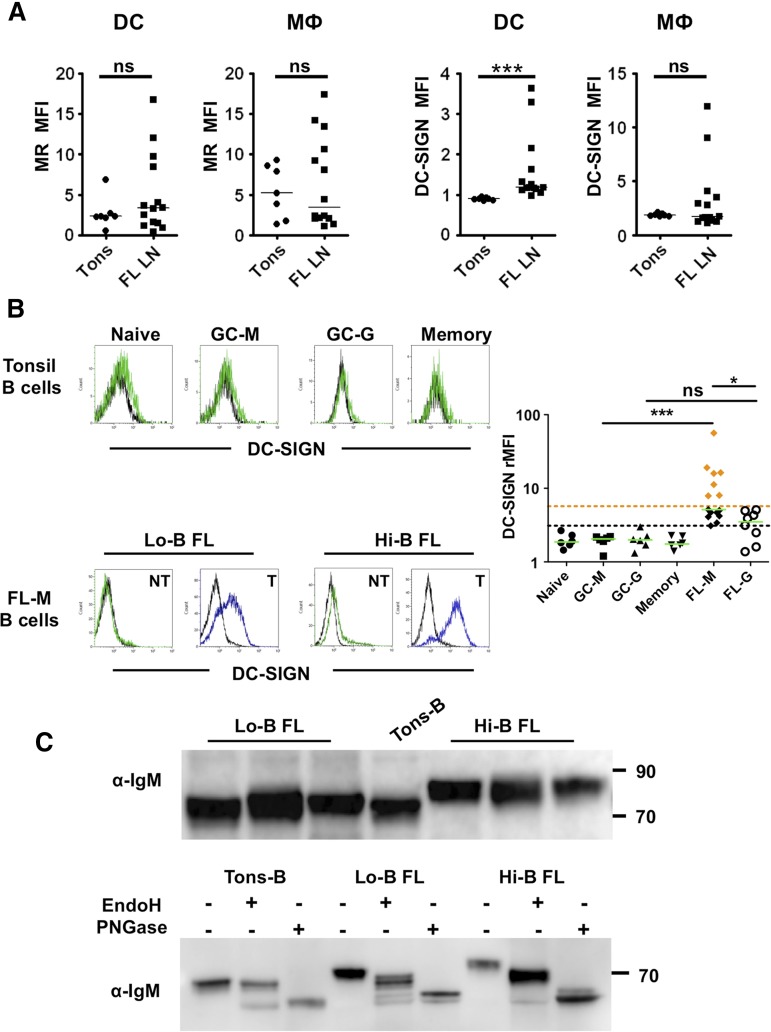
Figure 2.
DC-SIGN binding by FL B cells. (A) Expression of MR and DC-SIGN on gated CD3/CD19/CD335−CD11c+HLA-DR+CD14− dendritic cells (DCs) and CD3/CD19/CD335−CD11c+HLA-DR+CD14+ macrophages (MΦ) in tonsils (n = 7) vs FL lymph nodes (FL LN) (n = 14). ***P < .001. (B) A488-conjugated rhDC-SIGN was used to stain normal tonsil B cell subsets (n = 6) and FL B cells (15 IgM+ and 8 IgG+ samples). CD38−CD10−IgM+ naive B cells (naive), CD38−CD10−IgM− memory B cells (memory), CD38hiCD10+IgM+ GC B cells (GC-M), and CD38hiCD10+IgM− GC B cells (GC-G) were compared. Within FL samples, tumoral B cells (T) and nontumoral B cells (NT) were segregated within CD20+ B cells through the expression of heavy and light chains. DC-SIGN binding was expressed as the rMFI obtained in the presence (green or blue line)/in the absence (black line) of Ca2+. IgM+ FL B cells with a DC-SIGN–binding capacity higher than IgG+ FL cells (Hi-B FL) were highlighted with orange diamonds; IgM+ FL B cells with a DC-SIGN–binding capacity similar to IgG+ FL cells (Lo-B FL) were highlighted with black diamonds. The black dotted line represents the maximum value of normal B cells; the orange dotted line, the maximum value of IgG+ FL B cells. *P < .05; ***P < .001. (C) Cell lysates from purified tonsil B cells and IgM+ FL B cells were immunoblotted with goat anti-human IgM Ab (top panel). When indicated, cell lysates were treated with EndoH or PNGase (bottom panel, shown is 1 representative experiment of 3).