Abstract
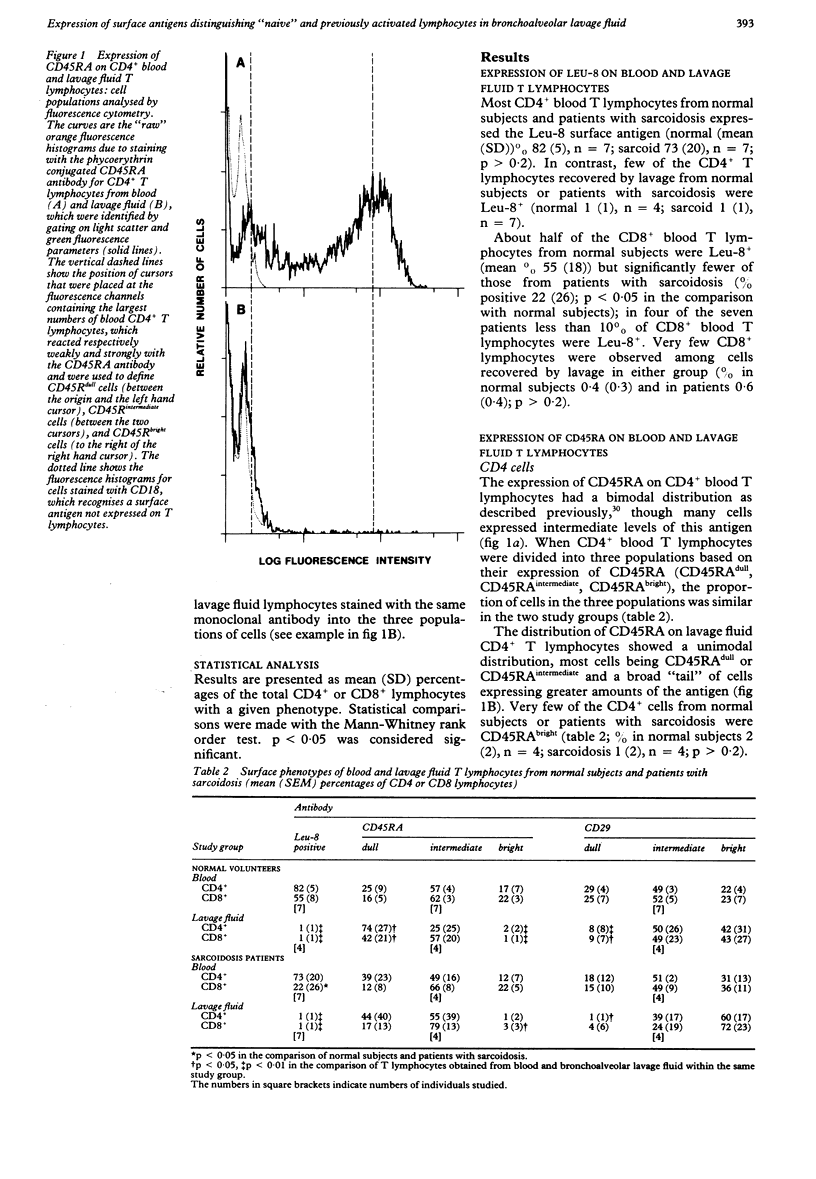
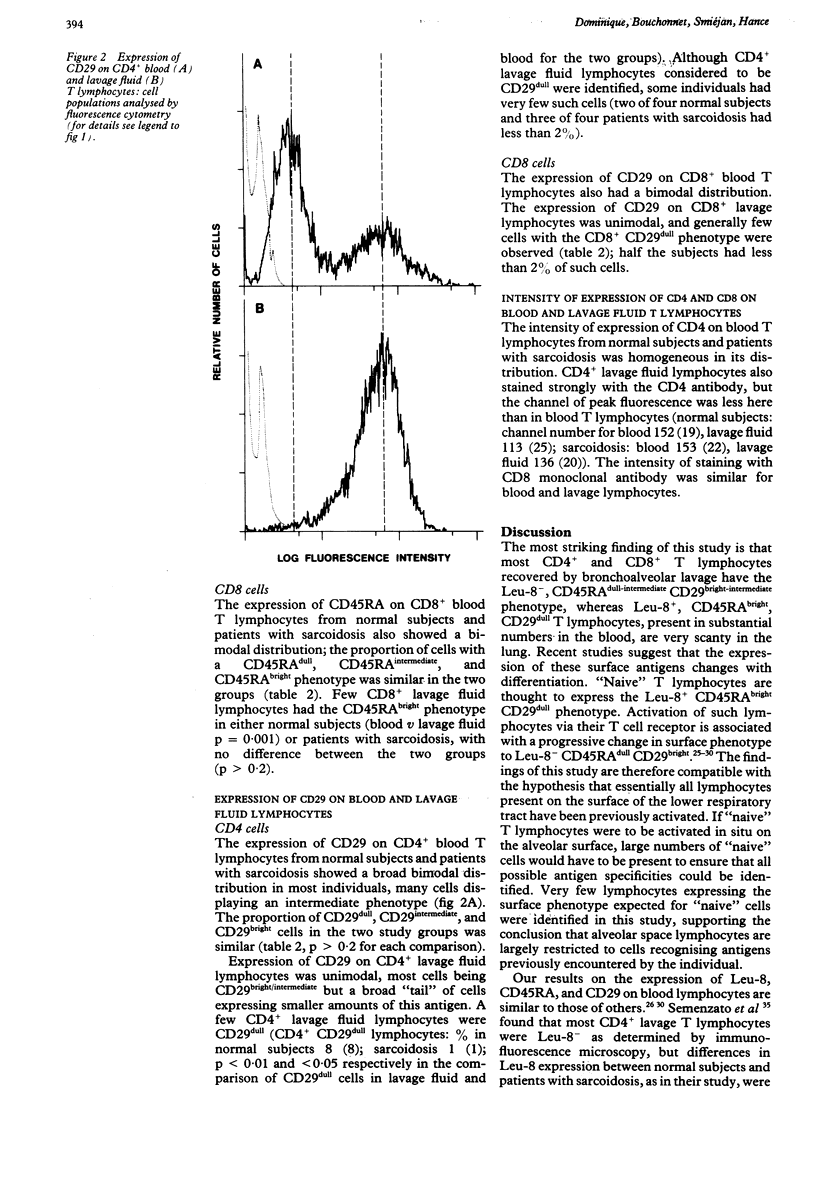
Studies in animals suggest that the initial activation of unprimed ("naive") T lymphocytes by inhaled antigens may occur outside the lung with later recruitment to the lung. If this is true all lymphocytes present in the lung should show evidence of prior activation. To test this hypothesis for lymphocytes present on the alveolar surface, the expression of surface antigens, which distinguish unprimed from previously activated cells (CD45RA, CD29, Leu-8), were measured on T lymphocytes recovered from blood and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from normal subjects and patients with sarcoidosis. Few T lymphocytes from the lavage fluid of normal subjects and patients with sarcoidosis expressed the Leu 8+ or CD45RAbright phenotype expected for "naive" cells; more cells had the CD29dull phenotype expected for "naive" cells, though five of eight subjects had under 2% of such cells. These findings support the conclusion that the only T lymphocytes present on the surface of the respiratory tract are those recognising antigens that have been previously encountered by the individual. Further studies are required to determine whether "naive" T lymphocytes are present in other lung compartments.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akbar A. N., Terry L., Timms A., Beverley P. C., Janossy G. Loss of CD45R and gain of UCHL1 reactivity is a feature of primed T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2171–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bice D. E., Degen M. A., Harris D. L., Muggenburg B. A. Recruitment of antibody-forming cells in the lung after local immunization is nonspecific. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Oct;126(4):635–639. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.4.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bice D. E., Harris D. L., Hill J. O., Muggenburg B. A., Wolff R. K. Immune responses after localized lung immunization in the dog. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Nov;122(5):755–760. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.5.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomly K. A functional dichotomy in CD4+ T lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 1988 Sep;9(9):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91308-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein D. G., Rebar A. H., Bice D. E., Muggenburg B. A., Hill J. O. Immunology of the lower respiratory tract. Serial morphologic changes in the lungs and tracheobronchial lymph nodes of dogs after intrapulmonary immunization with sheep erythrocytes. Am J Pathol. 1980 Feb;98(2):499–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini D., James S. P., Stamenkovic I., Seed B. Leu-8/TQ1 is the human equivalent of the Mel-14 lymph node homing receptor. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):78–82. doi: 10.1038/342078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Bitterman P. B., Rennard S. I., Hance A. J., Keogh B. A. Interstitial lung diseases of unknown cause. Disorders characterized by chronic inflammation of the lower respiratory tract (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 19;310(3):154–166. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401193100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson B. L., Faust J., Pessano S., Daniele R. P., Rovera G. Differentiation and activation phenotypes of lung T lymphocytes differ from those of circulating T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):60–65. doi: 10.1172/JCI111977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeson E. E., Norin A. J., Veith F. J. Antigen-induced recruitment of circulating lymphocytes to the lungs and hilar lymph nodes of mice challenged intratracheally with alloantigens. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Apr;125(4):453–459. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.4.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatenby P. A., Kansas G. S., Xian C. Y., Evans R. L., Engleman E. G. Dissection of immunoregulatory subpopulations of T lymphocytes within the helper and suppressor sublineages in man. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1997–2000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerli R., Darwish S., Broccucci L., Minotti V., Spinozzi F., Cernetti C., Bertotto A., Rambotti P. Analysis of CD4-positive T cell subpopulation in sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Aug;73(2):226–229. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada R. N., Repine J. E. Pulmonary host defense mechanisms. Chest. 1985 Feb;87(2):247–252. doi: 10.1378/chest.87.2.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joel D. D., Chanana A. D. Distribution of lung-associated lymphocytes from the caudal mediastinal lymph node: effect of antigen. Immunology. 1987 Dec;62(4):641–646. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltreider H. B., Byrd P. K., Daughety T. W., Shalaby M. R. The mechanism of appearance of specific antibody-forming cells in lungs of inbred mice after intratracheal immunization with sheep erythrocytes. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Mar;127(3):316–321. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.3.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltreider H. B., Kyselka L., Salmon S. E. Immunology of the lower respiratory tract. II. The plaque-forming response of canine lymphoid tissues to sheep erythrocytes after intrapulmonary or intravenous immunization. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):263–270. doi: 10.1172/JCI107761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanof M. E., James S. P. Leu-8 antigen expression is diminished during cell activation but does not correlate with effector function of activated T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3701–3706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecossier D., Valeyre D., Loiseau A., Battesti J. P., Soler P., Hance A. J. T-lymphocytes recovered by bronchoalveolar lavage from normal subjects and patients with sarcoidosis are refractory to proliferative signals. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Mar;137(3):592–599. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.3.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipscomb M. F., Lyons C. R., O'Hara R. M., Jr, Stein-Streilein J. The antigen-induced selective recruitment of specific T lymphocytes to the lung. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):111–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M. C., Ishizaka K., Plaut M. T lymphocyte responses of murine lung: immunization with alloantigen induces accumulation of cytotoxic and other T lymphocytes in the lung. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2653–2661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons C. R., Lipscomb M. F. Alveolar macrophages in pulmonary immune responses. I. Role in the initiation of primary immune responses and in the selective recruitment of T lymphocytes to the lung. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1113–1119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. R., Lukacher A. E., Braciale V. L., Braciale T. J., Bienenstock J. Characterization and in vivo distribution of influenza-virus-specific T-lymphocytes in the murine respiratory tract. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jan;135(1):245–249. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.1.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod E., Caldwell J. L., Kaltreider H. B. Pulmonary immune responses of inbred mice. Appearance of antibody-forming cells in C57BL/6 mice after intrapulmonary or systemic immunization with sheep erythrocytes. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Sep;118(3):561–571. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.118.3.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K., Nesbitt A. M. Identification and isolation of OKT4+ suppressor cells with the monoclonal antibody WR16. Immunology. 1986 Aug;58(4):659–664. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Boyd A. W., Hagan M., Brown H. M., Kornacki M. M., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human helper inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3762–3769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Distaso J. A., Aldrich W. R., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human suppressor inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Rudd C. E., Hagan M., Takeuchi T., Schlossman S. F. The role of the 2H4 molecule in the generation of suppressor function in Con A-activated T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3247–3253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro C. S., Campbell D. A., Du Bois R. M., Mitchell D. N., Cole P. J., Poulter L. W. Suppression associated lymphocyte markers in lesions of sarcoidosis. Thorax. 1988 Jun;43(6):471–474. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.6.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Quernheim J., Saltini C., Sondermeyer P., Crystal R. G. Compartmentalized activation of the interleukin 2 gene by lung T lymphocytes in active pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3475–3483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. A monoclonal antibody reactive with the human cytotoxic/suppressor T cell subset previously defined by a heteroantiserum termed TH2. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1301–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Separation of functional subsets of human T cells by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivas A., Takada S., Koide J., Sonderstrup-McDevitt G., Engleman E. G. CD4 molecules are associated with the antigen receptor complex on activated but not resting T cells. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):2912–2918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltini C., Hemler M. E., Crystal R. G. T lymphocytes compartmentalized on the epithelial surface of the lower respiratory tract express the very late activation antigen complex VLA-1. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Feb;46(2):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Sharrow S. O., Stephany D., Springer T. A., Young H. A., Shaw S. Human memory T lymphocytes express increased levels of three cell adhesion molecules (LFA-3, CD2, and LFA-1) and three other molecules (UCHL1, CDw29, and Pgp-1) and have enhanced IFN-gamma production. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1401–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Shaw S. Human naive and memory T cells: reinterpretation of helper-inducer and suppressor-inducer subsets. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91212-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenzato G., Agostini C., Zambello R., Trentin L., Chilosi M., Angi M. R., Ossi E., Cipriani A., Pizzolo G. Activated T cells with immunoregulatory functions at different sites of involvement in sarcoidosis. Phenotypic and functional evaluations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;465:56–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb18481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serra H. M., Krowka J. F., Ledbetter J. A., Pilarski L. M. Loss of CD45R (Lp220) represents a post-thymic T cell differentiation event. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1435–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venet A., Hance A. J., Saltini C., Robinson B. W., Crystal R. G. Enhanced alveolar macrophage-mediated antigen-induced T-lymphocyte proliferation in sarcoidosis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):293–301. doi: 10.1172/JCI111688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyand C. M., Goronzy J., Fathman C. G. Modulation of CD4 by antigenic activation. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1351–1354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



