Abstract
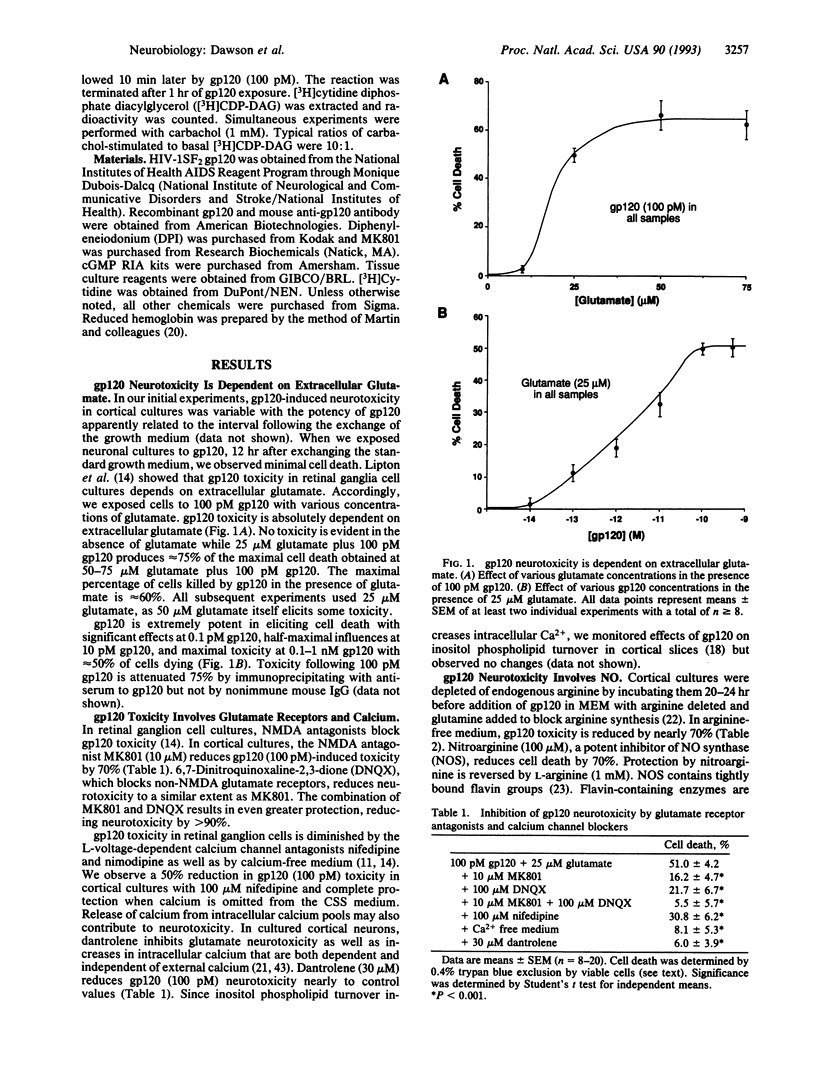
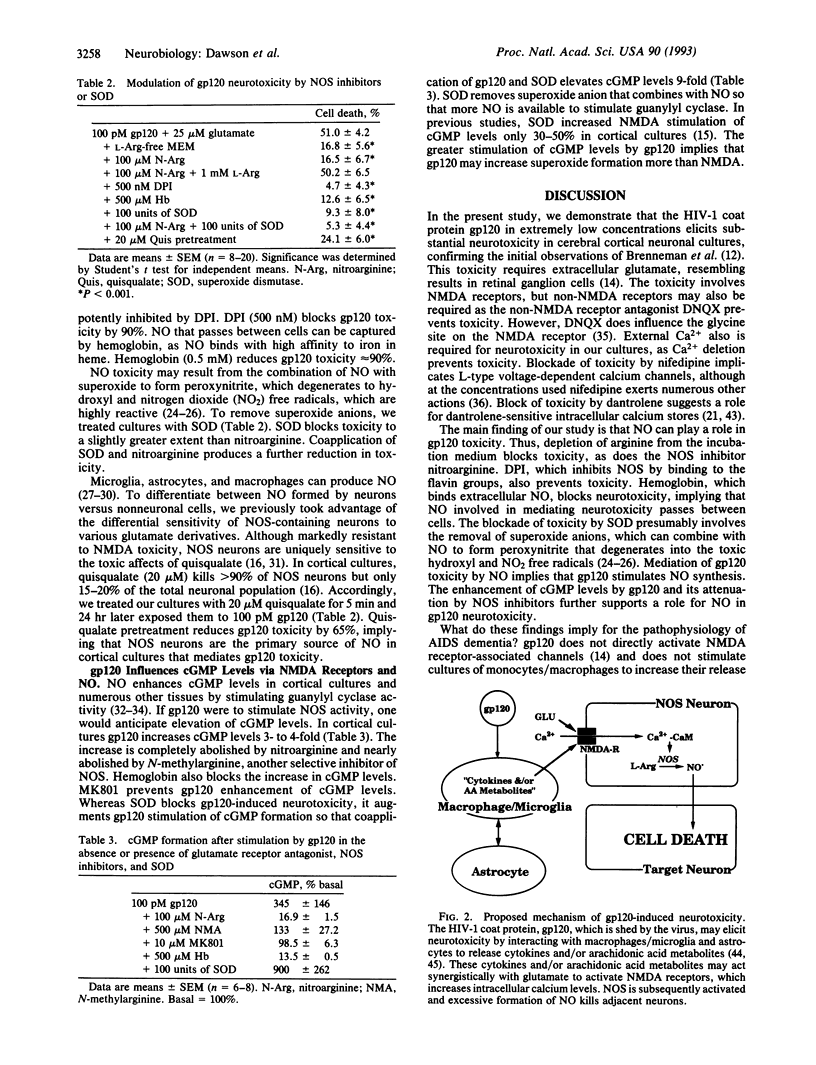
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 coat protein, gp120, kills neurons in primary cortical cultures at low picomolar concentrations. The toxicity requires external glutamate and calcium and is blocked by glutamate receptor antagonists. Nitric oxide (NO) contributes to gp120 toxicity, since nitroarginine, an inhibitor of NO synthase, prevents toxicity as does deletion of arginine from the incubation medium and hemoglobin, which binds NO. Superoxide dismutase also attenuates toxicity, implying a role for superoxide anions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckman J. S., Beckman T. W., Chen J., Marshall P. A., Freeman B. A. Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxynitrite: implications for endothelial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1620–1624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Ferris C. D., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide synthase regulatory sites. Phosphorylation by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, protein kinase C, and calcium/calmodulin protein kinase; identification of flavin and calmodulin binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10976–10981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenneman D. E., Westbrook G. L., Fitzgerald S. P., Ennist D. L., Elkins K. L., Ruff M. R., Pert C. B. Neuronal cell killing by the envelope protein of HIV and its prevention by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):639–642. doi: 10.1038/335639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao C. C., Hu S., Molitor T. W., Shaskan E. G., Peterson P. K. Activated microglia mediate neuronal cell injury via a nitric oxide mechanism. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 15;149(8):2736–2741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson T. M., Dawson V. L., Snyder S. H. A novel neuronal messenger molecule in brain: the free radical, nitric oxide. Ann Neurol. 1992 Sep;32(3):297–311. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson V. L., Dawson T. M., London E. D., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide mediates glutamate neurotoxicity in primary cortical cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6368–6371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M. A. Rat cortical neurons in cell culture: culture methods, cell morphology, electrophysiology, and synapse formation. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 30;149(2):279–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90476-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyer E. B., Kaiser P. K., Offermann J. T., Lipton S. A. HIV-1 coat protein neurotoxicity prevented by calcium channel antagonists. Science. 1990 Apr 20;248(4953):364–367. doi: 10.1126/science.2326646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frandsen A., Schousboe A. Mobilization of dantrolene-sensitive intracellular calcium pools is involved in the cytotoxicity induced by quisqualate and N-methyl-D-aspartate but not by 2-amino-3-(3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazol-4-yl)propionate and kainate in cultured cerebral cortical neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2590–2594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda D. H., Ho D. D., de la Monte S. M., Hirsch M. S., Rota T. R., Sobel R. A. Immunohistochemical identification of HTLV-III antigen in brains of patients with AIDS. Ann Neurol. 1986 Sep;20(3):289–295. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galea E., Feinstein D. L., Reis D. J. Induction of calcium-independent nitric oxide synthase activity in primary rat glial cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10945–10949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J. Glutamate, nitric oxide and cell-cell signalling in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Feb;14(2):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90022-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genis P., Jett M., Bernton E. W., Boyle T., Gelbard H. A., Dzenko K., Keane R. W., Resnick L., Mizrachi Y., Volsky D. J. Cytokines and arachidonic metabolites produced during human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected macrophage-astroglia interactions: implications for the neuropathogenesis of HIV disease. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1703–1718. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Vaca K., Noonan C. A. Secretion of neurotoxins by mononuclear phagocytes infected with HIV-1. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1593–1596. doi: 10.1126/science.2148832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey P. P. Potentiation by lithium of CMP-phosphatidate formation in carbachol-stimulated rat cerebral-cortical slices and its reversal by myo-inositol. Biochem J. 1989 Mar 1;258(2):621–624. doi: 10.1042/bj2580621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi Y., Benz A. M., Clifford D. B., Zorumski C. F. Nitric oxide inhibitors attenuate N-methyl-D-aspartate excitotoxicity in rat hippocampal slices. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Feb 3;135(2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90442-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh J. Y., Choi D. W. Vulnerability of cultured cortical neurons to damage by excitotoxins: differential susceptibility of neurons containing NADPH-diaphorase. J Neurosci. 1988 Jun;8(6):2153–2163. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-06-02153.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei S. Z., Zhang D., Abele A. E., Lipton S. A. Blockade of NMDA receptor-mediated mobilization of intracellular Ca2+ prevents neurotoxicity. Brain Res. 1992 Dec 11;598(1-2):196–202. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90183-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A. Calcium channel antagonists and human immunodeficiency virus coat protein-mediated neuronal injury. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jul;30(1):110–114. doi: 10.1002/ana.410300121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A. Models of neuronal injury in AIDS: another role for the NMDA receptor? Trends Neurosci. 1992 Mar;15(3):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A. Requirement for macrophages in neuronal injury induced by HIV envelope protein gp120. Neuroreport. 1992 Oct;3(10):913–915. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199210000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton S. A., Sucher N. J., Kaiser P. K., Dreyer E. B. Synergistic effects of HIV coat protein and NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90079-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo T. M., Fallert C. J., Piser T. M., Thayer S. A. HIV-1 envelope protein evokes intracellular calcium oscillations in rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1992 Oct 30;594(2):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Villani G. M., Jothianandan D., Furchgott R. F. Selective blockade of endothelium-dependent and glyceryl trinitrate-induced relaxation by hemoglobin and by methylene blue in the rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):708–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller B., Sarantis M., Traynelis S. F., Attwell D. Potentiation of NMDA receptor currents by arachidonic acid. Nature. 1992 Feb 20;355(6362):722–725. doi: 10.1038/355722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada C., Lekieffre D., Arvin B., Meldrum B. Effect of NO synthase inhibition on NMDA- and ischaemia-induced hippocampal lesions. Neuroreport. 1992 Jun;3(6):530–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourey R. J., Dawson T. M., Barrow R. K., Enna A. E., Snyder S. H. [3H]noscapine binding sites in brain: relationship to indoleamines and the phosphoinositide and adenylyl cyclase messenger systems. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;42(4):619–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. Nitric oxide as a secretory product of mammalian cells. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3051–3064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Cho E. S., Petito C. K., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):525–535. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Jordan B. D., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: I. Clinical features. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):517–524. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowicki J. P., Duval D., Poignet H., Scatton B. Nitric oxide mediates neuronal death after focal cerebral ischemia in the mouse. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov 12;204(3):339–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90862-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel J., Zinkand W. C., Klika A. B., Mangano T. J., Keith R. A., Salama A. I. 6,7-Dinitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione blocks the cytotoxicity of N-methyl-D-aspartate and kainate, but not quisqualate, in cortical cultures. J Neurochem. 1990 Jul;55(1):114–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb08828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz R. J., Kuritzkes D. R., de la Monte S. M., Rota T. R., Baker A. S., Albert D., Bor D. H., Feldman E. L., Schooley R. T., Hirsch M. S. Infection of the retina by human immunodeficiency virus type I. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 24;317(26):1643–1647. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712243172607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R. W., Brew B., Sidtis J., Rosenblum M., Scheck A. C., Cleary P. The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):586–592. doi: 10.1126/science.3277272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radi R., Beckman J. S., Bush K. M., Freeman B. A. Peroxynitrite oxidation of sulfhydryls. The cytotoxic potential of superoxide and nitric oxide. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4244–4250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radi R., Beckman J. S., Bush K. M., Freeman B. A. Peroxynitrite-induced membrane lipid peroxidation: the cytotoxic potential of superoxide and nitric oxide. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Aug 1;288(2):481–487. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90224-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds I. J., Snyder S. H. Calcium antagonist receptors. Ion Channels. 1988;1:213–249. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-7302-9_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa W. C., Hecker M., Mitchell J. A., Vane J. R. The metabolism of L-arginine and its significance for the biosynthesis of endothelium-derived relaxing factor: L-glutamine inhibits the generation of L-arginine by cultured endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8607–8611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons M. L., Murphy S. Induction of nitric oxide synthase in glial cells. J Neurochem. 1992 Sep;59(3):897–905. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide: first in a new class of neurotransmitters. Science. 1992 Jul 24;257(5069):494–496. doi: 10.1126/science.1353273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl L. M., Corcoran M. L., Pyle S. W., Arthur L. O., Harel-Bellan A., Farrar W. L. Human immunodeficiency virus glycoprotein (gp120) induction of monocyte arachidonic acid metabolites and interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):621–625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis R. A., Panizzon K., Wasterlain C. G. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase protects against hypoxic neuronal injury. Neuroreport. 1992 Jul;3(7):645–648. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199207000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins B. A., Dorn H. H., Kelly W. B., Armstrong R. C., Potts B. J., Michaels F., Kufta C. V., Dubois-Dalcq M. Specific tropism of HIV-1 for microglial cells in primary human brain cultures. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2200125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Masliah E., Morey M., Lemere C., DeTeresa R., Grafe M., Hansen L., Terry R. Neocortical damage during HIV infection. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jun;29(6):651–657. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



