Abstract
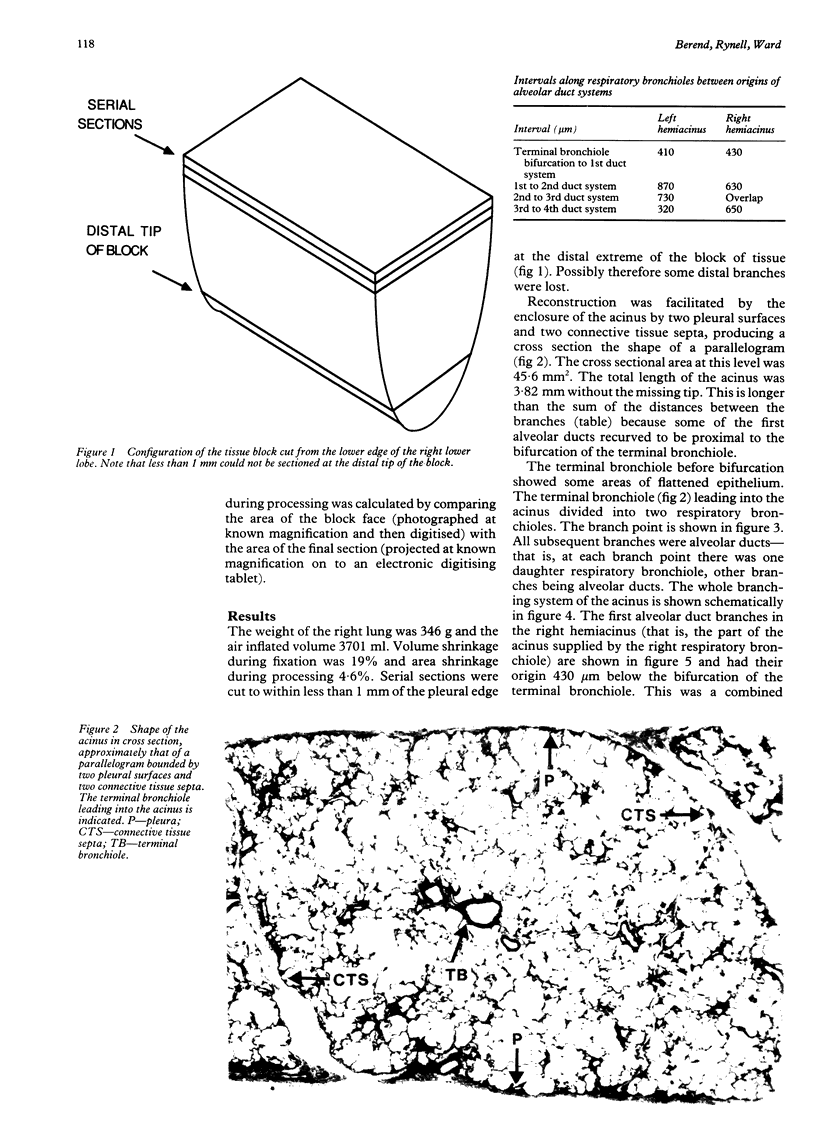
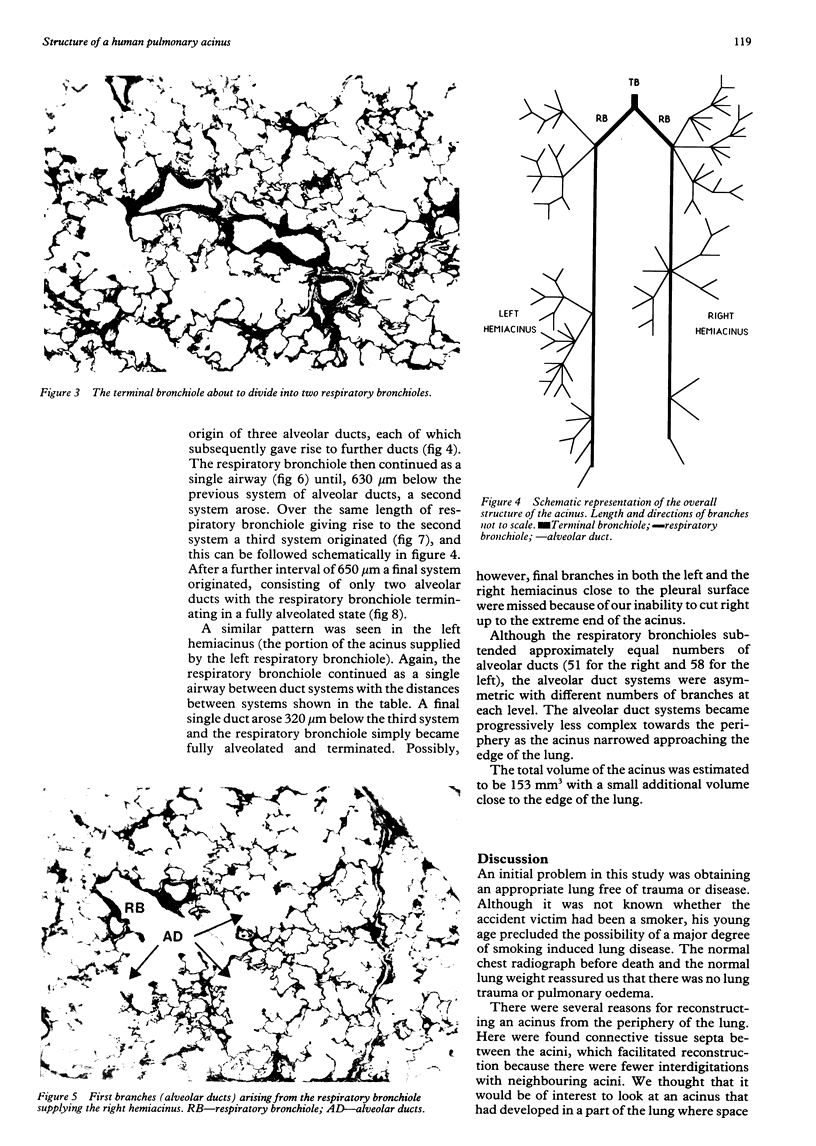
The structure of the human pulmonary acinus has been described infrequently. The aim of the study was to determine the branching pattern of respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts in a human acinus from the peripheral part of the lung, where space constraints may have affected airway branching patterns. The lungs were obtained from an 18 year old victim of a motor vehicle accident and fixed in inflation under a pressure of 25 cm H2O. A block was cut from the lower edge of the right lower lobe and embedded in plastic. Serial sections were cut and the branching pattern of airways subtended by a terminal bronchiole were followed. The acinus was bounded on two sides by pleura and on the remaining sides by connective tissue septa. The terminal bronchiole divided into two respiratory bronchioles, each of which gave rise to four systems of alveolar ducts. Between successive systems of alveolar ducts the respiratory bronchioles continued as single airways, becoming progressively more alveolated towards the periphery but not subtending further branches of respiratory bronchioles. The duct systems became less complex towards the periphery, near to the edge of the lung. The total volume of the acinus was similar to that found in previous studies. This branching pattern has not been described previously in a human acinus.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyden E. A. The structure of the pulmonary acinus in a child of six years and eight months. Am J Anat. 1971 Nov;132(3):275–299. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001320302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haefeli-Bleuer B., Weibel E. R. Morphometry of the human pulmonary acinus. Anat Rec. 1988 Apr;220(4):401–414. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092200410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. E., Ampaya E. P., Bryant G. H., Navin J. J. Branching pattern of airways and air spaces of a single human terminal bronchiole. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Jun;38(6):983–989. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.38.6.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. E., Ampaya E. P. Human air space shapes, sizes, areas, and volumes. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Jun;38(6):990–995. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.38.6.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsfield K., Cumming G. Morphology of the bronchial tree in man. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Mar;24(3):373–383. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.24.3.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer R. R., Crapo J. D. Three-dimensional reconstruction of the rat acinus. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Aug;63(2):785–794. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.2.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker H., Horsfield K., Cumming G. Morphology of distal airways in the human lung. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Sep;31(3):386–391. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.3.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pump K. K. Morphology of the acinus of the human lung. Dis Chest. 1969 Aug;56(2):126–134. doi: 10.1378/chest.56.2.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez M., Bur S., Favre A., Weibel E. R. Pulmonary acinus: geometry and morphometry of the peripheral airway system in rat and rabbit. Am J Anat. 1987 Oct;180(2):143–155. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001800204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreider J. P., Raabe O. G. Structure of the human respiratory acinus. Am J Anat. 1981 Nov;162(3):221–232. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001620304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]