Abstract
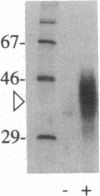
A protein (Z alpha) that appears to be highly specific for the left-handed Z-DNA conformer has been identified in chicken blood nuclear extracts. Z alpha activity is measured in a band-shift assay by using a radioactive probe consisting of a (dC-dG)35 oligomer that has 50% of the deoxycytosines replaced with 5-bromodeoxycytosine. In the presence of 10 mM Mg2+, the probe converts to the Z-DNA conformation and is bound by Z alpha. The binding of Z alpha to the radioactive probe is specifically blocked by competition with linear poly(dC-dG) stabilized in the Z-DNA form by chemical bromination but not by B-form poly(dC-dG) or boiled salmon-sperm DNA. In addition, the binding activity of Z alpha is competitively blocked by supercoiled plasmids containing a Z-DNA insert but not by either the linearized plasmid or by an equivalent amount of the parental supercoiled plasmid without the Z-DNA-forming insert. Z alpha can be crosslinked to the 32P-labeled brominated probe with UV light, allowing us to estimate that the minimal molecular mass of Z alpha is 39 kDa.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behe M., Felsenfeld G. Effects of methylation on a synthetic polynucleotide: the B--Z transition in poly(dG-m5dC).poly(dG-m5dC). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1619–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaho J. A., Wells R. D. Left-handed Z-DNA binding by the recA protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6082–6088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Drosophila nuclear proteins bind to regions of alternating C and T residues in gene promoters. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1487–1490. doi: 10.1126/science.2781290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gut S. H., Bischoff M., Hobi R., Kuenzle C. C. Z-DNA-binding proteins from bull testis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9691–9705. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. The in-vivo occurrence of Z DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Dec;1(3):593–609. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. I., Heuser J., Cox M. M. Enhanced recA protein binding to Z DNA represents a kinetic perturbation of a general duplex DNA binding pathway. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21848–21856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna P., Kennedy B. P., Waisman D. M., van de Sande J. H., McGhee J. D. Are many Z-DNA binding proteins actually phospholipid-binding proteins? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1292–1295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kłysik J., Stirdivant S. M., Larson J. E., Hart P. A., Wells R. D. Left-handed DNA in restriction fragments and a recombinant plasmid. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):672–677. doi: 10.1038/290672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Sousa R. J., Rich A. Z-DNA-binding proteins in Escherichia coli purification, generation of monoclonal antibodies and gene isolation. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):511–516. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller M. T., Spitzner J. R., DiDonato J. A., Mehta V. B., Tsutsui K., Tsutsui K. Single-strand DNA cleavages by eukaryotic topoisomerase II. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 1;27(22):8369–8379. doi: 10.1021/bi00422a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller A., Nordheim A., Kozlowski S. A., Patel D. J., Rich A. Bromination stabilizes poly(dG-dC) in the Z-DNA form under low-salt conditions. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 3;23(1):54–62. doi: 10.1021/bi00296a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Nordheim A., Rich A., Wang J. C. Flipping of cloned d(pCpG)n.d(pCpG)n DNA sequences from right- to left-handed helical structure by salt, Co(III), or negative supercoiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4560–4564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl F. M., Jovin T. M. Salt-induced co-operative conformational change of a synthetic DNA: equilibrium and kinetic studies with poly (dG-dC). J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):375–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmouni A. R., Wells R. D. Stabilization of Z DNA in vivo by localized supercoiling. Science. 1989 Oct 20;246(4928):358–363. doi: 10.1126/science.2678475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohner K. J., Hobi R., Kuenzle C. C. Z-DNA-binding proteins. Identification critically depends on the proper choice of ligands. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):19112–19115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroth G. P., Chou P. J., Ho P. S. Mapping Z-DNA in the human genome. Computer-aided mapping reveals a nonrandom distribution of potential Z-DNA-forming sequences in human genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11846–11855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheardy R. D. Preliminary spectroscopic characterization of a synthetic DNA oligomer containing a B-Z junction at high salt. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1153–1167. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi J., Brahmachari S. K. Distribution of simple repetitive (TG/CA)n and (CT/AG)n sequences in human and rodent genomes. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Oct;9(2):387–397. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittig B., Wölfl S., Dorbic T., Vahrson W., Rich A. Transcription of human c-myc in permeabilized nuclei is associated with formation of Z-DNA in three discrete regions of the gene. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4653–4663. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05567.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]