistical considerations. Exp Brain Res. 1986;63(1):60–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00235646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüders H., Dinner D. S., Lesser R. P., Morris H. H. Evoked potentials in cortical localization. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1986 Jan;3(1):75–84. doi: 10.1097/00004691-198601000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merzenich M. M., Kaas J. H., Wall J. T., Sur M., Nelson R. J., Felleman D. J. Progression of change following median nerve section in the cortical representation of the hand in areas 3b and 1 in adult owl and squirrel monkeys. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):639–665. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merzenich M. M., Kaas J. H., Wall J., Nelson R. J., Sur M., Felleman D. Topographic reorganization of somatosensory cortical areas 3b and 1 in adult monkeys following restricted deafferentation. Neuroscience. 1983 Jan;8(1):33–55. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merzenich M. M., Nelson R. J., Stryker M. P., Cynader M. S., Schoppmann A., Zook J. M. Somatosensory cortical map changes following digit amputation in adult monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Apr 20;224(4):591–605. doi: 10.1002/cne.902240408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y. C., Tanenbaum R., Williamson S. J., Kaufman L. Somatotopic organization of the human somatosensory cortex revealed by neuromagnetic measurements. Exp Brain Res. 1984;56(2):197–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00236274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. S., Skerry J. E., Tramo M. J., Gazzaniga M. S. Magnetic resonance imaging morphology of the corpus callosum in monozygotic twins. Ann Neurol. 1989 Jul;26(1):100–104. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons T. P., Garraghty P. E., Ommaya A. K., Kaas J. H., Taub E., Mishkin M. Massive cortical reorganization after sensory deafferentation in adult macaques. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1857–1860. doi: 10.1126/science.1843843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran V. S., Rogers-Ramachandran D., Stewart M. Perceptual correlates of massive cortical reorganization. Science. 1992 Nov 13;258(5085):1159–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.1439826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran V. S., Stewart M., Rogers-Ramachandran D. C. Perceptual correlates of massive cortical reorganization. Neuroreport. 1992 Jul;3(7):583–586. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199207000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suk J., Ribary U., Cappell J., Yamamoto T., Llinás R. Anatomical localization revealed by MEG recordings of the human somatosensory system. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1991 Mar;78(3):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(91)90032-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherling W. W., Crandall P. H., Darcey T. M., Becker D. P., Levesque M. F., Barth D. S. The magnetic and electric fields agree with intracranial localizations of somatosensory cortex. Neurology. 1988 Nov;38(11):1705–1714. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.11.1705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. C., Cohen D., Cuffin B. N., Yarita M., Allison T. Electrical sources in human somatosensory cortex: identification by combined magnetic and potential recordings. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):1051–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.3975600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. C., Spencer D. D., Allison T., McCarthy G., Williamson P. D., Goff W. R. Localization of human sensorimotor cortex during surgery by cortical surface recording of somatosensory evoked potentials. J Neurosurg. 1988 Jan;68(1):99–111. doi: 10.3171/jns.1988.68.1.0099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolsey C. N., Erickson T. C., Gilson W. E. Localization in somatic sensory and motor areas of human cerebral cortex as determined by direct recording of evoked potentials and electrical stimulation. J Neurosurg. 1979 Oct;51(4):476–506. doi: 10.3171/jns.1979.51.4.0476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]