Abstract
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) causes significant morbidity and remains the most expensive cancer to treat because of the need for repeated resections and lifelong monitoring for patients with non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). Novel therapeutics and stratification approaches are needed to improve the outlook for both NMIBC and muscle-invasive bladder cancer. We investigated the expression and effects of B Lymphoma Mo-MLV Insertion Region 1 (BMI1) in UC. BMI1 was found to be overexpressed in most UC cell lines and primary tumors by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemistry. In contrast to some previous reports, no association with tumor stage or grade was observed in two independent tumor panels. Furthermore, upregulation of BMI1 was detected in premalignant bladder lesions, suggesting a role early in tumorigenesis. BMI1 is not located within a common region of genomic amplification in UC. The CDKN2A locus (which encodes the p16 tumor suppressor gene) is a transcriptional target of BMI1 in some cellular contexts. In UC cell lines and primary tissues, no correlation between BMI1 and p16 expression was observed. Retroviral-mediated overexpression of BMI1 immortalized normal human urothelial cells (NHUC) in vitro and was associated with induction of telomerase activity, bypass of senescence, and repression of differentiation. The effects of BMI1 on gene expression were identified by expression microarray analysis of NHUC-BMI1. Metacore analysis of the gene expression profile implicated downstream effects of BMI1 on α4/β1 integrin-mediated adhesion, cytoskeleton remodeling, and CREB1-mediated transcription.
Introduction
Worldwide, urothelial carcinoma (UC) is the ninth most common cancer, with approximately 430,000 new cases diagnosed annually [1]. UC comprises two major tumor groups with different clinical behavior and pathogenesis pathways. One group (20%-25% at diagnosis) is invasive (≥ stage T2). Prognosis for muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) is poor, with a continued need for the development of personalized treatment strategies and identification of novel therapeutic targets. The second group (> 70% at diagnosis) is composed of non–muscle-invasive bladder cancers (NMIBCs) (stage Ta or T1), which recur frequently (> 70%) but infrequently progress to muscle invasion [2]. Although survival is good, multifocality, frequent recurrence, and risk of progression make NMIBC difficult to manage. Overall, UC is the most expensive cancer to treat because of the need for lifelong disease monitoring and repeated resections [3].
The development of novel therapeutic and stratifying approaches will only be possible by achieving a better understanding of the molecular events involved in the development of UC. Expression of telomerase is thought to be one of the earliest steps in tumorigenesis because it can be detected in premalignant lesions [4], [5]. During modeling of the early events in UC tumorigenesis in vitro, B Lymphoma Mo-MLV Insertion Region 1 (BMI1) was found to be overexpressed in genetically normal, telomerase-immortalized normal human urothelial cells (TERT-NHUC) compared with isogenic mortal NHUC [6]. BMI1 (10p11.23) encodes a key component of polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1). The protein contains a conserved RING finger domain and a central helix-turn-helix motif [7]. Although it is not enzymatically active itself, as part of PRC1, BMI1 is involved in the regulation of the transcription of many genes relevant to cancer and development [8]. In some but not all tissues, BMI1 is thought to promote tumorigenesis, in part, by silencing of the CDKN2A locus, which encodes the tumor suppressor gene p16 [9]. However, in the Ewing sarcoma family of tumors, BMI1 promotes the tumorigenicity of both p16 wild-type and p16-null cell lines, indicating that, in some cell types, the role of BMI1 in oncogenesis can be p16 independent [10]. BMI1 also contributes to tumorigenesis in an ink4a/arf-deficient mouse model of glioma [11], strongly implicating other BMI1-associated pathways in cancer. The relationship between BMI1 and the CDKN2A locus in urothelial cells is unknown. The effects of BMI1 on gene expression or phenotype are also not understood in this cell type, although since our study was initiated, effects on proliferation and migration of the T24 UC cell line have been reported by Liang et al. [12].
Here, we examined expression of BMI1 transcript in a large panel of UC cell lines and primary tumors and used immunohistochemical detection in two independent primary UC tumor panels and samples of potentially premalignant urothelium. Using stable retroviral-mediated transduction, we investigated the phenotypic effects of BMI1 overexpression in NHUC and UC cell lines in vitro. Gene expression analysis of BMI1-immortalized cells (NHUC-BMI1) identified consistent downstream changes in gene expression and novel associations with key signaling pathways. Therapeutic inhibition of BMI1 is showing promise in colorectal cancer [13]. Therefore, a better understanding of the contribution of BMI1 upregulation to bladder tumorigenesis will provide rationale and insight into targeting this key molecule and associated pathways in UC.
Materials and Methods
Cell Lines and Tissue Samples
UC cell lines and NHUC were cultured and cell line identity was verified as described previously [14]. NHUC are cultured on Primaria cell culture dishes or flasks (Corning). Tissue was obtained with written patient consent and the approval of the Local Research Ethics Committee from patients at St. James's University Hospital, Leeds, UK. In a panel of 71 tumors, there were 6 pTaG1, 26 pTa G2, 3 pTa G3, 6 pT1G2, 14 pT1 G3, 7 T2 G3, 3 pT3 G3, 4 pTxG2, and 2 pTxG3. For 14 cases, both initial and subsequent tumors were available for the same patient. A second tissue tumor microarray (TMA) panel was obtained from 93 UC patients at Hospital Guadalajara and Hospital Central de Asturias, Spain, as described previously [14]. Tumors were graded according to the 1973 WHO recommendations and staged according to tumor–node–metastasis classification. Clinicopathological data were collected from patient notes after completion of laboratory analyses a minimum of 3 years after collection of the initial sample. Samples of primary UC for quantitative real-time PCR (QRTPCR) have been described [15]. Tumor information is listed in Supplementary Data. Additional information towards meeting the reccomendations of the REMARK guidelines (REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies) [16] is included in Supplementary Information.
Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (QRTPCR)
QRTPCR was performed on 23 UC cell lines and 59 primary UC using Taqman assay on demand; BMI1 (Hs00180411_m1) (Life Technologies, Paisley, U.K). Expression was quantified relative to SDHA control (Hs00417200_m1) and normalized to pooled cDNA from NHUC. Reactions were performed in triplicate, and each plate contained a no template control.
Immunohistochemistry
For detection of BMI1, primary antibody was mouse anti-BMI1 (clone F6, Millipore). For antigen retrieval, slides were pressure cooked for 2 minutes at full pressure with 0.1 M citric acid buffer (pH 6). Positive controls were normal tonsil or placenta. Baseline expression was defined by normal urothelium in each batch of tumors or TMA. To prepare control cell pellets, cells were harvested with 0.1% EDTA/PBS and 0.05% Trypsin/EDTA, pelleted by centrifugation, fixed overnight in 4% formalin, and then transferred to 70% ethanol. Approximately 1-cm3 wells were formed using tinfoil spread over and slightly compressed into a laboratory rack. Pellets were transferred to these wells, agarose at 45°C was added to cover the pellet, agarose was allowed to set, and the agarose-enclosed cell pellet was refixed in formalin before embedding in paraffin wax. BMI1 expression in UC was homogeneous and nuclear. Expression was scored as follows: 0: absent or weak staining in < 50% urothelial nuclei, 1: weak staining in > 50% or moderate staining in < 50% nuclei, 2: moderate staining in > 50% nuclei, or 3: strong staining in > 50% nuclei. A score of 0 or 1 was deemed low expression and comparable to normal expression. A score of 2 or 3 was deemed to be overexpression relative to normal bladder urothelium. Sections were scored independently by E.C., J.R., and M.K., and any discrepancies between low or overexpression were resolved. For detection of p16, 5-μm deparaffinized and rehydrated sections were treated with 3% hydrogen peroxide (Sigma Aldrich, Poole, UK), Avidin Biotin blocking kit (Vector Laboratories, Peterborough, UK), and catalyzed signal amplification system (DakoCytomation, Buckinghamshire, UK). Primary antibody was mouse anti-p16 (Ab-7; Labvision, Suffolk, UK). Slides were counterstained with hematoxylin, dehydrated, and mounted. Positive control for p16 expression was cervical carcinoma. p16 was scored as negative, heterogeneous, or strong expression in > 50% of tumor cells as described [17].
Retroviral-Mediated Transduction
Retroviral transduction was performed as described previously [18]. For stable BMI1 knockdown, plasmids were kindly provided by Elizabeth Lawlor [10]. siBMI1-A and siBMI1-B DNA oligonucleotide sequences (siBMI1-A, 5'-CCGUCUUAAUUUUCCAUUG-3'; or siBMI1-B, 5'-GCGGUAACCACCAAUCUUC-3') were cloned into the pSuper-retro-puro short-hairpin vector backbone (shBMI1-A and shBMI1-B; Oligoengine). A nonsilencing sequence with no significant homology to any mammalian gene sequence (5'-ACGCATGCATGCTTGCTTT-3') was cloned for use as a negative control [10]. pBabe-BMI1 for ectopic overexpression of BMI1 was a kind gift from Goberdhan Dimri and resulted in overexpression within the range of endogenous overexpression observed in primary UC.
Phenotypic Assays
Cells expressing senescence-associated β galactosidase were detected using the senescent cells histochemical staining kit (Sigma, Poole, UK). At 200 × magnification, total and stained cells were counted within a 1-mm2 area. Three unselected areas were counted in each of triplicate wells. For measurement of cumulative population doublings, cells were seeded at 3 × 104 cells per 9.6-cm2 well in triplicate and passaged before confluence. Growth kinetics were examined during the log phase of growth. Anoikis, anchorage-independent colony formation, and induction of differentiation were assessed as described previously [14], [19]. For assessment of adhesive capacity, 3 × 104 cells were seeded under standard conditions. After 30 minutes, adherent cells were trypsinized and counted. To assess migration, 7.5 × 104 cells in unsupplemented medium were seeded onto triplicate 4.67-cm2, 0.8-μm–pore Transwells with complete growth medium below the Transwell (BD Biosciences, Oxford, U.K). After 48 hours, Transwells were fixed in methanol:acetone. Cells that had transversed the membrane were stained with diamidino-2-phenylindole and visualized at × 4. Images were recorded from four unselected areas of each Transwell, and cell number was scored using ImageJ particle analysis (imagej.nih.gov).
Telomerase Activity
Telomerase activity was quantified using the TRAPEZE XL Telomerase detection kit (Millipore, Watford, UK). Sample cell pellets and the control pellet provided with the kit were prepared from 1 × 106 cells and lysed with 200 μl of CHAPS. Protein content of lysates was determined using the Biorad protein assay (Biorad, Hemel Hempstead, UK), and samples were diluted to 1 μg of protein in 2 μl of CHAPS. Samples were assayed in triplicate, and an aliquot of the sample was heat inactivated at 70°C as a negative control. Cycling conditions were as follows: 30°C for 30 minutes, 95°C for 2 minutes, followed by 45 cycles of 94°C for 15 seconds, 59°C for 1 minute, and 45°C for 35 seconds. Quantification was performed using an ABI PRISM 7500 Sequence detector.
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) for Copy Number Analysis
Libraries were prepared for sequencing using NEB NGS library preparation kits with custom tags in an updated version of methods found in Wood et al. (2010) [20]. Samples were pooled onto an Illumina HiSeq2500 for 2 × 101-bp sequencing. Sequence was trimmed to remove adapters using cutadapt [21] and then aligned to the human genome hg19 using Burrows-Wheeler alignment tool [22]. Copy number was calculated by splitting the genome into equal-sized windows with an average of 400 reads per window and comparing ratio of tumor and normal samples, and plots were produced using CNAnorm [23] with breakpoints called using DNAcopy [24]. NHUC-BMI1 samples were compared with isogenic mock or vector transduced cells.
Expression Array Analysis
Gene expression analysis was performed using Affymetrix HG_U133 PLUS 2.0 arrays as described previously [6]. Data were analyzed using Partek Genomics Suite 6.5 (Partek Inc., Missouri, USA). Genes differentially expressed in BMI1-transduced NHUC (NHUC-BMI1) compared with isogenic NHUC were identified using a two-sample t test. Genes consistently altered by at least two-fold in cells from both donors were identified (P < .05 and Q false discovery rate < 0.1). This gene list was input into Metacore (www.http://thomsonreuters.com/metacore/ for further analysis.
Results
Up-Regulation of BMI1 Transcript in UC Cell Lines and Primary Tumors
An initial screen of BMI1 expression by QRTPCR found overexpression in 9/23 (39%) UC cell lines (Figure 1A) and 55/57 (96%) of primary UC relative to NHUC (Figure 1B). There was no association between BMI1 transcript level and stage or grade in these primary tumors. Gene expression array analysis of UC cell lines (Hurst et al., manuscript in preparation) demonstrated that there was a slight positive correlation (P = .0146, r = 0.3617) between BMI1 and p16 transcript expression. This indicates concurrent expression of BMI1 and p16 rather than the negative correlation that would indicate BMI1-mediated repression of CDKN2A transcription (Figure 1C). BMI1 at 10p11.23 is not in a region commonly amplified in UC [25], and examination of copy number data for our UC cell line panel (unpublished data) confirmed that upregulation of BMI1 transcript expression was not due to genetic amplification or duplication in this region. Furthermore, analysis of cBioportal data confirmed a < 2% rate of genetic amplification of BMI1 in bladder cancer and < 5% in other tumor types analyzed (http://www.cbioportal.org).
Figure 1.
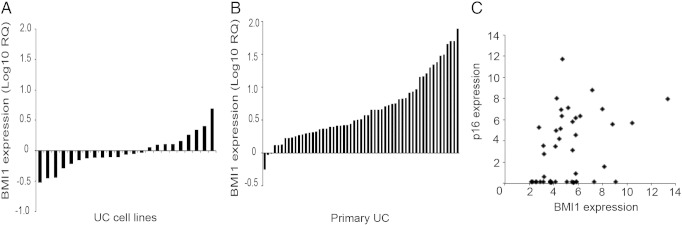
(A) Overexpression of BMI1 in UC tumor cell line panel as detected by QRTPCR. Expression is normalized to NHUC. Cell lines from left to right are as follows: RT112M, 97-1, BFTC905, TCCSUP, SD, T24, SCaBER, CAL29, 253J, HT1376, DSH1, 5637, RT4, 97-24, VMCUB3, SW1710, BFTC909, KU1919, JON, 97-7, 96-1, 94-10, and LUCC1. (B) Expression of BMI1 in a primary UC panel. Tumor information is given in supplementary data. (C) Expression array analysis showed a slight positive correlation between BMI1 and p16 transcript in UC cell lines in contrast to the theory that BMI1 is a transcriptional repressor of the CDKN2A locus in this cell type. Expression is shown relative to pooled NHUC.
BMI1 Protein Expression
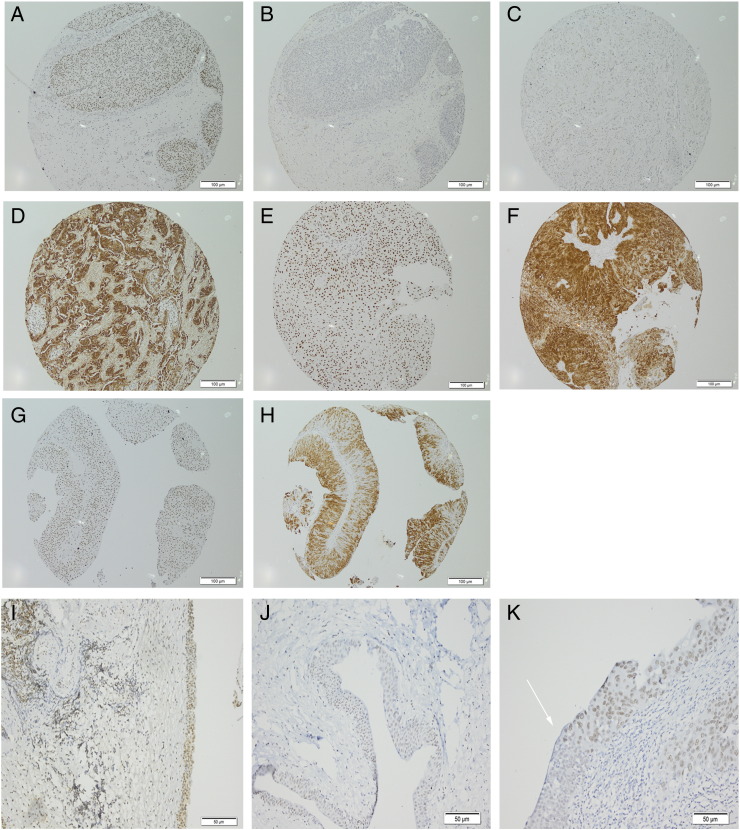
Having observed common upregulation of BMI1 transcript in UC and UC cell lines, we investigated protein expression in primary UC. Normal tonsil showed nuclear positivity in germinal regions as described previously [26] (Supplementary Figure 1A). An additional positive control was human placenta (Supplementary Figure 1B). No primary antibody negative controls showed no staining (Supplementary Figure 1C), and in normal urothelium, BMI1 expression was absent, or nuclear and weak (Supplementary Figure 1, D and E). Additional controls were pellets of cultured cells with known BMI1 transcript expression; NHUC, low expression (Supplementary Figure 1F) or TERT-NHUC, high expression (Supplementary Figure 1G). Sections were scored for BMI1 expression on a 4-point scale as described in Materials and Methods (Supplementary Figure 1, A–K). As BMI1 is reported to inhibit expression from the CDKN2A locus, sections of the same tumor block or TMA were stained for both p16 and BMI1 expression to investigate the relationship between these two proteins. Individual tumors with high BMI1 expression and loss of p16 expression (Figure 2, A and B) or loss of BMI coupled to high p16 expression (Figure 2, C and D) were observed. Coexpression of high levels of both proteins was also seen (Figure 2, E–H). In the initial tumor panel (comprising 71 tumors from 54 patients), 63/71 (89%) tumors had overexpression of BMI1 relative to normal urothelium. No correlation with tumor grade or stage was seen. High BMI1 expression could be detected in noninvasive, stage pTa tumors (Figure 2G) or muscle-invasive, pT2 tumors (Figure 2E). Only eight tumors in this panel had low or no BMI1 expression. These were TaG1 (1 case), TaG2 (1 case), T1G2 (1 case), T1G3 (1 case), and T2G3 (2 cases). For 17 patients, there was an earlier and subsequent tumor in the panel. In 13 of these, the initial and recurrent tumor both had high expression of BMI1. In one case, BMI1 was low in the earlier tumor but upregulated in the later recurrence, and in two cases, it was high in the first presentation but low in the recurrence. Twenty-nine of 71 (40%) tumors in this panel had loss of p16 expression, which is concordant with the rate of homozygous deletion of the CDKN2A locus that we previously described in UC [17]. Twenty-eight of 71 (39%) cases showed coexpression of high levels of BMI1 and p16.
Figure 2.
Examples of immunohistochemistry on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human tissues or cell pellets. Panels (A–H) are shown at 200 × magnification; (I–K), 100 ×. (A) UC BMI1 score 3; (B) same UC, p16 negative; (C) UC, BMI1, score 0; (D) same UC, p16 strong; (E) UC, BMI1, score 3; (F) same UC, p16 strong; (G) UC, BMI1 score 3; (H) same UC, p16 strong; (I) CIS, BMI1, score 3; (J) CIS, BMI1, score 2; (K) CIS, BMI1, score 2. Arrow highlights border of normal urothelium and CIS.
Common overexpression of BMI1 in UC was confirmed in an independent TMA panel comprising 28 pTaG1, 8 pTaG2, 4 pTaG3, 1 pTaGx, 5 pT1G2, 19 pT1G3, 19 pT2G3, 1 pT2Gx, 3 pT3G3, 1 pT3Gx, 4 pT4G3, and 1 pT4Gx. In this panel, 89/94 (95%) of tumors had overexpression of BMI1, and again there was no association between overexpression and tumor stage or grade (chi-square test, P ≥ .05). Tumors of unknown grade or stage were not included in this analysis. Loss of p16 expression was observed in 43/94 (46%). Fifteen of 94 cases (16%) exhibited strong coexpression of p16 and BMI1, again indicating no significant transcriptional repression of the CDKN2A locus.
Expression of BMI1 in Premalignant Bladder Lesions and Carcinoma In Situ (CIS)
The observation that upregulation of BMI1 in UC was not associated with stage or grade indicates that it may be an early event in UC tumorigenesis. We hypothesized that, if this was the case, upregulation of BMI1 expression would also be detected in premalignant bladder lesions. We stained sections from the non–tumor-associated regions of the bladder in cystectomy specimens (n = 6) and noncancerous lesions that were detected at check cystoscopy in patients previously diagnosed with UC (n = 12). Upregulation of BMI1 was detected in examples of CIS (Figure 2, I and J), chronic inflammation (in the absence or presence of CIS), and urothelium reported to show no evidence of malignancy (Supplementary Information 1). Areas of urothelium distant from the tumor in cystectomy specimens showed upregulation of BMI1 in CIS but not normal urothelium. In one case, upregulated BMI1 expression was seen in CIS but not in the adjacent normal urothelium, delineating the margin of CIS (Figure 2K).
Immortalizing Effects of Ectopic Overexpression of BMI1
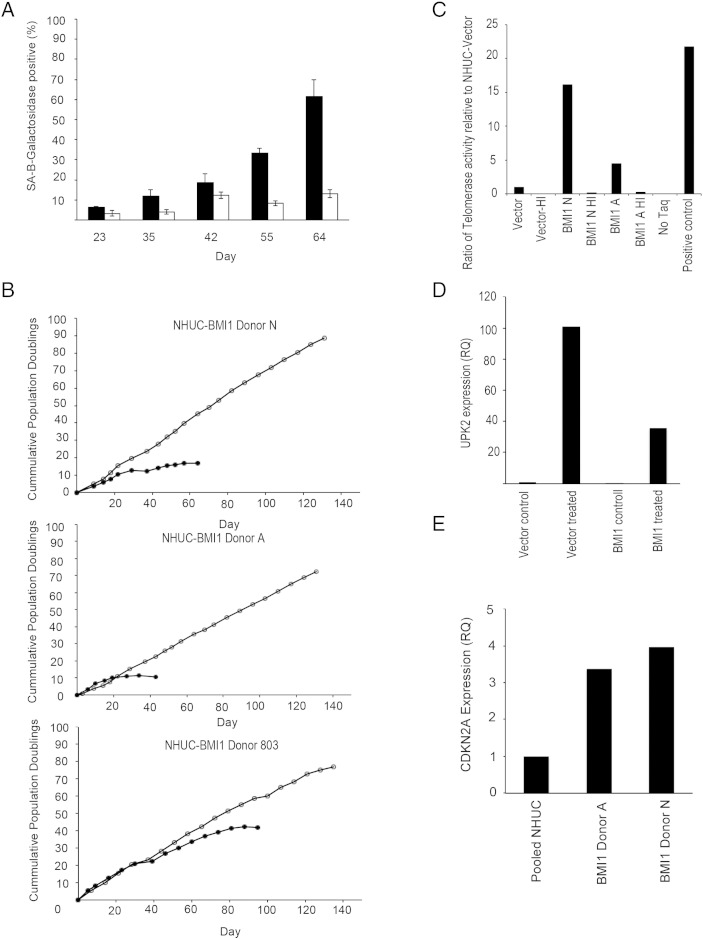
To investigate the role of BMI1 in urothelial tumorigenesis, retroviral transduction was used to stably overexpress BMI1 in NHUC. The resulting NHUC-BMI1 showed a bypass of replicative senescence, as determined by a lack of elevation of senescence-associated β galactosidase expression (Figure 3A). Ectopic expression of BMI1 appeared to immortalize NHUC from two initial donors (A and N) in a single step. Cells proliferated continuously for over 100 days (Figure 3B). Immortalization was then confirmed using NHUC from a third donor (803). NHUC-BMI1 cell lines did not exhibit anchorage-independent growth (data not shown).
Figure 3.
(A) Overexpression of BMI1 led to a bypass of senescence in NHUC. Filled bars show senescence-associated β-galactosidase expression in empty vector-transduced NHUC; and unfilled bars, BMI1-transduced cells. (B) Ectopic expression of BMI1 led to exponential growth of the cell population and apparent immortalization in cells from three independent donors. Filled symbol shows vector-transduced cells; and unfilled symbols, NHUC-BMI1. (C) Detection of telomerase activity in NHUC-BMI1 using quantitative real-time PCR-based method. HI represents heat-inactivated sample, No Taq is a no polymerase negative control, and positive control is a lysate of the control pellet from the TRAPEZE XL kit. (D) Overexpression of BMI1 repressed induction of differentiation in NHUC. Induction of uroplakin 2 (UPK2), a marker of urothelial differentiation, was repressed in NHUC-BMI1 compared with vector control cells after treatment with trogiltazone and EGFR inhibitor. Expression is normalized to NHUC-vector control treatment cells. (E) Quantitative real-time PCR confirmed that overexpression of BMI1 did not repress CDKN2A transcription in NHUC. Expression was quantified relative to pooled cultured NHUC.
Characterization of NHUC-BMI1
Using NGS for copy number analysis, between 2.4 and 4.7 million read pairs were produced per sample, equating to between 480 and 950 Mb of sequence or 0.16 to 0.32X coverage of the human genome. No copy number alterations were detected in NHUC-BMI1 from donors N and 803, but gains on chromosome 20 and 9q were found in NHUC-BMI1 from donor A (Supplementary Figure 2). Interestingly, an hTERT immortalized NHUC (TERT-NHUC) cell line previously derived from the same donor contained an abnormal clone with an unbalanced rearrangement of 20q (46,XY, add (20)(q12)) that resulted in partial loss of 20q and gain of unidentified material [18], suggesting a donor-specific effect rather than an event necessary for immortalization. Telomerase activity was greater in NHUC-BMI1 relative to empty vector transduced cells (Figure 3C). Previously, we have shown that NHUC immortalized by hTERT exhibit a reduced differentiation capacity [27]. Here, we found that induction of uroplakin 2, a marker of urothelial differentiation, was also repressed in NHUC immortalized by BMI1 compared with empty vector-transduced controls (Figure 3D).
Gene Expression Profile of NHUC-BMI1
Expression array analysis revealed at least two-fold changes in expression of 2614 probes (1050 genes) in NHUC-BMI1 relative to isogenic NHUC control cells from both donors investigated (Supplementary Data 1). Transcription of the CDKN2A gene was not downregulated in NHUC-BMI1 as confirmed by QRTPCR (Figure 3E). Metacore enrichment analysis was used to examine how enriched the data set (Supplementary Data 1) is in a particular map or network within the program, taking into account the number of objects in the gene list, the number of objects in the map/network, and the number of objects within the entire Metacore database. GO processes, process networks, and diseases most overrepresented in the data set are shown in Supplementary Data 1. The top 30 upregulated and downregulated probes are shown in Table 1, and the top 30 overconnected genes are shown in Table 2. Reassuringly, this analysis highlighted known functions of BMI1. The top process network was mRNA processing, and the top 7 disease-associated biomarkers identified were consistent with the known association of BMI1 upregulation in colorectal cancer.
Table 1.
Top 30 Upregulated and Downregulated Probes in Affymetrix Expression Array Analysis
| Top 30 upregulated probes in NHUC-BMI1 relative to isogenic NHUC-vector | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donor 1 |
Donor 2 |
Average |
||||
| Probeset ID | Gene Symbol | Fold Change | P Value | Fold Change | P Value | Fold Change |
| 202237_at | NNMT | 176.00 | 4.48E-05 | 24.92 | 2.19E-03 | 100.46 |
| 202238_s_at | NNMT | 51.50 | 9.67E-06 | 21.41 | 8.08E-04 | 36.46 |
| 209949_at | NCF2 | 4.30 | 3.51E-02 | 24.66 | 1.64E-03 | 14.48 |
| 210809_s_at | POSTN | 3.08 | 1.30E-01 | 25.74 | 3.76E-02 | 14.41 |
| 1560679_at | LOC151438 | 21.13 | 5.02E-03 | 3.30 | 3.89E-01 | 12.22 |
| 225911_at | NPNT | 9.85 | 2.32E-04 | 13.28 | 1.58E-03 | 11.56 |
| 209351_at | KRT14 | 14.65 | 5.71E-03 | 7.83 | 5.77E-02 | 11.24 |
| 201141_at | GPNMB | 2.05 | 4.97E-01 | 19.30 | 7.32E-02 | 10.68 |
| 219630_at | PDZK1IP1 | 14.47 | 3.31E-05 | 6.83 | 1.35E-02 | 10.65 |
| 206912_at | FOXE1 | 12.95 | 1.69E-05 | 6.84 | 4.51E-04 | 9.89 |
| 232861_at | PDP2 | 9.89 | 1.77E-04 | 9.12 | 3.35E-04 | 9.51 |
| 220014_at | PRR16 | 13.05 | 4.97E-05 | 5.76 | 2.78E-02 | 9.41 |
| 224823_at | MYLK | 6.94 | 3.05E-03 | 11.64 | 9.66E-04 | 9.29 |
| 244780_at | SGPP2 | 2.80 | 1.11E-01 | 14.98 | 5.54E-02 | 8.89 |
| 231331_at | – | 11.28 | 2.45E-05 | 5.34 | 7.21E-04 | 8.31 |
| 202766_s_at | FBN1 | 2.91 | 6.49E-03 | 13.49 | 7.69E-04 | 8.20 |
| 1553589_a_at | PDZK1IP1 | 10.11 | 3.39E-04 | 6.09 | 8.71E-03 | 8.10 |
| 1556499_s_at | COL1A1 | 5.76 | 1.56E-03 | 10.06 | 2.03E-03 | 7.91 |
| 214701_s_at | FN1 | 12.13 | 1.22E-03 | 3.65 | 5.85E-02 | 7.89 |
| 228854_at | – | 3.43 | 1.77E-01 | 11.77 | 3.31E-02 | 7.60 |
| 219911_s_at | SLCO4A1 | 8.13 | 1.27E-03 | 6.36 | 2.92E-03 | 7.25 |
| 213040_s_at | NPTXR | 4.06 | 1.57E-02 | 9.89 | 6.24E-04 | 6.98 |
| 236044_at | PPAPDC1A | 5.46 | 5.68E-03 | 8.32 | 3.46E-04 | 6.89 |
| 211478_s_at | DPP4 | 4.93 | 6.20E-04 | 8.53 | 2.31E-03 | 6.73 |
| 226388_at | TCEA3 | 6.40 | 4.22E-03 | 6.88 | 9.70E-04 | 6.64 |
| 205547_s_at | TAGLN | 2.34 | 2.51E-01 | 10.62 | 1.73E-02 | 6.48 |
| 226281_at | DNER | 2.12 | 3.72E-02 | 10.68 | 9.26E-03 | 6.40 |
| 213385_at | CHN2 | 5.16 | 3.75E-03 | 7.62 | 4.38E-03 | 6.39 |
| AFFX-DapX-5_at | – | 7.40 | 4.89E-04 | 5.33 | 1.21E-03 | 6.37 |
| 1555724_s_at | TAGLN | 2.18 | 2.51E-01 | 9.85 | 1.09E-02 | 6.01 |
| Top 30 downregulated probes in NHUC-BMI1 relative to isogenic NHUC-vector | ||||||
| Donor 1 | Donor 2 | Average | ||||
| Probeset ID |
Gene Symbol | Fold Change | P Value | Fold Change | P Value | Fold Change |
| 233011_at | ANXA1 | − 19.86 | 5.33E-03 | − 47.91 | 5.49E-04 | − 33.88 |
| 202265_at | BMI1⁎ | − 26.36 | 1.79E-05 | − 41.21 | 2.76E-06 | − 33.79⁎ |
| 244026_at | – | − 42.42 | 1.47E-04 | − 34.65 | 1.84E-04 | − 38.54 |
| 232113_at | – | − 18.18 | 6.90E-03 | − 31.34 | 1.13E-03 | − 24.76 |
| 232541_at | – | − 21.04 | 2.31E-04 | − 30.72 | 2.24E-04 | − 25.88 |
| 224567_x_at | MALAT1 | − 25.83 | 1.55E-03 | − 25.61 | 2.05E-03 | − 25.72 |
| 226675_s_at | MALAT1 | − 34.50 | 1.01E-03 | − 24.15 | 1.68E-03 | − 29.33 |
| 1558678_s_at | MALAT1 | − 39.70 | 2.94E-04 | − 23.55 | 1.16E-03 | − 31.62 |
| 240815_at | – | − 13.81 | 4.12E-05 | − 21.98 | 2.29E-04 | − 17.90 |
| 209550_at | NDN | − 4.62 | 5.67E-04 | − 21.65 | 4.71E-05 | − 13.13 |
| 227062_at | NCRNA00084 | − 19.22 | 8.02E-03 | − 21.58 | 1.97E-02 | − 20.40 |
| 219795_at | SLC6A14 | − 5.89 | 2.17E-02 | − 20.82 | 4.19E-06 | − 13.36 |
| 224559_at | MALAT1 | − 20.19 | 3.59E-04 | − 20.51 | 2.38E-03 | − 20.35 |
| 235592_at | – | − 11.66 | 1.44E-03 | − 20.30 | 1.02E-05 | − 15.98 |
| 240038_at | – | − 16.43 | 2.64E-05 | − 20.01 | 2.65E-05 | − 18.22 |
| 205513_at | TCN1 | − 17.30 | 1.34E-03 | − 19.98 | 7.03E-05 | − 18.64 |
| 217523_at | CD44 | − 14.96 | 1.19E-03 | − 19.86 | 4.83E-04 | − 17.41 |
| 236879_at | – | − 23.07 | 8.36E-06 | − 19.48 | 2.27E-05 | − 21.28 |
| 236545_at | – | − 9.68 | 8.53E-04 | − 19.12 | 6.65E-05 | − 14.40 |
| 233300_at | – | − 12.36 | 4.85E-04 | − 18.34 | 5.70E-05 | − 15.35 |
| 220940_at | ANKRD36B | − 14.52 | 6.40E-06 | − 17.71 | 3.15E-06 | − 16.12 |
| 231929_at | IKZF2 | − 11.76 | 7.49E-03 | − 17.55 | 8.09E-05 | − 14.66 |
| 242476_at | – | − 12.15 | 2.13E-05 | − 17.37 | 9.94E-05 | − 14.76 |
| 230746_s_at | – | − 2.17 | 2.12E-01 | − 16.38 | 7.62E-03 | − 9.28 |
| 228483_s_at | TAF9B | − 3.51 | 2.93E-03 | − 16.08 | 1.27E-03 | − 9.79 |
| 244741_s_at | MGC9913 | − 4.71 | 5.82E-04 | − 15.78 | 3.08E-04 | − 10.24 |
| 236322_at | – | − 22.66 | 4.14E-03 | − 15.54 | 1.15E-03 | − 19.10 |
| 230229_at | DLG1 | − 11.57 | 2.47E-04 | − 15.47 | 1.38E-04 | − 13.52 |
| 235879_at | MBNL1 | − 15.59 | 2.12E-05 | − 15.08 | 1.58E-04 | − 15.33 |
| 235138_at | – | − 17.81 | 1.69E-04 | − 14.98 | 2.68E-04 | − 16.39 |
Fold change is expression in NHUC-BMI1 relative to the isogenic, empty vector transduced NHUC.
Endogenous BMI1 was downregulated in NHUC-BMI1. Retroviral-transduced BMI1 was not detected by the probe because it is located in the 3’ UTR not expressed from the retroviral vector.
Table 2.
Top 30 Overconnected Objects
| Object Type | Network Object Name | Actual | R | Expected | Ratio | p Value | z-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transcription factors | YY1 | 255 | 2891 | 113.7 | 2.242 | 3.689E-37 | 14.37 |
| Other | ELAVL1 (HuR) | 205 | 2042 | 80.32 | 2.552 | 4.018E-37 | 14.81 |
| Other | SUMO-2 | 145 | 1339 | 52.67 | 2.753 | 2.881E-29 | 13.34 |
| Other | SUMO-1 | 125 | 1102 | 43.35 | 2.884 | 4.777E-27 | 12.94 |
| Transcription factors | CREB1 | 352 | 5302 | 208.5 | 1.688 | 5.774E-27 | 11.41 |
| Transcription factors | c-Myc | 227 | 2941 | 115.7 | 1.962 | 2.056E-24 | 11.24 |
| Enzymes | Sirtuin7 | 87 | 661 | 26 | 3.346 | 2.851E-23 | 12.37 |
| Other | 14-3-3 zeta/delta | 102 | 984 | 38.7 | 2.635 | 2.901E-19 | 10.59 |
| Transcription factors | p53 | 141 | 1774 | 69.78 | 2.021 | 5.539E-16 | 9.022 |
| Other | Cullin 3 | 97 | 1095 | 43.07 | 2.252 | 5.824E-14 | 8.572 |
| Enzymes | E2I | 49 | 380 | 14.95 | 3.278 | 2.913E-13 | 9.055 |
| Other | CNOT3 | 101 | 1209 | 47.55 | 2.124 | 6.369E-13 | 8.104 |
| Other | SF3A2 | 27 | 128 | 5.035 | 5.363 | 6.837E-13 | 10.01 |
| Other | miR-155-5p | 40 | 274 | 10.78 | 3.711 | 8.527E-13 | 9.131 |
| Kinases | PLK1 | 92 | 1063 | 41.81 | 2.2 | 1.031E-12 | 8.091 |
| Transcription factors | TARDBP | 54 | 463 | 18.21 | 2.965 | 1.071E-12 | 8.636 |
| Other | FUS | 37 | 240 | 9.44 | 3.919 | 1.149E-12 | 9.195 |
| Other | p15(PAF) | 76 | 808 | 31.78 | 2.391 | 1.99E-12 | 8.134 |
| Other | SUMO-3 | 57 | 515 | 20.26 | 2.814 | 2.193E-12 | 8.416 |
| Other | 14-3-3 gamma | 57 | 523 | 20.57 | 2.771 | 4.113E-12 | 8.281 |
| Transcription factors | Oct-3/4 | 114 | 1489 | 58.57 | 1.946 | 5.58E-12 | 7.619 |
| Other | U2AF-65 | 27 | 146 | 5.743 | 4.702 | 1.792E-11 | 9.076 |
| Transcription factors | ESR1 (nuclear) | 137 | 1966 | 77.33 | 1.772 | 2.851E-11 | 7.21 |
| Other | TIF1-beta | 122 | 1681 | 66.12 | 1.845 | 3.139E-11 | 7.258 |
| Transcription factors | YB-1 | 46 | 393 | 15.46 | 2.976 | 4.601E-11 | 7.988 |
| Other | miR-93-5p | 24 | 122 | 4.799 | 5.001 | 6.132E-11 | 8.964 |
| Kinases | CDK9 | 40 | 314 | 12.35 | 3.239 | 6.559E-11 | 8.077 |
| Proteases | Caspase-3 | 57 | 561 | 22.07 | 2.583 | 6.703E-11 | 7.673 |
| Other | hnRNP A1 | 44 | 373 | 14.67 | 2.999 | 9.442E-11 | 7.87 |
| Other | TIP120A | 61 | 634 | 24.94 | 2.446 | 1.319E-10 | 7.462 |
There were 990 objects identified in the NHUC-BMI1 data set that were eligible for this analysis which were analyzed based upon the 25,169 gene-based objects present in the complete database. Key: Actual is the number of network objects in the BMI1-NHUC data set which interact with the chosen object, R = number of objects in the complete Metacore database which interact with the chosen object, Expected is mean value for hypergeometric distribution (n*R/N), Ratio is connectivity ratio (actual/expected), P value is the probability to have the given value of actual or higher (or lower for negative z-score), z-score is ((actual − expected)/sqrt(variance)).
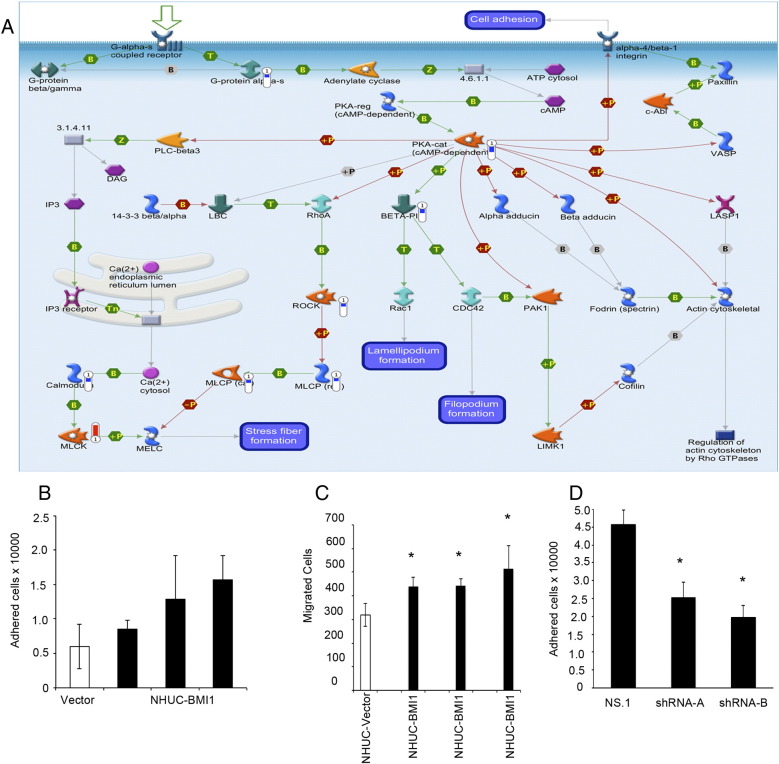
Meng et al. previously performed genomewide mapping of targets of BMI1 in the epithelial HeLa tumor cell line using chromatin immunoprecipitation [28]. To identify true BMI1-mediated changes in gene expression, we overlaid the NHUC-BMI1 data set with the data set of Meng et al. There was an overlap of 88 genes (Table 4), which could be arranged into three networks (Supplementary Figure 3). The first and second networks both showed involvement of CREB transcriptional targets. Of note, there was upregulation of p90RSK, an activator of CREB1, coupled to overexpression of CREB1 targets. The top process network identified was cytoskeleton-actin filaments, and the top pathway map further implicated overexpression of BMI1 in altered phosphorylation events and subsequent effects on cytoskeleton remodeling (Figure 4). For example, NHUC-BMI1 exhibited overexpression of ROCK2 kinase. This upregulation is expected to impact on downstream actin- and tubulin-mediated cytoskeleton remodeling and subsequent cellular migration.
Table 4.
Analysis of NHUC-BMI1 Gene List by Protein Function
| # | Pathway Maps | Total | P Value | Min FDR | P Value | FDR | In Data | Network Objects from NHUC-BMI1 Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cytoskeleton remodeling_Role of PKA in cytoskeleton reorganization | 40 | 9.613E-06 | 3.711E-03 | 9.613E-06 | 3.711E-03 | 8 | ROCK, MLCK, PKA-cat (cAMP-dependent), G-protein alpha-s, Calmodulin, BETA-PIX, MLCP (reg), MLCP (cat) |
| 2 | Apoptosis and survival_BAD phosphorylation | 42 | 1.408E-05 | 3.711E-03 | 1.408E-05 | 3.711E-03 | 8 | PKA-cat (cAMP-dependent), JNK1(MAPK8), PI3K cat class IA, G-protein alpha-s, p90Rsk, PP2C, IRS-1, Cytochrome c |
| 3 | Development_A2A receptor signaling | 43 | 1.689E-05 | 3.711E-03 | 1.689E-05 | 3.711E-03 | 8 | CREB1, PDZ-GEF1, PKA-cat (cAMP-dependent), JNK(MAPK8-10), PI3K cat class IA, G-protein alpha-s, p90Rsk, BETA-PIX |
| 4 | Transcription_CREB pathway | 49 | 4.563E-05 | 5.979E-03 | 4.563E-05 | 5.979E-03 | 8 | CREB1, PKA-cat (cAMP-dependent), PI3K cat class IA, G-protein alpha-s, Calmodulin, p90Rsk, IRS-1, PP1-cat |
| 5 | Signal transduction_cAMP signaling | 38 | 6.170E-05 | 5.979E-03 | 6.170E-05 | 5.979E-03 | 7 | GSK3 alpha/beta, RAP-2A, CREB1, PKA-cat (cAMP-dependent), G-protein alpha-s, PKC, Calmodulin |
| 6 | Translation_Regulation of translation initiation | 27 | 6.940E-05 | 5.979E-03 | 6.940E-05 | 5.979E-03 | 6 | eIF4A, eIF1, eIF3S8, eIF5, eIF1A, eIF5B (IF-2) |
| 7 | Signal transduction_Activation of PKC via G-Protein coupled receptor | 52 | 7.098E-05 | 5.979E-03 | 7.098E-05 | 5.979E-03 | 8 | GSK3 beta, MLCK, PKC-lambda/iota, Calmodulin, PKC-mu, NF-AT2(NFATC1), MLCP (reg), MLCP (cat) |
| 8 | Translation _Regulation of EIF2 activity | 39 | 7.348E-05 | 5.979E-03 | 7.348E-05 | 5.979E-03 | 7 | GSK3 alpha/beta, PI3K cat class IA, Casein kinase I, DYRK2, IRS-1, PKR, PP1-cat |
| 9 | Cell cycle_Influence of Ras and Rho proteins on G1/S Transition | 53 | 8.166E-05 | 5.979E-03 | 8.166E-05 | 5.979E-03 | 8 | GSK3 beta, ROCK2, MLCK, JNK1(MAPK8), PI3K cat class IA, CDK6, MLCP (reg), MLCP (cat) |
| 10 | Cytoskeleton remodeling_Cytoskeleton remodeling | 102 | 9.588E-05 | 6.318E-03 | 9.588E-05 | 6.318E-03 | 11 | eIF4A, GSK3 beta, ROCK, ROCK2, MYLK1, MLCK, PI3K cat class IA, TGF-beta receptor type I, PTEN, MLCP (reg), MLCP (cat) |
Figure 4.
(A) BMI1-associated changes in gene expression could affect pathways relevant to cellular adhesion. Blue thermometers indicate a downregulation of gene expression in NHUC-BMI1 (relative to NHUC); and red thermometers, overexpression. (B) A trend of increased adhesion was seen in NHUC ectopically overexpressing BMI1 from three donors compared with NHUC. (C) Overexpression of BMI1 increased Transwell migration of NHUC from three of three donors investigated. Data are representative of three or two independent experiments. Errors bars show plus and minus standard deviation of triplicates repeats within each experiment. *P < .05, unpaired t test. (D) Knockdown of BMI1 repressed adhesion in 97-7, UC cell line.
Phenotypic Effects of BMI1 Expression
Analysis of the NHUC-BMI1 gene list by protein function (Table 3) identified the key pathway map enriched in NHUC-BMI1 expression profile as “cytoskeleton remodeling_Role of PKA in cytoskeleton reorganisation” (Figure 4A). NHUC-BMI1 had downregulation of PKA-cat, a protein responsible for the phosphorylation and deactivation of α4/β1 integrin, a key molecule in cell adhesion. Downregulation of the deactivator of α4/β1 integrin would be expected to result in an increase in cellular adhesion. Indeed, overexpression of BMI1 in NHUC promoted adhesion under standard culture conditions (Figure 4B). Analysis of the overlap with the Meng et al. data set indicated that effects of BMI1 overexpression would include ROCK-mediated modulation of the cytoskeleton. Accordingly, NHUC-BMI1 had increased cellular motility as measured by Transwell migration (Figure 4C). Retroviral-mediated transduction was then used to stably downregulate BMI1 expression in the UC cell line 97-7. This cell line was derived from a T1 G2/3 UC and has a low level of p16 that is considered functionally inactivated as it is coupled to hyperphosphorylated Rb [29]. Transduction of 97-7 with shBMI1-A or shBMI1-B resulted in 37% or 88% decreases in BMI1 transcript level, respectively. 97-7 siRNA B therefore had BMI1 levels reduced to slightly less than the endogenous level detectable in pooled NHUC. Knockdown of BMI1 repressed adhesion in 97-7 (Figure 4D) in contrast to the trend in increased adhesion seen with overexpression in NHUC.
Table 3.
BMI1-Target Genes (Identified by Meng et al., 2010) Whose Expression Was Consistently Altered in NHUC-BMI1 Compared with NHUC
| AIG1 | Androgen-induced gene 1 protein | KLHL42 | Kelch-like protein 42 | RPS6KA2 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALOXE3 | Hydroperoxide isomerase ALOXE3 | KMT2E | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 2E | RUFY2 | RUN and FYVE domain-containing protein 2 |
| AP4E1 | Adaptor-Related Protein Complex 4, Epsilon 1 Subunit | LMLN | Leishmanolysin-like peptidase | SEC14L1 | SEC14-like protein 1 |
| ARHGEF10 | Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 10 | LRPPRC | Leucine-rich PPR motif-containing protein, mitochondrial | SEC62 | Translocation protein SEC62 |
| ASXL1 | Putative Polycomb group protein ASXL1 | MAP4K4 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 4 | SEPT7 | Septin-7 |
| BAZ2B | Bromodomain adjacent to zinc finger domain protein 2B | MBOAT2 | Lysophospholipid acyltransferase 2 | SKA2 | Spindle and kinetochore-associated protein 2 |
| BIRC6 | Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 6 | MIPOL1 | Mirror-image polydactyly gene 1 protein | SOX6 | Transcription factor SOX-6 |
| CAMTA1 | Calmodulin-binding transcription activator 1 | MKLN1 | Muskelin | SRGAP2 | SLIT-ROBO Rho GTPase-activating protein 2 |
| CDK6 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 | MRPS10 | 28S ribosomal protein S10, mitochondrial | SRRM2 | Serine/arginine repetitive matrix protein 2 |
| CFI | Complement factor I | MSI2 | RNA-binding protein Musashi homolog 2 | STAM2 | Signal transducing adapter molecule 2 |
| CLOCK | Circadian locomoter output cycles protein kaput | MTDH | Protein LYRIC | SUGCT | Succinate-hydroxymethylglutarate CoA-transferase |
| CUX1 | Homeobox protein cut-like 1 | NBN | Artemin (ARTN) | SULF2 | Extracellular sulfatase Sulf-2 |
| DIP2A | Disco-interacting protein 2 homolog A | NBPF1 | Neuroblastoma breakpoint family member 1 | TACC2 | Transforming acidic coiled-coil-containing protein 2 |
| DST | Dystonin | NIN | Ninein | TC2N | Tandem C2 domains nuclear protein |
| DYNC2H1 | Cytoplasmic dynein 2 heavy chain 1 | NT5C2 | Cytosolic purine 5'-nucleotidase | TCF12 | Transcription factor 12 |
| EHBP1 | EH domain-binding protein 1 | PAPOLA | Poly(A) polymerase alpha | THOC2 | THO complex subunit 2 |
| FAM120A | Constitutive coactivator of PPAR-gamma-like protein 1 | PGGT1B | Geranylgeranyl transferase type-1 subunit beta | TMED10 | Transmembrane emp24 domain-containing protein 10 |
| FAM83F | Protein FAM83F | PIAS1 | E3 SUMO-protein ligase PIAS1 | TNS1 | Tensin-1 |
| FBN1 | Fibrillin-1 | PMS1 | PMS1 protein homolog 1 | TPRG1 | Tumor protein p63-regulated gene 1 protein |
| FBXO9 | F-box only protein 9 | PPAPDC1A | Phosphatidate phosphatase PPAPDC1A | TRIM33 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM33 |
| FGD6 | FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain-containing protein 6 | PPM1D | Protein phosphatase 1D | UFL1 | E3 UFM1-protein ligase 1 |
| FKBP5 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP5 | PPP2R2C | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A 55 kDa regulatory subunit B gamma isoform | USP34 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 34 |
| FOXA1 | Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3-alpha | PSMD14 | 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 14 | UTRN | Utrophin |
| FRMD4A | FERM domain-containing protein 4A | PSMG1 | Proteasome assembly chaperone 1 | VMP1 | Vacuole membrane protein 1 |
| GOLGA8B | Golgin subfamily A member 8B | QPCT | Glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase | VPS13B | Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 13B |
| GPD2 | Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | RAB18 | Ras-related protein Rab-18 | VTA1 | Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein VTA1 homolog |
| GRB10 | Growth factor receptor-bound protein 10 | RAB3GAP2 | Rab3 GTPase-activating protein non-catalytic subunit | WBSCR27 | Williams-Beuren syndrome chromosomal region 27 protein |
| H2AFY | Core histone macro-H2A.1 | RASAL1 | RasGAP-activating-like protein 1 | ZMYND8 | Protein kinase C-binding protein 1 |
| IFT80 | Intraflagellar transport protein 80 homolog | RNF213 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF213 | ||
| KLHL28 | Kelch-like protein 28 | ROCK2 | Rho-associated protein kinase 2 |
Discussion
Overexpression of BMI1 is reported in many cancer types [30], [31], [32], [33], and in some, its expression correlates with clinicopathological parameters [34], [35], [36], [37]. However, its role in urothelial tumorigenesis has not been clearly defined, and conflicting data have arisen from existing studies. Following careful validation of IHC staining, we found nuclear overexpression of BMI1 in the majority of UC. Unlike previous studies [30], [38], these IHC results were confirmed in a second independent tumor panel. There was no correlation of BMI1 protein expression with the stage or grade of the tumor, supporting our observation of no association of BMI1 transcript level with tumor stage or grade. Since our study was initiated, Liang et al. used the same BMI1 antibody, a smaller UC panel of differing stage and grade distribution, and a different scoring system to investigate BMI1 expression in UC. In contrast to our results, an association of BMI1 expression with tumor stage and grade was reported [12]. To account for the effect of different scoring classification, we also performed statistical analysis using criteria equivalent to Liang et al. (grouping tumors as Ta, T1, and T2 + and staining of 0 or 1 vs 2 and 3). Still, we found no association of BMI1 expression with stage or grade, as was expected from the overall low frequency of BMI1-negative/low tumors in our panel.
Although extremely frequent, overexpression of BMI1 was not a ubiquitous event in UC. It is known that BMI1-negative tumors are a distinct subpopulation in Ewing’s sarcoma, with a distinct gene expression profile [39]. Only eight UCs in our original tumor panel and only five in the second TMA panel were BMI1 negative. The small numbers of tumors studied here make interpretation impossible, but it is conceivable that BMI1-negative tumors follow a distinct PRC1-independent pathway to tumorigenesis, and this is a subject worthy of further investigation.
In hematological malignancy, BMI1 is targeted by chromosomal rearrangements [40], but in solid epithelial cancers, there is no evidence to support this. The 10p11.23 region is not a common site of amplification in UC [41], and accordingly, correlation between BMI1 copy number and overexpression in UC cell lines was not observed.
Previously, we observed upregulation of BMI1 in telomerase-immortalized normal human urothelial cells during experiments aimed at modeling the early steps in bladder tumor development [6]. Our results indicate that upregulation of BMI1 is an early event in UC development. We consider that, in bladder cancer patients, the entire urothelium is altered because of the spread of tumor and premalignant cells. Initiation of MIBC arises from a CIS precursor lesion which expands to colonize the urothelium [42]. BMI1 expression was examined in a pilot study of premalignant bladder lesions including CIS. BMI1 was upregulated in a subset. Previous studies also support the notion of upregulation of BMI1 in potentially premalignant urothelium. Shafaroudi et al. describe 25% of tumor margins exhibiting expression of BMI1 transcript [38], and Qin et al. demonstrated upregulation of BMI1 transcript in adjacent “normal” tissue in bladder cancer patients [30]. The concept of a role for BMI1 in early tumorigenesis is not unprecedented because upregulation is reported in other epithelial premalignancies such as colorectal, lung, oral tissue, and esophageal tissue [43], [44], [45]. As is expected for an early event, in some of the associated tumor types, such as esophageal carcinoma, no association is seen between BMI1 overexpression and subsequent tumor stage or grade [46]. In parallel to our results, in oral tissue, BMI1 is upregulated at a very early stage in oral tumorigenesis and is thought to act through p16-independent mechanisms [45]. As suggested by Kang et al., the detection of BMI1 has potential for use in the identification of potentially premalignant lesions. Of note, in our study, the patient from whom the check cystoscopy biopsy that was classified as “no evidence of malignancy” by standard histological analysis and showed strong nuclear BMI1 upregulation was derived went on to develop fatal metastatic UC. Whether upregulation of BMI1 in potentially premalignant lesions is predictive of outcome is currently unknown, but further investigation of the significance of detection of BMI1 is planned.
BMI1 is commonly cited as being a transcriptional repressor of the CDKN2A locus. The promoter of p16 contains a BMI1 responding unit, and BMI1 and p16 expression correlate in some tumor types [28]. We have previously shown that, in UC, downregulation of p16 expression is most often associated with homozygous deletion or loss of heterozygosity of the 9p21 region, and it is this rather than transcriptional repression which may be key in determining the p16 level [17]. Indeed, in the whole tumor section panel, 28 UCs exhibited strong expression of both BMI1 and p16, and coexpression was confirmed in the second TMA panel.
Having established upregulation of BMI1 as a frequent and potentially early event in bladder cancer, we set out to investigate the phenotypic significance of its overexpression in NHUC. In vitro, overexpression of BMI1 induced telomerase activity (as is reported for mammary epithelial cells [49]) and immortalized NHUC without the need for silencing of p16. Similarly, in Ewing’s sarcoma, the actions of BMI1 are independent of repression of p16 expression [10]. Overexpression of BMI1 alone also immortalizes nasopharyngeal epithelial cells [47], whereas in other human cell types, expression of hTERT [48] or prior silencing of p16 is also required [49]. The fact that BMI1 and hTERT are required for immortalization of some cell types such as gingival keratinocytes [50] indicates that the role of BMI1 in tumorigenesis is greater than merely induction of telomerase activity and its subsequent downstream effects. In UC, it appears that the functions of BMI1 in tumorigenesis also extend beyond suppression of the CDKN2A locus.
Gene expression analysis of NHUC-BMI1 was performed to investigate the potential transcriptional effects of BMI1 in urothelial tumorigenesis. A profile of genes consistently altered in BMI1-transduced cells was obtained. The NHUC-BMI1 gene list was subjected to Metacore analyses. The most significant process network affected was transcription and mRNA processing, supporting the wealth of existing literature describing BMI1 as a key molecule in control of downstream gene expression. Chromatin remodeling genes have been shown to be frequent targets of mutation in UC [51]. Notably, downregulation of transcripts for chromodomain-helicase DNA binding protein 1 (CHD1), CHD1L, CHD2, CHD7, and CHD9 was observed. CHD2 is proposed as a tumor suppressor gene that regulates DNA damage response [52]. Interestingly, TCGA data show that 9% of bladder carcinomas exhibit mutation in this gene (www.cbioportal.org).
The key pathway map enriched in NHUC-BMI1 expression profile was “cytoskeleton remodeling_Role of PKA in cytoskeleton reorganisation”. Epithelial–mesenchymal transition is a multistep process by which epithelial cells acquire migratory and invasive properties, and in some cell types, activation of BMI1 is required for epithelial–mesenchymal transition [53]. The ability of mesenchymal-like migration, as observed in cancer cells, relies on an intricate balance between adhesion assembly and disassembly. Overexpression of BMI1 led to downregulation of PKA-cat. This molecule is responsible for the phosphorylation and deactivation of α4/β1 integrin, a key molecule in cell adhesion. The resulting BMI1-transduced cells had increased adhesion coupled to enhanced cellular migration. Our results support the recent report that knockdown of BMI1 in the T24 UC cell line inhibits invasion in vitro[12] and may represent an action of BMI1 that is more relevant to the later stages of cancer development.
Using Metacore, data were analyzed to identify interactions of the BMI1-associated changes in gene expression by protein function. YY1, a transcription factor and key component of the polycomb initiation complex PRC2, was the most significant network object. In concordance with published literature, genes that interacted with c-Myc, p53, and ESR1 were overrepresented. However, a novel finding was that genes that were targets of cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein 1 (CREB1) were highly overrepresented and both CREB1 and its target genes were downregulated in NHUC-BMI1. The CREB signaling pathway potentially modulates up to 25% of human genes [54]. CREB-mediated transcription is activated through cAMP-induced phospohorylation, and NHUC-BMI1 had upregulation of p90RSK kinase, a known CREB1 activator.
Having identified a “profile” of BMI1-associated changes in gene expression in NHUC, we compared this with other BMI1-associated signatures in other cell types and contexts. An 11-gene BMI1 pathway gene signature has been identified in metastatic prostate cancer and neural stem cells and is predictive of poor outcome in multiple tumor types including bladder [55]. We found that only one of these signature genes, encoding the ankyrin protein (ANK3), was also altered in NHUC-BMI1. The NHUC-BMI1 gene expression profile did show downregulation of 3 of the 11 previously identified telomerase “signature genes” [6] in NHUC (TSPYL5, NME5, CEACAM6) and the putative tumor suppressor gene NDN [14], suggesting cell type– and cell context–specific effects. In particular, loss of CEACAM6 (CD66c) expression has been associated with the so-called “highly tumorigenic basal cell compartment” of UC, which is believed to exhibit stem cell–like properties [56]. CEACAM6 was downregulated in both TERT-NHUC [6] and NHUC-BMI1, suggesting that, to some extent, these immortal cell lines resemble “stem cell–like” cells. BMI1 is overexpressed in human bladder cancer stem cell–like populations. In these cells, knockdown of BMI1 inhibited proliferation, migration, and tumor sphere formation; increased cisplatin sensitivity; and is essential for their tumorigenicity in mouse models [57].
BMI1 is a target for the development of novel small molecule inhibitors [58] and also a transcriptional target of histone deacetylase inhibitor drugs [59]. BMI1-null mice gradually succumb because of a progressive neurological and hematopoietic dysfunction [60] presumably due to stem cell dysfunction. As with many conventional cancer treatments, it would be expected that a BMI1 inhibitor would be toxic to normal human adult stem cells in addition to targeting tumor cells. However, an increased knowledge of the downstream effects of BMI1 on gene expression may aid the development of alternative strategies with a lower toxicity or indicate ways to ameliorate the side effects of BMI1 inhibition. If overexpression of BMI1 is a key feature of CIS, identification of BMI1-associated changes in gene expression could point toward pathways that could be targeted in this highly clinically relevant subpopulation.
Conclusion
BMI1 has many p16-independent actions that may contribute to neoplasia. As a key modulator of gene expression, cellular phenotype, and keystone signaling pathways, BMI1 is worthy of future investigation as a therapeutic target in UC. Future studies are required to confirm of the role of BMI1 in α4/β1 integrin-mediated adhesion, kinase-mediated changes in cytoskeleton, and CREB-1 transcriptional regulation in cancer. Further analysis of BMI1 expression in premalignant bladder lesions and its correlation with outcome and expression in subsequent tumors is merited.
The following are the supplementary data related to this article.
Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Figure 2.
Supplementary Figure 3.
Supplementary Figure 4.
Supplementary Material 1.
Supplementary Material 2.
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2015.08.002.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the patients who donated tissue and data for research as without them this study would not have been possible. We thank Filomena Esteves for performing immunohistochemistry. NGS library preparation was performed by Phil Egan and NGS by the University of Leeds, Next-Generation Sequencing Facility. pBabe-BMI1 puro plasmid was a kind gift from Goberdhan Dimri, The George Washington University Medical Center, Washington, USA. BMI1 shRNA plus nonsilencing control plasmids was a kind gift from Elizabeth Lawlor, University of Michigan, USA. Telomerase quantification was performed using a modified protocol for the TRAPEZE XL Telomerase quantification kit, as recommended by Samantha Brownhill of the Children’s Cancer Research Group, Leeds. This work was sponsored by Yorkshire Cancer Research project grant L355 (L.D.F., E.C.).
Footnotes
This work was sponsored by Yorkshire Cancer Research project grant L355 (L.D.F., E.C.).
References
- 1.Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Ervik M., Dikshit R., Eser S., Mathers C., Rebelo M., Parkin D.M., Forman D., Bray F. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2013. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 [Internet] [[cited 2013]. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Knowles M.A., Hurst C.D. Molecular biology of bladder cancer: new insights into pathogenesis and clinical diversity. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;15(1):25–41. doi: 10.1038/nrc3817. [PubMed PMID: 25533674] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sangar V.K., Ragavan N., Matanhelia S.S., Watson M.W., Blades R.A. The economic consequences of prostate and bladder cancer in the UK. BJU Int. 2005;95(1):59–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2005.05249.x. [PubMed PMID: 15638895] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Engelhardt M., Drullinsky P., Guillem J., Moore M.A. Telomerase and telomere length in the development and progression of premalignant lesions to colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3(11):1931–1941. [PubMed PMID: 9815582. Epub 1998/11/17. eng] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kolquist K.A., Ellisen L.W., Counter C.M., Meyerson M., Tan L.K., Weinberg R.A., Haber D.A., Gerald W.L. Expression of TERT in early premalignant lesions and a subset of cells in normal tissues. Nat Genet. 1998;19(2):182–186. doi: 10.1038/554. [PubMed PMID: 9620778. Epub 1998/06/10. eng] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chapman E.J., Kelly G., Knowles M.A. Genes involved in differentiation, stem cell renewal, and tumorigenesis are modulated in telomerase-immortalized human urothelial cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2008;6(7):1154–1168. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-07-2168. [PubMed PMID: 18644980. Epub 2008/07/23. eng] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li Z., Cao R., Wang M., Myers M.P., Zhang Y., Xu R.M. Structure of a Bmi-1-Ring1B polycomb group ubiquitin ligase complex. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(29):20643–20649. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602461200. [PubMed PMID: 16714294] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cao R., Tsukada Y., Zhang Y. Role of Bmi-1 and Ring1A in H2A ubiquitylation and Hox gene silencing. Mol Cell. 2005;20(6):845–854. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.12.002. [PubMed PMID: 16359901] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fan C., He L., Kapoor A., Gillis A., Rybak A.P., Cutz J.C., Tang D. Bmi1 promotes prostate tumorigenesis via inhibiting p16(INK4A) and p14(ARF) expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1782(11):642–648. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.08.009. [PubMed PMID: 18817867] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Douglas D., Hsu J.H., Hung L., Cooper A., Abdueva D., van Doorninck J., Peng G., Shimada H., Triche T.J., Lawlor E.R. BMI-1 promotes ewing sarcoma tumorigenicity independent of CDKN2A repression. Cancer Res. 2008;68(16):6507–6515. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6152. [PubMed PMID: 18701473. Epub 2008/08/15. eng] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bruggeman S.W., Hulsman D., Tanger E., Buckle T., Blom M., Zevenhoven J., van Tellingen O., van Lohuizen M. Bmi1 controls tumor development in an Ink4a/Arf-independent manner in a mouse model for glioma. Cancer Cell. 2007;12(4):328–341. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2007.08.032. [PubMed PMID: 17936558. Epub 2007/10/16. eng] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Liang W., Zhu D., Cui X., Su J., Liu H., Han J., Zhao F., Xie W. Knockdown BMI1 expression inhibits proliferation and invasion in human bladder cancer T24 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013;382(1-2):283–291. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1745-0. [PubMed PMID: 23820733. Pubmed Central PMCID: 3771375] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kreso A., van Galen P., Pedley N.M., Lima-Fernandes E., Frelin C., Davis T., Cao L., Baiazitov R., Du W., Sydorenko N. Self-renewal as a therapeutic target in human colorectal cancer. Nat Med. 2014;20(1):29–36. doi: 10.1038/nm.3418. [PubMed PMID: 24292392] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.De Faveri L.E., Hurst C.D., Platt F.M., Taylor C.F., Roulson J.A., Sanchez-Carbayo M., Knowles M.A., Chapman E.J. Putative tumour suppressor gene necdin is hypermethylated and mutated in human cancer. Br J Cancer. 2013;108(6):1368–1377. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.104. [PubMed PMID: 23549060. Pubmed Central PMCID: 3619261. Epub 2013/04/04. eng] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Forster J.A., Paul A.B., Harnden P., Knowles M.A. Expression of NRG1 and its receptors in human bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 2011;104(7):1135–1143. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.39. [PubMed PMID: 21364580. Pubmed Central PMCID: 3068491] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.McShane L.M., Altman D.G., Sauerbrei W., Taube S.E., Gion M., Clark G.M. Statistics Subcommittee of the NCIEWGoCD. REporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK) Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2005;2(8):416–422. [PubMed PMID: 16130938] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chapman E.J., Harnden P., Chambers P., Johnston C., Knowles M.A. Comprehensive analysis of CDKN2A status in microdissected urothelial cell carcinoma reveals potential haploinsufficiency, a high frequency of homozygous co-deletion and associations with clinical phenotype. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(16):5740–5747. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0411. [PubMed PMID: 16115911. Epub 2005/08/24. eng] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chapman E.J., Hurst C.D., Pitt E., Chambers P., Aveyard J.S., Knowles M.A. Expression of hTERT immortalises normal human urothelial cells without inactivation of the p16/Rb pathway. Oncogene. 2006;25(36):5037–5045. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209513. [PubMed PMID: 16619045. Epub 2006/04/19. eng] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Varley C.L., Stahlschmidt J., Lee W.C., Holder J., Diggle C., Selby P.J., Trejdosiewicz L.K., Southgate J. Role of PPARgamma and EGFR signalling in the urothelial terminal differentiation programme. J Cell Sci. 2004;117(Pt 10):2029–2036. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01042. [PubMed PMID: 15054105. Epub 2004/04/01. eng] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wood H.M., Belvedere O., Conway C., Daly C., Chalkley R., Bickerdike M., McKinley C., Egan P., Ross L., Hayward B. Using next-generation sequencing for high resolution multiplex analysis of copy number variation from nanogram quantities of DNA from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded specimens. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(14):e151. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq510. [PubMed PMID: 20525786. Pubmed Central PMCID: 2919738] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Martin M. Cutadapt removes adapter reads from high-throughput sequencng reads. EMBnet. 2011;17(1):10–12. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Li H., Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(14):1754–1760. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324. [PubMed PMID: 19451168. Pubmed Central PMCID: 2705234] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gusnanto A., Wood H.M., Pawitan Y., Rabbitts P., Berri S. Correcting for cancer genome size and tumour cell content enables better estimation of copy number alterations from next-generation sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2012;28(1):40–47. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr593. [PubMed PMID: 22039209] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Venkatraman E.S., Olshen A.B. A faster circular binary segmentation algorithm for the analysis of array CGH data. Bioinformatics. 2007;23(6):657–663. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl646. [PubMed PMID: 17234643] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hurst C.D., Platt F.M., Taylor C.F., Knowles M.A. Novel tumor subgroups of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder defined by integrated genomic analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(21):5865–5877. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1807. [PubMed PMID: 22932667] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Raaphorst F.M., van Kemenade F.J., Fieret E., Hamer K.M., Satijn D.P., Otte A.P., Meijer C.J. Cutting edge: polycomb gene expression patterns reflect distinct B cell differentiation stages in human germinal centers. J Immunol. 2000;164(1):1–4. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.1.1. [PubMed PMID: 10604983] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Aaboe M., Marcussen N., Jensen K.M., Thykjaer T., Dyrskjot L., Orntoft T.F. Gene expression profiling of noninvasive primary urothelial tumours using microarrays. Br J Cancer. 2005;93(10):1182–1190. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602813. [PubMed PMID: 16265353. Epub 2005/11/03. eng] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Meng S., Luo M., Sun H., Yu X., Shen M., Zhang Q., Zhou R., Ju X., Tao W., Liu D. Identification and characterization of Bmi-1-responding element within the human p16 promoter. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(43):33219–33229. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.133686. [PubMed PMID: 20551323. Pubmed Central PMCID: 2963359] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sarkar S., Julicher K.P., Burger M.S., Della Valle V., Larsen C.J., Yeager T.R., Grossman T.B., Nickells R.W., Protzel C., Jarrard D.F. Different combinations of genetic/epigenetic alterations inactivate the p53 and pRb pathways in invasive human bladder cancers. Cancer Res. 2000;60(14):3862–3871. [PubMed PMID: 10919661. Epub 2000/08/05. eng] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Qin Z.K., Yang J.A., Ye Y.L., Zhang X., Xu L.H., Zhou F.J., Han H., Liu Z.W., Song L.B., Zeng M.S. Expression of Bmi-1 is a prognostic marker in bladder cancer. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:61. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-61. [PubMed PMID: 19228380. Pubmed Central PMCID: 2652492] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang Y., Zhe H., Ding Z., Gao P., Zhang N., Li G. Cancer stem cell marker Bmi-1 expression is associated with basal-like phenotype and poor survival in breast cancer. World J Surg. 2012;36(5):1189–1194. doi: 10.1007/s00268-012-1514-3. [PubMed PMID: 22366984] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Abd El Hafez A., El-Hadaad H.A. Immunohistochemical expression and prognostic relevance of Bmi-1, a stem cell factor, in epithelial ovarian cancer. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2014;18(2):58–62. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2013.11.004. [PubMed PMID: 24342665] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Vonlanthen S., Heighway J., Altermatt H.J., Gugger M., Kappeler A., Borner M.M., van Lohuizen M., Betticher D.C. The bmi-1 oncoprotein is differentially expressed in non-small cell lung cancer and correlates with INK4A-ARF locus expression. Br J Cancer. 2001;84(10):1372–1376. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.2001.1791. [PubMed PMID: 11355949. Epub 2001/05/18. eng] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mihara K., Chowdhury M., Nakaju N., Hidani S., Ihara A., Hyodo H., Yasunaga S., Takihara Y., Kimura A. Bmi-1 is useful as a novel molecular marker for predicting progression of myelodysplastic syndrome and patient prognosis. Blood. 2006;107(1):305–308. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-06-2393. [PubMed PMID: 16160010. Epub 2005/09/15. eng] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chowdhury M., Mihara K., Yasunaga S., Ohtaki M., Takihara Y., Kimura A. Expression of Polycomb-group (PcG) protein BMI-1 predicts prognosis in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2007;21(5):1116–1122. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404623. [PubMed PMID: 17377594] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Liu J.H., Song L.B., Zhang X., Guo B.H., Feng Y., Li X.X., Liao W.T., Zeng M.S., Huang K.H. Bmi-1 expression predicts prognosis for patients with gastric carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2008;97(3):267–272. doi: 10.1002/jso.20934. [PubMed PMID: 18041745. Epub 2007/11/29. eng] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wang H., Pan K., Zhang H.K., Weng D.S., Zhou J., Li J.J., Huang W., Song H.F., Chen M.S., Xia J.C. Increased polycomb-group oncogene Bmi-1 expression correlates with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008;134(5):535–541. doi: 10.1007/s00432-007-0316-8. [PubMed PMID: 17917742. Epub 2007/10/06. Eng] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Shafaroudi A.M., Mowla S.J., Ziaee S.A., Bahrami A.R., Atlasi Y., Malakootian M. Overexpression of BMI1, a polycomb group repressor protein, in bladder tumors: a preliminary report. Urol J. 2008;5(2):99–105. [PubMed PMID: 18592462. Epub 2008/07/02. eng] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cooper A., van Doorninck J., Ji L., Russell D., Ladanyi M., Shimada H., Krailo M., Womer R.B., Hsu J.H., Thomas D. Ewing tumors that do not overexpress BMI-1 are a distinct molecular subclass with variant biology: a report from the Children's Oncology Group. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(1):56–66. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1417. [PubMed PMID: 21047978. Pubmed Central PMCID: 3711406] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rouhigharabaei L., Ferreiro J.F., Put N., Michaux L., Tousseyn T., Lefebvre C., Gardiner A., De Kelver W., Demuynck H., Verschuere J. BMI1, the polycomb-group gene, is recurrently targeted by genomic rearrangements in progressive B-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2013;52(10):928–944. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22088. [PubMed PMID: 23873701] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lindgren D., Sjodahl G., Lauss M., Staaf J., Chebil G., Lovgren K., Gudjonsson S., Liedberg F., Patschan O., Mansson W. Integrated genomic and gene expression profiling identifies two major genomic circuits in urothelial carcinoma. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038863. [PubMed PMID: 22685613. Pubmed Central PMCID: 3369837] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.McConkey D.J., Lee S., Choi W., Tran M., Majewski T., Lee S., Siefker-Radtke A., Dinney C., Czerniak B. Molecular genetics of bladder cancer: Emerging mechanisms of tumor initiation and progression. Urol Oncol. 2010;28(4):429–440. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2010.04.008. [PubMed PMID: 20610280. Pubmed Central PMCID: 2901550] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Breuer R.H., Snijders P.J., Sutedja G.T., Sewalt R.G., Otte A.P., Postmus P.E., Meijer C.J., Raaphorst F.M., Smit E.F. Expression of the p16(INK4a) gene product, methylation of the p16(INK4a) promoter region and expression of the polycomb-group gene BMI-1 in squamous cell lung carcinoma and premalignant endobronchial lesions. Lung Cancer. 2005;48(3):299–306. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2004.11.026. [PubMed PMID: 15892997] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tateishi K., Ohta M., Kanai F., Guleng B., Tanaka Y., Asaoka Y., Tada M., Seto M., Jazag A., Lianjie L. Dysregulated expression of stem cell factor Bmi1 in precancerous lesions of the gastrointestinal tract. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(23):6960–6966. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0449. [PubMed PMID: 17145814] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kang M.K., Kim R.H., Kim S.J., Yip F.K., Shin K.H., Dimri G.P., Christensen R., Han T., Park N.H. Elevated Bmi-1 expression is associated with dysplastic cell transformation during oral carcinogenesis and is required for cancer cell replication and survival. Br J Cancer. 2007;96(1):126–133. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603529. [PubMed PMID: 17179983. Epub 2006/12/21. eng] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Choy B., Bandla S., Xia Y., Tan D., Pennathur A., Luketich J.D., Godfrey T.E., Peters J.H., Sun J., Zhou Z. Clinicopathologic characteristics of high expression of Bmi-1 in esophageal adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012;12:146. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-12-146. [PubMed PMID: 23078618. Pubmed Central PMCID: 3544684] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Dimri G.P., Martinez J.L., Jacobs J.J., Keblusek P., Itahana K., Van Lohuizen M., Campisi J., Wazer D.E., Band V. The Bmi-1 oncogene induces telomerase activity and immortalizes human mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2002;62(16):4736–4745. [PubMed PMID: 12183433. Epub 2002/08/17. eng] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Song L.B., Zeng M.S., Liao W.T., Zhang L., Mo H.Y., Liu W.L., Shao J.Y., Wu Q.L., Li M.Z., Xia Y.F. Bmi-1 is a novel molecular marker of nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and immortalizes primary human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66(12):6225–6232. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0094. [PubMed PMID: 16778197. Epub 2006/06/17. eng] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Saito M., Handa K., Kiyono T., Hattori S., Yokoi T., Tsubakimoto T., Harada H., Noguchi T., Toyoda M., Sato S. Immortalization of cementoblast progenitor cells with Bmi-1 and TERT. J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20(1):50–57. doi: 10.1359/JBMR.041006. [PubMed PMID: 15619669] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Moffatt-Jauregui C.E., Robinson B., de Moya A.V., Brockman R.D., Roman A.V., Cash M.N., Culp D.J., Lamont R.J. Establishment and characterization of a telomerase immortalized human gingival epithelial cell line. J Periodontal Res. 2013;48(6):713–721. doi: 10.1111/jre.12059. [PubMed PMID: 23441958. Pubmed Central PMCID: 3709015] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Gui Y., Guo G., Huang Y., Hu X., Tang A., Gao S., Wu R., Chen C., Li X., Zhou L. Frequent mutations of chromatin remodeling genes in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Nat Genet. 2011;43(9):875–878. doi: 10.1038/ng.907. [PubMed PMID: 21822268] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nagarajan P., Onami T.M., Rajagopalan S., Kania S., Donnell R., Venkatachalam S. Role of chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 2 in DNA damage response signaling and tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2009;28(8):1053–1062. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.440. [PubMed PMID: 19137022. Pubmed Central PMCID: 2648865] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Qiao B., Chen Z., Hu F., Tao Q., Lam A.K. BMI-1 activation is crucial in hTERT-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oral epithelial cells. Exp Mol Pathol. 2013;95(1):57–61. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2013.05.004. [PubMed PMID: 23712029] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Altarejos J.Y., Montminy M. CREB and the CRTC co-activators: sensors for hormonal and metabolic signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12(3):141–151. doi: 10.1038/nrm3072. [PubMed PMID: 21346730] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Glinsky G.V., Berezovska O., Glinskii A.B. Microarray analysis identifies a death-from-cancer signature predicting therapy failure in patients with multiple types of cancer. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(6):1503–1521. doi: 10.1172/JCI23412. [PubMed PMID: 15931389. Epub 2005/06/03. eng] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.He X., Marchionni L., Hansel D.E., Yu W., Sood A., Yang J., Parmigiani G., Matsui W., Berman D.M. Differentiation of a highly tumorigenic basal cell compartment in urothelial carcinoma. Stem Cells. 2009;27(7):1487–1495. doi: 10.1002/stem.92. [PubMed PMID: 19544456. Pubmed Central PMCID: 3060766] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhu D., Wan X., Huang H., Chen X., Liang W., Zhao F., Lin T., Han J., Xie W. Knockdown of Bmi1 inhibits the stemness properties and tumorigenicity of human bladder cancer stem cell-like side population cells. Oncol Rep. 2014;31(2):727–736. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2919. [PubMed PMID: 24337040] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Cao L., Bombard J., Cintron K., Sheedy J., Weetall M.L., Davis T.W. BMI1 as a novel target for drug discovery in cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(10):2729–2741. doi: 10.1002/jcb.23234. [PubMed PMID: 21678481] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Bommi P.V., Dimri M., Sahasrabuddhe A.A., Khandekar J., Dimri G.P. The polycomb group protein BMI1 is a transcriptional target of HDAC inhibitors. Cell Cycle. 2010;9(13):2663–2673. doi: 10.4161/cc.9.13.12147. [PubMed PMID: 20543557. Pubmed Central PMCID: 3010287] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.van der Lugt N.M., Domen J., Linders K., van Roon M., Robanus-Maandag E., te Riele H., van der Valk M., Deschamps J., Sofroniew M., van Lohuizen M. Posterior transformation, neurological abnormalities, and severe hematopoietic defects in mice with a targeted deletion of the bmi-1 proto-oncogene. Genes Dev. 1994;8(7):757–769. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.7.757. [PubMed PMID: 7926765] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Figure 2.
Supplementary Figure 3.
Supplementary Figure 4.
Supplementary Material 1.
Supplementary Material 2.