Abstract
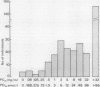
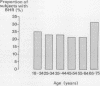
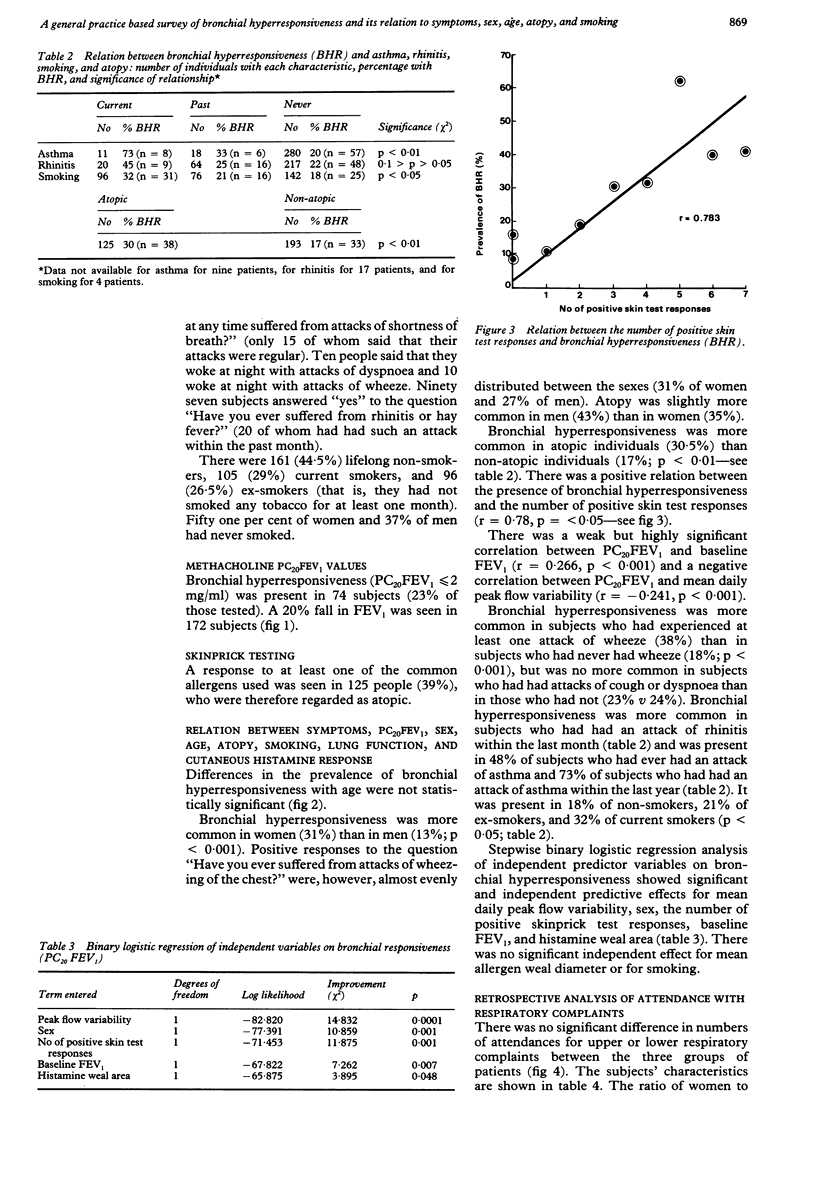
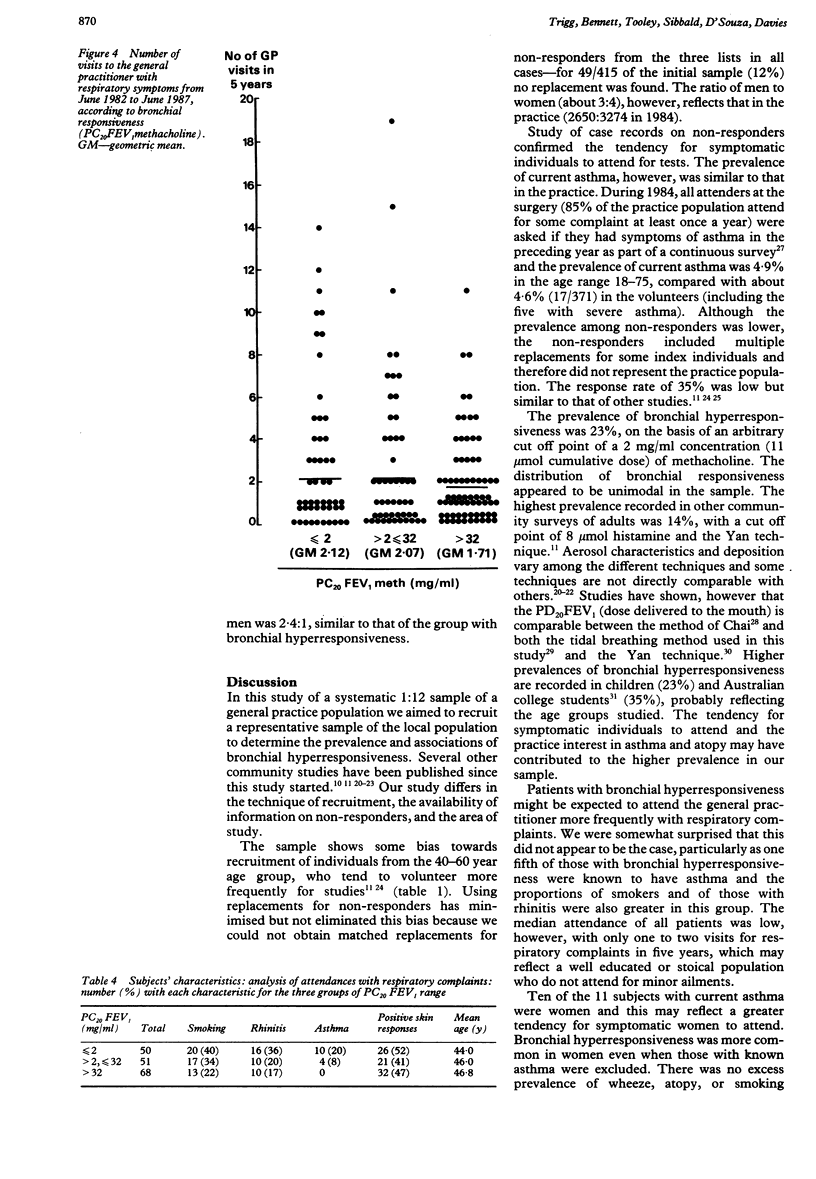
The prevalence and associations of bronchial hyperresponsiveness were investigated in a general practice population. The sample was obtained by using every 12th patient on the practice age-sex register, replacing non-responders with corresponding age and sex matched individuals from up to two further 1 in 12 samples. The response rate was 43%; 366 patients were studied. Doubling concentrations of methacholine were given to a maximum of 32 mg/ml or until a 20% fall in forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) occurred (provocation concentration, PC20FEV1). Bronchial hyperresponsiveness was defined arbitrarily as a PC20FEV1 of 2 mg/ml or less (or 11 mumol cumulative dose, PD20FEV1). The prevalence of bronchial hyperresponsiveness was 23%. Bronchial hyperresponsiveness was not associated with age but was more prevalent in women than men (31%:13%). It was also more common in those who had ever wheezed (39%) and in those who had had an attack of rhinitis in the preceding month (45%, p less than 0.1), in atopic individuals (30%), and in smokers (32%), but it was not associated with cough or dyspnoea. There was a positive correlation between PC20FEV1 and resting FEV1 (r = 0.288) and a negative correlation between PC20FEV1 and mean daily peak flow variability (r = -0.356). Stepwise binary logistic regression analysis showed significant independent effects on PC20FEV1 for mean daily peak flow variability, gender, number of positive skin test responses, resting FEV1, and mean histamine skin weal area, but no relation with smoking or mean allergen weal area. The prevalence of bronchial hyperresponsiveness was much higher than the prevalence of diagnosed asthma in the practice in 1984 (4.9%). Analysis of case notes of 169 individuals showed that those with bronchial hyperresponsiveness had not attended the practice more frequently for respiratory complaints during the previous five years.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. J. The third nervous system in the lung: physiology and clinical perspectives. Thorax. 1984 Aug;39(8):561–567. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.8.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. B., Davies R. J. A comparison of histamine and methacholine bronchial challenges using the DeVilbiss 646 nebulizer and the Rosenthal-French dosimeter. Br J Dis Chest. 1987 Jul;81(3):252–259. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(87)90158-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulet L. P., Cartier A., Thomson N. C., Roberts R. S., Dolovich J., Hargreave F. E. Asthma and increases in nonallergic bronchial responsiveness from seasonal pollen exposure. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Apr;71(4):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boushey H. A., Holtzman M. J., Sheller J. R., Nadel J. A. Bronchial hyperreactivity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Feb;121(2):389–413. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.2.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton J. Is hyperreactivity the same as asthma? Eur Respir J. 1988 May;1(5):478–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton J., Tattersfield A. E. Does measurement of bronchial hyperreactivity help in the clinical diagnosis of asthma? Eur J Respir Dis. 1986 Apr;68(4):233–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D. H., Burns M. W. The relationship between bronchial histamine reactivity and atopic status. Clin Allergy. 1976 Jul;6(4):373–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burney P. G., Britton J. R., Chinn S., Tattersfield A. E., Papacosta A. O., Kelson M. C., Anderson F., Corfield D. R. Descriptive epidemiology of bronchial reactivity in an adult population: results from a community study. Thorax. 1987 Jan;42(1):38–44. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burney P. G., Chinn S., Britton J. R., Tattersfield A. E., Papacosta A. O. What symptoms predict the bronchial response to histamine? Evaluation in a community survey of the bronchial symptoms questionnaire (1984) of the International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease. Int J Epidemiol. 1989 Mar;18(1):165–173. doi: 10.1093/ije/18.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chai H., Farr R. S., Froehlich L. A., Mathison D. A., McLean J. A., Rosenthal R. R., Sheffer A. L., Spector S. L., Townley R. G. Standardization of bronchial inhalation challenge procedures. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Oct;56(4):323–327. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Berscheid B. A., Murdock K. Y. Bronchial response to inhaled histamine in asymptomatic young smokers. Eur J Respir Dis. 1983 Apr;64(3):207–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Berscheid B. A., Murdock K. Y. Unimodal distribution of bronchial responsiveness to inhaled histamine in a random human population. Chest. 1983 May;83(5):751–754. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.5.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Killian D. N., Mellon J. J., Hargreave F. E. Bronchial reactivity to inhaled histamine: a method and clinical survey. Clin Allergy. 1977 May;7(3):235–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1977.tb01448.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson W. O., Musk A. W., Ryan G. Associations between asthma history, atopy, and non-specific bronchial responsiveness in young adults. Clin Allergy. 1986 Sep;16(5):425–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1986.tb01977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crockcroft D. W., Murdock K. Y., Berscheid B. A. Relationship between atopy and bronchial responsiveness to histamine in a random population. Ann Allergy. 1984 Jul;53(1):26–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry J. J. THE ACTION OF HISTAMINE ON THE RESPIRATORY TRACT IN NORMAL AND ASTHMATIC SUBJECTS. J Clin Invest. 1946 Nov;25(6):785–791. doi: 10.1172/JCI101764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Empey D. W., Laitinen L. A., Jacobs L., Gold W. M., Nadel J. A. Mechanisms of bronchial hyperreactivity in normal subjects after upper respiratory tract infection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Feb;113(2):131–139. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrard J. W., Cockcroft D. W., Mink J. T., Cotton D. J., Poonawala R., Dosman J. A. Increased nonspecific bronchial reactivity in cigarette smokers with normal lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Oct;122(4):577–581. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.4.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins B. G., Britton J. R., Chinn S., Jones T. D., Vathenen A. S., Burney P. G., Tattersfield A. E. Comparison of histamine and methacholine for use in bronchial challenge tests in community studies. Thorax. 1988 Aug;43(8):605–610. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.8.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. A., Winslow N. R., Speight A. N., Hey E. N. Prevalence and spectrum of asthma in childhood. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Apr 16;286(6373):1256–1258. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6373.1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malo J. L., Pineau L., Cartier A., Martin R. R. Reference values of the provocative concentrations of methacholine that cause 6% and 20% changes in forced expiratory volume in one second in a normal population. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Jul;128(1):8–11. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortagy A. K., Howell J. B., Waters W. E. Respiratory symptoms and bronchial reactivity: identification of a syndrome and its relation to asthma. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Aug 30;293(6546):525–529. doi: 10.1136/bmj.293.6546.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsdell J. W., Nachtwey F. J., Moser K. M. Bronchial hyperreactivity in chronic obstructive bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;126(5):829–832. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.5.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijcken B., Schouten J. P., Weiss S. T., Meinesz A. F., de Vries K., van der Lende R. The distribution of bronchial responsiveness to histamine in symptomatic and in asymptomatic subjects. A population-based analysis of various indices of responsiveness. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Sep;140(3):615–623. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.3.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijcken B., Schouten J. P., Weiss S. T., Speizer F. E., van der Lende R. The relationship of nonspecific bronchial responsiveness to respiratory symptoms in a random population sample. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jul;136(1):62–68. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.1.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson C., Holgate S. T. New perspectives on the putative role of eicosanoids in airway hyperresponsiveness. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985 Aug;76(2 Pt 1):140–144. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(85)90691-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan G., Latimer K. M., Dolovich J., Hargreave F. E. Bronchial responsiveness to histamine: relationship to diurnal variation of peak flow rate, improvement after bronchodilator, and airway calibre. Thorax. 1982 Jun;37(6):423–429. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.6.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears M. R., Jones D. T., Holdaway M. D., Hewitt C. J., Flannery E. M., Herbison G. P., Silva P. A. Prevalence of bronchial reactivity to inhaled methacholine in New Zealand children. Thorax. 1986 Apr;41(4):283–289. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sly R. M. Increases in deaths from asthma. Ann Allergy. 1984 Jul;53(1):20–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stănescu D. C., Frans A. Bronchial asthma without increased airway reactivity. Eur J Respir Dis. 1982 Jan;63(1):5–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIFFENEAU R. Hypersensibilité cholinergo-histaminique pulmonaire de l'asthmatique; relation avec l'hypersensibilité allergénique pulmonaire. Acta Allergol Suppl (Copenh) 1958;5:187–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. T., Tager I. B., Weiss J. W., Munoz A., Speizer F. E., Ingram R. H. Airways responsiveness in a population sample of adults and children. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Jun;129(6):898–902. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.6.898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt C., Stuckey M. S., Woolcock A. J., Dawkins R. L. Positive allergy prick tests associated with bronchial histamine responsiveness in an unselected population. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986 May;77(5):698–702. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(86)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock A. J., Peat J. K., Salome C. M., Yan K., Anderson S. D., Schoeffel R. E., McCowage G., Killalea T. Prevalence of bronchial hyperresponsiveness and asthma in a rural adult population. Thorax. 1987 May;42(5):361–368. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.5.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan K., Salome C., Woolcock A. J. Rapid method for measurement of bronchial responsiveness. Thorax. 1983 Oct;38(10):760–765. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.10.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]