Abstract
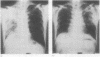
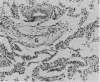
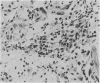
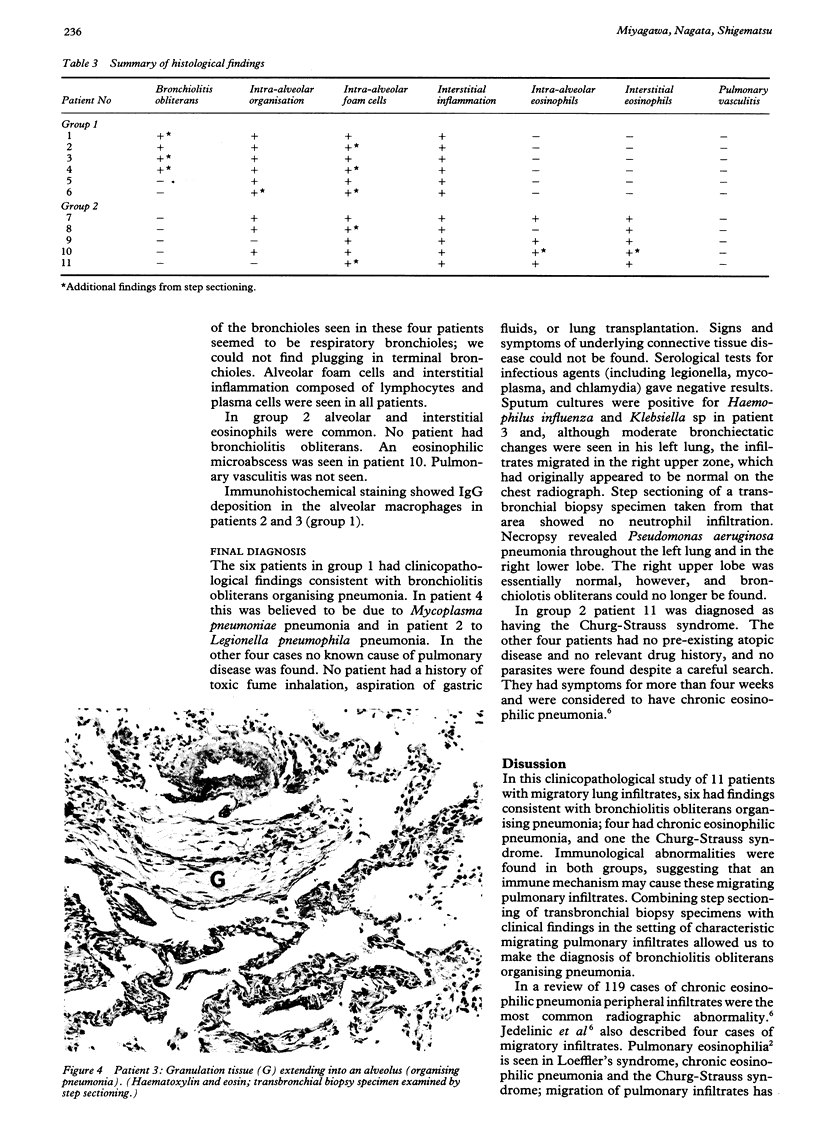
Clinical features and the histological appearances of transbronchial lung biopsy specimens were investigated in 11 patients with migratory infiltrates on the chest radiograph. Serum circulating immune complexes were increased at the time that infiltrates were present in all patients and the levels returned to normal as patients recovered clinically and radiologically. The Mantoux test response was negative in most patients. Fifty serial sections were obtained from each paraffin embedded biopsy specimen block and every 10th section was stained (step sectioning) with haematoxylin and eosin. Six patients (group 1) did not have eosinophilic infiltration; four of these had granulation tissue plugs within respiratory bronchioles when the tissue was examined by step sectioning. All had organising pneumonia and interstitial inflammation in the setting of a clinical picture consistent with bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumonia. In two cases IgG had been deposited in intraalveolar macrophages. Biopsy specimens in five patients (group 2) showed eosinophilic infiltration; four patients had chronic eosinophilic pneumonia and one the Churg-Strauss syndrome. Step sectioning of transbronchial biopsy specimens in patients with migratory pulmonary infiltrates is useful and may support the diagnosis of bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumonia.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartter T., Irwin R. S., Nash G., Balikian J. P., Hollingsworth H. H. Idiopathic bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia with peripheral infiltrates on chest roentgenogram. Arch Intern Med. 1989 Feb;149(2):273–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordier J. F., Loire R., Brune J. Idiopathic bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Definition of characteristic clinical profiles in a series of 16 patients. Chest. 1989 Nov;96(5):999–1004. doi: 10.1378/chest.96.5.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coultas D. B., Samet J. M., Butler C. Bronchiolitis obliterans due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. West J Med. 1986 Apr;144(4):471–474. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epler G. R., Colby T. V., McLoud T. C., Carrington C. B., Gaensler E. A. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 17;312(3):152–158. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501173120304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox B., Seed W. A. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Thorax. 1980 Aug;35(8):570–580. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.8.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosink B. B., Friedman P. J., Liebow A. A. Bronchiolitis obliterans. Roentgenologic-pathologic correlation. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1973 Apr;117(4):816–832. doi: 10.2214/ajr.117.4.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry-Force M. L., Müller N. L., Wright J. L., Wiggs B., Coppin C., Pare P. D., Hogg J. C. A comparison of bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia, usual interstitial pneumonia, and small airways disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Mar;135(3):705–712. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.3.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkiss G. D., Brown D. L. Detection of immune complexes by a new assay, the polyethylene glycol precipitation-complement consumption test (PEG-CC). Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Apr;36(1):117–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jederlinic P. J., Sicilian L., Gaensler E. A. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. A report of 19 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1988 May;67(3):154–162. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198805000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenstein A. L., Myers J. L., Prophet W. D., Corley L. S., 3rd, Shin M. S. Bronchiolitis obliterans and usual interstitial pneumonia. A comparative clinicopathologic study. Am J Surg Pathol. 1986 Jun;10(6):373–381. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198606000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. E., Jr Bronchiolitis obliterans. Lung. 1989;167(2):69–93. doi: 10.1007/BF02714935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch P. S., Reid B. J., Haggitt R. C., Norwood T. H., Rubin C. E. Progression to cancer in Barrett's esophagus is associated with genomic instability. Lab Invest. 1989 Jan;60(1):65–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins S., Colby T., Clayton F. Open lung biopsy in Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 Jan;110(1):34–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato P., Madtes D. K., Thorning D., Albert R. K. Bronchiolitis obliterans caused by Legionella pneumophila. Chest. 1985 Jun;87(6):840–842. doi: 10.1378/chest.87.6.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]