Background
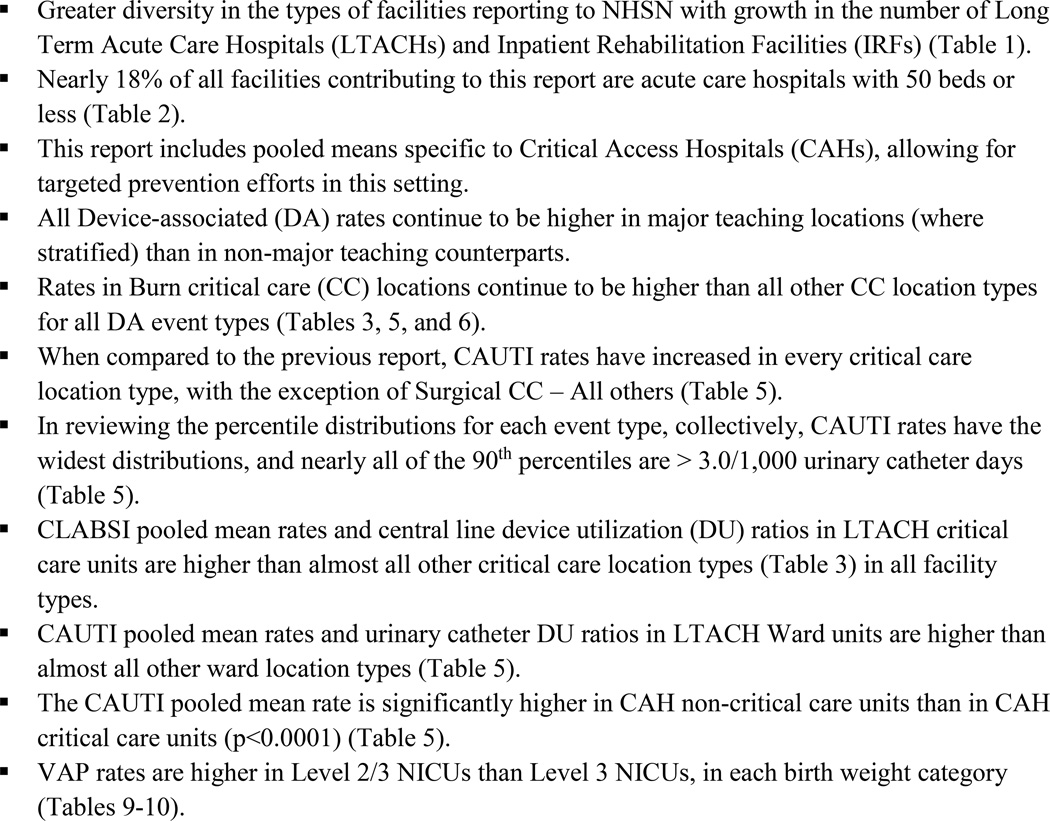
This report is a summary of Device-associated (DA) Module data collected by hospitals participating in the National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) for events occurring from January through December 2012 and reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) by July 1, 2013. This report updates previously published DA Module data from NHSN and provides contemporary comparative rates.1 Figure 1 provides a brief summary of key findings from this report. This report complements other NHSN reports, including national and state-specific reports of standardized infection ratios (SIRs) for select healthcare-associated infections (HAIs).2, 3
Figure 1.
Highlights from this report
NHSN data collection, reporting, and analysis are organized into four components: Patient Safety, Healthcare Personnel Safety, Biovigilance, and Long-term Care, and use standardized methods and definitions in accordance with specific module protocols.4,5,6,7 Institutions may use modules singly or simultaneously, but once selected, they must be used for a minimum of one calendar month for the data to be included in CDC analyses. All infections are categorized using standard CDC definitions that include laboratory and clinical criteria.5–7 The DA Module within the Patient Safety Component may be used by facilities other than general acute care hospitals, including inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRFs) and long term acute care hospitals (LTACHs). NHSN facilities contributing HAI surveillance data to this report did so voluntarily, in response to state mandatory reporting requirements or in compliance with the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services’ (CMS’s) Quality Reporting Programs.8,9 CDC aggregated these data into a single national database for 2012, consistent with the stated purposes of NHSN, which are to:
Collect data from a sample of healthcare facilities in the United States to permit valid estimation of the magnitude of adverse events among patients and healthcare personnel.
Collect data from a sample of healthcare facilities in the United States to permit valid estimation of the adherence to practices known to be associated with prevention of these adverse events.
Analyze and report collected data to permit recognition of trends.
Provide facilities with risk-adjusted metrics that can be used for inter-facility comparisons and local quality improvement activities.
Assist facilities in developing surveillance and analysis methods that permit timely recognition of patient and healthcare worker safety problems and prompt intervention with appropriate measures.
Conduct collaborative research studies with NHSN member facilities (e.g., describe the epidemiology of emerging healthcare-associated infection [HAI] and pathogens, assess the importance of potential risk factors, further characterize HAI pathogens and their mechanisms of resistance, and evaluate alternative surveillance and prevention strategies).
Comply with legal requirements – including but not limited to state or federal laws, regulations, or other requirements – for mandatory reporting of healthcare facility-specific adverse event, prevention practice adherence, and other public health data.
Enable healthcare facilities to report HAI and prevention practice adherence data via NHSN to the U.S. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) in fulfillment of CMS’s quality measurement reporting requirements for those data.
Provide state departments of health with information that identifies the healthcare facilities in their state that participate in NHSN.
Provide to state agencies, at their request, facility-specific, NHSN patient safety component and healthcare personnel safety component adverse event and prevention practice adherence data for surveillance, prevention, or mandatory public reporting.
Patient- and facility-specific data reported to CDC are kept confidential in accordance with sections 304, 306, and 308(d) of the Public Health Service Act (42 USC 242b, 242k, and 242m(d)).
Methods
Data Collection Methods
For reporting to the DA Module, healthcare facility personnel responsible for infection prevention and patient safety may choose, with consideration of state mandates, federal reporting programs, and prevention initiatives, to collect data on central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSI), ventilator-associated pneumonias (VAP), or urinary catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTI) that occur in patients staying in a patient care location such as a critical or intensive care unit (ICU), specialty care area, or inpatient ward. In NHSN, locations are further stratified according to patient population: adults, children, or neonates (in tables, pediatric and neonatal locations are so noted). In neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) locations (level III or level II/III), infection preventionists (IPs) collect data on CLABSI or VAP that occur in patients in each of five birth-weight categories (≤750 g, 751–1000 g, 1001 – 1500 g, 1501 – 2500 g, and >2500 g); data on CAUTI are not collected as part of the NHSN protocols in any NICU location. Corresponding location-specific denominator data consisting of patient-days and specific device-days are also collected by IPs or other trained personnel.
In non-NICU locations, the device-days consist of the total number of central line-days, urinary catheter-days, or ventilator-days. For specialty care areas and oncology units, such as hematology/oncology and hematopoietic stem cell transplant locations, central line-days are split into those with only a permanent central line vs. those with temporary central lines (with or without a permanent central line). In NICU locations, the device-days consist of the total number of central line-days (inclusive of umbilical catheters), or ventilator-days for each birth-weight category.
Data Analysis Methods
Compared to the previous report, five new locations – gastrointestinal ward, pediatric orthopedic ward, inpatient hospice ward, solid tumor ward, and pediatric inpatient rehabilitation facility– had sufficient data to be included in this report.1
Locations were further stratified by facility type, unit bed size and/or major teaching status to determine if pooled mean rates, medians, and empirical distributions significantly differed between two groups for all DA infections; if differences were present, the strata were retained for reporting. Comparisons of pooled mean rates were performed using Poisson regression. These comparisons could be influenced by potential outlier rates from locations with disproportionately large denominators. Therefore, greater weight was given to the results of nonparametric tests comparing the medians for location shift and empirical distributions for assessing differences across the range of reported rates. These nonparametric comparisons by definition require no validity assumptions and provide test results that are not subject to the potential weighting influence of high or low rates with large denominators. Comparisons of the pooled mean, median and percentile distribution were made if there were at least 50 locations contributing to one or more strata and at least 20 locations contributing to the percentile distribution in both strata.
Existing strata were retained for adult combined medical/surgical ICUs, medical ICUs, and surgical ICUs. The data for adult combined medical/surgical ICUs were split by medical school affiliation and unit bedsize, resulting in three groups: “major teaching,” “all others” with unit bedsize ≤15 beds, and “all others” with unit bedsize >15. The data for adult medical ICUs and adult surgical ICUs were split into two groups by teaching status. Hospitals self-identified their teaching hospital status through the annual NHSN facility survey. A major teaching hospital was defined as a hospital that has a program for medical students and post-graduate medical training. Locations within critical access hospitals (CAHs) were compared to their counterparts in all other acute care hospitals. The statistical evidence indicated that there was a significant difference in these strata and therefore, data from CAHs have been reported separate from all other location types. Adult hematology/oncology locations were also evaluated to assess importance of status as an oncology hospital, but differences were not significant and no new strata for this population were retained.
Device utilization (DU) was calculated as a ratio of device-days to patient-days for each location type. As such, the DU of a location is one measure of the use of invasive devices and constitutes an extrinsic risk factor for healthcare-associated infection.10 DU may also serve as a marker for severity of illness of patients (i.e. more severely ill patients are more likely to require an invasive device) which is another reflection of the intrinsic susceptibility to infection.
Data from at least 5 different reporting units of a given location type were used to determine pooled mean DA infection rates and DU ratios. Percentile distributions were determined if there were data from at least 20 different locations, excluding rates or DU ratios for locations that did not report at least 50 device-days or patient-days. Because of these requirements, the number of locations contributing data may vary among the tables.
Results
In 2012, 4,444 enrolled facilities reported at least one month of DA denominator data for some patient cohorts under surveillance. These 4,444 facilities were located in 53 states, territories, and the District of Columbia and were predominantly general acute care hospitals (Table 1); 27% of all facilities that reported data were smaller organizations of 50 beds or less, comprised mostly of acute care hospitals that were not identified as critical access. Among LTACHs and IRFs, 59% and 86%, respectively, were categorized as physically free-standing from a hospital setting. Where data volume was sufficient for this report, we tabulated DA infection rates and DU ratios for January through December 2012 (Tables 3–10). Data on the specific criteria used to report DA infections are provided in Tables 11–18.
Table 1.
NHSN facilities contributing data used in this report
| Hospital type | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Children's | 70 (1.6) |
| Critical access | 324 (7.3) |
| General, including acute, trauma, and teaching | 3,200 (72.0) |
| Long-term acute care | 465 (10.5) |
| Military | 34 (0.8) |
| Oncology | 12 (0.3) |
| Orthopedic | 14 (0.3) |
| Psychiatric | 10 (0.2) |
| Rehabilitation | 237 (5.3) |
| Surgical | 51 (1.1) |
| Veterans' Affairs | 12 (0.3) |
| Women's | 6 (0.1) |
| Women's and Children's | 9 (0.2) |
| Total | 4,444 |
Table 3.
Pooled means and key percentiles of the distribution of laboratory-confirmed central line-associated BSI rates and central line utilization ratios, by type of location, DA module, 2012
| Central line-associated BSI rate* | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Location | No. of locations† |
No. of CLABSI |
Central line- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| Acute Care Hospitals | |||||||||
| Critical Care | |||||||||
| Burn | 73 (72) | 265 | 78,825 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 2.2 | 5.2 | 9.3 |
| Medical -Major teaching |
231 (230) | 792 | 625,053 | 1.3 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 2.8 |
| Medical -All other |
459 (433) | 684 | 627,374 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 2.9 |
| Medical cardiac | 409 (403) | 630 | 597,529 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 2.5 |
| Medical/surgical -Major teaching |
328 (324) | 940 | 765,267 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 3.0 |
| Medical/surgical -All other ≤15 beds |
1,690 (1,562) | 1,226 | 1,312,634 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 2.6 |
| Medical/surgical -All other > 15 beds |
803 (801) | 1,894 | 2,110,694 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 1.4 | 2.2 |
| Neurologic | 55 (54) | 83 | 80,900 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 2.5 |
| Neurosurgical | 174 | 361 | 314,752 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 1.9 | 2.8 |
| Pediatric cardiothoracic | 41 | 189 | 134,529 | 1.4 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 1.3 | 2.1 | 2.5 |
| Pediatric medical | 33 (24) | 29 | 24,297 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 2.7 | 3.8 |
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 317 (293) | 573 | 401,074 | 1.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 2.1 | 2.9 |
| Pediatric surgical | 6 | 3 | 3,457 | 0.9 | |||||
| Prenatal | 6 (3) | 1 | 376 | 2.7 | |||||
| Respiratory | 10 | 18 | 15,254 | 1.2 | |||||
| Surgical -Major teaching |
178 | 529 | 445,486 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 1.8 | 2.8 |
| Surgical -All other |
210 (203) | 357 | 387,095 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 1.5 | 2.5 |
| Surgical cardiothoracic | 459 (457) | 803 | 950,847 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 2.0 |
| Trauma | 153 | 547 | 341,619 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.3 | 2.4 | 3.9 |
| Step-Down Units | |||||||||
| Adult step-down (post-critical care) | 585 (570) | 527 | 667,879 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 2.3 |
| Step-down NICU (level II) | 42 (20) | 4 | 5,096 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Pediatric step-down (post-critical care) | 14 | 26 | 13,962 | 1.9 | |||||
| Inpatient Wards | |||||||||
| Acute stroke | 20 | 15 | 14,038 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.4 | 3.4 |
| Antenatal | 18 (6) | 1 | 1,554 | 0.6 | |||||
| Behavioral health/psychiatry | 104 (31) | 5 | 9,032 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Burn | 17 | 21 | 8,877 | 2.4 | |||||
| Gastrointestinal | 6 | 19 | 10,619 | 1.8 | |||||
| Genitourinary | 14 (12) | 19 | 17,005 | 1.1 | |||||
| Geronotology | 10 (9) | 3 | 5,940 | 0.5 | |||||
| Gynecology | 51 (28) | 6 | 10,916 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| Jail | 14 (12) | 12 | 7,350 | 1.6 | |||||
| Labor and delivery | 57 (2) | 0 | 802 | 0.0 | |||||
| Labor, delivery, recovery, postpartum suite | 111 (16) | 4 | 3,182 | 1.3 | |||||
| Medical | 917 (877) | 962 | 1,080,386 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.3 | 2.5 |
| Medical/surgical | 2,048 (1,932) | 1,592 | 1,938,992 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 2.2 |
| Neurologic | 64 (63) | 54 | 64,719 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.4 | 2.6 |
| Neurosurgical | 63 (61) | 44 | 54,802 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 2.2 |
| Orthopedic | 274 (247) | 78 | 172,241 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.7 |
| Orthopedic trauma | 21 (20) | 26 | 22,588 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 2.1 |
| Pediatric medical | 52 (47) | 48 | 49,399 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 2.3 |
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 286 (216) | 226 | 212,654 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 2.3 |
| Pediatric orthopedic | 10 (3) | 1 | 2,034 | 0.5 | |||||
| Pediatric rehabilitation - non-IRF‡ | 8 | 8 | 4,418 | 1.8 | |||||
| Pediatric surgical | 14 | 15 | 15,668 | 1.0 | |||||
| Postpartum | 155 (23) | 2 | 3,647 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Pulmonary | 41 | 69 | 66,228 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 2.7 |
| Rehabilitation - non-IRF‡ | 32 (26) | 4 | 15,786 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Surgical | 507 (482) | 452 | 555,766 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 2.8 |
| Telemetry | 298 (293) | 241 | 277,559 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.3 | 2.7 |
| Vascular Surgery | 25 | 21 | 37,652 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.3 | 1.9 |
| Well-Baby Nursery | 16 (3) | 0 | 486 | 0.0 | |||||
| Chronic Care Units§ | |||||||||
| Chronic care | 24 | 18 | 24,932 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 1.8 |
| Inpatient hospice | 5 | 0 | 3,089 | 0.0 | |||||
| Ventilator dependent unit | 7 | 15 | 13,193 | 1.1 | |||||
| Critical Access Hospitals | |||||||||
| Critical care units‖ | 153 (74) | 10 | 17,942 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Non-critical care units¶ | 181 (126) | 21 | 37,932 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Long-Term Acute Care Hospitals# | |||||||||
| Adult critical care | 63 | 147 | 90,703 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 2.6 | 4.4 |
| Adult ward | 574 (564) | 1,967 | 1,879,822 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 2.4 |
| Inpatient Rehabilitation Facilities** | |||||||||
| Adult rehabilitation units - Freestanding | 69 (64) | 17 | 44,818 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 |
| Adult rehabilitation units - Within healthcare facility | 323 (288) | 86 | 133,910 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.4 |
| Central line utilization ratio†† | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of locations+ |
Central line- days |
Patient- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% | |
| Acute Care Hospitals | |||||||||
| Critical Care | |||||||||
| Burn | 73 | 78,825 | 165,242 | 0.48 | 0.21 | 0.32 | 0.46 | 0.61 | 0.75 |
| Medical -Major teaching |
231 | 625,053 | 1,065,875 | 0.59 | 0.39 | 0.50 | 0.59 | 0.68 | 0.76 |
| Medical -All other |
459 (454) | 627,374 | 1,403,932 | 0.45 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 0.41 | 0.57 | 0.69 |
| Medical cardiac | 409 | 597,529 | 1,421,371 | 0.42 | 0.18 | 0.30 | 0.41 | 0.56 | 0.69 |
| Medical/surgical -Major teaching |
328 (327) | 765,267 | 1,380,023 | 0.55 | 0.27 | 0.41 | 0.53 | 0.65 | 0.71 |
| Medical/surgical -All other ≤15 beds |
1,690 (1,669) | 1,312,634 | 3,774,615 | 0.35 | 0.10 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.49 | 0.62 |
| Medical Surgical -All other > 15 beds |
803 | 2,110,694 | 4,378,657 | 0.48 | 0.29 | 0.40 | 0.51 | 0.60 | 0.69 |
| Neurologic | 55 (54) | 80,900 | 160,483 | 0.50 | 0.22 | 0.35 | 0.49 | 0.59 | 0.74 |
| Neurosurgical | 174 | 314,752 | 721,754 | 0.44 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.43 | 0.53 | 0.63 |
| Pediatric cardiothoracic | 41 | 134,529 | 187,490 | 0.72 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.76 | 0.87 | 0.91 |
| Pediatric medical | 33 (29) | 24,297 | 56,936 | 0.43 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.39 | 0.48 |
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 317 (313) | 401,074 | 880,238 | 0.46 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.36 | 0.51 | 0.60 |
| Pediatric surgical | 6 | 3,457 | 9,252 | 0.37 | |||||
| Prenatal | 6 | 376 | 6,974 | 0.05 | |||||
| Respiratory | 10 | 15,254 | 32,728 | 0.47 | |||||
| Surgical -Major teaching |
178 | 445,486 | 753,588 | 0.59 | 0.37 | 0.47 | 0.58 | 0.70 | 0.77 |
| Surgical -All other |
210 (208) | 387,095 | 717,985 | 0.54 | 0.33 | 0.44 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 0.75 |
| Surgical cardiothoracic | 459 (458) | 950,847 | 1,428,269 | 0.67 | 0.37 | 0.50 | 0.68 | 0.81 | 0.90 |
| Trauma | 153 | 341,619 | 631,876 | 0.54 | 0.35 | 0.45 | 0.54 | 0.63 | 0.70 |
| Step-Down Units | |||||||||
| Adult step-down (post-critical care) | 585 (583) | 667,879 | 3,188,720 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.29 | 0.40 |
| Step-down NICU (level II) | 42 (40) | 5,096 | 79,525 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.15 |
| Pediatric step-down (post-critical care) | 14 | 13,962 | 51,428 | 0.27 | |||||
| Inpatient Wards | |||||||||
| Acute stroke | 20 | 14,038 | 111,017 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.16 |
| Antenatal | 18 | 1,554 | 27,399 | 0.06 | |||||
| Behavioral health/psychiatry | 104 | 9,032 | 257,975 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| Burn | 17 | 8,877 | 41,957 | 0.21 | |||||
| Gastrointestinal | 6 | 10,619 | 38,469 | 0.28 | |||||
| Genitourinary | 14 | 17,005 | 72,775 | 0.23 | |||||
| Geronotology | 10 | 5,940 | 51,878 | 0.11 | |||||
| Gynecology | 51 (50) | 10,916 | 124,952 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.14 |
| Jail | 14 | 7,350 | 46,237 | 0.16 | |||||
| Labor and delivery | 57 (56) | 802 | 53,708 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| Labor, delivery, recovery, postpartum suite | 111 (110) | 3,182 | 147,766 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| Medical | 917 (911) | 1,080,386 | 6,325,631 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.30 |
| Medical/surgical | 2,048 (2,038) | 1,938,992 | 13,323,221 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.26 |
| Neurologic | 64 | 64,719 | 460,682 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.21 |
| Neurosurgical | 63 | 54,802 | 400,128 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.22 |
| Orthopedic | 274 | 172,241 | 1,629,594 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.17 |
| Orthopedic Trauma | 21 | 22,588 | 149,270 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.21 |
| Pediatric medical | 52 | 49,399 | 234,474 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.26 | 0.39 |
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 286 (284) | 212,654 | 1,142,975 | 0.19 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.22 | 0.34 |
| Pediatric orthopedic | 10 | 2,034 | 12,684 | 0.16 | |||||
| Pediatric rehabilitation - non-IRF‡ | 8 | 4,418 | 24,829 | 0.18 | |||||
| Pediatric surgical | 14 | 15,668 | 70,738 | 0.22 | |||||
| Postpartum | 155 | 3,647 | 318,836 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| Pulmonary | 41 | 66,228 | 290,991 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 0.38 |
| Rehabilitation - non-IRF‡ | 32 | 15,786 | 122,348 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.18 | 0.31 |
| Surgical | 507 (506) | 555,766 | 3,336,490 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.27 |
| Telemetry | 298 | 277,559 | 2,111,059 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.23 |
| Vascular surgery | 25 | 37,652 | 178,330 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.27 | 0.40 |
| Well-Baby Nursery | 16 (14) | 486 | 11,649 | 0.04 | |||||
| Chronic Care Units§ | |||||||||
| Chronic care unit | 24 (23) | 24,932 | 104,024 | 0.24 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.61 |
| Inpatient hospice | 5 | 3,089 | 10,670 | 0.29 | |||||
| Ventilator dependent unit | 7 | 13,193 | 41,749 | 0.32 | |||||
| Critical Access Hospitals | |||||||||
| Critical care units‖ | 153 (136) | 17,942 | 113,098 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.34 |
| Non-critical care units¶ | 181 (177) | 37,932 | 415,592 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.16 |
| Long-Term Acute Care Hospitals# | |||||||||
| Adult critical care | 63 | 90,703 | 147,465 | 0.62 | 0.53 | 0.66 | 0.78 | 0.88 | 0.93 |
| Adult ward | 574 (573) | 1,879,822 | 3,069,199 | 0.61 | 0.30 | 0.52 | 0.66 | 0.76 | 0.86 |
| Inpatient Rehabilitation Facilities** | |||||||||
| Adult rehabilitation units - Freestanding | 69 | 44,818 | 578,554 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.15 |
| Adult rehabilitation units - Within healthcare facility | 323 (322) | 133,910 | 1,394,340 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.16 |
BSI, bloodstream infection; CLABSI, central line-associated BSI; NICU, neonatal intensive care unit.
The number in parentheses is the number of locations meeting minimum requirements for percentile distributions (i.e., ≥50 device days for rate distributions, ≥50 patient days for device utilization ratios) if less than total number of locations. If this number is <20, percentile distributions are not calculated.
Includes only in-hospital rehabilitation wards that are not defined as inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRF) per the CMS Inpatient Rehabilitation Facility Quality Reporting Program.
Includes chronic care locations within the general acute care hospital setting.
Combines all critical care unit types within critical access hospitals.
Combines all units not identified as critical care (e.g., inpatient wards, step-down units) within critical access hospitals.
Includes free-standing long-term acute care hospitals and long-term acute care locations within the general acute care hospital setting.
Includes free-standing inpatient rehabilitation facilities and inpatient rehabilitation facilities within the acute care hospital setting, as defined by the CMS Inpatient Rehabilitation Facility Quality Reporting Program.
Table 10.
Pooled means and key percentiles of the distribution of ventilator-associated PNEU rates and ventilator utilization ratios for level II/III NICUs, DA module, 2012
| Ventilator-associated PNEU rate * | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth-weight category | No. of locations † |
No. of VAP |
Ventilator- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| ≤ 750 grams | 147 (110) | 76 | 44,399 | 1.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.4 | 5.8 |
| 751–1000 grams | 157 (100) | 33 | 23,481 | 1.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5.6 |
| 1001–1500 grams | 184 (75) | 8 | 14,065 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1501–2500 grams | 194 (54) | 5 | 12,029 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| > 2500 grams | 201 (58) | 5 | 16,163 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ventilator utilization ratio ‡ | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth-weight category | No. of locations † |
Ventilator- days |
Patient- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| ≤ 750 grams | 147 (121) | 44,399 | 1,17,397 | 0.38 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.43 | 0.53 | 0.71 |
| 751–1000 grams | 157 (137) | 23,481 | 1,06,652 | 0.22 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.22 | 0.33 | 0.45 |
| 1001–1500 grams | 184 (166) | 14,065 | 1,51,764 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.24 |
| 1501–2500 grams | 194 (188) | 12,029 | 2,46,360 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.09 |
| > 2500 grams | 201 (189) | 16,163 | 1,94,888 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.13 |
VAP, ventilator-associated pneumonia; NICU, neonatal intensive care unit.
The number in parentheses is the number of locations meeting minimum requirements for percentile distributions (i.e., ≥50 device days for rate distributions, ≥50 patient days for device utilization ratios) if less than total number of locations. If this number is <20, percentile distributions are not calculated.
Table 11.
Distribution of criteria for central line-associated laboratory-confirmed BSI by location, 2012
| LCBI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Location | Criterion 1 n (%) |
Criterion 2/3 n (%) |
Total | ||
| Acute Care Hospitals | |||||
| Critical Care | |||||
| Burn | 251 | 94.7% | 14 | 5.3% | 265 |
| Medical -Major teaching |
692 | 87.4% | 100 | 12.6% | 792 |
| Medical -All other |
560 | 81.9% | 124 | 18.1% | 684 |
| Medical cardiac | 487 | 77.3% | 143 | 22.7% | 630 |
| Medical/surgical -Major teaching |
803 | 85.4% | 137 | 14.6% | 940 |
| Medical/surgical -All other ≤15 beds |
996 | 81.2% | 230 | 18.8% | 1,226 |
| Medical/surgical -All other > 15 beds |
1,542 | 81.4% | 352 | 18.6% | 1,894 |
| Neurologic | 63 | 75.9% | 20 | 24.1% | 83 |
| Neurosurgical | 275 | 76.2% | 86 | 23.8% | 361 |
| Pediatric cardiothoracic | 154 | 81.5% | 35 | 18.5% | 189 |
| Pediatric medical | 24 | 82.8% | 5 | 17.2% | 29 |
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 466 | 81.3% | 107 | 18.7% | 573 |
| Pediatric surgical | 3 | 100.0% | 3 | ||
| Prenatal | 1 | 100.0% | 1 | ||
| Respiratory | 16 | 88.9% | 2 | 11.1% | 18 |
| Surgical -Major teaching |
443 | 83.7% | 86 | 16.3% | 529 |
| Surgical -All other |
276 | 77.3% | 81 | 22.7% | 357 |
| Surgical cardiothoracic | 657 | 81.8% | 146 | 18.2% | 803 |
| Trauma | 458 | 83.7% | 89 | 16.3% | 547 |
| Step-Down Units | |||||
| Adult step-down (post-critical care) | 459 | 87.1% | 68 | 12.9% | 527 |
| Step-down NICU (level II) | 2 | 50.0% | 2 | 50.0% | 4 |
| Pediatric step-down (post-critical care) | 21 | 80.8% | 5 | 19.2% | 26 |
| Inpatient Wards | |||||
| Acute stroke | 14 | 93.3% | 1 | 6.7% | 15 |
| Antenatal | 1 | 100.0% | 1 | ||
| Behavioral health/psychiatry | 4 | 80.0% | 1 | 20.0% | 5 |
| Burn | 19 | 90.5% | 2 | 9.5% | 21 |
| Gastrointestinal | 18 | 94.7% | 1 | 5.3% | 19 |
| Genitourinary | 13 | 68.4% | 6 | 31.6% | 19 |
| Geronotology | 2 | 66.7% | 1 | 33.3% | 3 |
| Gynecology | 5 | 83.3% | 1 | 16.7% | 6 |
| Jail | 11 | 91.7% | 1 | 8.3% | 12 |
| Labor and delivery | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Labor, delivery, recovery, postpartum suite | 4 | 100.0% | 0 | 0.0% | 4 |
| Medical | 854 | 88.8% | 108 | 11.2% | 962 |
| Medical/surgical | 1,349 | 84.7% | 243 | 15.3% | 1,592 |
| Neurologic | 43 | 79.6% | 11 | 20.4% | 54 |
| Neurosurgical | 37 | 84.1% | 7 | 15.9% | 44 |
| Orthopedic | 65 | 83.3% | 13 | 16.7% | 78 |
| Orthopedic trauma | 21 | 80.8% | 5 | 19.2% | 26 |
| Pediatric medical | 43 | 89.6% | 5 | 10.4% | 48 |
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 195 | 86.3% | 31 | 13.7% | 226 |
| Pediatric orthopedic | 1 | 100.0% | 1 | ||
| Pediatric rehabilitation - non-IRF* | 8 | 100.0% | 8 | ||
| Pediatric surgical | 13 | 86.7% | 2 | 13.3% | 15 |
| Postpartum | 2 | 100.0% | 2 | ||
| Pulmonary | 60 | 87.0% | 9 | 13.0% | 69 |
| Rehabilitation - non-IRF* | 3 | 75.0% | 1 | 25.0% | 4 |
| Surgical | 388 | 85.8% | 64 | 14.2% | 452 |
| Telemetry | 212 | 88.0% | 29 | 12.0% | 241 |
| Vascular Surgery | 20 | 95.2% | 1 | 4.8% | 21 |
| Well-Baby Nursery | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Chronic Care Units† | |||||
| Chronic care | 14 | 77.8% | 4 | 22.2% | 18 |
| Inpatient hospice | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Ventilator dependent unit | 15 | 100.0% | 15 | ||
| Critical Access Hospitals | |||||
| Critical care units‡ | 7 | 70.0% | 3 | 30.0% | 10 |
| Non-critical care units§ | 16 | 76.2% | 5 | 23.8% | 21 |
| Long-Term Acute Care Hospitals‖ | |||||
| Adult critical care | 132 | 89.8% | 15 | 10.2% | 147 |
| Adult ward | 1,734 | 88.2% | 233 | 11.8% | 1,967 |
| Inpatient Rehabilitation Facilities¶ | |||||
| Adult rehabilitation units - Freestanding | 17 | 100.0% | 17 | ||
| Adult rehabilitation units - Within healthcare facility | 77 | 89.5% | 9 | 10.5% | 86 |
| TOTAL | 14,065 | 84.2% | 2,645 | 15.8% | 16,710 |
BSI, bloodstream infection; LCBI, laboratory-confirmed BSI.5
Includes only in-hospital rehabilitation wards that are not defined as inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRF) per the CMS Inpatient Rehabilitation Facility Quality Reporting Program.
Includes chronic care locations within the general acute care hospital setting.
Combines all critical care unit types within critical access hospitals.
Combines all units not identified as critical care (e.g., inpatient wards, step-down units) within critical access hospitals.
Includes free-standing long-term acute care hospitals and long-term acute care locations within the general acute care hospital setting.
Includes free-standing inpatient rehabilitation facilities and inpatient rehabilitation facilities within the acute care hospital setting, as defined by the CMS Inpatient Rehabilitation Facility Quality Reporting Program.
Table 18.
Distribution of specific sites of ventilator-associated pneumonia among Level II/III NICUs by birthweight, 2012
| Birth-weight category | PNU1 n (%) | PNU2 n (%) | PNU3 n (%) | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤ 750 grams | 54 | 71.1% | 20 | 26.3% | 2 | 2.6% | 76 |
| 750–1000 grams | 29 | 87.9% | 3 | 9.1% | 1 | 3.0% | 33 |
| 1001–1500 grams | 5 | 62.5% | 2 | 25.0% | 1 | 12.5% | 8 |
| 1501–2500 grams | 2 | 40.0% | 2 | 40.0% | 1 | 20.0% | 5 |
| > 2500 grams | 4 | 80.0% | 1 | 20.0% | 5 | ||
| Total | 94 | 74.0% | 28 | 22.0% | 5 | 3.9% | 127 |
PNU1, clinically defined pneumonia; PNU2, pneumonia with specific laboratory findings; PNU3, pneumonia in immunocompromised patients.7
Tables 3–6 update and augment previously published DA rates and DU ratios by type of non-NICU locations.1 Based on results of statistical comparisons, data from CAHs are reported separately from all other acute care hospitals. These data are further stratified into combined critical care units and combined non-critical care units.
Table 6.
Pooled means and key percentiles of the distribution of ventilator-associated PNEU rates and ventilator utilization ratios, by type of location, DA module, 2012
| Ventilator-associated PNEU rate* | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of location | No. of locations† |
No. of VAP |
Ventilator -days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| Acute Care Hospitals | |||||||||
| Critical Care Units | |||||||||
| Burn | 36 (34) | 86 | 19,503 | 4.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 6.7 | 10.9 |
| Medical -Major teaching |
112 (111) | 205 | 212,392 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 2.9 |
| Medical -All other |
223 (197) | 191 | 206,731 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.3 | 3.4 |
| Medical cardiac | 178 (170) | 135 | 139,864 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 3.6 |
| Medical/surgical -Major teaching |
152 (145) | 372 | 234,972 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 2.2 | 3.9 |
| Medical/surgical -All other ≤15 beds |
841 (660) | 419 | 383,926 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 3.6 |
| Medical/surgical -All other >15 beds |
405 (400) | 666 | 711,280 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 2.8 |
| Neurologic | 23 | 62 | 20,859 | 3.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 2.5 | 7.0 |
| Neurosurgical | 76 (74) | 210 | 98,026 | 2.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 2.9 | 3.8 |
| Pediatric cardiothoracic | 20 | 9 | 36,187 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| Pediatric medical | 16 (9) | 2 | 6,634 | 0.3 | |||||
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 142 (132) | 113 | 147,441 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 2.4 |
| Pediatric surgical | 5 (4) | 1 | 2,328 | 0.4 | |||||
| Respiratory | 7 | 4 | 6,037 | 0.7 | |||||
| Surgical -Major teaching |
81 (80) | 280 | 127,251 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 3.1 | 5.6 |
| Surgical -All other |
93 (88) | 192 | 96,388 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 2.8 | 5.9 |
| Surgical cardiothoracic | 207 (203) | 319 | 190,785 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 2.5 | 5.1 |
| Trauma | 75 (74) | 508 | 141,314 | 3.6 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 2.6 | 6.0 | 9.4 |
| Specialty Care Areas/Oncology | |||||||||
| Hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 5 | 0 | 1,951 | 0.0 | |||||
| Step-Down Units | |||||||||
| Adult step-down (post-critical care) | 102 (82) | 31 | 42,462 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.8 |
| Pediatric step-down (post-critical care) | 5 (4) | 1 | 5,813 | 0.2 | |||||
| Step-down NICU (level II) | 7 (1) | 0 | 119 | 0.0 | |||||
| Inpatient Wards | |||||||||
| Medical | 39 (22) | 3 | 6,472 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.4 |
| Medical/surgical | 64 (35) | 22 | 25,731 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.3 |
| Pediatric medical | 6 (5) | 0 | 2,026 | 0.0 | |||||
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 11 (8) | 0 | 3,146 | 0.0 | |||||
| Pulmonary | 9 (8) | 7 | 7,241 | 1.0 | |||||
| Surgical | 8 (1) | 0 | 107 | 0.0 | |||||
| Telemetry | 10 (5) | 1 | 1,770 | 0.6 | |||||
| Critical Access Hospitals | |||||||||
| Critical care units‖ | 67 (14) | 3 | 2964 | 1.0 | |||||
| Non-critical care units¶ | 9 (1) | 4 | 2660 | 1.5 | |||||
| Long-Term Acute Care Hospitals‡ | |||||||||
| Adult critical care | 18 (17) | 8 | 12,544 | 0.6 | |||||
| Adult ward | 195 (190) | 103 | 316,632 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 1.4 |
| Ventilator utilization ratio¶ | Percentile | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of location | No. of locations† | Ventilator -days |
Patient- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) | 75% | 90% | |
| Acute Care Hospitals | ||||||||||
| Critical Care Units | ||||||||||
| Burn | 36 | 19,503 | 71,198 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.34 | 0.43 | |
| Medical -Major teaching |
112 | 212,392 | 477,003 | 0.45 | 0.28 | 0.37 | 0.45 | 0.54 | 0.63 | |
| Medical -All other |
223 (220) | 206,731 | 606,883 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.28 | 0.42 | 0.55 | |
| Medical cardiac | 178 (177) | 139,864 | 547,699 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.40 | |
| Medical/surgical -Major teaching |
152 (150) | 234,972 | 618,025 | 0.38 | 0.16 | 0.25 | 0.37 | 0.46 | 0.54 | |
| Medical/surgical -All other ≤15 beds |
841 (815) | 383,926 | 1,616,191 | 0.24 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.19 | 0.32 | 0.43 | |
| Medical/surgical -All other >15 beds |
405 | 711,280 | 2,114,095 | 0.34 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.41 | 0.49 | |
| Neurologic | 23 | 20,859 | 64,005 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 0.39 | 0.42 | |
| Neurosurgical | 76 | 98,026 | 323,269 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.30 | 0.39 | 0.45 | |
| Pediatric cardiothoracic | 20 | 36,187 | 86,054 | 0.42 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.50 | 0.54 | |
| Pediatric medical | 16 | 6,634 | 21,470 | 0.31 | ||||||
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 142 (141) | 147,441 | 400,413 | 0.37 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.30 | 0.42 | 0.48 | |
| Pediatric surgical | 5 (4) | 2,328 | 8,039 | 0.29 | ||||||
| Respiratory | 7 | 6,037 | 22,926 | 0.26 | ||||||
| Surgical -Major teaching |
81 | 127,251 | 320,792 | 0.40 | 0.23 | 0.29 | 0.40 | 0.48 | 0.53 | |
| Surgical -All other |
93 (92) | 96,388 | 281,455 | 0.34 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.41 | 0.47 | |
| Surgical cardiothoracic | 207 (206) | 190,785 | 606,801 | 0.31 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.29 | 0.39 | 0.49 | |
| Trauma | 75 | 141,314 | 301,607 | 0.47 | 0.34 | 0.41 | 0.47 | 0.53 | 0.63 | |
| Specialty Care Areas/Oncology | ||||||||||
| Hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 5 | 1,951 | 22,808 | 0.09 | ||||||
| Step-Down Units | ||||||||||
| Adult step-down (post-critical care) | 102 (101) | 42,462 | 437,346 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.24 | |
| Pediatric step-down (post-critical care) | 5 | 5,813 | 19,832 | 0.29 | ||||||
| Step-down NICU (level II) | 7 (6) | 119 | 4,073 | 0.03 | ||||||
| Inpatient Wards | ||||||||||
| Medical | 39 | 6,472 | 209,363 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.07 | |
| Medical/surgical | 64 | 25,731 | 378,747 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.13 | |
| Pediatric medical | 6 | 2,026 | 25,314 | 0.08 | ||||||
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 11 | 3,146 | 62,702 | 0.05 | ||||||
| Pulmonary | 9 | 7,241 | 51,428 | 0.14 | ||||||
| Surgical | 8 | 107 | 15,644 | 0.01 | ||||||
| Telemetry | 10 | 1,770 | 42,097 | 0.04 | ||||||
| Critical Access Hospitals | ||||||||||
| Critical care units‡ | 67 (54) | 2964 | 30983 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.16 | |
| Non-critical care units§ | 9 (9) | 2660 | 12632 | 0.21 | ||||||
| Long-Term Acute Care Hospitals‖ | ||||||||||
| Adult critical care | 18 (17) | 12,544 | 41,665 | 0.30 | ||||||
| Adult ward | 195 | 316,632 | 1,474,536 | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.29 | 0.39 | |
VAP, ventilator-associated pneumonia.
The number in parentheses is the number of locations meeting minimum requirements for percentile distributions (i.e., ≥50 device days for rate distributions, ≥50 patient days for device utilization ratios) if less than total number of locations. If this number is <20, percentile distributions are not calculated.
Combines all critical care unit types within critical access hospitals.
Combines all units not identified as critical care (e.g., inpatient wards, step-down units) within critical access hospitals.
Includes free-standing long-term acute care hospitals and long-term acute care locations within the general acute care hospital setting.
Tables 7–10 update and augment the previously published DA rates and DU ratios by birth-weight category for NICU locations.1 Beginning in January 2012, CLABSI data in NICU locations were no longer collected according to central line type (i.e., central line and umbilical catheter); therefore, CLABSI rates and DU ratios for NICUs are not stratified by line type in this report.
Table 7.
Pooled means and key percentiles of the distribution of central line-associated BSI rates and central line utilization ratios for level III NICUs, DA module, 2012
| Central line-associated BSI rate * | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth-weight category | No. of locations † |
No. of CLABSI |
Central line- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| ≤ 750 grams | 380 (334) | 420 | 1,85,851 | 2.3 | 0 | 0 | 1.5 | 3.7 | 7.5 |
| 751–1000 grams | 401 (339) | 256 | 1,60,230 | 1.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.6 | 4.6 |
| 1001–1500 grams | 418 (370) | 195 | 1,72,732 | 1.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.6 | 3.9 |
| 1501–2500 grams | 415 (338) | 104 | 1,61,361 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.3 |
| > 2500 grams | 422 (322) | 136 | 1,76,853 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.3 | 2.0 |
| Central line utilization ratio‡ | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth-weight category | No. of locations † |
Central line- days |
Patient- days |
Pooled Mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| ≤ 750 grams | 380 (346) | 1,85,851 | 4,55,113 | 0.41 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.42 | 0.55 | 0.67 |
| 751–1000 grams | 401 (369) | 1,60,230 | 4,57,406 | 0.35 | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 0.46 | 0.60 |
| 1001–1500 grams | 418 (407) | 1,72,732 | 6,53,953 | 0.26 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.24 | 0.35 | 0.49 |
| 1501–2500 grams | 415 (410) | 1,61,361 | 9,08,957 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.37 |
| > 2500 grams | 422 (412) | 1,76,853 | 7,38,196 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.26 | 0.42 |
BSI, bloodstream infection; CLABSI, central line-associated BSI; NICU, neonatal intensive care unit.
The number in parentheses is the number of locations meeting minimum requirements for percentile distributions (i.e., ≥50 device days for rate distributions, ≥50 patient days for device utilization ratios) if less than total number of locations. If this number is <20, percentile distributions are not calculated.
Tables 11–18 provide data on select attributes of the DA infections for each location. For example, Tables 11, 12, 15 and 16 show the frequency and percent distribution of the specific sites of CLABSI and the criteria used for identifying these infections. Note that for these tables, criteria 2 and 3, which involve common commensals only, have been combined.
Table 12.
Distribution of criteria for permanent and temporary central line-associated laboratory-confirmed BSI by location, 2012
| LCBI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Location | Criterion 1 n (%) |
Criterion 2/3 n (%) |
Total | ||
| Permanent Central Line | |||||
| General hematology/oncology | 308 | 76.6% | 94 | 23.4% | 402 |
| Hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 200 | 78.1% | 56 | 21.9% | 256 |
| Pediatric general hematology/oncology | 187 | 72.8% | 70 | 27.2% | 257 |
| Pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 67 | 72.0% | 26 | 28.0% | 93 |
| Solid organ transplant | 16 | 80.0% | 4 | 20.0% | 20 |
| Solid tumor | 11 | 73.3% | 4 | 26.7% | 15 |
| Total | 789 | 75.6% | 254 | 24.4% | 1,043 |
| Temporary Central Line | |||||
| General hematology/oncology | 399 | 81.3% | 92 | 18.7% | 491 |
| Hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 229 | 77.9% | 65 | 22.1% | 294 |
| Pediatric general hematology/oncology | 73 | 77.7% | 21 | 22.3% | 94 |
| Pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 17 | 77.3% | 5 | 22.7% | 22 |
| Solid organ transplant | 57 | 89.1% | 7 | 10.9% | 64 |
| Solid tumor | 10 | 58.8% | 7 | 41.2% | 17 |
| Total | 785 | 79.9% | 197 | 20.1% | 982 |
BSI, bloodstream infection; LCBI, laboratory-confirmed BSI.5
Table 15.
Distribution of specific sites and criteria for central line-associated laboratory-confirmed BSI among Level III NICUs by birthweight, 2012
| LCBI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth-weight category | Criterion 1 n (%) | Criterion 2/3 n (%) | Total | ||
| ≤ 750 grams | 316 | 75.2% | 104 | 24.8% | 420 |
| 750–1000 grams | 176 | 68.8% | 80 | 31.3% | 256 |
| 1001–1500 grams | 135 | 69.2% | 60 | 30.8% | 195 |
| 1501–2500 grams | 76 | 73.1% | 28 | 26.9% | 104 |
| > 2500 grams | 101 | 74.3% | 35 | 25.7% | 136 |
| Total | 804 | 72.4% | 307 | 27.6% | 1,111 |
BSI, bloodstream infection; LCBI, laboratory-confirmed BSI.5
Table 16.
Distribution of specific sites and criteria for central line-associated laboratory-confirmed BSI among Level II/III NICUs by birthweight, 2012
| LCBI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth-weight category | Criterion 1 n (%) | Criterion 2/3 n (%) | Total | ||
| ≤ 750 grams | 211 | 70.3% | 89 | 29.7% | 300 |
| 750–1000 grams | 127 | 64.5% | 70 | 35.5% | 197 |
| 1001–1500 grams | 73 | 63.5% | 42 | 36.5% | 115 |
| 1501–2500 grams | 49 | 73.1% | 18 | 26.9% | 67 |
| > 2500 grams | 43 | 63.2% | 25 | 36.8% | 68 |
| Total | 503 | 67.3% | 244 | 32.7% | 747 |
BSI, bloodstream infection; LCBI, laboratory-confirmed BSI.5
Discussion
This report summarizes the HAI data reported to the DA module of NHSN during 2012.Compared to the healthcare facility types for which HAI data were summarized in the last published report, in this report there is a slight increase in smaller hospitals, IRFs, and LTACHs.1 Based on the number of facilities reporting, overall contribution from all facility types to the device-associated module increased by 15% from the last report.1 This increase in reporting is largely attributable to healthcare facilities’ participation in CMS’s Quality Reporting Programs which require participants to use NHSN as the tool to report CLABSI data from all acute care hospital adult, pediatric, and neonatal ICUs (effective as of January 2011)and all LTACH locations, as well as CAUTI data from all acute care hospital adult and pediatric ICUs, and all LTACH and IRF locations (effective as of January 2012).8,9 While this growth impacted the volume of reporting in these designated settings, there is also an indication of increased participation in ward locations for CLABSI and CAUTI surveillance.
Extensive analyses of the impact of facility type and medical school affiliation on all DA infection rates were performed for select locations. Medical school affiliation continues to be a significant factor for all three DA infection rates and/or percentile distributions in medical ICUs and surgical ICUs. All DA infection rate pooled means in this report continue to be higher in those locations stratified as major teaching compared to their non-major teaching counterparts. This suggests room for targeted prevention efforts in these settings that care for higher complexity patients. Additionally, medical school affiliation and bed size both continue to be significant factors in DA infection rates for medical/surgical ICUs. Note that while the CLABSI rates between unit bedsize strata in medical/surgical “all other” ICUs are equal (Table 3), the percentile distributions were shown to be significantly different as a result of nonparametric statistical tests. Therefore, this stratification by unit bedsize in “all other” medical/surgical ICUs was retained. Adult hematology/oncology locations were not further stratified by hospital type (i.e., oncology hospital vs. all other acute care hospitals) as the results of the statistical tests indicated that the differences in the strata were not statistically significant. In 2013, oncology and general acute care hospitals were provided with fourteen oncology-specific CDC locations with which to identify for device-associated infection surveillance. As the volume of these data become sufficient, future analyses will continue to assess any potential differences in this specialized population.
In 2012, facilities participating in NHSN were able to designate themselves as CAHs. This information allowed for the comparison of DA rates and DU ratios in these hospitals to all other hospitals. The results of the statistical tests indicated that DA rates and DU ratios in CAHs are significantly different from all other hospitals and therefore, CAHs are now able to compare themselves to pooled means generated from like-hospitals. This allows for more targeted prevention efforts in this unique setting.
In producing this report, there were several areas identified for which prevention activities and further investigation may be needed, both at the national and local levels. For example, the CLABSI pooled mean rate for LTACH critical care units is higher than most other critical care unit types (Table 3). Similarly, the CAUTI pooled mean rate for LTACH wards is higher than CAUTI pooled mean rates in the majority of other ward-level locations (Table 5). Further, when compared to the previous report, CAUTI rates have increased in every critical care unit type, with the exception of “Surgical critical care – all others” (Table 5).1 Additional key findings from this report can be found in Figure 1.
Table 5.
Pooled means and key percentiles of the distribution of urinary catheter-associated UTI rates and urinary catheter utilization ratios, by type of location, DA module, 2012
| Urinary catheter-associated UTI rate* | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of location | No. of locations† |
No. of CAUTI |
Urinary catheter- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| Acute Care Hospitals | |||||||||
| Critical care units | |||||||||
| Burn | 73 | 384 | 82,039 | 4.7 | 0.0 | 1.7 | 4.3 | 8.1 | 11.5 |
| Medical -Major teaching |
230 | 2,181 | 741,268 | 2.9 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 2.3 | 3.9 | 5.5 |
| Medical -All other |
460 (454) | 1,438 | 852,627 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.3 | 3.7 |
| Medical cardiac | 405 | 1,517 | 703,734 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 1.8 | 3.4 | 4.9 |
| Medical/Surgical -Major teaching |
328 (325) | 2,280 | 935,001 | 2.4 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 2.0 | 3.5 | 5.2 |
| Medical/Surgical -All other, ≤15 beds |
1,688 (1,651) | 2,521 | 2,032,215 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 1.8 | 3.2 |
| Medical/Surgical -All other, >15 beds |
797 | 4,387 | 2,766,887 | 1.6 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 1.3 | 2.2 | 3.3 |
| Neurologic | 55 (54) | 441 | 118,556 | 3.7 | 0.3 | 1.7 | 2.8 | 5.0 | 7.9 |
| Neurosurgical | 173 | 2,464 | 489,391 | 5.0 | 1.1 | 2.7 | 4.3 | 6.2 | 8.3 |
| Pediatric cardiothoracic | 32 (31) | 61 | 28,823 | 2.1 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 2.1 | 3.4 | 5.0 |
| Pediatric medical | 30 (21) | 35 | 10,389 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 3.1 | 6.7 |
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 297 (268) | 452 | 166,710 | 2.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.6 | 3.8 | 6.0 |
| Pediatric surgical | 5 (4) | 1 | 1,346 | 0.7 | |||||
| Respiratory | 9 | 30 | 19,324 | 1.6 | |||||
| Surgical -Major teaching |
176 | 1,800 | 558,102 | 3.2 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 2.7 | 4.5 | 6.6 |
| Surgical -All other |
209 (205) | 918 | 491,868 | 1.9 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 1.3 | 2.5 | 3.9 |
| Surgical cardiothoracic | 456 (455) | 1,657 | 939,044 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 1.4 | 2.5 | 3.8 |
| Trauma | 153 (152) | 1,991 | 490,351 | 4.1 | 0.9 | 1.6 | 3.3 | 5.6 | 8.2 |
| Specialty Care Areas/Oncology | |||||||||
| General hematology/oncology | 148 (143) | 257 | 119,248 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.6 | 3.6 | 5.7 |
| Hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 42 (38) | 41 | 21,134 | 1.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 3.4 | 7.3 |
| Pediatric general hematology/oncology | 24 (18) | 9 | 3,252 | 2.8 | |||||
| Pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 5 (2) | 1 | 277 | 3.6 | |||||
| Solid organ transplant | 16 | 37 | 22,667 | 1.6 | |||||
| Solid tumor | 6 | 58 | 25,785 | 2.2 | |||||
| Step-down Units | |||||||||
| Adult step-down (post-critical care) | 470 (466) | 1,139 | 615,962 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 2.7 | 4.6 |
| Pediatric step-down (post-critical care) | 12 (7) | 1 | 970 | 1.0 | |||||
| Inpatient Wards | |||||||||
| Acute stroke | 15 | 26 | 17,456 | 1.5 | |||||
| Antenatal | 15 (12) | 2 | 2,234 | 0.9 | |||||
| Behavioral health/psychiatry | 118 (50) | 32 | 11,605 | 2.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.2 | 9.1 |
| Burn | 16 (15) | 32 | 6,061 | 5.3 | |||||
| Genitourinary | 12 (11) | 11 | 11,409 | 1.0 | |||||
| Gerontology | 11 | 8 | 7,489 | 1.1 | |||||
| Gynecology | 59 (51) | 26 | 29,614 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 3.1 |
| Jail | 11 (7) | 6 | 3,372 | 1.8 | |||||
| Labor and delivery | 95 (69) | 15 | 28,435 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.6 |
| Labor, delivery, recovery, postpartum suite | 167 (144) | 30 | 63,794 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 |
| Medical | 813 (788) | 1,334 | 882,392 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 2.4 | 4.5 |
| Medical/Surgical | 1,825 (1,765) | 2,752 | 2,038,073 | 1.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 2.1 | 3.6 |
| Neurologic | 56 (55) | 159 | 78,211 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 1.6 | 3.0 | 5.3 |
| Neurosurgical | 48 | 175 | 61,879 | 2.8 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 2.3 | 3.8 | 5.3 |
| Orthopedic | 249 (239) | 425 | 356,156 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 2.1 | 3.2 |
| Orthopedic trauma | 17 | 68 | 31,586 | 2.2 | |||||
| Pediatric medical | 33 (16) | 6 | 4,188 | 1.4 | |||||
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 209 (111) | 55 | 31,738 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.4 | 6.6 |
| Pediatric orthopedic | 5 (4) | 1 | 2,086 | 0.5 | |||||
| Pediatric rehabilitation - non-IRF‡ | 5 (1) | 1 | 245 | 4.1 | |||||
| Pediatric surgical | 12 (8) | 4 | 5,846 | 0.7 | |||||
| Postpartum | 215 (195) | 61 | 115,138 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.4 |
| Pulmonary | 29 (28) | 88 | 44,393 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 1.4 | 2.2 | 4.7 |
| Rehabilitation - non-IRF‡ | 37 (31) | 29 | 11,285 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.9 | 6.2 |
| Surgical | 458 (450) | 1,099 | 647,041 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 2.6 | 4.8 |
| Telemetry | 207 (203) | 400 | 286,809 | 1.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 2.1 | 3.6 |
| Vascular surgery | 20 | 25 | 23,153 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 2.7 |
| Well-baby nursery | 6 (0) | 0 | 24 | 0.0 | |||||
| Chronic Care Units§ | |||||||||
| Chronic care | 30 (29) | 31 | 14,553 | 2.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.6 | 4.3 |
| Chronic care rehabilitation unit | 12 (10) | 6 | 2,278 | 2.6 | |||||
| Inpatient hospice | 5 | 2 | 5,509 | 0.4 | |||||
| Ventilator dependent unit | 5 | 40 | 8,311 | 4.8 | |||||
| Critical Access Hospitals | |||||||||
| Critical care units‖ | 140 (119) | 25 | 35,833 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.8 |
| Non-critical care units¶ | 276 (239) | 173 | 98,900 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.0 | 6.2 |
| Long-Term Acute Care Hospitals# | |||||||||
| Adult critical care | 61 | 148 | 57,468 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 4.3 | 6.4 |
| Adult ward | 588 (580) | 2,537 | 1,282,295 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.6 | 3.0 | 4.9 |
| Inpatient Rehabilitation Facilities** | |||||||||
| Adult rehabilitation units - Freestanding | 286 (260) | 348 | 119,422 | 2.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 4.8 | 9.3 |
| Adult rehabilitation units - Within hospital | 888 (662) | 569 | 180,177 | 3.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 4.5 | 9.9 |
| Pediatric rehabilitation units - Within hospital | 10 (5) | 2 | 1,087 | 1.8 | |||||
| Urinary catheter utilization ratio†† | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of location | No. of locations† |
Urinary catheter- days |
Patient days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| Acute Care Hospitals | |||||||||
| Critical care units | |||||||||
| Burn | 73 | 82,039 | 163,298 | 0.50 | 0.24 | 0.35 | 0.48 | 0.64 | 0.84 |
| Medical -Major teaching |
230 | 741,268 | 1,061,826 | 0.70 | 0.53 | 0.64 | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.85 |
| Medical -All other |
460 (456) | 852,627 | 1,401,026 | 0.61 | 0.32 | 0.50 | 0.64 | 0.74 | 0.82 |
| Medical cardiac | 405 | 703,734 | 1,393,767 | 0.50 | 0.29 | 0.42 | 0.54 | 0.66 | 0.76 |
| Medical/Surgical -Major teaching |
328 (327) | 935,001 | 1,371,681 | 0.68 | 0.46 | 0.58 | 0.69 | 0.77 | 0.83 |
| Medical/Surgical -All other, ≤15 beds |
1,688 (1,670) | 2,032,215 | 3,800,961 | 0.53 | 0.31 | 0.45 | 0.60 | 0.72 | 0.79 |
| Medical/Surgical -All other, >15 beds |
797 | 2,766,887 | 4,338,434 | 0.64 | 0.46 | 0.59 | 0.70 | 0.77 | 0.82 |
| Neurologic | 55 | 118,556 | 157,449 | 0.75 | 0.48 | 0.64 | 0.76 | 0.85 | 0.88 |
| Neurosurgical | 173 | 489,391 | 713,836 | 0.69 | 0.46 | 0.61 | 0.72 | 0.80 | 0.86 |
| Pediatric cardiothoracic | 32 | 28,823 | 129,344 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.36 |
| Pediatric medical | 30 (27) | 10,389 | 49,809 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.34 |
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 297 (292) | 166,710 | 775,828 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.32 |
| Pediatric surgical | 5 | 3,792 | 0.35 | ||||||
| Respiratory | 9 | 19,324 | 32,296 | 0.60 | |||||
| Surgical -Major teaching |
176 | 558,102 | 745,658 | 0.75 | 0.55 | 0.67 | 0.77 | 0.84 | 0.89 |
| Surgical -All other |
209 (205) | 491,868 | 708,482 | 0.69 | 0.52 | 0.64 | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.88 |
| Surgical cardiothoracic | 456 (455) | 939,044 | 1,417,609 | 0.66 | 0.41 | 0.55 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.89 |
| Trauma | 153 | 490,351 | 631,132 | 0.78 | 0.60 | 0.71 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 0.93 |
| Specialty Care Areas/Oncology | |||||||||
| General hematology/oncology | 148 (147) | 119,248 | 812,884 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.28 |
| Hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 42 | 21,134 | 192,836 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.23 |
| Pediatric general hematology/oncology | 24 | 3,252 | 113,041 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.08 |
| Pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 5 | 277 | 8,384 | 0.03 | |||||
| Solid organ transplant | 16 | 22,667 | 94,290 | 0.24 | |||||
| Solid tumor | 6 | 25,785 | 78,482 | 0.33 | |||||
| Step-down Units | |||||||||
| Adult step-down (post-critical care) | 470 (469) | 615,962 | 2,480,340 | 0.25 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.37 | 0.50 |
| Pediatric step-down (post-critical care) | 12 | 970 | 37,889 | 0.03 | |||||
| Inpatient Wards | |||||||||
| Acute stroke | 15 | 17,456 | 77,769 | 0.22 | |||||
| Antenatal | 15 | 2,234 | 33,101 | 0.07 | |||||
| Behavioral health/psychiatry | 118 | 11,605 | 318,371 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| Burn | 16 | 6,061 | 35,863 | 0.17 | |||||
| Genitourinary | 12 | 11,409 | 65,152 | 0.18 | |||||
| Gerontology | 11 | 7,489 | 60,604 | 0.12 | |||||
| Gynecology | 59 (58) | 29,614 | 170,866 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.38 |
| Jail | 11 | 3,372 | 37,316 | 0.09 | |||||
| Labor and delivery | 95 (94) | 28,435 | 168,958 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.21 | 0.35 |
| Labor, delivery, recovery, postpartum suite | 167 (166) | 63,794 | 411,335 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.29 |
| Medical | 813 (809) | 882,392 | 5,552,794 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.26 |
| Medical/Surgical | 1,825 (1,814) | 2,038,073 | 11,501,523 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.22 | 0.29 |
| Neurologic | 56 | 78,211 | 376,137 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.34 |
| Neurosurgical | 48 | 61,879 | 315,157 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.35 |
| Orthopedic | 249 (248) | 356,156 | 1,389,082 | 0.26 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.43 |
| Orthopedic trauma | 17 | 31,586 | 132,749 | 0.24 | |||||
| Pediatric medical | 33 (32) | 4,188 | 102,201 | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.10 |
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 209 (205) | 31,738 | 654,343 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.12 |
| Pediatric orthopedic | 5 | 2,086 | 11,202 | 0.19 | |||||
| Pediatric rehabilitation - non-IRF‡ | 5 | 245 | 6,965 | 0.04 | |||||
| Pediatric surgical | 12 | 5,846 | 48,474 | 0.12 | |||||
| Postpartum | 215 | 115,138 | 880,621 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.24 |
| Pulmonary | 29 | 44,393 | 206,424 | 0.22 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.30 | 0.51 |
| Rehabilitation - non-IRF‡ | 37 (36) | 11,285 | 113,203 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.24 |
| Surgical | 458 | 647,041 | 2,887,968 | 0.22 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.39 |
| Telemetry | 207 | 286,809 | 1,484,465 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 0.30 |
| Vascular surgery | 20 | 23,153 | 139,105 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.27 |
| Well-baby nursery | 6 (4) | 24 | 1,024 | 0.02 | |||||
| Chronic Care Units§ | |||||||||
| Chronic care | 30 (27) | 14,553 | 95,809 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.28 |
| Chronic care rehabilitation unit | 12 | 2,278 | 26,153 | 0.09 | |||||
| Inpatient hospice | 5 | 5,509 | 10,670 | 0.52 | |||||
| Ventilator dependent unit | 5 | 8,311 | 28,901 | 0.29 | |||||
| Critical Access Hospitals | |||||||||
| Critical care units‖ | 140 (129) | 35,833 | 118,365 | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.31 | 0.43 | 0.54 | 0.66 |
| Non-critical care units¶ | 276 (239) | 98,900 | 609,462 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.22 | 0.30 |
| Long-Term Acute Care Hospitals# | |||||||||
| Adult critical care | 61 | 57,468 | 128,089 | 0.45 | 0.35 | 0.46 | 0.65 | 0.80 | 0.87 |
| Adult ward | 588 (587) | 1,282,295 | 2,757,396 | 0.47 | 0.20 | 0.35 | 0.46 | 0.57 | 0.66 |
| Inpatient Rehabilitation Facilities** | |||||||||
| Adult rehabilitation units - Freestanding | 286 | 119,422 | 1,382,477 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.15 |
| Adult rehabilitation units - Within hospital | 888 (887) | 180,177 | 2,171,747 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.17 |
| Pediatric rehabilitation units - Within hospital | 10 | 1,087 | 13,564 | 0.08 | |||||
UTI, urinary tract infection; CAUTI, catheter-associated UTI.
The number in parentheses is the number of locations meeting minimum requirements for percentile distributions (i.e., ≥50 device days for rate distributions, ≥50 patient days for device utilization ratios) if less than total number of locations. If this number is <20, percentile distributions are not calculated.
Includes only in-hospital rehabilitation wards that are not defined as inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRF) per the CMS Inpatient Rehabilitation Facility Quality Reporting Program.
Includes chronic care locations within the general acute care hospital setting.
Combines all critical care unit types within critical access hospitals.
Combines all units not identified as critical care (e.g., inpatient wards, step-down units) within critical access hospitals.
Includes free-standing long-term acute care hospitals and long-term acute care locations within the general acute care hospital setting.
Includes free-standing inpatient rehabilitation facilities and inpatient rehabilitation facilities within the acute care hospital setting, as defined by the CMS Inpatient Rehabilitation Facility Quality Reporting Program.
Tables 11–18 were included to aid the reader in interpreting the DA infection rates data. One important use of data in these tables is to better understand the distribution of DA infections by type of reporting criterion nationally. For example, nearly 85% of the CLABSIs from adult and pediatric ICUs and inpatient wards were identified using criterion (1) which attributes the CLABSI to a recognized pathogen; however, for NICUs, only 70% used this criterion, resulting in a greater percentage of CLABSIs in this population that were identified with common commensals. Similarly, the specific type of ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) most frequently reported, regardless of location, was the clinical criterion (PNU1) which relies on the somewhat subjective interpretations of clinical findings.
As diverse types of facilities continue to participate in NHSN, either voluntarily or by mandate, the need for careful scrutiny of the data increases. NHSN will continue to assess how changing facility composition and changes in the proportion of data contributed by facility types impact the rates and their distributions so that the best possible risk-adjusted comparative data may be provided in future reports.
To improve the reliability of data reported to NHSN, several protocol changes were introduced in January 2013. The majority of these changes were with respect to timing and implementation of two-day rules to clarify infections that are healthcare-associated, association of device use to HAI, and attribution of HAI to an inpatient location after transfer or to a hospital after discharge. In addition, NHSN added criteria for mucosal barrier injury laboratory-confirmed bloodstream infections, which have not been removed or accounted for separately in this report. Finally, the VAP definition no longer applies to adult patients (i.e., ≥ 18 years of age) and this definition has been replaced by ventilator-associated events (VAEs).11 We will carefully assess the potential impact of these changes on HAI incidence as these data are reported.
For those who do not report to NHSN but would like to use these data for comparison, the information must first be collected from your hospital in accordance with the methods described for NHSN.5–7 Refer to Appendices A and B for further instructions. Appendix A discusses the calculation of infection rates and DU ratios for the DA Module. Appendix B gives a step-by-step method for interpretation of percentiles of infection rates or DU ratios. Although a high rate or ratio (>90th percentile) does not necessarily define a problem, it does suggest an area for further investigation. Similarly, a low rate or ratio (<10th percentile) may be the result of inadequate infection detection.
Facilities should use the data in this report and their own data to guide local prevention strategies and other quality improvement efforts to reduce the occurrence of infections as much as possible. The data presented in this report can be used to prioritize prevention efforts in those patient care areas that are shown to have the highest incidence of DA infections and/or high device utilization. Facilities may also wish to set targets based on the percentile distributions provided in this report in an effort to strive for lower rates and greater prevention success.
Supplementary Material
Table 2.
Enrolled NHSN facilities contributing data used in this report by facility type and bedsize
| Facility type | Bed size category | Total N (%) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤ 50 | 51–200 | 201–500 | > 500 | ||
| N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | ||
| Acute care hospitals | 802 (18.0) | 1,596 (35.9) | 1,086 (24.4) | 258 (5.8) | 3,742 (84.2) |
| Major teaching | 16 (0.4) | 99 (2.2) | 215 (4.8) | 145 (3.3) | 475 (10.7) |
| Graduate teaching | 33 (0.7) | 202 (4.5) | 238 (5.4) | 55 (1.2) | 528 (11.9) |
| Undergraduate teaching | 16 (0.4) | 63 (1.4) | 38 (0.8) | 3 (0.1) | 120 (2.7) |
| Nonteaching | 737 (16.6) | 1,232 (27.7) | 595 (13.4) | 55 (1.2) | 2,619 (58.9) |
| Long term acute care hospitals | 274 (6.2) | 181 (4.1) | 10 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 465 (10.5) |
| Free-standing | 104 (2.3) | 161 (3.6) | 9 (0.2) | 0 (0.0) | 274 (6.2) |
| Within a hospital | 170 (3.8) | 20 (0.5) | 1 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 191 (4.3) |
| Inpatient rehabilitation facilities | 102 (2.3) | 131 (2.9) | 3 (0.1) | 1 (0.0) | 237 (5.3) |
| Free-standing | 82 (1.8) | 118 (2.6) | 3 (0.1) | 1 (0.0) | 204 (4.6) |
| Within a healthcare facility* | 20 (0.5) | 13 (0.3) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 33 (0.7) |
| Total | 1,178 (26.5) | 1,908 (42.9) | 1,099 (24.7) | 259 (5.8) | 4,444 |
Major: Facility has a program for medical students and post-graduate medical training.
Graduate: Facility has a program for post-graduate medical training (i.e., residency and/or fellowships).
Undergraduate: Facility has a program for medical students only.
Free-standing/within a hospital or healthcare facility: Describes physical placement of LTACH or IRF and does not define financial or administrative relationship with other healthcare facility types.
does not include inpatient rehabilitation facilities reporting to NHSN as locations within enrolled acute care hospitals.
Table 4.
Pooled means and key percentiles of the distribution of laboratory-confirmed permanent and temporary central line-associated BSI rates and central line utilization ratios, by type of speciality care area/oncology location, DA module, 2012
| Permanent Central line-associated BSI rate* | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Location | No. of locations† |
No. of PCLABSI |
Permanent Central line- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| Specialty Care Area/Oncology | |||||||||
| General hematology/oncology | 178 (174) | 402 | 300,231 | 1.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 1.7 | 3.0 |
| Hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 54 (53) | 256 | 118,924 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 1.3 | 2.9 | 5.0 |
| Pediatric general hematology/oncology | 46 | 257 | 151,942 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 2.4 | 3.5 |
| Pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 16 | 93 | 33,176 | 2.8 | |||||
| Solid organ transplant | 20 (17) | 20 | 11,675 | 1.7 | |||||
| Solid tumor | 6 | 15 | 18,032 | 0.8 | |||||
| Temporary Central line-associated BSI rate‡ | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Location | No. of locations† |
No. of TCLABSI |
Temporary Central line- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| Specialty Care Area/Oncology | |||||||||
| General hematology/oncology | 185 (180) | 491 | 257,889 | 1.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 2.5 | 4.5 |
| Hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 56 | 294 | 109,591 | 2.7 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 3.7 | 4.8 |
| Pediatric general hematology/oncology | 44 | 94 | 40,141 | 2.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 2.8 | 4.5 |
| Pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 15 (13) | 22 | 9,549 | 2.3 | |||||
| Solid organ transplant | 23 (22) | 64 | 44,202 | 1.4 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 1.2 | 1.9 | 3.4 |
| Solid tumor | 6 | 17 | 6,730 | 2.5 | |||||
| Permanent Central line utilization ratio§ | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of location | No. of locations† |
Permanent Central line- days |
Patient- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| Specialty Care Area/Oncology | |||||||||
| General hematology/oncology | 178 (177) | 300,231 | 999,114 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.39 | 0.52 |
| Hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 54 | 118,924 | 243,340 | 0.49 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.44 | 0.63 | 0.83 |
| Pediatric general hematology/oncology | 46 | 151,942 | 243,377 | 0.62 | 0.36 | 0.47 | 0.60 | 0.72 | 0.85 |
| Pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 16 | 33,176 | 46,688 | 0.71 | |||||
| Solid organ transplant | 20 | 11,675 | 106,289 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.26 |
| Solid tumor | 6 | 18,032 | 77,293 | 0.23 | |||||
| Temporary Central line utilization ratio‖ | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of location | No. of locations† |
Temporary Central line- days |
Patient- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| Specialty Care Area/Oncology | |||||||||
| General hematology/oncology | 185 (184) | 257,889 | 1,044,242 | 0.25 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 0.44 |
| Hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 56 | 109,591 | 252,048 | 0.43 | 0.11 | 0.24 | 0.44 | 0.62 | 0.79 |
| Pediatric general hematology/oncology | 44 | 40,141 | 224,294 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.36 |
| Pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 15 | 9,549 | 45,420 | 0.21 | |||||
| Solid organ transplant | 23 (22) | 44,202 | 127,153 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.34 | 0.49 | 0.73 |
| Solid tumor | 6 | 6,730 | 78,482 | 0.09 | |||||
BSI, bloodstream infection; PCLABSI, permanent central line-associated BSI; TCLABSI, temporary central line-associated BSI
The number in parentheses is the number of locations meeting minimum requirements for percentile distributions (i.e., ≥50 device days for rate distributions, ≥50 patient days for device utilization ratios) if less than total number of locations. If this number is <20, percentile distributions are not calculated.
Table 8.
Pooled means and key percentiles of the distribution of central line-associated BSI rates and central line utilization ratios for level II/III NICUs, DA module, 2012
| Central line-associated BSI rate * | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth-weight category | No. of locations † |
No. of CLABSI |
Central line- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| ≤ 750 grams | 377 (283) | 300 | 1,18,042 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.9 | 10.1 |
| 751–1000 grams | 443 (312) | 197 | 1,01,014 | 2.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.3 | 7.8 |
| 1001–1500 grams | 524 (373) | 115 | 1,23,617 | 0.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.4 |
| 1501–2500 grams | 555 (351) | 67 | 1,09,035 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.9 |
| > 2500 grams | 555 (313) | 68 | 1,12,147 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.4 |
| Central line utilization ratio ‡ | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth-weight category | No. of locations † |
Central line- days |
Patient- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| ≤ 750 grams | 377 (311) | 1,18,042 | 3,10,004 | 0.38 | 0.23 | 0.33 | 0.45 | 0.57 | 0.75 |
| 751–1000 grams | 443 (356) | 1,01,014 | 3,04,330 | 0.33 | 0.19 | 0.27 | 0.36 | 0.47 | 0.61 |
| 1001–1500 grams | 524 (466) | 1,23,617 | 4,84,544 | 0.26 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.49 |
| 1501–2500 grams | 555 (532) | 1,09,035 | 7,56,073 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.17 | 0.28 |
| > 2500 grams | 555 (528) | 1,12,147 | 6,14,939 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.19 | 0.29 |
BSI, bloodstream infection; CLABSI, central line-associated BSI; NICU, neonatal intensive care unit.
The number in parentheses is the number of locations meeting minimum requirements for percentile distributions (i.e., ≥50 device days for rate distributions, ≥50 patient days for device utilization ratios) if less than total number of locations. If this number is <20, percentile distributions are not calculated.
Table 9.
Pooled means and key percentiles of the distribution of ventilator-associated PNEU rates and ventilator utilization ratios for level III NICUs, DA module, 2012
| Ventilator-associated PNEU rate * | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth-weight category | No. of locations † |
No. of VAP |
Ventilator- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| ≤ 750 grams | 157 (133) | 97 | 73,987 | 1.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.0 | 4.4 |
| 751–1000 grams | 163 (123) | 47 | 39,689 | 1.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4.0 |
| 1001–1500 grams | 167 (95) | 14 | 22,701 | 0.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.1 |
| 1501–2500 grams | 165 (83) | 4 | 20,945 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| > 2500 grams | 167 (87) | 10 | 30,305 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ventilator utilization ratio ‡ | Percentile | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth-weight category | No. of locations † |
Ventilator- days |
Patient- days |
Pooled mean |
10% | 25% | 50% (median) |
75% | 90% |
| ≤ 750 grams | 157 (143) | 73,987 | 1,95,281 | 0.38 | 0.21 | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.50 | 0.65 |
| 751–1000 grams | 163 (149) | 39,689 | 1,71,975 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.35 | 0.48 |
| 1001–1500 grams | 167 (157) | 22,701 | 2,25,630 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.26 |
| 1501–2500 grams | 165 (163) | 20,945 | 3,08,507 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.18 |
| > 2500 grams | 167 (162) | 30,305 | 2,72,791 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.19 |
VAP, ventilator-associated pneumonia; NICU, neonatal intensive care unit.
The number in parentheses is the number of locations meeting minimum requirements for percentile distributions (i.e., ≥50 device days for rate distributions, ≥50 patient days for device utilization ratios) if less than total number of locations. If this number is <20, percentile distributions are not calculated.
Table 13.
Distribution of specific sites of urinary catheter-associated UTI by location, 2012
| Type of location | SUTI n (%) |
ABUTI n (%) |
Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Care Hospitals | |||||
| Critical care units | |||||
| Burn | 382 | 99.5% | 2 | 0.5% | 384 |
| Medical -Major teaching |
2,150 | 98.6% | 31 | 1.4% | 2,181 |
| Medical -All other |
1,408 | 97.9% | 30 | 2.1% | 1,438 |
| Medical cardiac | 1,497 | 98.7% | 20 | 1.3% | 1,517 |
| Medical/Surgical -Major teaching |
2,244 | 98.4% | 36 | 1.6% | 2,280 |
| Medical/Surgical -All other, ≤15 beds |
2,472 | 98.1% | 49 | 1.9% | 2,521 |
| Medical/Surgical -All other, >15 beds |
4,323 | 98.5% | 64 | 1.5% | 4,387 |
| Neurologic | 437 | 99.1% | 4 | 0.9% | 441 |
| Neurosurgical | 2,459 | 99.8% | 5 | 0.2% | 2,464 |
| Pediatric cardiothoracic | 60 | 98.4% | 1 | 1.6% | 61 |
| Pediatric medical | 35 | 100.0% | 35 | ||
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 450 | 99.6% | 2 | 0.4% | 452 |
| Pediatric surgical | 1 | 100.0% | 1 | ||
| Respiratory | 29 | 96.7% | 1 | 3.3% | 30 |
| Surgical -Major teaching |
1,782 | 99.1% | 17 | 0.9% | 1,799 |
| Surgical -All other |
910 | 99.1% | 8 | 0.9% | 918 |
| Surgical cardiothoracic | 1,628 | 98.2% | 29 | 1.8% | 1,657 |
| Trauma | 1,973 | 99.1% | 18 | 0.9% | 1,991 |
| Specialty Care Areas/Oncology | |||||
| General hematology/oncology | 253 | 98.4% | 4 | 1.6% | 257 |
| Hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 39 | 95.1% | 2 | 4.9% | 41 |
| Pediatric general hematology/oncology | 9 | 100.0% | 9 | ||
| Pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 1 | 100.0% | 1 | ||
| Solid organ transplant | 35 | 94.6% | 2 | 5.4% | 37 |
| Solid tumor | 58 | 100.0% | 58 | ||
| Step-down Units | |||||
| Adult step-down (post-critical care) | 1,120 | 98.3% | 19 | 1.7% | 1,139 |
| Pediatric step-down (post-critical care) | 1 | 100.0% | 1 | ||
| Inpatient Wards | |||||
| Acute stroke | 25 | 96.2% | 1 | 3.8% | 26 |
| Antenatal | 2 | 100.0% | 2 | ||
| Behavioral health/psychiatry | 31 | 96.9% | 1 | 3.1% | 32 |
| Burn | 30 | 93.8% | 2 | 6.3% | 32 |
| Genitourinary | 11 | 100.0% | 11 | ||
| Gerontology | 8 | 100.0% | 8 | ||
| Gynecology | 25 | 96.2% | 1 | 3.8% | 26 |
| Jail | 5 | 83.3% | 1 | 16.7% | 6 |
| Labor and delivery | 15 | 100.0% | 15 | ||
| Labor, delivery, recovery, postpartum suite | 30 | 100.0% | 30 | ||
| Medical | 1,320 | 99.0% | 14 | 1.0% | 1,334 |
| Medical/Surgical | 2,711 | 98.5% | 40 | 1.5% | 2,751 |
| Neurologic | 159 | 100.0% | 159 | ||
| Neurosurgical | 175 | 100.0% | 175 | ||
| Orthopedic | 422 | 99.3% | 3 | 0.7% | 425 |
| Orthopedic trauma | 68 | 100.0% | 68 | ||
| Pediatric medical | 6 | 100.0% | 6 | ||
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 55 | 100.0% | 55 | ||
| Pediatric orthopedic | 1 | 100.0% | 1 | ||
| Pediatric rehabilitation - non-IRF* | 1 | 100.0% | 1 | ||
| Pediatric surgical | 4 | 100.0% | 4 | ||
| Postpartum | 61 | 100.0% | 61 | ||
| Pulmonary | 87 | 98.9% | 1 | 1.1% | 88 |
| Rehabilitation - non-IRF* | 28 | 96.6% | 1 | 3.4% | 29 |
| Surgical | 1,082 | 98.5% | 17 | 1.5% | 1,099 |
| Telemetry | 390 | 97.5% | 10 | 2.5% | 400 |
| Vascular surgery | 25 | 100.0% | 25 | ||
| Well-baby nursery | 0 | ||||
| Chronic Care Units† | |||||
| Chronic care | 30 | 96.8% | 1 | 3.2% | 31 |
| Chronic care rehabilitation unit | 6 | 100.0% | 6 | ||
| Inpatient hospice | 2 | 100.0% | 2 | ||
| Ventilator dependent unit | 39 | 97.5% | 1 | 2.5% | 40 |
| Critical Access Hospitals | |||||
| Critical care units‡ | 25 | 100.0% | 25 | ||
| Non-critical care units§ | 167 | 96.5% | 6 | 3.5% | 173 |
| Long-Term Acute Care Hospitals‖ | |||||
| Adult critical care | 145 | 98.0% | 3 | 2.0% | 148 |
| Adult ward | 2,490 | 98.1% | 47 | 1.9% | 2,537 |
| Inpatient Rehabilitation Facilities¶ | |||||
| Adult rehabilitation units - Freestanding | 345 | 99.4% | 2 | 0.6% | 347 |
| Adult rehabilitation units - Within hospital | 560 | 98.4% | 9 | 1.6% | 569 |
| Pediatric rehabilitation units - Within hospital | 2 | 100.0% | 2 | ||
| TOTAL | 36,344 | 98.6% | 505 | 1.4% | 36,849 |
UTI, urinary tract infection; SUTI, symptomatic UTI; ABUTI, asymptomatic bacteremic UTI.6
Includes only in-hospital rehabilitation wards that are not defined as inpatient rehabilitation facilities (IRF) per the CMS Inpatient Rehabilitation Facility Quality Reporting Program.
Includes chronic care locations within the general acute care hospital setting.
Combines all critical care unit types within critical access hospitals.
Combines all units not identified as critical care (e.g., inpatient wards, step-down units) within critical access hospitals.
Includes free-standing long-term acute care hospitals and long-term acute care locations within the general acute care hospital setting.
Includes free-standing inpatient rehabilitation facilities and inpatient rehabilitation facilities within the acute care hospital setting, as defined by the CMS Inpatient Rehabilitation Facility Quality Reporting Program.
Table 14.
Distribution of specific sites of ventilator-associated pneumonia by location, 2012
| Type of location | PNU1 n (%) |
PNU2 n (%) |
PNU3 n (%) |
Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Care Hospitals | |||||||
| Critical Care Units | |||||||
| Burn | 25 | 29.1% | 61 | 70.9% | 86 | ||
| Medical -Major teaching |
127 | 62.0% | 74 | 36.1% | 4 | 2.0% | 205 |
| Medical -All other |
119 | 62.3% | 65 | 34.0% | 7 | 3.7% | 191 |
| Medical cardiac | 88 | 65.2% | 46 | 34.1% | 1 | 0.7% | 135 |
| Medical/surgical -Major teaching |
208 | 55.9% | 160 | 43.0% | 4 | 1.1% | 372 |
| Medical/surgical -All other ≤15 beds |
267 | 63.7% | 138 | 32.9% | 14 | 3.3% | 419 |
| Medical/surgical -All other >15 beds |
454 | 68.2% | 201 | 30.2% | 11 | 1.7% | 666 |
| Neurologic | 24 | 38.7% | 37 | 59.7% | 1 | 1.6% | 62 |
| Neurosurgical | 114 | 54.3% | 95 | 45.2% | 1 | 0.5% | 210 |
| Pediatric cardiothoracic | 6 | 66.7% | 2 | 22.2% | 1 | 11.1% | 9 |
| Pediatric medical | 1 | 50.0% | 1 | 50.0% | 2 | ||
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 80 | 70.8% | 28 | 24.8% | 5 | 4.4% | 113 |
| Pediatric surgical | 1 | 100.0% | 1 | ||||
| Respiratory | 4 | 100.0% | 4 | ||||
| Surgical -Major teaching |
157 | 56.1% | 122 | 43.6% | 1 | 0.4% | 280 |
| Surgical -All other |
89 | 46.4% | 98 | 51.0% | 5 | 2.6% | 192 |
| Surgical cardiothoracic | 194 | 60.8% | 119 | 37.3% | 6 | 1.9% | 319 |
| Trauma | 232 | 45.7% | 275 | 54.1% | 1 | 0.2% | 508 |
| Specialty Care Areas/Oncology | |||||||
| Hematopoietic stem cell transplant | 0 | ||||||
| Step-Down Units | |||||||
| Adult step-down (post-critical care) | 26 | 83.9% | 5 | 16.1% | 31 | ||
| Pediatric step-down (post-critical care) | 1 | 100.0% | 1 | ||||
| Step-down NICU (level II) | 0 | ||||||
| Inpatient Wards | |||||||
| Medical | 2 | 66.7% | 1 | 33.3% | 3 | ||
| Medical/surgical | 4 | 18.2% | 17 | 77.3% | 1 | 4.5% | 22 |
| Pediatric medical | 0 | ||||||
| Pediatric medical/surgical | 0 | ||||||
| Pulmonary | 6 | 85.7% | 1 | 14.3% | 0 | 0.0% | 7 |
| Surgical | 0 | ||||||
| Telemetry | 1 | 100.0% | 1 | ||||
| Critical Access Hospitals | |||||||
| Critical care units* | 3 | 100.0% | 3 | ||||
| Non-critical care units† | 2 | 50.0% | 1 | 25.0% | 1 | 25.0% | 4 |
| Long-Term Acute Care Hospitals‡ | |||||||
| Adult critical care | 7 | 87.5% | 1 | 12.5% | 8 | ||
| Adult ward | 78 | 75.7% | 24 | 23.3% | 1 | 1.0% | 103 |
| Total | 2,320 | 58.6% | 1,572 | 39.7% | 65 | 1.6% | 3,957 |
PNU1, clinically defined pneumonia; PNU2, pneumonia with specific laboratory findings; PNU3, pneumonia in immunocompromised patients.7
Combines all critical care unit types within critical access hospitals.
Combines all units not identified as critical care (e.g., inpatient wards, step-down units) within critical access hospitals.
Includes free-standing long-term acute care hospitals and long-term acute care locations within the general acute care hospital setting.
Table 17.
Distribution of specific sites of ventilator-associated pneumonia among Level III NICUs by birthweight, 2012
| Birth-weight category | PNU1 n (%) | PNU2 n (%) | PNU3 n (%) | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤ 750 grams | 60 | 61.9% | 34 | 35.1% | 3 | 3.1% | 97 |
| 750–1000 grams | 30 | 63.8% | 17 | 36.2% | 47 | ||
| 1001–1500 grams | 10 | 71.4% | 4 | 28.6% | 14 | ||
| 1501–2500 grams | 1 | 25.0% | 3 | 75.0% | 4 | ||
| > 2500 grams | 7 | 70.0% | 3 | 30.0% | 10 | ||
| Total | 108 | 62.8% | 61 | 35.5% | 3 | 1.7% | 172 |
PNU1, clinically defined pneumonia; PNU2, pneumonia with specific laboratory findings; PNU3, pneumonia in immunocompromised patients.7
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the NHSN participants for their ongoing efforts to monitor infections and improve patient safety. We also gratefully acknowledge our colleagues in the Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion who tirelessly support this unique public health network, especially our colleagues in:
NHSN Education and Data Quality Assurance Team
NHSN Development Team
NHSN Protocol and Public Reporting Team
NHSN Statistics Team
NHSN User Support Team
Footnotes
The findings and conclusions of the report are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official position of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
References
- 1.Dudeck MA, Horan TC, Peterson KD, Allen-Bridson K, Morrell GC, Pollock DA, Edwards JR. National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) report, data summary for 2011, device-associated module. Am J Infect Control. 2013;41:286–300. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2013.01.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Malpiedi PJ, Peterson KD, Soe MM, Edwards JR, Scott RD, II, Wise ME, et al. 2011 National and State Healthcare-Associated Infection Standardized Infection Ratio Report. [Accessed August 7, 2013]; Published February 11, 2013. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/hai/pdfs/SIR/SIR-Report_02_07_2013.pdf.
- 3.Sievert DM, Ricks P, Edwards JR, Schneider A, Patel J, Srinivasan A, et al. Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogens Associated with Healthcare-Associated Infections: Summary of Data Reported to the National Healthcare Safety Network at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2009–2010. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2013;34:1–14. doi: 10.1086/668770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Outline for healthcare-associated infection surveillance. [Accessed August 1, 2013]; Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/PDFS/OutlineForHAISurveillance.pdf.
- 5.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Protocol for reporting Central Line-Associated Bloodstream Infections to the National Healthcare Safety Network (in use during 2012) [Accessed August1, 2013]; Archived at http://www.cdc.gov/hai/pdfs/NHSN/4PSC_CLABSSAMPLE.pdf.
- 6.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Protocol for reporting Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections to the National Healthcare Safety Network (in use during 2011) [Accessed August 1, 2013]; Archived at http://www.cdc.gov/hai/pdfs/NHSN/7pscCAUTISAMPLE.pdf.
- 7.Horan TC, Andrus M, Dudeck MA. CDC/NHSN surveillance definition of health care-associated infection and criteria for specific types of infections in the acute care setting. Am J Infect Control. 2008;36:309–332. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2008.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hospital Inpatient Prospective Payment Systems for Acute Care Hospitals and the Long-Term Care Hospital Prospective Payment System and FY 2012 Rates; Final Rule. 76 FR 51476–51846. 2011 Aug 18; [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Inpatient Rehabilitation Facility Prospective Payment System for Federal Fiscal Year 2012; Final Rule. 76 FR 47836–47915. 2011 Aug 5;76 FR:47836–47915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jarvis WR, Edwards JR, Culver DH, Hughes JM, Horan T, Emori TG, et al. Nosocomial infection rates in adult and pediatric intensive care units in the United States. Am J Med. 1991;91(Suppl 3B):185S–191S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90367-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ventilator-associated events. [Accessed July 10, 2013]; Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/acute-care-hospital/vae/index.html.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.