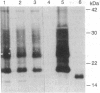
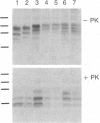
Abstract
The only known component of the infectious prion is a posttranslationally modified protein known as the scrapie isoform of the prion protein, PrPSc. Upon limited proteolysis, a protease-resistant fragment designated PrP 27-30 is formed. Using in vitro mutagenesis, we examined the role of the N and C termini in the formation of PrPSc in persistently infected, mouse neuroblastoma (ScN2a) cells. Neither deletion of amino acids 23-88, which are also removed by proteinase K in the formation of PrP 27-30, nor deletion of the five octapeptide repeats within this region altered synthesis of PrPSc. Elongation of PrP with one, two, four, or six octapeptide repeats in addition to the five found in wild-type PrP did not alter the synthesis of PrPSc. Truncation of the C terminus was accomplished by substituting a translation stop codon for the predicted glycosylinositol phospholipid (GPI) anchor-attachment signal corresponding to amino acids 231-254. Expression of this C-terminal PrP mutant in ScN2a cells produced PrPSc that appeared to lack a GPI anchor. We conclude that neither the GPI anchor nor the N-terminal 66 amino acids are required for the synthesis of PrPSc as measured by the acquisition of limited resistance to proteinase K digestion. Whether these truncated or elongated PrP molecules are competent to participate in the formation of infectious prions remains to be established.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basler K., Oesch B., Scott M., Westaway D., Wälchli M., Groth D. F., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B., Weissmann C. Scrapie and cellular PrP isoforms are encoded by the same chromosomal gene. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90662-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borchelt D. R., Scott M., Taraboulos A., Stahl N., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie and cellular prion proteins differ in their kinetics of synthesis and topology in cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):743–752. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büeler H., Fischer M., Lang Y., Bluethmann H., Lipp H. P., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B., Aguet M., Weissmann C. Normal development and behaviour of mice lacking the neuronal cell-surface PrP protein. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):577–582. doi: 10.1038/356577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B., Raymond G. J., Ernst D., Race R. E. N-terminal truncation of the scrapie-associated form of PrP by lysosomal protease(s): implications regarding the site of conversion of PrP to the protease-resistant state. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6597–6603. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6597-6603.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B., Raymond G. J. The scrapie-associated form of PrP is made from a cell surface precursor that is both protease- and phospholipase-sensitive. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18217–18223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F. E., Abarbanel R. M., Kuntz I. D., Fletterick R. J. Turn prediction in proteins using a pattern-matching approach. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):266–275. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinge J., Brown J., Hardy J., Mullan M., Rossor M. N., Baker H., Crow T. J., Lofthouse R., Poulter M., Ridley R. Inherited prion disease with 144 base pair gene insertion. 2. Clinical and pathological features. Brain. 1992 Jun;115(Pt 3):687–710. doi: 10.1093/brain/115.3.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinge J., Harding A. E., Owen F., Poulter M., Lofthouse R., Boughey A. M., Shah T., Crow T. J. Diagnosis of Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome in familial dementia with prion protein gene analysis. Lancet. 1989 Jul 1;2(8653):15–17. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90256-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collinge J., Owen F., Poulter M., Leach M., Crow T. J., Rossor M. N., Hardy J., Mullan M. J., Janota I., Lantos P. L. Prion dementia without characteristic pathology. Lancet. 1990 Jul 7;336(8706):7–9. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91518-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Homans S. W., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol moiety that anchors Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein to the membrane. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):753–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3340856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasset M., Baldwin M. A., Lloyd D. H., Gabriel J. M., Holtzman D. M., Cohen F., Fletterick R., Prusiner S. B. Predicted alpha-helical regions of the prion protein when synthesized as peptides form amyloid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10940–10944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb L. G., Brown P., McCombie W. R., Goldgaber D., Swergold G. D., Wills P. R., Cervenakova L., Baron H., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Transmissible familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease associated with five, seven, and eight extra octapeptide coding repeats in the PRNP gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10926–10930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker R., Taraboulos A., Scott M., Pan K. M., Yang S. L., Torchia M., Jendroska K., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Replication of distinct scrapie prion isolates is region specific in brains of transgenic mice and hamsters. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1213–1228. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemström C., Virtanen A., Bridge E., Ketner G., Pettersson U. Adenovirus E4-dependent activation of the early E2 promoter is insufficient to promote the early-to-late-phase transition. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1440–1449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1440-1449.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao K. K., Scott M., Foster D., Groth D. F., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Spontaneous neurodegeneration in transgenic mice with mutant prion protein. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1587–1590. doi: 10.1126/science.1980379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kascsak R. J., Rubenstein R., Merz P. A., Tonna-DeMasi M., Fersko R., Carp R. I., Wisniewski H. M., Diringer H. Mouse polyclonal and monoclonal antibody to scrapie-associated fibril proteins. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3688–3693. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3688-3693.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laplanche J. L., Chatelain J., Launay J. M., Gazengel C., Vidaud M. Deletion in prion protein gene in a Moroccan family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6745–6745. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. K., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Braunfeld M. B., Barry R. A., Prusiner S. B. Separation and properties of cellular and scrapie prion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2310–2314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch B., Westaway D., Wälchli M., McKinley M. P., Kent S. B., Aebersold R., Barry R. A., Tempst P., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E. A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen F., Poulter M., Collinge J., Leach M., Lofthouse R., Crow T. J., Harding A. E. A dementing illness associated with a novel insertion in the prion protein gene. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1992 Mar;13(1-2):155–157. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(92)90056-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen F., Poulter M., Collinge J., Leach M., Shah T., Lofthouse R., Chen Y. F., Crow T. J., Harding A. E., Hardy J. Insertions in the prion protein gene in atypical dementias. Exp Neurol. 1991 May;112(2):240–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(91)90075-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen F., Poulter M., Lofthouse R., Collinge J., Crow T. J., Risby D., Baker H. F., Ridley R. M., Hsiao K., Prusiner S. B. Insertion in prion protein gene in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Lancet. 1989 Jan 7;1(8628):51–52. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91713-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen F., Poulter M., Shah T., Collinge J., Lofthouse R., Baker H., Ridley R., McVey J., Crow T. J. An in-frame insertion in the prion protein gene in familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990 Apr;7(3):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90038-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan K. M., Stahl N., Prusiner S. B. Purification and properties of the cellular prion protein from Syrian hamster brain. Protein Sci. 1992 Oct;1(10):1343–1352. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560011014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter M., Baker H. F., Frith C. D., Leach M., Lofthouse R., Ridley R. M., Shah T., Owen F., Collinge J., Brown J. Inherited prion disease with 144 base pair gene insertion. 1. Genealogical and molecular studies. Brain. 1992 Jun;115(Pt 3):675–685. doi: 10.1093/brain/115.3.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D. F., Bolton D. C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Purification and structural studies of a major scrapie prion protein. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90533-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1515–1522. doi: 10.1126/science.1675487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Scott M., Foster D., Pan K. M., Groth D., Mirenda C., Torchia M., Yang S. L., Serban D., Carlson G. A. Transgenetic studies implicate interactions between homologous PrP isoforms in scrapie prion replication. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):673–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90134-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M., Serban D., Gyuris T., Scott M., Torchia T., Prusiner S. B. Epitope mapping of the Syrian hamster prion protein utilizing chimeric and mutant genes in a vaccinia virus expression system. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 15;147(10):3568–3574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M., Taraboulos A., Scott M., Groth D., Prusiner S. B. Intracellular accumulation of the cellular prion protein after mutagenesis of its Asn-linked glycosylation sites. Glycobiology. 1990 Sep;1(1):101–109. doi: 10.1093/glycob/1.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitta B., Timpl R., Chu M. L. Human alpha 2(VI) collagen gene. Heterogeneity at the 5'-untranslated region generated by an alternate exon. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6188–6196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. R., Butler D. A., Bredesen D. E., Wälchli M., Hsiao K. K., Prusiner S. B. Prion protein gene expression in cultured cells. Protein Eng. 1988 Apr;2(1):69–76. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. R., Köhler R., Foster D., Prusiner S. B. Chimeric prion protein expression in cultured cells and transgenic mice. Protein Sci. 1992 Aug;1(8):986–997. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M., Foster D., Mirenda C., Serban D., Coufal F., Wälchli M., Torchia M., Groth D., Carlson G., DeArmond S. J. Transgenic mice expressing hamster prion protein produce species-specific scrapie infectivity and amyloid plaques. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90608-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Baldwin M. A., Hecker R., Pan K. M., Burlingame A. L., Prusiner S. B. Glycosylinositol phospholipid anchors of the scrapie and cellular prion proteins contain sialic acid. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 2;31(21):5043–5053. doi: 10.1021/bi00136a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl N., Borchelt D. R., Hsiao K., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie prion protein contains a phosphatidylinositol glycolipid. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraboulos A., Raeber A. J., Borchelt D. R., Serban D., Prusiner S. B. Synthesis and trafficking of prion proteins in cultured cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Aug;3(8):851–863. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.8.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraboulos A., Rogers M., Borchelt D. R., McKinley M. P., Scott M., Serban D., Prusiner S. B. Acquisition of protease resistance by prion proteins in scrapie-infected cells does not require asparagine-linked glycosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8262–8266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraboulos A., Serban D., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie prion proteins accumulate in the cytoplasm of persistently infected cultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2117–2132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vnencak-Jones C. L., Phillips J. A., 3rd Identification of heterogeneous PrP gene deletions in controls by detection of allele-specific heteroduplexes (DASH) Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Apr;50(4):871–872. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., Mirenda C. A., Foster D., Zebarjadian Y., Scott M., Torchia M., Yang S. L., Serban H., DeArmond S. J., Ebeling C. Paradoxical shortening of scrapie incubation times by expression of prion protein transgenes derived from long incubation period mice. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90074-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]