Abstract
Prior studies demonstrate altered organization of functional brain networks in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). However, the structural underpinnings of these functional disturbances are poorly understood. In the current study, we applied a graph-theoretic approach to whole-brain diffusion magnetic resonance imaging data to investigate the organization of structural brain networks in adults with ADHD and unaffected controls using deterministic fiber tractography. Groups did not differ in terms of global network metrics — small-worldness, global efficiency and clustering coefficient. However, there were widespread ADHD-related effects at the nodal level in relation to local efficiency and clustering. The affected nodes included superior occipital, supramarginal, superior temporal, inferior parietal, angular and inferior frontal gyri, as well as putamen, thalamus and posterior cerebellum. Lower local efficiency of left superior temporal and supramarginal gyri was associated with higher ADHD symptom scores. Also greater local clustering of right putamen and lower local clustering of left supramarginal gyrus correlated with ADHD symptom severity. Overall, the findings indicate preserved global but altered local network organization in adult ADHD implicating regions underpinning putative ADHD-related neuropsychological deficits.
Keywords: Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder, Diffusion MRI, Deterministic tractography, Graph theory
Highlights
-
•
Structural brain network organization was studied in adult ADHD.
-
•
Deterministic tractography and graph theory were applied.
-
•
Preserved global but altered local brain network organization in adult ADHD.
-
•
These findings contrast to the global disturbances seen in children with ADHD.
1. Introduction
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is associated with widespread but often subtle alterations in multiple brain regions affecting brain function (Cortese et al., 2012). From a system's neuroscience perspective ADHD is increasingly seen as the product of disturbances in intrinsic organization of brain networks comprised of these regions (Aboitiz et al., 2014, Konrad and Eickhoff, 2010, Menon, 2011, Ray et al., 2014). Studies using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) report altered intrinsic connectivity within and between networks including the dorsal and ventral attention, salience (Mccarthy et al., 2013, Sripada et al., 2014), and default mode networks (Castellanos et al., 2008, Fair et al., 2010, Franzen et al., 2013, Mccarthy et al., 2013, Sripada et al., 2014, Uddin et al., 2008). Structural connectivity studies are less common and the extent to which these functional alterations are underpinned by deep-seated structural effects remains to be determined (Cao et al., 2014).
Diffusion MRI (dMRI) is a powerful neuroimaging technique used to examine microstructural brain properties and connections (Basser et al., 2000, O'Donnell and Pasternak, 2014, Weyandt et al., 2013). In ADHD there is evidence for alterations of white matter fiber tracts and structures encompassing inferior and superior longitudinal fasciculus, cingulum bundle, anterior corona radiata, internal capsule, forceps minor, cerebellar tracts, thalamic radiation and isthmus of corpus callosum (Kobel et al., 2010, Konrad et al., 2010, Makris et al., 2009, Pavuluri et al., 2009, Peterson et al., 2011, Silk et al., 2009, Weyandt et al., 2013, Zhang and Li, 2010), however, results lack consistency (for reviews, see Cao et al., 2014, Van Ewijk et al., 2012, Weyandt et al., 2013). Region of interest (ROI) studies typically report lower fractional anisotropy (FA; a measure of white matter integrity) in ADHD, while whole-brain studies find the opposite result (Ashtari et al., 2005, Davenport et al., 2010, Konrad et al., 2010, Nagel et al., 2011, Zhang and Li, 2010), perhaps because these include a larger set of brain regions containing so-called “crossing fibers”.
Graph theory, which is a branch of mathematics focusing on the formal characterization and analysis of graphs (i.e., mathematical structures for modeling pairwise object relationships), has been recognized as an informative approach to investigate brain networks (Bullmore and Sporns, 2009, Griffa et al., 2013, Xia and He, 2011). It represents the brain as a formal graph comprised of a selection of nodes (vertices) and inter-nodal links (edges). Nodes represent anatomical brain regions, while edges describe the properties of the connections (e.g., functional, effective or structural). Structural connections between brain areas (nodes) parallel white matter tracts and are effectively reconstructed using dMRI (Hagmann et al., 2008, Rubinov and Sporns, 2010, Van den Heuvel and Sporns, 2011). Graph theoretic analysis suggests compromised brain network organization in several conditions (e.g., Alzheimer's disease (Lo et al., 2010), schizophrenia (van den Heuvel et al., 2010), and autism spectrum disorder (Rudie et al., 2012)). With regard to ADHD, Cao et al. (2013) found reductions in both global (lower global efficiency and higher shortest path length) and local efficiency (in left parietal, left frontal and left occipital cortices) in a sample of drug-naive boys (8–14 years) with ADHD. Ray et al. (2014) found that children with ADHD (7–13 years) had lower internal, but higher external rich-club connectivity (i.e., highly connected regions that are also very highly connected between them).
The current study is the first to extend the graph theory approach to study structural brain network organization in adult ADHD. Based on the findings from studies with children, we predicted that adults with ADHD would exhibit both global (e.g., clustering coefficient, characteristic path length) and local network disruptions (specifically in frontal, parietal and occipital cortices) and that these would be correlated with ADHD symptom severity.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
Eighteen adults with ADHD (12 combined and 6 inattentive type) and 21 healthy controls participated. The study was approved by the medical ethics committee of Ghent University hospital. Participants gave informed consent before participation and received a monetary reward afterwards. All participants with ADHD had an official clinical diagnosis of ADHD, as well as a research diagnosis of ADHD confirmed by the DSM-IV-based structured Diagnostic Interview for Adult ADHD (DIVA; Kooij and Francken, 2010). They also scored above the cut-offs on childhood and adulthood ADHD self-report questionnaires: The Wender Utah Rating Scale (WURS; Ward et al., 1993); M = 63.66; SD = 14.21; cut-off for childhood ADHD — the score higher than 46 and a DSM-based self-report questionnaire on problems of inattention and hyperactivity in adulthood and childhood (Kooij and Buitelaar, 1997) — adults with ADHD had to exhibit at least 4 symptoms in the inattentinve and/or hyperactive/impulsive domain to meet the adulthood ADHD criteria. Additionally, ADHD symptom severity was measured with the DSM-oriented ADHD scale of the Adult Self-Report (ASR; Achenbach and Rescorla, 2003; M = 77.83, SD = 8.99). None of the controls qualified for ADHD based on the scores of any of these questionnaires (WURS: M = 26.95, SD = 12.70; ASR: M = 54.19, SD = 4.44). All participants had a normal or above normal full scale IQ (> 80) derived from a seven subtests version of the Wechsler Adult Intelligent Scale (Ryan and Ward, 1999). Nine participants with ADHD taking stimulant medication (8 – methylphenidate and 1 – dextroamphetamine) refrained from use for at least 24 h prior to testing. Three ADHD participants were taking antidepressant medication, which they were allowed to continue (2 – selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and 1 – buproprion chloride). Participants were excluded if they had a neurological or psychiatric condition or a history of brain damage. All participants had normal or corrected to normal vision. Four were left-handed (1 ADHD).
2.2. Data acquisition
MRI data were acquired with a Siemens Magnetom Trio MRI system (Siemens Medical Systems, Erlangen, Germany) operating at 3 T, using a standard 32-channel head-coil. The participants were positioned supine head first inside the scanner. Structural high resolution 1-mm3 T1-weighted images were obtained using a magnetization prepared rapid gradient echo sequence (MPRAGE); repetition time (TR) = 2300 ms; echo time (TE) = 3.03 ms; inversion time = 1100 ms; flip angle = 8°; field of view (FoV) = 256. dMRI data were acquired using diffusion-weighted spin-echo echoplanar imaging (TR = 7000 ms; TE = 85 ms; flip angle = 90°; matrix size = 128 × 128; slice thickness = 2 mm; voxel size = 2 × 2 × 2 mm3; 60 diffusion directions with b = 1000 s/mm2; and additional 2 images without diffusion weighting [i.e., b = 0 s/mm2]) covering the whole brain, with a total acquisition time of 13 min.
2.3. dMRI data preprocessing
dMRI data were preprocessed using ExploreDTI version 4.8.3 (Leemans et al., 2009) employing: 1) correction for geometrical distortion, caused by eddy currents and subject motion; 2) diffusion tensors calculations; 3) performance of dMRI data coregistration to the MNI space. Subject-specific field maps were not acquired in the current study and thus, EPI distortion correction using subject-specific field maps was not run.
2.4. Whole-brain tractography and connectivity matrix construction
Deterministic streamline whole-brain tractography algorithm was applied on our dMRI data. Fiber seeds were placed on a uniform grid throughout the data at a 2 mm isotropic resolution. Fiber trajectory (‘streamline’) reconstruction was initiated by following the primary eigenvector which defined the main diffusion direction. When the fiber touched a voxel with an FA (ranging from 0 to 1) value < 0.2 or it made a high angular turn (angle > 30°) compared to the neighboring eigenvectors the tractography was terminated. The step size was set at 1 mm and only tracts with a minimum length of 50 mm were considered. Anatomical labeling atlas (AAL; Tzourio-Mazoyer et al., 2002), which is a commonly used parcellation scheme to establish network nodes (Cao et al., 2013, Hosseini et al., 2012, Zalesky et al., 2010), comprising 116 cortical and subcortical regions (58 for each hemisphere), was employed to derive whole-brain fiber tracts. The labels and masks of the AAL atlas were registered to the dMRI data using a nonlinear transformation (Klein et al., 2010). Coregistration accuracy of the reconstructed data was visually inspected for every participant in three orthogonal planes. This was done to ascertain that the registration was successful and that no additional artifacts were introduce to the data.
The number of streamlines connecting each pair of the AAL atlas regions was used to create a 116 × 116 connectivity matrix. Atlas-parcellated regions represented network nodes and streamlines connecting them represented network edges. Two regions were assumed connected if a fiber originated from either of the two areas and terminated in the other area. Furthermore, all non-zero weights (i.e., all connections) were set to one and to zero otherwise (van den Heuvel et al., 2010). The end result of this procedure was an unweighted binary network. Thus, for each participant, there were two different kinds of white matter networks (‘streamline count’ and binary), each of which was represented by a symmetric 116 × 116 matrix. Binary matrices were used in further graph analysis.
Of note, as a control analysis we also investigated matrices formed by assuming that two regions were connected when a fiber originated from either of the two areas and passed through the other area. The results using both end and pass matrices gave very similar results (Supplementary material Table 1, 2).
2.5. Graph-theoretical analysis
The graph-theoretical analysis toolbox (GAT; Hosseini et al., 2012) was employed. Global network metrics of interest included small-worldness, normalized clustering coefficient, normalized path length and global network efficiency. Small-worldness represents the properties of simultaneous segregation and integration (Bassett and Bullmore, 2006). Segregation represents local, and integration global processing capability (Hosseini et al., 2013). A small-world network represents an ideal combination of local and global information processing. Small-world networks can be distinguished from other classes of networks (e.g., random or regular) in terms of clustering coefficient (C) and the characteristic path length (L) (He and Evans, 2010). The clustering coefficient measures the existing number of connections between the node and its nearest neighbors as a ratio of all the possible connections (Bullmore and Sporns, 2009). The network clustering coefficient is the average of clustering coefficients across network nodes and characterizes network segregation. Hence, the clustering coefficient represents the network's specialization in information processing (Hosseini et al., 2013). The characteristic path length is a measure of network integration and reflects the shortest path length between all network node pairs. Thus, the characteristic path length reflects the network's ability to distributed information processing (Rubinov and Sporns, 2010). Metrics are compared to random graph mean values in order to evaluate the organization of a brain network. Small-world networks are characterized by a clustering coefficient higher than one of a random network, whereas the characteristic path length is comparable to that from a random network. Thus, the small-worldness (S) of a network is formally expressed as follows: S = (C/Crand)/(L/Lrand) with a value > 1. The global efficiency (Eglobal), which is inversely related to path length, is also a measure of network integration (Rubinov and Sporns, 2010).
Second, we examined the regional network measures, including the nodal clustering coefficient and local efficiency. The former is the ratio of the sum of the weights across all complete triangles around the node and the number of edges connecting the node. Furthermore, local efficiency is equivalent to the global efficiency computed for each node (Sporns and Zwi, 2004). Finally, we also calculated betweenness centrality as a nodal metric, which is defined as the fraction of all shortest paths in the network that pass through a given node. This measures the importance of nodes to an overall network integrity. The nodes with the largest betweenness centrality were considered pivotal network nodes (i.e., hubs). Specifically, we considered a node a hub if its nodal betweenness centrality was at least two SDs higher than the mean network betweenness centrality.
2.6. Statistical analysis
The GAT toolbox, which uses the routines of the Brain Connectivity Toolbox (BCT; Rubinov and Sporns, 2010) to calculate different graph metrics, was also used to estimate between group differences in different network metrics. Namely, group networks were first normalized using the mean network density and then different graph metrics were estimated for these networks. The statistical significance of group effects on graph metrics were tested using a non-parametric permutation test with 1000 repetitions (Bassett et al., 2008). In every repetition the calculated regional data of every participant were randomly allocated to one of the two groups so that each randomized group had the same number of subjects as the initial groups, and for both randomized groups the association matrix was obtained (Hosseini et al., 2012). The binary adjacency matrices were estimated thresholding at a range of network densities and network metrics were calculated at each density. The differences between randomized groups on different networks metrics were then calculated which resulted in a permutation distribution of difference. Then the actual between group differences on network metrics were put in the corresponding permutation distributions and two-tailed p-values were determined with respect to their percentile position (Hosseini et al., 2012). Global and regional graph metrics for each group were extracted using the GAT toolbox applying the area under the curve (AUC) correction for multiple comparisons. The GAT toolbox compares the AUCs for every graph metric. All these curves depict a change in a particular graph metric as a function of network density. The significance testing of the between group differences in AUC of every graph metric is done by placing the actual between-group difference in AUC for every network metric in the corresponding permutation distribution and the p-value is derived depending on its percentile position (Hosseini et al., 2012).
For adults with ADHD, Pearson correlation coefficients between structural network metrics and measures of ADHD symptom severity indicated by self-report questionnaires were computed.
3. Results
3.1. Demographic data
The ADHD and control group did not differ on IQ (controls: M = 116.90, SD = 11.24; ADHD: M = 112.05, SD = 13.99, p = 0.238), age (controls: M = 26.95 years, SD = 8.52; ADHD: M = 30.11 years, SD = 9.78, p = 0.288), or male to female ratio (controls: 9 females; ADHD: 9 females).
3.2. Global network metrics
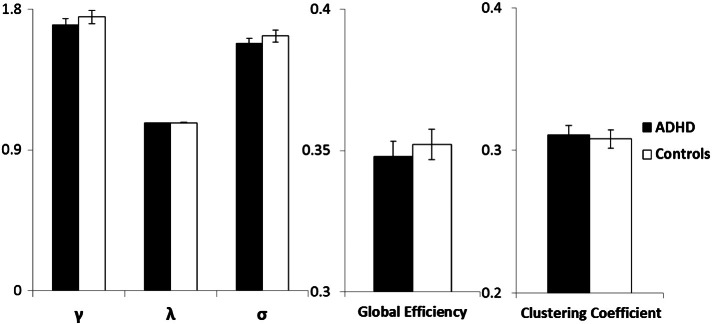
Both groups showed small-worldness of brain organization and did not differ in the three relevant metrics (normalized clustering coefficient: γ > 1; normalized path length: λ ~ 1; small-worldness: σ > 1; γ: t(37) = 0.84, p = 0.405; λ: t(37) = 0.62, p = 0.539; σ: t(37) = 0.80, p = 0.425) or in terms of global efficiency (t(37) = 0.60, p = 0.550) or clustering coefficient (t(37) = − 0.35, p = 0.728; Fig. 1). Of note, we also investigated the between group differences in global network metrics thresholded at a range of densities (i.e., 0.13:0.01:0.07). The results were consistent across different densities showing no group differences in any of the global network metrics (see supplementary material Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
A graphical representation of global graph metrics. Small-worldness parameters (γ, λ and σ ± SE), global efficiency and clustering (± SE) in the ADHD and control group. No differences between groups in either γ, λ, σ or global efficiency and clustering.
3.3. Local network metrics
3.3.1. Nodal efficiency
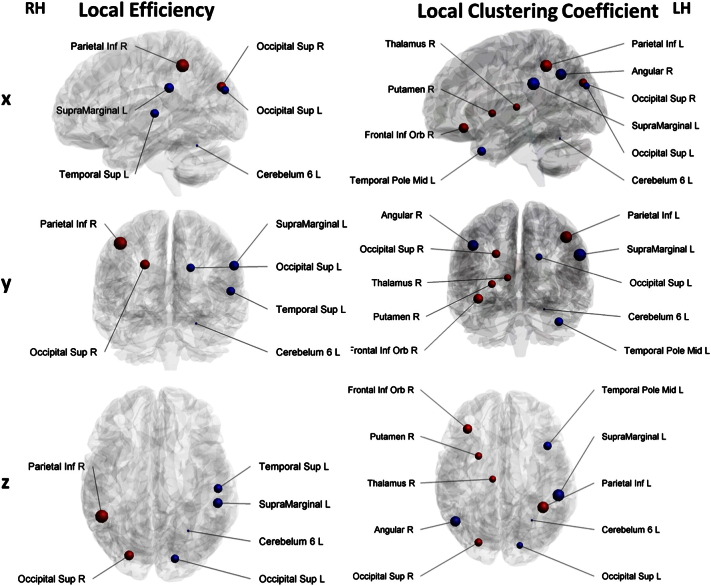
The ADHD group displayed left lateralized, significantly lower local efficiency in superior occipital gyrus, supramarginal gyrus, superior temporal gyrus and posterior cerebellum (lobule VI) (see Table 1). Nodal efficiency was significantly greater right lateralized, in superior occipital gyrus and inferior parietal gyrus in ADHD (see Table 1, Fig. 2).
Table 1.
Regions showing ADHD-related significant changes in local efficiency.
| Region | Hemisphere | t value | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADHD-related lower nodal efficiency | |||
| Superior occipital gyrus | L | 2.21 | 0.040 |
| Supramarginal gyrus | L | 2.47 | 0.018 |
| Superior temporal gyrus | L | 2.13 | 0.040 |
| Cerebellum VI | L | 2.46 | 0.019 |
| ADHD-related higher nodal efficiency | |||
| Superior occipital gyrus | R | − 2.91 | 0.006 |
| Inferior parietal gyrus | R | − 3.06 | 0.004 |
t – statistical value indicating a difference between groups (p < 0.05). Positive t value denotes ADHD-related lower nodal efficiency, while the negative t value indicates ADHD-related significant higher nodal efficiency. R – right; L – left.
Fig. 2.
Nodes exhibiting significant group differences in local efficiency and local clustering. The sizes of the spheres are based on local efficiency and local clustering estimates in the ADHD group, blue color represents significantly lower local efficiency and local clustering in the ADHD group, red color represents significantly higher local efficiency and local clustering in the ADHD group. RH – right hemisphere; LH – left hemisphere; x, y, z – anatomical planes.
3.3.2. Nodal clustering
Significantly lower values for nodal clustering were observed in the ADHD group left lateralized in superior occipital gyrus, supramarginal gyrus, superior temporal gyrus, posterior cerebellum (lobule VI) and right angular gyrus (see Table 2). ADHD-related significantly higher nodal clustering was observed in the right lateralized areas of inferior frontal gyrus, superior occipital gyrus, putamen, thalamus and in left inferior parietal gyrus (see Table 1, Fig. 2).
Table 2.
Regions showing ADHD-related significant changes in local clustering.
| Region | Hemisphere | t value | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADHD-related lower local clustering | |||
| Superior occipital gyrus | L | 2.39 | 0.022 |
| Supramarginal gyrus | L | 2.35 | 0.024 |
| Angular gyrus | R | 2.08 | 0.044 |
| Temporal pole: superior temporal gyrus | L | 2.10 | 0.042 |
| Cerebellum IV | L | 2.59 | 0.013 |
| ADHD-related higher local clustering | |||
| Inferior frontal gyrus, orbital part | R | − 2.58 | 0.014 |
| Superior occipital gyrus | R | − 2.25 | 0.030 |
| Inferior parietal gyrus | L | − 2.97 | 0.005 |
| Putamen | R | − 2.09 | 0.043 |
| Thalamus | R | − 2.49 | 0.017 |
t – statistical value indicating a difference between groups (p < 0.05). Positive t value denotes ADHD-related lower local clustering, while the negative t value indicates ADHD-related significant higher local clustering. R – right; L – left
3.3.3. Hub analysis
Right superior frontal gyrus, bilateral precuneus, and left thalamus were hubs in both groups. Of note, right putamen was also identified as hub in the control group, but not in the ADHD group, while the opposite was seen for right thalamus.
3.4. ADHD symptoms severity
Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated between the network metrics exhibiting significant group differences and ADHD symptoms in the ADHD group. It is important to note that correlation coefficients reported here should be treated with caution. First, we did not have any specific predictions about the exact nodes to relate to ADHD symptoms and thus, the correlation coefficients do not survive correction for multiple comparisons. Second, the results are potentially biased by the fact that the correlation analysis was conducted on the nodes and their local metrics that already showed between group differences (Vul et al., 2009).
3.4.1. Local efficiency
Lower values of local efficiency in left superior temporal gyrus and in left supramarginal gyrus were associated with higher ADHD symptom scores. Left superior temporal gyrus negatively correlated with adult inattention (r(18) = − 0.572, p = 0.013) and hyperactivity/impulsivity (r(18) = − 0.476, p = 0.046) symptoms measured using the Kooij and Buitelaar (1997) questionnaire. Left supramarginal gyrus, showing lower values of local efficiency in the ADHD group, negatively correlated with ADHD symptoms as measured with the ASR questionnaire (r(18) = − 0.571, p = 0.013).
3.4.2. Local clustering
Higher local clustering of right putamen and lower local clustering of left supramarginal gyrus were associated with more ADHD symptoms. Right putamen correlated with adult hyperactivity/impulsivity symptoms measured with the Kooij and Buitelaar (1997) questionnaire (r(18) = 0.499, p = 0.035). Left supramarginal gyrus, exhibiting significantly lower local clustering in the ADHD group, correlated negatively with ADHD symptoms measured with ASR questionnaire (r(18) = − 0.571, p = 0.013).
4. Discussion
The current study provides the first evidence of alterations in white matter brain network organization in adults with ADHD using deterministic tractography and graph theoretical analysis. The analyses did not identify deficits in global network properties, but rather suggest localized nodal disturbances in adult ADHD.
4.1. Global network metrics
In both groups structural brain networks exhibited small-world properties and groups did not differ in global network metrics. This suggests that global structural brain network organization is preserved in adult ADHD. It also adds to the evidence that small-worldness can survive in psychopathological and neurodevelopmental conditions (Griffa et al., 2013). Although the finding of preserved small-worldness in ADHD is in line with Cao et al. (2013), the absence of ADHD-related alterations in other global metrics is not. Cao et al. (2013) found lower global efficiency and greater path length in ADHD, while our results did not indicate group differences in those metrics. Moreover, our results contrast with the findings from other graph analyses of brain function in ADHD. These indicate that functional brain networks in ADHD are characterized by increases in local and decreases in global efficiency (Ahmadlou et al., 2012, Fair et al., 2012, Wang et al., 2009). It is however of importance to note that all these studies included children or adolescents with ADHD. In the only equivalent graph analytic study on adult ADHD using fMRI data, Cocchi et al. (2012) found that adults with ADHD did not differ from controls in terms of global network metrics. Taken together with our findings, this suggests more localized and subtle disturbances in adults compared to children with ADHD. Studies suggest that the maturation of the normal brain is characterized by a local to distributed trajectory development, which is consistent with the idea of delayed network maturation in individuals with ADHD (Dosenbach et al., 2010, Fair et al., 2009). Longitudinal studies are required to examine the potential developmental delay in individuals with ADHD.
4.2. Local network metrics
We identified widespread ADHD-related differences in local efficiency and clustering. This is in line with current models where individual mental disorders are increasingly associated with deficits in multiple brain networks (Cao et al., 2013, Cocchi et al., 2012, Cortese et al., 2012, Rubinov and Bassett, 2011, Xia and He, 2011). We observed ADHD-related lower local efficiency and local clustering in left superior temporal, supramarginal, superior occipital gyri and posterior cerebellum (lobule VI) (Table 1, Table 2). Additionally, lower local clustering was also identified in right angular gyrus. Lower local efficiency in left superior temporal gyrus, a region implicated in attention allocation to rare stimuli (Rubia et al., 2007, Vaidya, 2012), was associated with more current symptoms of inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity. Furthermore, less local efficiency and clustering of left supramarginal gyrus were associated with higher ADHD scores on the ASR questionnaire. This region is part of a ventral attention system — currently increasingly implicated in ADHD (Aboitiz et al., 2014), responsible for attentional shifts and detection of specific or salient stimuli (Tamm et al., 2006).
Our results also indicated greater local efficiency and clustering in adults with ADHD. These areas included right inferior parietal and superior occipital gyri. Additionally, greater local clustering was observed in right inferior frontal gyrus, putamen and thalamus (Table 1, Table 2), and left inferior parietal gyrus. Moreover, higher local clustering of right putamen was related to more ADHD symptoms as measured by the ASR. Generally these areas of disturbed local efficiency and/or local clustering are commonly found to exhibit functional and structural alterations in ADHD and (e.g., inferior parietal gyrus, angular gyrus, inferior frontal gyrus) relate to neuropsychological impairments (Bush, 2010, Van Ewijk et al., 2012). Moreover, previous studies have also shown ADHD-related lower cortical thickness in temporal and parietal areas, and volumetric reductions of posterior cerebellum (Krain and Castellanos, 2006, Proal et al., 2011). In addition, diffuse white matter alterations in frontal, temporal and parietal areas, involving regions implicated in higher order cognitive and attentional processing, are reported (Cortese et al., 2013, Konrad and Eickhoff, 2010, Van Ewijk et al., 2012). Furthermore, functional disturbances of these regions identified by a wide range of task-based (Cortese et al., 2012), and task-free resting state studies (Posner et al., 2014) have been observed in ADHD. In addition Ray et al. (2014), suggested that ADHD-related abnormalities are related to rich-club nodes, encompassing (pre)frontal, anterior (posterior) cingulate, temporal, parietal regions.
Our results point to a tendency for adults with ADHD to exhibit less nodal efficiency and clustering in the left hemisphere, and greater efficiency and clustering predominantly observed in the right hemisphere. This tendency to show less left lateralized nodal efficiency has been previously reported by Cao et al. (2013) in children with ADHD. Moreover, Wang et al. (2009) observed higher local efficiency of right inferior frontal gyrus while in the current study we found greater local clustering of the same region. In addition, some functional activation studies also provide evidence for a right hemisphere dominance in ADHD (Hale et al., 2006), while others indicate weaker task-related left-lateralized activation (Kobel et al., 2009, Valera et al., 2005). Hence, these findings highlight the potential importance of laterality effects, and are in line with the existing evidence of atypical cerebral asymmetry in ADHD and may indicate abnormal brain development (Giedd et al., 2006).
In addition to parietal and occipital areas, greater local network metrics in ADHD also included several subcortical regions such as thalamus and putamen (local clustering). Thalamus and putamen (part of striatum) have previously been implicated in ADHD in terms of weaker connections with cortical regions and activation abnormalities (Clerkin et al., 2013, Kasparek et al., 2013, Mills et al., 2012). Those disturbances have been suggested to relate to higher cognitive processes, such as cognitive flexibility, working memory and attentional processes (Kimura et al., 2004, Van Schouwenburg et al., 2014). Thus, the current findings add to the existing literature by indicating a greater segregation of thalamus and putamen in adults with ADHD.
5. Limitations
In the current study a deterministic tractography approach was applied to construct structural brain networks (Basser et al., 2000, Mori and van Zijl, 2002). Although, this method is widely used, it has a limited capacity of fiber tracking in the brain regions that comprise so-called “crossing fibers” (Gong et al., 2009, Jeurissen et al., 2011, Tournier et al., 2011). Hence, more advanced acquisition methods such as, diffusion spectrum magnetic resonance imaging (DSI; Wedeen et al., 2008) or high angular resolution diffusion imaging (HARDI; Hess et al., 2006), that allow the reconstruction of multiple fiber orientations could be considered. Another limiting factor of deterministic fiber tractography is the uncertainty about the reliability of the reconstructed trajectory, especially in brain areas in close to gray matter (Mukherjee et al., 2008, Prčkovska et al., 2013). Thus the probabilistic tractography algorithm, which takes direction-uncertainty into account could be considered in the future (Jones, 2008). Moreover, in the current study subject-specific field maps were not generated and thus could not be employed to aid the correction for geometrical distortion. Nevertheless, this is an important aspect and it should be addressed in future studies (Glasser et al., 2013, Sotiropoulos et al., 2013). Furthermore, it must be noted that network metrics in the current study were calculated based on binary connectivity matrices which may limit the interpretation of results. Therefore, future studies should also explore these results using weighted connectivity matrices. Moreover, although we applied AUC-correction for the number of density steps, we did not correct for the number of regions and thus, the results should be treated with caution. We did not take into account the history and duration of stimulant medication use, which may have an effect on brain's microstructural organization of the ADHD group and should be addressed by future research (Shaw et al., 2009).
6. Conclusions
Despite these limitations, our results, for the first time, indicate that structural brain networks in adult ADHD display widespread localized disturbances in regions implicated in cognitive and attentional control but are normal in terms of their global organization. This contrasts to the global disturbances observed in children with ADHD.
Disclosure statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Fund for Scientific Research – Flanders (project number: 3G084810). We thank Eric Achten for his help with the imaging protocols and Eliana Vassena for her help with data collection.
Footnotes
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2015.10.001.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
Supplementary material.
References
- Aboitiz F., Ossandón T., Zamorano F., Palma B., Carrasco X. Irrelevant stimulus processing in ADHD: catecholamine dynamics and attentional networks. Front. Psychol. 2014;5:183. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achenbach T.M., Rescorla L. University of Vermont, Research Centre for Children, Youth, and Families; Burlington, Vermont: 2003. Manual for the ASEBA Adult Forms & Profiles. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadlou M., Adeli H., Adeli A. Graph theoretical analysis of organization of functional brain networks in ADHD. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2012;43(1):5–13. doi: 10.1177/1550059411428555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashtari M., Kumra S., Bhaskar S.L., Clarke T., Thaden E., Cervellione K.L.…Ardekani B.A. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a preliminary diffusion tensor imaging study. Biol. Psychiatry. 2005;57(5):448–455. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.11.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basser P.J., Pajevic S., Pierpaoli C., Duda J., Aldroubi A. In vivo fiber tractography using DT-MRI data. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000;44(4):625–632. doi: 10.1002/1522-2594(200010)44:4<625::aid-mrm17>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett D.S., Bullmore E. Small-world brain networks. Neuroscientist. 2006;12(6):512–523. doi: 10.1177/1073858406293182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett D.S., Bullmore E., Verchinski B.a., Mattay V.S., Weinberger D.R., Meyer-Lindenberg A. Hierarchical organization of human cortical networks in health and schizophrenia. J. Neurosci. 2008;28(37):9239–9248. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1929-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullmore E., Sporns O. Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat. Rev. Neuroscience. 2009;10(3):186–198. doi: 10.1038/nrn2575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush G. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and attention networks. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35(1):278–300. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Q., Shu N., An L., Wang P., Sun L., Xia M.-R.…He Y. Probabilistic diffusion tractography and graph theory analysis reveal abnormal white matter structural connectivity networks in drug-naive boys with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J. Neurosci. 2013;33(26):10676–10687. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4793-12.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao M., Shu N., Cao Q., Wang Y., He Y. Imaging functional and structural brain connectomics in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014;50(3):1111–1123. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8685-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellanos F.X., Margulies D.S., Kelly C., Uddin L.Q., Ghaffari M., Kirsch A.…Milham M.P. Cingulate-precuneus interactions: a new locus of dysfunction in adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol. Psychiatry. 2008;63(3):332–337. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.06.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerkin S.M., Schulz K.P., Berwid O.G., Fan J., Newcorn J.H., Tang C.Y., Halperin J.M. Thalamo-cortical activation and connectivity during response preparation in adults with persistent and remitted ADHD. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2013;170(9):1011–1019. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.12070880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocchi L., Bramati I.E., Zalesky A., Furukawa E., Fontenelle L.F., Moll J.…Mattos P. Altered functional brain connectivity in a non-clinical sample of young adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J. Neurosci. 2012;32(49):17753–17761. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3272-12.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese S., Kelly C., Chabernaud C., Proal E., Di Martino A., Milham M.P., Castellanos F.X. Toward systems neuroscience of ADHD: a meta-analysis of 55 fMRI studies. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2012;169(10):1038–1055. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.11101521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese S., Imperati D., Zhou J., Proal E., Klein R.G., Mannuzza S.…Castellanos F.X. White matter alterations at 33-year follow-up in adults with childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol. Psychiatry. 2013;74(8):591–598. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.02.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport N.D., Karatekin C., White T., Lim K.O. Differential fractional anisotropy abnormalities in adolescents with ADHD or schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2010;181(3):193–198. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2009.10.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosenbach N.U.F., Nardos B., Cohen A.L., Fair D.A., Power J.D., Church J.A.…Schlaggar B.L. Prediction of individual brain maturity using fMRI. Science. 2010;329(5997):1358–1361. doi: 10.1126/science.1194144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fair D.A., Cohen A.L., Power J.D., Dosenbach N.U.F., Church J.A., Miezin F.M.…Petersen S.E. Functional brain networks develop from a “local to distributed” organization. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009;5(5) doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fair D.A., Posner J., Nagel B.J., Bathula D., Dias T.G.C., Mills K.L.…Nigg J.T. Atypical default network connectivity in youth with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol. Psychiatry. 2010;68(12):1084–1091. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.07.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fair D.A., Nigg J.T., Iyer S., Bathula D., Mills K.L., Dosenbach N.U.F.…Milham M.P. Distinct neural signatures detected for ADHD subtypes after controlling for micro-movements in resting state functional connectivity MRI data. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2012;6(February):80. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2012.00080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzen J.D., Heinrichs-Graham E., White M.L., Wetzel M.W., Knott N.L., Wilson T.W. Atypical coupling between posterior regions of the default mode network in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a pharmaco-magnetoencephalography study. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2013;38(5):333–340. doi: 10.1503/jpn.120054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giedd J.N., Blumenthal J., Molloy E., Castellanos F.X. Brain Imaging of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006;931(1):33–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb05772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasser M.F., Sotiropoulos S.N., Wilson J.A., Coalson T.S., Fischl B., Andersson J.L.…Jenkinson M. The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the Human Connectome Project. NeuroImage. 2013;80:105–124. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong G., He Y., Concha L., Lebel C., Gross D.W., Evans A.C., Beaulieu C. Mapping anatomical connectivity patterns of human cerebral cortex using in vivo diffusion tensor imaging tractography. Cereb. Cortex. 2009;19(3):524–536. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhn102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffa A., Baumann P.S., Thiran J.-P., Hagmann P. Structural connectomics in brain diseases. NeuroImage. 2013;80:515–526. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagmann P., Cammoun L., Gigandet X., Meuli R., Honey C.J., Wedeen V.J., Sporns O. Mapping the structural core of human cerebral cortex. PLoS Biol. 2008;6(7) doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T.S., Zaidel E., McGough J.J., Phillips J.M., McCracken J.T. Atypical brain laterality in adults with ADHD during dichotic listening for emotional intonation and words. Neuropsychologia. 2006;44(6):896–904. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2005.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He Y., Evans A. Graph theoretical modeling of brain connectivity. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2010;23(4):341–350. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e32833aa567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess C.P., Mukherjee P., Han E.T., Xu D., Vigneron D.B. Q-ball reconstruction of multimodal fiber orientations using the spherical harmonic basis. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006;56(1):104–117. doi: 10.1002/mrm.20931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini S.M.H., Hoeft F., Kesler S.R. GAT: a graph-theoretical analysis toolbox for analyzing between-group differences in large-scale structural and functional brain networks. PLoS One. 2012;7(7) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini S.M.H., Black J.M., Soriano T., Bugescu N., Martinez R., Raman M.M.…Hoeft F. Topological properties of large-scale structural brain networks in children with familial risk for reading difficulties. NeuroImage. 2013;71:260–274. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.01.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeurissen B., Leemans A., Jones D.K., Tournier J.-D., Sijbers J. Probabilistic fiber tracking using the residual bootstrap with constrained spherical deconvolution. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2011;32(3):461–479. doi: 10.1002/hbm.21032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D.K. Tractography gone wild: probabilistic fibre tracking using the wild bootstrap with diffusion tensor MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2008;27(9):1268–1274. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2008.922191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasparek T., Theiner P., Filova A. Neurobiology of ADHD from childhood to adulthood: findings of imaging methods. J. Atten. Disord. 2013;XX(X):1–XX. doi: 10.1177/1087054713505322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Minamimoto T., Matsumoto N., Hori Y. Monitoring and switching of cortico-basal ganglia loop functions by the thalamo-striatal system. Neurosci. Res. 2004;48(4):355–360. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2003.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S., Staring M., Murphy K., Viergever M.A., Pluim J.P.W. Elastix: a toolbox for intensity-based medical image registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2010;29(1):196–205. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2009.2035616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobel M., Bechtel N., Weber P., Specht K., Klarhöfer M., Scheffler K.…Penner I.-K. Effects of methylphenidate on working memory functioning in children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2009;13(6):516–523. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2008.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobel M., Bechtel N., Specht K., Klarhöfer M., Weber P., Scheffler K.…Penner I.-K. Structural and functional imaging approaches in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: does the temporal lobe play a key role? Psychiatry Res. 2010;183(3):230–236. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2010.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konrad K., Eickhoff S.B. Is the ADHD brain wired differently? A review on structural and functional connectivity in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2010;31(6):904–916. doi: 10.1002/hbm.21058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konrad A., Dielentheis T.F., El Masri D., Bayerl M., Fehr C., Gesierich T.…Winterer G. Disturbed structural connectivity is related to inattention and impulsivity in adult attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010;31(5):912–919. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooij S., Buitelaar K. 1997. Zelf-rapportage vragenlijst over aandachtsproblemen en hyperactiviteit voor volwassenheid en kindertijd. [Google Scholar]
- Kooij J.J.S., Francken M.H. DIVA Foundation; Den Haag: 2010. Diagnostisch Interview Voor ADHD bij volwassenen. [Google Scholar]
- Krain A.L., Castellanos F.X. Brain development and ADHD. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2006;26(4):433–444. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2006.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leemans A., Jeurissen B., Sijbers J., Jones D.K. 17th Annual meeting of the international society for magnetic resonance medicine. 2009. ExploreDTI: A Graphical Toolbox for Processing, Analyzing and Visualizing Diffusion MR Data; p. 3537. (Hawai, USA) [Google Scholar]
- Lo C.-Y., Wang P.-N., Chou K.-H., Wang J., He Y., Lin C.-P. Diffusion tensor tractography reveals abnormal topological organization in structural cortical networks in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. 2010;30(50):16876–16885. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4136-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makris N., Biederman J., Monuteaux M.C., Seidman L.J. Towards conceptualizing a neural systems-based anatomy of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Dev. Neurosci. 2009;31(1–2):36–49. doi: 10.1159/000207492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mccarthy H., Skokauskas N., Mulligan A., Donohoe G., Mullins D., Kelly J.…Frodl T. Attention network hypoconnectivity with default and affective network hyperconnectivity in adults diagnosed with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in childhood. JAMA Psychiatry. 2013;70(12):1329–1337. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.2174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon V. Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: a unifying triple network model. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011;15(10):483–506. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2011.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills K.L., Bathula D., Dias T.G.C., Iyer S.P., Fenesy M.C., Musser E.D.…Fair D.A. Altered cortico-striatal-thalamic connectivity in relation to spatial working memory capacity in children with ADHD. Front. Psychiatry. 2012;3(January):2. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2012.00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori S., van Zijl P.C.M. Fiber tracking: principles and strategies — a technical review. NMR Biomed. 2002;15(7–8):468–480. doi: 10.1002/nbm.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee P., Berman J.I., Chung S.W., Hess C.P., Henry R.G. Diffusion tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: theoretic underpinnings. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008;29(4):632–641. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel B.J., Bathula D., Herting M., Schmitt C., Kroenke C.D., Fair D., Nigg J.T. Altered white matter microstructure in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry. 2011;50(3):283–292. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2010.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell L.J., Pasternak O. Does diffusion MRI tell us anything about the white matter? An overview of methods and pitfalls. Schizophr. Res. 2014;161(1):133–141. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.09.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavuluri M.N., Yang S., Kamineni K., Passarotti A.M., Srinivasan G., Harral E.M.…Zhou X.J. Diffusion tensor imaging study of white matter fiber tracts in pediatric bipolar disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol. Psychiatry. 2009;65(7):586–593. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.10.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D.J., Ryan M., Rimrodt S.L., Cutting L.E., Denckla M.B., Kaufmann W.E., Mahone E.M. Increased regional fractional anisotropy in highly screened attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) J. Child Neurol. 2011;26(10):1296–1302. doi: 10.1177/0883073811405662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner J., Park C., Wang Z. Connecting the dots: a review of resting connectivity MRI studies in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2014;24(1):3–15. doi: 10.1007/s11065-014-9251-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prčkovska V.I., Achterberg H.C., Bastiani M., Pullens P., Balmashnova E., M, B.…Roebroeck A. Optimal short-time acquisition schemes in high angular resolution diffusion-weighted imaging. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging. 2013;2013(2013) doi: 10.1155/2013/658583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proal E., Reiss P.T., Klein R.G., Mannuzza S., Gotimer K. Brain gray matter deficits at 33-year follow-up in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder established in childhood. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 2011;68(11):1122–1134. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray S., Miller M., Karalunas S., Robertson C., Grayson D.S., Cary R.P.…Fair D.A. Structural and functional connectivity of the human brain in autism spectrum disorders and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a rich club-organization study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014;35(12):6032–6048. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubia K., Smith A.B., Brammer M.J., Taylor E. Temporal lobe dysfunction in medication-naïve boys with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder during attention allocation and its relation to response variability. Biol. Psychiatry. 2007;62(9):999. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.02.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinov M., Bassett D.S. Emerging evidence of connectomic abnormalities in schizophrenia. J. Neurosci. 2011;31(17):6263–6265. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0382-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinov M., Sporns O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. NeuroImage. 2010;52(3):1059–1069. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudie J.D., Brown J.A., Beck-Pancer D., Hernandez L.M., Dennis E.L., Thompson P.M.…Dapretto M. Altered functional and structural brain network organization in autism. NeuroImage: Clin. 2012;2:79–94. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2012.11.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J.J., Ward L.C. Validity, reliability, and standard errors of measurement for two seven-subtest short forms of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale—III. Psychol. Assess. 1999;11(2):207–211. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P., Ph D., Sharp W.S., Morrison M., Eckstrand K., Greenstein D.K.…Rapoport J.L. Psychostimulant treatment and the developing cortex in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2009;166(1):58–63. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2008.08050781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk T.J., Vance A., Rinehart N., Bradshaw J.L., Cunnington R. Structural development of the basal ganglia in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Psychiatry Res. 2009;172(3):220–225. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2008.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotiropoulos S.N., Jbabdi S., Xu J., Andersson J.L., Moeller S., Auerbach E.J.…Behrens T.E.J. Advances in diffusion MRI acquisition and processing in the Human Connectome Project. NeuroImage. 2013;80:125–143. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporns O., Zwi J.D. The small world of the cerebral cortex. Neuroinformatics. 2004;2(2):145–162. doi: 10.1385/NI:2:2:145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sripada C., Kessler D., Fang Y., Welsh R.C., Prem Kumar K., Angstadt M. Disrupted network architecture of the resting brain in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014;35(9):4693–4705. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm L., Menon V., Reiss A.L. Parietal attentional system aberrations during target detection in adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: event-related fMRI evidence. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2006;163(6):1033–1043. doi: 10.1176/ajp.2006.163.6.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tournier J.-D., Mori S., Leemans A. Diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011;65(6):1532–1556. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzourio-Mazoyer N., Landeau B., Papathanassiou D., Crivello F., Etard O., Delcroix N.…Joliot M. Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage. 2002;15(1):273–289. doi: 10.1006/nimg.2001.0978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uddin L.Q., Kelly A.M.C., Biswal B.B., Margulies D.S., Shehzad Z., Shaw D.…Milham M.P. Network homogeneity reveals decreased integrity of default-mode network in ADHD. J. Neurosci. Methods. 2008;169(1):249–254. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2007.11.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya C.J. Neurodevelopmental abnormalities in ADHD. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2012;9:49–66. doi: 10.1007/7854_2011_138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valera E.M., Faraone S.V., Biederman J., Poldrack R.A., Seidman L.J. Functional neuroanatomy of working memory in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol. Psychiatry. 2005;57(5):439–447. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.11.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Heuvel M.P., Sporns O. Rich-club organization of the human connectome. J. Neurosci. 2011;31(44):15775–15786. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3539-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Heuvel M.P., Mandl R.C.W., Stam C.J., Kahn R.S., Hulshoff Pol H.E. Aberrant frontal and temporal complex network structure in schizophrenia: a graph theoretical analysis. J. Neurosci. 2010;30(47):15915–15926. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2874-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ewijk H., Heslenfeld D.J., Zwiers M.P., Buitelaar J.K., Oosterlaan J. Diffusion tensor imaging in attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012;36(4):1093–1106. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schouwenburg M.R., Onnink A.M.H., ter Huurne N., Kan C.C., Zwiers M.P., Hoogman M.…Cools R. Cognitive flexibility depends on white matter microstructure of the basal ganglia. Neuropsychologia. 2014;53:171–177. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2013.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vul E., Harris C., Winkielman P., Pashler H. Puzzlingly high correlations in fMRI studies of emotion, personality, and social cognition. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2009;4(3):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6924.2009.01132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Zhu C., He Y., Zang Y., Cao Q., Zhang H.…Wang Y. Altered small-world brain functional networks in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009;30(2):638–649. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M.F., Wender P.H., Reimherr F.H. The Wender Utah Rating Scale: an aid in the retrospective diagnosis of childhood attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry. 1993;150(6):885–890. doi: 10.1176/ajp.150.6.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedeen V.J., Wang R.P., Schmahmann J.D., Benner T., Tseng W.Y.I., Dai G.…de Crespigny A.J. Diffusion spectrum magnetic resonance imaging (DSI) tractography of crossing fibers. NeuroImage. 2008;41(4):1267–1277. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.03.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weyandt L., Swentosky A., Gudmundsdottir B.G. Neuroimaging and ADHD: fMRI, PET, DTI findings, and methodological limitations. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2013;38(4):211–225. doi: 10.1080/87565641.2013.783833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia M., He Y. Magnetic resonance imaging and graph theoretical analysis of complex brain networks in neuropsychiatric disorders. Brain Connect. 2011;1(5):349–365. doi: 10.1089/brain.2011.0062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalesky A., Fornito A., Harding I.H., Cocchi L., Yücel M., Pantelis C., Bullmore E.T. Whole-brain anatomical networks: does the choice of nodes matter? NeuroImage. 2010;50(3):970–983. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.12.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M.Q., Li Y.Q. Changes of brain structure and function in ADHD children. Brain Topogr. 2010;24(3–4):243–252. doi: 10.1007/s10548-010-0168-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material.