Abstract
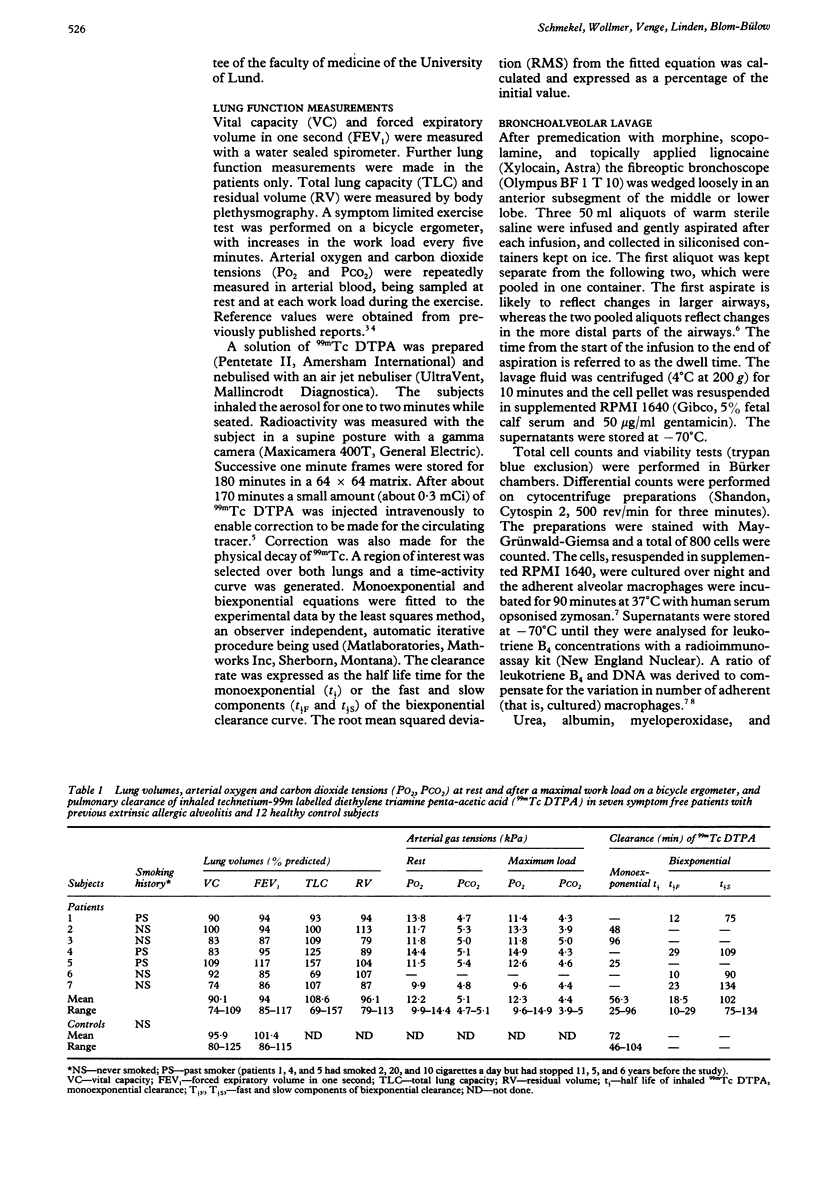
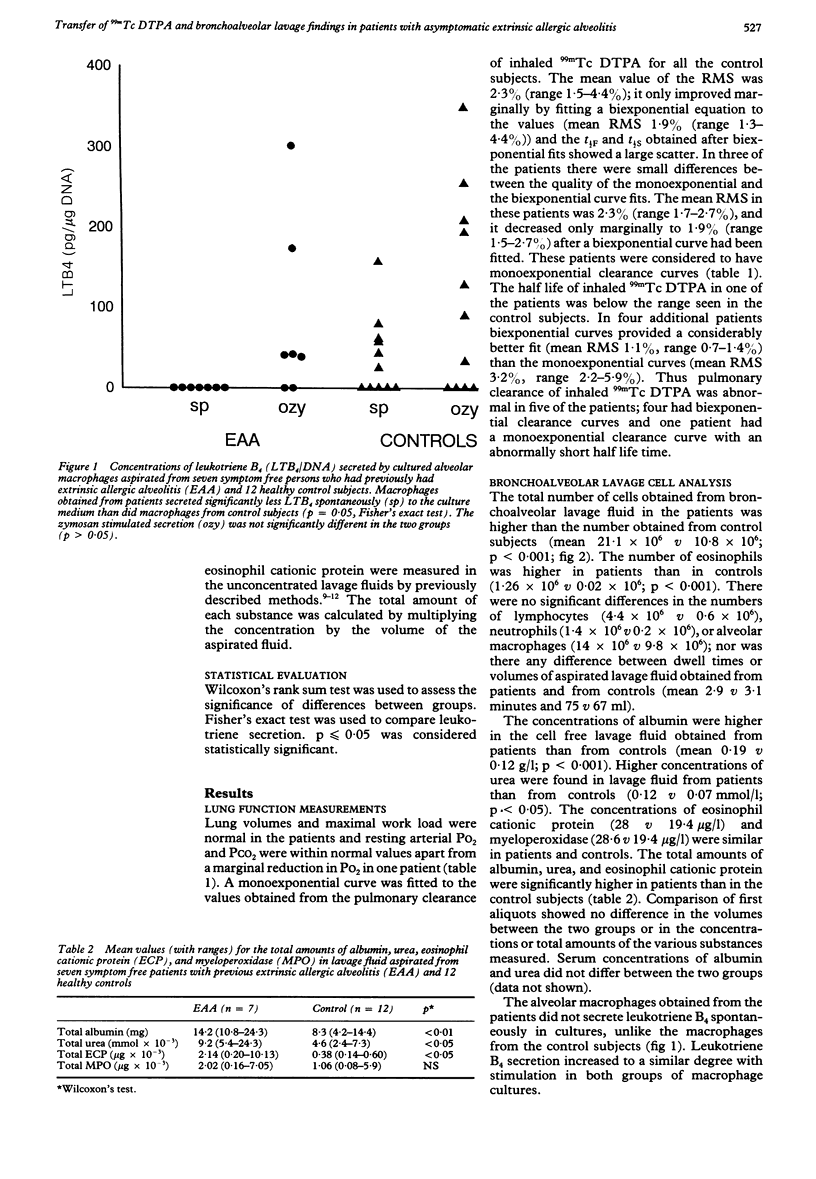
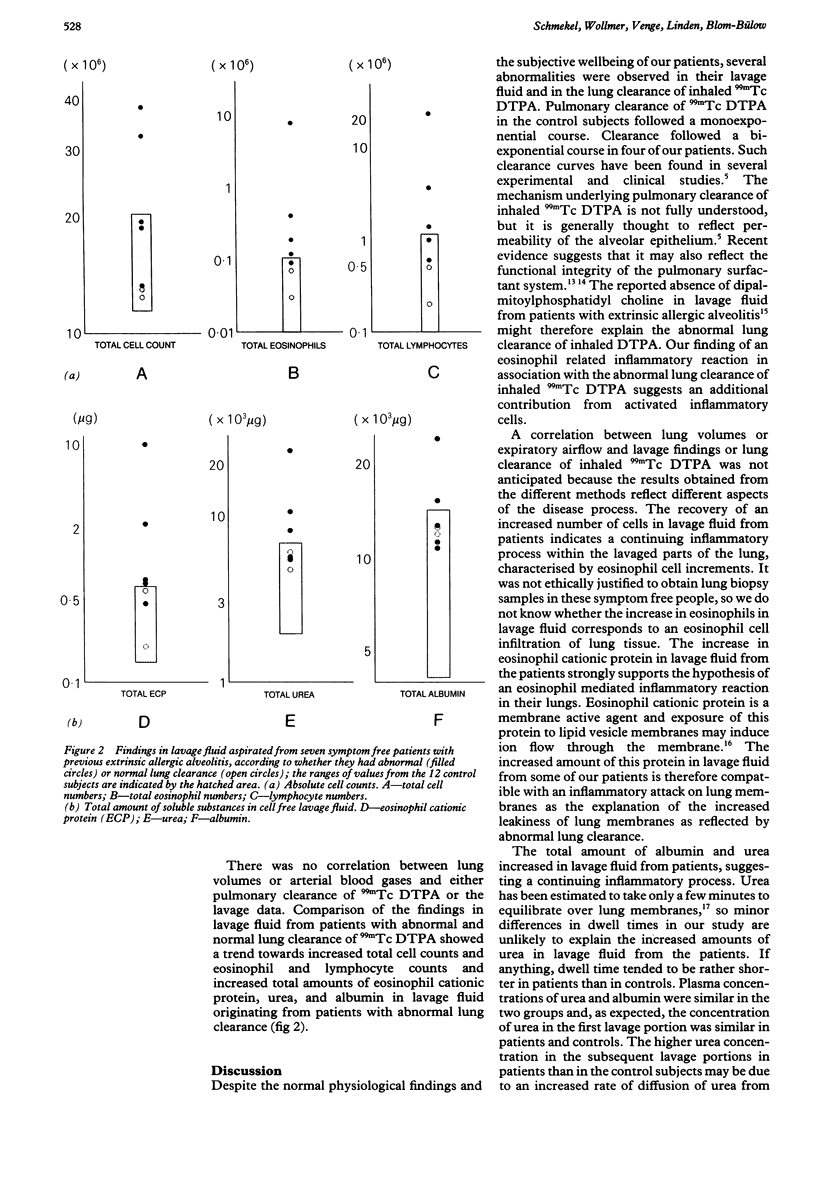
An investigation was performed to determine whether symptom free patients with previously diagnosed extrinsic allergic alveolitis had signs of inflammation in the lung. Pulmonary clearance of inhaled technetium-99m labelled diethylene triamine penta-acetic acid (DTPA) was measured in seven patients with a history of extrinsic allergic alveolitis but with no symptoms at the time of the study and in 12 control subjects. Monoexponential clearance curves were obtained in all 12 control subjects. In contrast, lung clearance was abnormal in five of the seven patients: biexponential clearance curves were noted in four and an abnormally rapid monoexponential curve in one. Bronchoalveolar lavage was performed in all patients. Fluid from the second and third aliquots showed increased concentrations of albumin and urea in fluids from the patients, suggesting increased plasma leakage through the alveolocapillary membranes. More eosinophils and more eosinophil cationic protein were also found in the lavage fluid from the patients. The trend towards increased numbers of eosinophils in patients with abnormal lung clearance of DTPA suggests that this may be due to a continuing inflammatory reaction. Lung inflammation was also suggested by the fact that less leukotriene B4 was secreted by cultured alveolar macrophages obtained from patients than by control macrophages. It is concluded that symptom free patients with previous extrinsic allergic alveolitis have continuing alveolar disease as shown by lung clearance and lavage findings.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGLUND E., BIRATH G., BJURE J., GRIMBY G., KJELLMER I., SANDQVIST L., SODERHOLM B. Spirometric studies in normal subjects. I. Forced expirograms in subjects between 7 and 70 years of age. Acta Med Scand. 1963 Feb;173:185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowcliffe M. P., Jones J. G. Solute permeability of the alveolar capillary barrier. Thorax. 1987 Jan;42(1):1–10. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormier Y., Bélanger J., Laviolette M. Persistent bronchoalveolar lymphocytosis in asymptomatic farmers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 May;133(5):843–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. S., Giancola M. S., Costanza M. C., Low R. B. Analyses of sequential bronchoalveolar lavage samples from healthy human volunteers. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Oct;126(4):611–616. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.4.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evander E., Wollmer P., Jonson B., Lachmann B. Pulmonary clearance of inhaled 99mTc-DTPA: effects of surfactant depletion by lung lavage. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Apr;62(4):1611–1614. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.62.4.1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink J. N. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984 Jul;74(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(84)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly C. A., Kotre C. J., Ward C., Hendrick D. J., Walters E. H. Anatomical distribution of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid as assessed by digital subtraction radiography. Thorax. 1987 Aug;42(8):624–628. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.8.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laviolette M., Coulombe R., Picard S., Braquet P., Borgeat P. Decreased leukotriene B4 synthesis in smokers' alveolar macrophages in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):54–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI112301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lizana J., Hellsing K. Polymer enhancement of automated immunological nephelometric analysis, as illustrated by determination of urinary albumin. Clin Chem. 1974 Apr;20(4):415–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcy T. W., Merrill W. W., Rankin J. A., Reynolds H. Y. Limitations of using urea to quantify epithelial lining fluid recovered by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jun;135(6):1276–1280. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.6.1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson T., Olsson I., Venge P., Elgefors B. Serum myeloperoxidase and lactoferrin in neutropenia. Scand J Haematol. 1977 Jan;18(1):73–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1977.tb01480.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. G., Skoog V., Venge P. Human eosinophil cationic proteins (ECP and EPX) and their suppressive effects on lymphocyte proliferation. Immunobiology. 1986 Mar;171(1-2):1–13. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(86)80013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Basset G., Lecossier D., O'Donnell K. M., Pinkston P., Martin P. G., Crystal R. G. Estimation of volume of epithelial lining fluid recovered by lavage using urea as marker of dilution. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Feb;60(2):532–538. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.2.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz M., Patterson R. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis--general considerations. Clin Rev Allergy. 1983 Dec;1(4):451–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venge P., Roxin L. E., Olsson I. Radioimmunoassay of human eosinophil cationic protein. Br J Haematol. 1977 Nov;37(3):331–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb01003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander E., Linden M., Håkansson L., Eklund A., Blaschke E., Brattsand R., Venge P. Human alveolar macrophages from smokers have an impaired capacity to secrete LTB4 but not other chemotactic factors. Eur J Respir Dis. 1987 Oct;71(4):263–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Peterson C. G., Venge P., Cohn Z. A. Mechanism of membrane damage mediated by human eosinophil cationic protein. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):613–616. doi: 10.1038/321613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



