Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach H. S., Williams M., Kirkpatrick J. A., Colten H. R. Alternate-day prednisone reduces morbidity and improves pulmonary function in cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1985 Sep 28;2(8457):686–688. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92929-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore R. S., Christie C. D., Smith G. J. Immunohistopathologic localization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in lungs from patients with cystic fibrosis. Implications for the pathogenesis of progressive lung deterioration. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Dec;140(6):1650–1661. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.6.1650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedrossian C. W., Greenberg S. D., Singer D. B., Hansen J. J., Rosenberg H. S. The lung in cystic fibrosis. A quantitative study including prevalence of pathologic findings among different age groups. Hum Pathol. 1976 Mar;7(2):195–204. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(76)80023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borregaard N. Bactericidal mechanisms of the human neutrophil. An integrated biochemical and morphological model. Scand J Haematol. 1984 Mar;32(3):225–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1984.tb01685.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole P. J. Inflammation: a two-edged sword--the model of bronchiectasis. Eur J Respir Dis Suppl. 1986;147:6–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie D. C., Saverymuttu S. H., Peters A. M., Needham S. G., George P., Dhillon D. P., Lavender J. P., Cole P. J. Indium-111-labelled granulocyte accumulation in respiratory tract of patients with bronchiectasis. Lancet. 1987 Jun 13;1(8546):1335–1339. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90647-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta M. K., Lam J., Döring G., Harley F. L., Zuberbuhler P., Lam K., Reichert A., Costerton J. W., Dossetor J. B. Prognostic implications of circulating immune complexes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa-specific antibodies in cystic fibrosis. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1987 May;23(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehring D. J., Wismar B. L. Intravascular macrophages in pulmonary capillaries of humans. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Apr;139(4):1027–1029. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.4.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring G., Goldstein W., Botzenhart K., Kharazmi A., Schiøtz P. O., Høiby N., Dasgupta M. Elastase from polymorphonuclear leucocytes: a regulatory enzyme in immune complex disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Jun;64(3):597–605. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson A., Granström M., Möllby R., Strandvik B. Antibodies to staphylococcal teichoic acid and alpha toxin in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1986 Jan;75(1):139–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1986.tb10170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiby N., Kilian M. Haemophilus from the lower respiratory tract of patients with cystic fibrosis. Scand J Respir Dis. 1976;57(3):103–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard A. J., Dunkin K. T., Millar G. W. Nasopharyngeal carriage and antibiotic resistance of Haemophilus influenzae in healthy children. Epidemiol Infect. 1988 Apr;100(2):193–203. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka A., Wu Z. H., Stephens K. E., Harada H., Hogue R. S., O'Hanley P. T., Raffin T. A. Attenuation of acute lung injury in septic guinea pigs by pentoxifylline. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Aug;138(2):376–382. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.2.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerem E., Corey M., Gold R., Levison H. Pulmonary function and clinical course in patients with cystic fibrosis after pulmonary colonization with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Pediatr. 1990 May;116(5):714–719. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82653-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konstan M. W., Vargo K. M., Davis P. B. Ibuprofen attenuates the inflammatory response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a rat model of chronic pulmonary infection. Implications for antiinflammatory therapy in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Jan;141(1):186–192. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.1.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulczycki L. L., Murphy T. M., Bellanti J. A. Pseudomonas colonization in cystic fibrosis. A study of 160 patients. JAMA. 1978 Jul 7;240(1):30–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapa e Silva J. R., Guerreiro D., Noble B., Poulter L. W., Cole P. J. Immunopathology of experimental bronchiectasis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1989 Oct;1(4):297–304. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/1.4.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. S., Teter M. J., Gilligan P. H. Biotype of Haemophilus influenzae: correlation with virulence and ampicillin resistance. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):800–806. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. I. The pathogenesis and treatment of pulmonary infections in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1981 Feb;98(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80631-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. I. The pathogenesis and treatment of pulmonary infections in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1981 Feb;98(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80631-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer E. H., Esterly J. R. Pathology of cystic fibrosis review of the literature and comparison with 146 autopsied cases. Perspect Pediatr Pathol. 1975;2:241–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
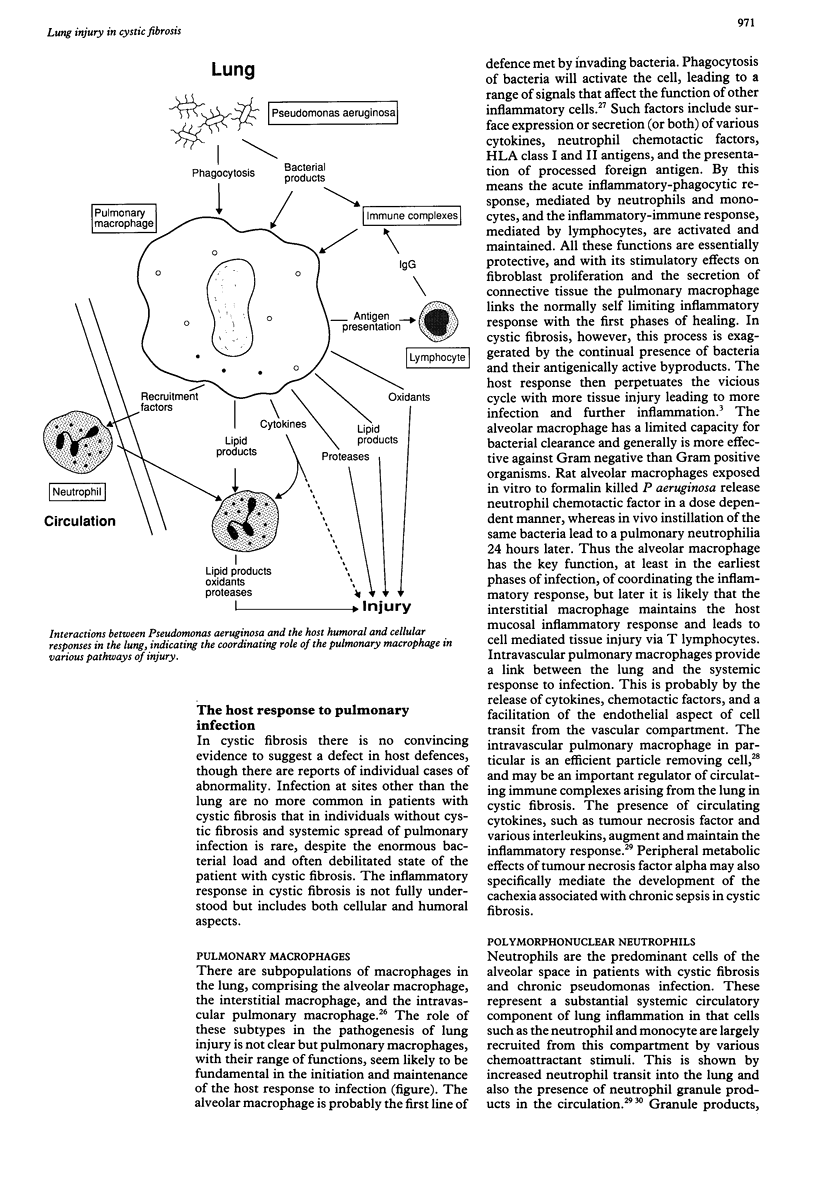
- Ozaki T., Maeda M., Hayashi H., Nakamura Y., Moriguchi H., Kamei T., Yasuoka S., Ogura T. Role of alveolar macrophages in the neutrophil-dependent defense system against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in the lower respiratory tract. Amplifying effect of muramyl dipeptide analog. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Dec;140(6):1595–1601. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.6.1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen N. T., Høiby N., Mordhorst C. H., Lind K., Flensborg E. W., Bruun B. Respiratory infections in cystic fibrosis patients caused by virus, chlamydia and mycoplasma--possible synergism with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1981 Sep;70(5):623–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1981.tb05757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pier G. B., Saunders J. M., Ames P., Edwards M. S., Auerbach H., Goldfarb J., Speert D. P., Hurwitch S. Opsonophagocytic killing antibody to Pseudomonas aeruginosa mucoid exopolysaccharide in older noncolonized patients with cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Sep 24;317(13):793–798. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198709243171303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressler T., Mansa B., Jensen T., Pedersen S. S., Høiby N., Koch C. Increased IgG2 and IgG3 concentration is associated with advanced Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and poor pulmonary function in cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1988 Jul;77(4):576–582. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1988.tb10703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayner R. J., Hiller E. J., Ispahani P., Baker M. Haemophilus infection in cystic fibrosis. Arch Dis Child. 1990 Mar;65(3):255–258. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.3.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D. E., Cole P. Use of selective media in bacteriological investigation of patients with chronic suppurative respiratory infection. Lancet. 1980 Apr 12;1(8172):796–797. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91295-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D., Higgs E., Rutman A., Cole P. Isolation of spheroplastic forms of Haemophilus influenzae from sputum in conventionally treated chronic bronchial sepsis using selective medium supplemented with N-acetyl-D-glucosamine: possible reservoir for re-emergence of infection. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Nov 24;289(6456):1409–1412. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6456.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocker G. M., Wiseman M. S., Pearson D., Shale D. J. Diagnostic criteria for adult respiratory distress syndrome: time for reappraisal. Lancet. 1989 Jan 21;1(8630):120–123. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shann F., Gratten M., Germer S., Linnemann V., Hazlett D., Payne R. Aetiology of pneumonia in children in Goroka Hospital, Papua New Guinea. Lancet. 1984 Sep 8;2(8402):537–541. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90764-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheinman B. D., Devalia J. L., Davies R. J., Crook S. J., Tabaqchali S. Synthesis of histamine by Haemophilus influenzae. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Mar 29;292(6524):857–858. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6524.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibille Y., Reynolds H. Y. Macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils in lung defense and injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Feb;141(2):471–501. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.2.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suter S., Schaad U. B., Roux-Lombard P., Girardin E., Grau G., Dayer J. M. Relation between tumor necrosis factor-alpha and granulocyte elastase-alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor complexes in the plasma of patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Dec;140(6):1640–1644. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.6.1640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes D. A., Wilson R., Greenstone M., Currie D. C., Steinfort C., Cole P. J. Deleterious effects of purulent sputum sol on human ciliary function in vitro: at least two factors identified. Thorax. 1987 Apr;42(4):256–261. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.4.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szaff M., Høiby N. Antibiotic treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infection in cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1982 Sep;71(5):821–826. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1982.tb09526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Zaid N. S., al-Adnani M. S., Gumaa K. A. Collagen of the dystrophic hamster diaphragm. Thorax. 1990 Nov;45(11):878–879. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.11.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]