Abstract
Background/Aims
Pediatric inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has been increasing worldwide. The characteristics of pediatric-onset IBD have mainly been reported in Western countries. We investigated the clinical characteristics of pediatric IBD in Korea and compared these with the data from the 5-year European multicenter study of children with new-onset IBD (EUROKIDS registry).
Methods
Children who were diagnosed with IBD between July 1987 and January 2012 were investigated at five Korean university hospitals. Their clinical characteristics were retrospectively evaluated by medical record review. The results were compared with the EUROKIDS data.
Results
A total of 30 children with Crohn’s disease (CD) and 33 children with ulcerative colitis (UC) were enrolled. In comparison with the EUROKIDS group, Korean pediatric IBD patients showed a male predominance (86.7% vs 59.2%, p=0.002 in CD; 75.8% vs 50%, p=0.003 in UC). Korean pediatric CD patients had a higher prevalence of terminal ileal disease (36.7% vs 16.3%, p=0.004) and perianal disease (33.3% vs 8.2%, p<0.001) than patients in the EUROKIDS group. Korean pediatric UC patients had a higher prevalence of proctitis than patients in the EUROKIDS group.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that the characteristics of Korean pediatric IBD patients and European pediatric IBD patients may be different.
Keywords: Inflammatory bowel diseases, Pediatrics, Characteristics, Korea
INTRODUCTION
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic gastrointestinal inflammation, including Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). It is a life-long idiopathic disorder and etiology is unknown.1
The number of pediatric patients with IBD has gradually increased over the last several decades.2,3 Approximately 15% to 25% of patients with IBD have the onset of their symptoms before 20 years of age.4,5 Previous epidemiological studies reported that characteristics of pediatric onset IBD differ from those of adults.6 Incidence of IBD is greater among Caucasians than in other races, so the characteristics of pediatric onset IBD have been reported mainly from Western countries.2,7,8
Although IBD is rare in Korean children, increasing numbers of pediatric patients with IBD have been noted in recent years. However, there are few studies that have focused on pediatric onset IBD in Korea.9–12 Furthermore there are no studies comparing Western pediatric IBD and Korean pediatric IBD patients. In an attempt to answer the question, we investigated the clinical characteristics of pediatric IBD in Korea and compare with cases reported from the 5-year European multicenter study of children with new-onset IBD (EUROKIDS registry).13,14
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Five institutions in Korea participated in this retrospective study with the approval of each institutional review board: Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Samsung Medical Center, Kyung Hee University Hospital, Konyang University Hospital, and St. Vincent’s Hospital. The medical records from July 1987 through January 2012 were reviewed to identify patients who treated for IBD. All patients had to be <18 years of age at diagnosis of IBD and diagnoses were confirmed by previously established international criteria based on clinical, endoscopic, histopathological, and radiological findings.15 Disease location and disease behavior were classified according to the Montreal classification.16 The extent of UC patients of EUROKIDS group were analyzed by the Paris classification, while our study used Montreal classification for data analysis. Therefore, we reanalyzed the extent of UC patients of EUROKIDS group using Montreal classification to compare the data from two different studies. In this reason, E2 and E3 of Paris classification were combined as a single E2 of Montreal classification and E4 of Paris classification are replaced E3.
Patients with less than 6 months of follow-up and incomplete clinical data were excluded.
The software program SPSS version 12.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for statistical analyses. The chi-square or Fisher exact test was used to compare categorical variables. p-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
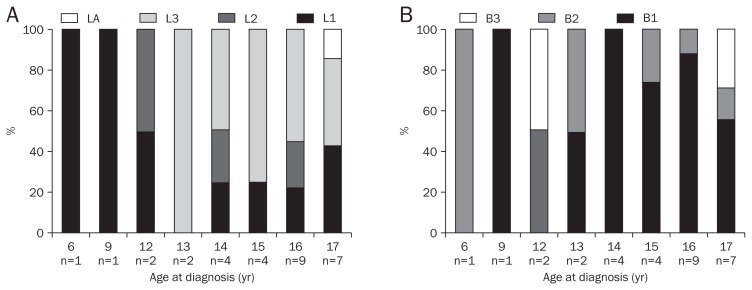
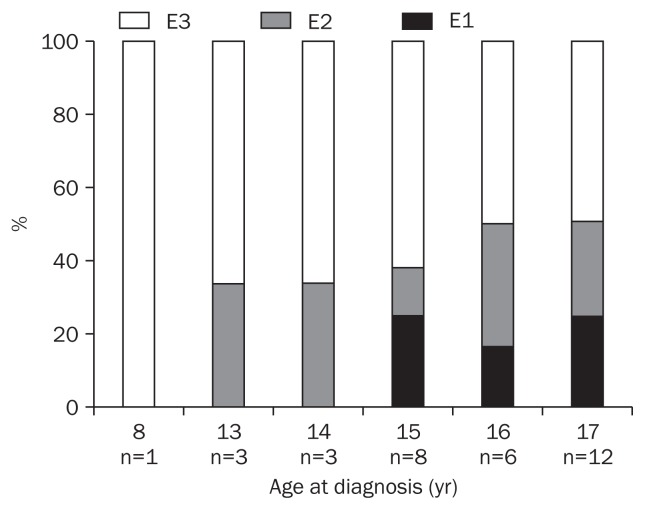
A total of 30 children with CD and 33 children with UC were enrolled. Fig. 1 shows distribution of disease location and disease behavior in Korean pediatric patients with CD according to age at diagnosis. Fig. 2 shows distribution of disease extent in Korean pediatric patients with UC according to age at diagnosis.
Fig. 1.
Disease location and disease behavior in children with Crohn’s disease by age at diagnosis. (A) Disease location. (B) Disease behavior.
L1, terminal ileal disease; L2, colonic disease; L3, ileocolonic disease; L4, concomitant upper gastrointestinal disease; B1, nonstricturing, non-penetrating; B2, stricturing; B3, penetrating.
Fig. 2.
Disease extent in children with ulcerative colitis (UC) by age at diagnosis.
E1, ulcerative proctitis; E2, left-sided UC; E3, extensive UC.
In comparison with EUROKIDS group, Korean pediatric IBD patients showed male predominance (86.7% vs 59.2%, p=0.002 in CD; 75.8% vs 50%, p=0.003 in UC). The mean ages at diagnosis of Korean IBD children were older than EUROKIDS group (15.3 years vs 12.5 years in CD; 15.8 years vs 11.6 years in UC) (Table 1).
Table 1.
Patient Demographics at Diagnosis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
| Demographics | Korean patients | EUROKIDS | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD | n=30 | n=1,221 | |
| Age at diagnosis | 15.3 (6.9–17.9) | 12.5 (0.8–17.9) | |
| Sex | 0.002 | ||
| Male | 26 (86.7) | 723 (59.2) | |
| Female | 4 (13.3) | 498 (40.8) | |
| Male:female ratio | 6.5:1 | 1.5:1 | |
| UC | n=33 | n=643 | |
| Age at diagnosis | 15.8 (8.8–17.7) | 11.6 (0.6–17.9) | |
| Sex | 0.003 | ||
| Male | 25 (75.8) | 319 (49.6) | |
| Female | 8 (24.2) | 324 (50.4) | |
| Male:female ratio | 3.1:1 | 1:1 |
Data are presented as mean (range) or number (%).
CD, Crohn’s disease; UC, ulcerative colitis.
Table 2 shows the results comparing disease characteristics of pediatric CD in Korean group and EUROKIDS group. In comparison to EUROKIDS group, Korean children had higher rates of terminal ileal disease (36.7% vs 16.3%, p=0.004). There is no difference between Korean group and EUROKIDS group on disease behavior of CD, but perianal disease is higher rates in Korean children (33.3% vs 8.2%, p<0.001).
Table 2.
Comparison of the Characteristics of Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Patients in Korea and EUROKIDS, Using the Montreal Classification
| Characteristic | Korean patients (n=30) | EUROKIDS (n=582) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disease distribution | |||
| L1 (terminal ileal disease) | 11 (36.7) | 95 (16.3) | 0.004 |
| L2 (colonic disease) | 4 (13.3) | 159 (27.3) | 0.136 |
| L3 (ileocolonic disease) | 15 (50.0) | 307 (52.8) | 0.769 |
| L4 (concomitant/isolated UGI disease) | 1 (3.4) | 269 (46.2) | <0.001 |
| Disease behavior | |||
| B1 (nonstricturing, nonpenetrating) | 21 (70.0) | 477 (82.0) | 0.101 |
| B2 (stricturing) | 6 (20.0) | 77 (13.2) | 0.291 |
| B3 (penetrating) | 3 (10.0) | 28 (4.8) | 0.189 |
| Perianal disease | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 10 (33.3) | 48 (8.2) | |
| No | 20 (66.7) | 534 (91.8) | |
Data are presented as number (%).
UGI, upper gastrointestinal.
The comparison of disease extent of pediatric UC patients in Korea and EUROKIDS was seen on the Table 3. Both groups showed high proportion of extensive disease (E3, Korea 57.6% and EUROKIDS 68.7%), and its prevalence was inversely correlated with age (Fig. 2); however, Korean children had higher rates of proctitis than EUROKIDS group (18.2% vs 4.7%, p=0.001).
Table 3.
Comparison of the Characteristics of Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis Patients in Korea and EUROKIDS, Using the Montreal Classification
| Characteristic | Korean patients (n=33) | EUROKIDS (n=578) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| UC | |||
| E1 (ulcerative proctitis) | 6 (18.2) | 27 (4.7) | 0.001 |
| E2 (left-sided UC*) | 8 (24.2) | 154 (26.6)† | 0.761 |
| E3 (extensive UC‡) | 19 (57.6) | 397 (68.7)§ | 0.183 |
Data are presented as number (%).
UC, ulcerative colitis.
Distal to splenic flexure;
E2 and E3 of the Paris classification;
Proximal to splenic flexure;
E4 of the Paris classification.
DISCUSSION
This study is the first paper reporting the clinical characteristics of pediatric IBD in Korea based on multicenter data. We examined the clinical characteristics of pediatric IBD diagnosed in the five centers and compared our data with the data from EUROKIDS which is the largest pediatric IBD study conducted in Europe. There are several, significant differences in clinical characteristics between two groups. Pediatric CD patients in our study showed higher ratio in terms of terminal ileal disease and perianal disease than EUROKIDS patients. In case of pediatric UC patients, the ratio of proctitis was higher in Korean pediatric patients than EUROKIDS group.
Our study presented a marked male predominance in the pediatric CD patients (male:female ratio, 6.5:1). As the other studies of Korean pediatric CD also identified the male predominance, reporting male-to-female ratio of CD as 2:1, 2.2:1,10,11 this study reconfirmed the male predominance in Korea pediatric CD patients. Male predominance was also reported in recent Western pediatric studies, but EUROKIDS data did not showed sexual predominance.7,8,13 Similar to our results, studies conducted in Asian countries, such as Korea, China, and Japan, reported male predominance, whereas the studies conducted in Western countries reported that there is no difference in sex ratio or even female predominance.8,17,18
In location of the CD, both our study group and EUROKIDS group reported about 50% in ileocolic disease (L3). The next largest group was terminal ileal disease (L1) in our study, but colonic disease (L2) in EUROKIDS study. Looking at the other pediatric CD studies conducted in Korea, they showed different results. In the case of Lee & Park,11 this L1 predominance was observed as 33.3% and Kim et al.10 reported 13% of L1 as shown in EUROKIDS group. Therefore, more studies are needed to verify whether L1 predominance than L2 disease is a main characteristic of Korean pediatric CD. Studies about adult CD in Korea also showed L1 predominance than L2.19,20
The results of our study showed that the predominance of perianal disease can be the distinguishable difference in Asian and Western in pediatric CDs. Other studies about Korean pediatric CD also support the result of the current study, presenting that about half of the patients have perianal disease (50% to 54%).10,11 However, the studies conducted in Western countries reported perianal disease of pediatric CD as 8% to 14.5%.21–24 Perianal disease has also seemed to be more commonly occurred in Korean adult CD patients than Western countries. Studies from Asian area reported 30% to 40% of perianal disease and studies from North America reported 13% to 38%.19,25–28
Pediatiric UC patients also showed male predominance. However, the other Korean pediatric study about IBD reported female predominance, and Korean adult study reported no gender bias.9,10 Western study about UC have shown no sexual differences in either adults or children.7,8
Our study showed high proportion of children of UC with extensive disease which was inversely correlated with age. EU-ROKIDS study also verified same result and it correspond with the previous literature.14,29,30 Adult UC presented relatively less extensive disease than pediatric UC in both Western and Eastern and most frequent location of UC in adult UC varied between different studies.31,32
Korean children with UC had higher proportion of proctitis (E1) than EUROKIDS group. Similar to the present study, a single-center study of pediatric IBD in Korea, reported that proctitis of Korean pediatric UC was 21%.10 On the other hand, other pediatric UC studies in Western countries report that E1 was found less than 5% to 10%.21,23,24
Our study has some limitations. First, there is limited validation because of small amount of samples of this study comparing to the number of patients used in large studies such as EUROKIDS study. Because the incidence of IBD is low in Korea, and thus, the incidence of IBD in children is lower, absolute number of patients is inevitably small in Korea. However, it is believed that the results of our study can reflect tendency of Korean pediatric IBD, because the patients of this study were collected from five different hospitals in three provinces in Korea. Second, we used Montreal classification instead of Paris classification which can be more sophisticate in examining pediatrics.
In conclusion, Korean children with CD have higher prevalence of ileal disease and perianal disease and Korean children with UC have high prevalence of proctitis compared with EU-ROKIDS. Our results suggest that the characteristics of Korean pediatric IBD patients and European pediatric IBD patients may be different.
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
REFERENCES
- 1.Podolsky DK. Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:417–429. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra020831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Armitage E, Drummond HE, Wilson DC, Ghosh S. Increasing incidence of both juvenile-onset Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis in Scotland. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;13:1439–1447. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200112000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Auvin S, Molinié F, Gower-Rousseau C, et al. Incidence, clinical presentation and location at diagnosis of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: a prospective population-based study in northern France (1988–1999) J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005;41:49–55. doi: 10.1097/01.MPG.0000162479.74277.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Goodhand J, Hedin CR, Croft NM, Lindsay JO. Adolescents with IBD: the importance of structured transition care. J Crohns Colitis. 2011;5:509–519. doi: 10.1016/j.crohns.2011.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jung YS, Song CS, Kim ER, et al. Seasonal variation in months of birth and symptom flares in Korean patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Liver. 2013;7:661–667. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2013.7.6.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mamula P, Markowitz JE, Baldassano RN. Inflammatory bowel disease in early childhood and adolescence: special considerations. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2003;32:967–995. doi: 10.1016/S0889-8553(03)00046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sawczenko A, Sandhu BK. Presenting features of inflammatory bowel disease in Great Britain and Ireland. Arch Dis Child. 2003;88:995–1000. doi: 10.1136/adc.88.11.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kugathasan S, Judd RH, Hoffmann RG, et al. Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of children with newly diagnosed inflammatory bowel disease in Wisconsin: a statewide population-based study. J Pediatr. 2003;143:525–531. doi: 10.1067/S0022-3476(03)00444-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yang SK, Yun S, Kim JH, et al. Epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease in the Songpa-Kangdong district, Seoul, Korea, 1986–2005: a KASID study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008;14:542–549. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kim BJ, Song SM, Kim KM, et al. Characteristics and trends in the incidence of inflammatory bowel disease in Korean children: a single-center experience. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55:1989–1995. doi: 10.1007/s10620-009-0963-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lee NY, Park JH. Clinical features and course of Crohn disease in children. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;34:193–199. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Song SM, Kim Y, Oh SH, Kim KM. Nutritional status and growth in Korean children with Crohn’s disease: a single-center study. Gut Liver. 2014;8:500–507. doi: 10.5009/gnl13183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.de Bie CI, Paerregaard A, Kolacek S, et al. Disease phenotype at diagnosis in pediatric Crohn’s disease: 5-year analyses of the EU-ROKIDS Registry. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013;19:378–385. doi: 10.1002/ibd.23008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Levine A, de Bie CI, Turner D, et al. Atypical disease phenotypes in pediatric ulcerative colitis: 5-year analyses of the EUROKIDS Registry. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013;19:370–377. doi: 10.1002/ibd.23013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lennard-Jones JE. Classification of inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1989;170:2–6. doi: 10.3109/00365528909091339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Satsangi J, Silverberg MS, Vermeire S, Colombel JF. The Montreal classification of inflammatory bowel disease: controversies, consensus, and implications. Gut. 2006;55:749–753. doi: 10.1136/gut.2005.082909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ouyang Q, Tandon R, Goh KL, Ooi CJ, Ogata H, Fiocchi C. The emergence of inflammatory bowel disease in the Asian Pacific region. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2005;21:408–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Loftus EV, Jr, Schoenfeld P, Sandborn WJ. The epidemiology and natural history of Crohn’s disease in population-based patient cohorts from North America: a systematic review. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002;16:51–60. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2002.01140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ye BD, Yang SK, Cho YK, et al. Clinical features and long-term prognosis of Crohn’s disease in Korea. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2010;45:1178–1185. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2010.497936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Park JB, Yang SK, Myung SJ, et al. Clinical characteristics at diagnosis and course of Korean patients with Crohn’s disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2004;43:8–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Müller KE, Lakatos PL, Arató A, et al. Incidence, Paris classification, and follow-up in a nationwide incident cohort of pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2013;57:576–582. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31829f7d8c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hope B, Shahdadpuri R, Dunne C, et al. Rapid rise in incidence of Irish paediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Arch Dis Child. 2012;97:590–594. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2011-300651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Malmborg P, Grahnquist L, Lindholm J, Montgomery S, Hildebrand H. Increasing incidence of paediatric inflammatory bowel disease in northern Stockholm County, 2002–2007. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2013;57:29–34. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31828f21b4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Eszter Müller K, Laszlo Lakatos P, Papp M, Veres G. Incidence and paris classification of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2014;2014:904307. doi: 10.1155/2014/904307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ng SC, Tang W, Ching JY, et al. Incidence and phenotype of inflammatory bowel disease based on results from the Asia-pacific Crohn’s and colitis epidemiology study. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:158–165. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lok KH, Hung HG, Ng CH, Li KK, Li KF, Szeto ML. The epidemiology and clinical characteristics of Crohn’s disease in the Hong Kong Chinese population: experiences from a regional hospital. Hong Kong Med J. 2007;13:436–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.American Gastroenterological Association Clinical Practice Committee. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement: perianal Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1503–1507. doi: 10.1016/j.gastro.2003.08.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schwartz DA, Loftus EV, Jr, Tremaine WJ, et al. The natural history of fistulizing Crohn’s disease in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:875–880. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.32362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Van Limbergen J, Russell RK, Drummond HE, et al. Definition of phenotypic characteristics of childhood-onset inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1114–1122. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.06.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Levine A, Griffiths A, Markowitz J, et al. Pediatric modification of the Montreal classification for inflammatory bowel disease: the Paris classification. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011;17:1314–1321. doi: 10.1002/ibd.21493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.da Silva BC, Lyra AC, Rocha R, Santana GO. Epidemiology, demographic characteristics and prognostic predictors of ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:9458–9467. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Park SH, Kim YM, Yang SK, et al. Clinical features and natural history of ulcerative colitis in Korea. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2007;13:278–283. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]