Abstract
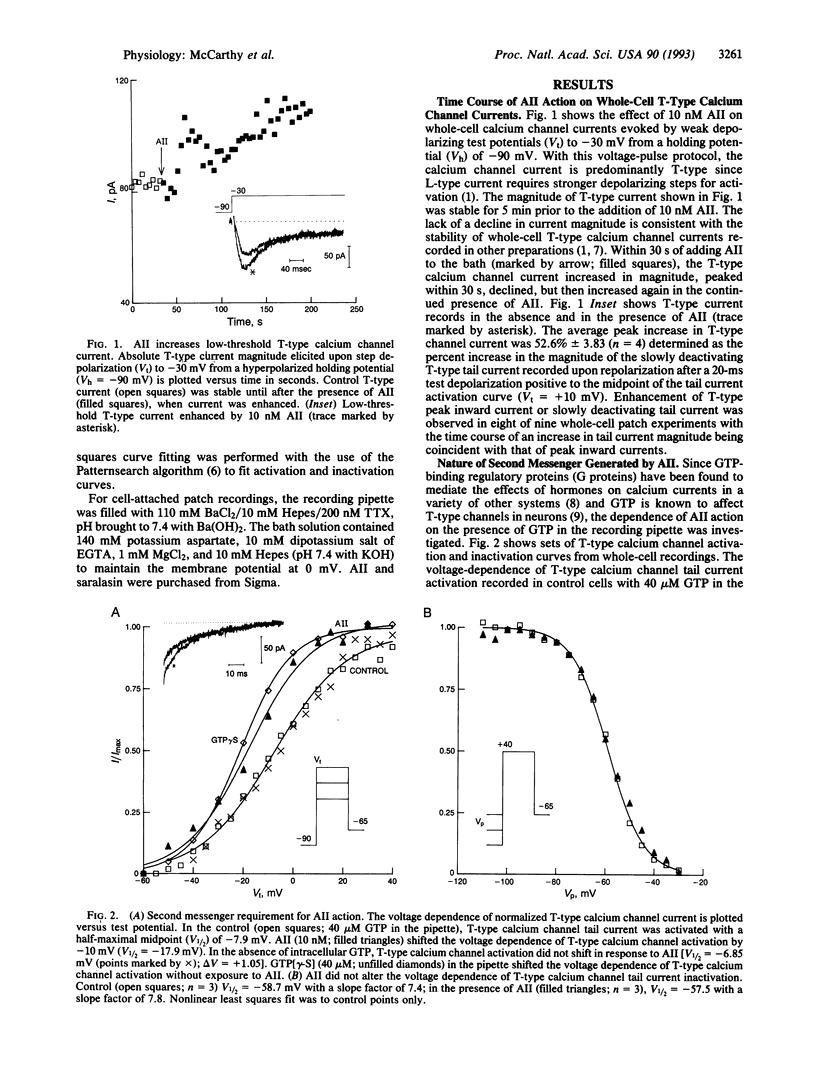
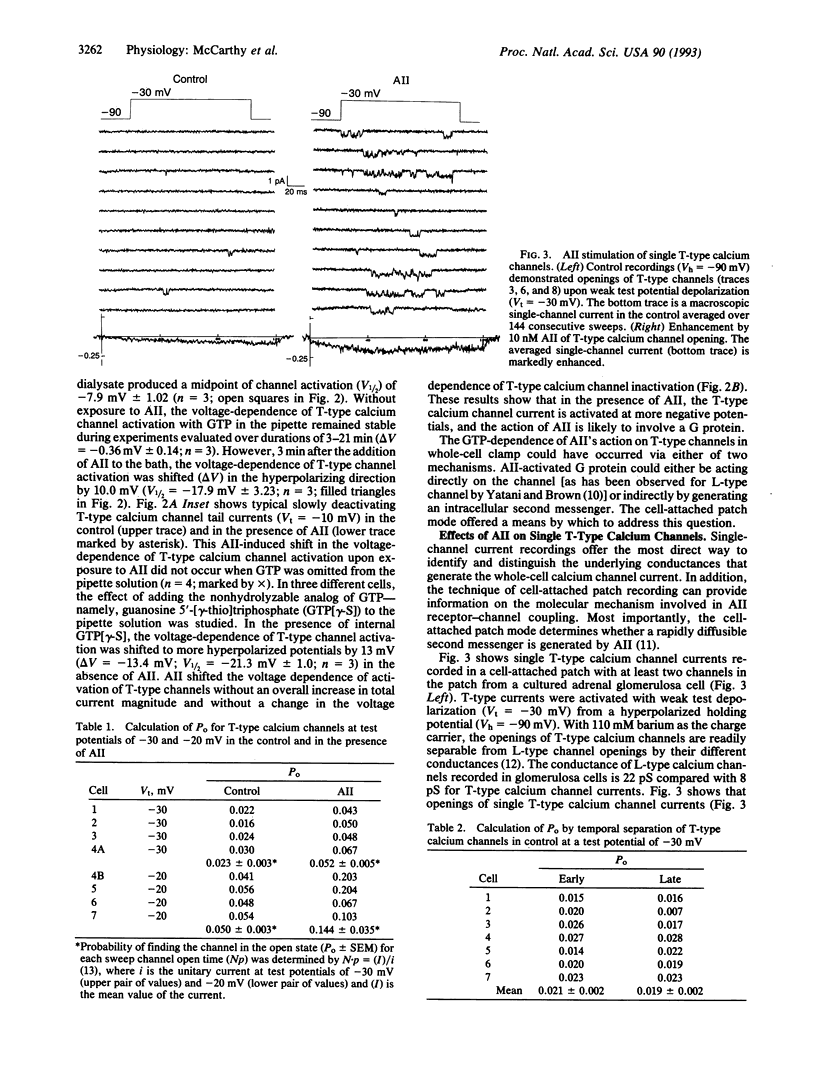
With the use of whole-cell and single-channel current recordings, we have examined in more detail the site of action of angiotensin II (AII) on multiple populations of voltage-gated calcium channels in bovine adrenal glomerulosa cells. AII (10 nM) enhances whole-cell T-type calcium channel current and increases the activity of single T-type calcium channels in cell-attached patch recordings. The AII-induced enhancement of whole-cell calcium channel currents is dependent on the presence of internal GTP and can be inhibited by the competitive AII-receptor antagonist saralasin (1 microM). These results show that AII augments the T-type calcium channel current in bovine adrenal glomerulosa cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett P. Q., Isales C. M., Bollag W. B., McCarthy R. T. Ca2+ channels and aldosterone secretion: modulation by K+ and atrial natriuretic peptide. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 2):F706–F719. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.4.F706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag W. B., Barrett P. Q., Isales C. M., Rasmussen H. Angiotensin-II-induced changes in diacylglycerol levels and their potential role in modulating the steroidogenic response. Endocrinology. 1991 Jan;128(1):231–241. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-1-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. J., McCarthy R. T., Barrett P. Q., Rasmussen H. Ca channels in adrenal glomerulosa cells: K+ and angiotensin II increase T-type Ca channel current. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enyedi P., Williams G. H. Heterogenous inositol tetrakisphosphate binding sites in the adrenal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):7940–7942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman L. F., Chahwala S. B., Cantley L. ras-transformed cells: altered levels of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate and catabolites. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):407–410. doi: 10.1126/science.3001936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forscher P., Oxford G. S. Modulation of calcium channels by norepinephrine in internally dialyzed avian sensory neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1985 May;85(5):743–763. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.5.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Baukal A., Catt K. J. Angiotensin II receptors in bovine adrenal cortex. Modification of angiotensin II binding by guanyl nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):664–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillon G., Gallo-Payet N., Balestre M. N., Lombard C. Cholera-toxin and corticotropin modulation of inositol phosphate accumulation induced by vasopressin and angiotensin II in rat glomerulosa cells. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):765–775. doi: 10.1042/bj2530765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington J., Lingle C. J. Kinetic and pharmacological properties of low voltage-activated Ca2+ current in rat clonal (GH3) pituitary cells. J Neurophysiol. 1992 Jul;68(1):213–232. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.1.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Hinsch K. D., Wulfern M., Trautwein W., Schultz G. Angiotensin II-induced stimulation of voltage-dependent Ca2+ currents in an adrenal cortical cell line. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):619–624. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P. Calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:337–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima I., Kojima K., Kreutter D., Rasmussen H. The temporal integration of the aldosterone secretory response to angiotensin occurs via two intracellular pathways. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14448–14457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Gardner P. Ion channels activated by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in plasma membrane of human T-lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):301–304. doi: 10.1038/326301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. L., Weight F. F., Luini A. A guanine nucleotide-binding protein mediates the inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium current by somatostatin in a pituitary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9035–9039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga H., Maruyama Y., Kojima I., Hoshi T. Transient Ca2+-channel current characterized by a low-threshold voltage in zona glomerulosa cells of rat adrenal cortex. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Apr;408(4):351–355. doi: 10.1007/BF00581128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga H., Yamashita N., Maruyama Y., Kojima I., Kurokawa K. Evidence for two distinct voltage-gated calcium channel currents in bovine adrenal glomerulosa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 31;149(3):1049–1054. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90514-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy R. T., Isales C. M., Bollag W. B., Rasmussen H., Barrett P. Q. Atrial natriuretic peptide differentially modulates T- and L-type calcium channels. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):F473–F478. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.3.F473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Long-opening mode of gating of neuronal calcium channels and its promotion by the dihydropyridine calcium agonist Bay K 8644. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2178–2182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., Wootton J. F., Dolphin A. C. Modulation of neuronal T-type calcium channel currents by photoactivation of intracellular guanosine 5'-O(3-thio) triphosphate. Neuroscience. 1990;38(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Brown A. M. Rapid beta-adrenergic modulation of cardiac calcium channel currents by a fast G protein pathway. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):71–74. doi: 10.1126/science.2544999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



