Abstract
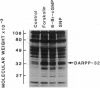
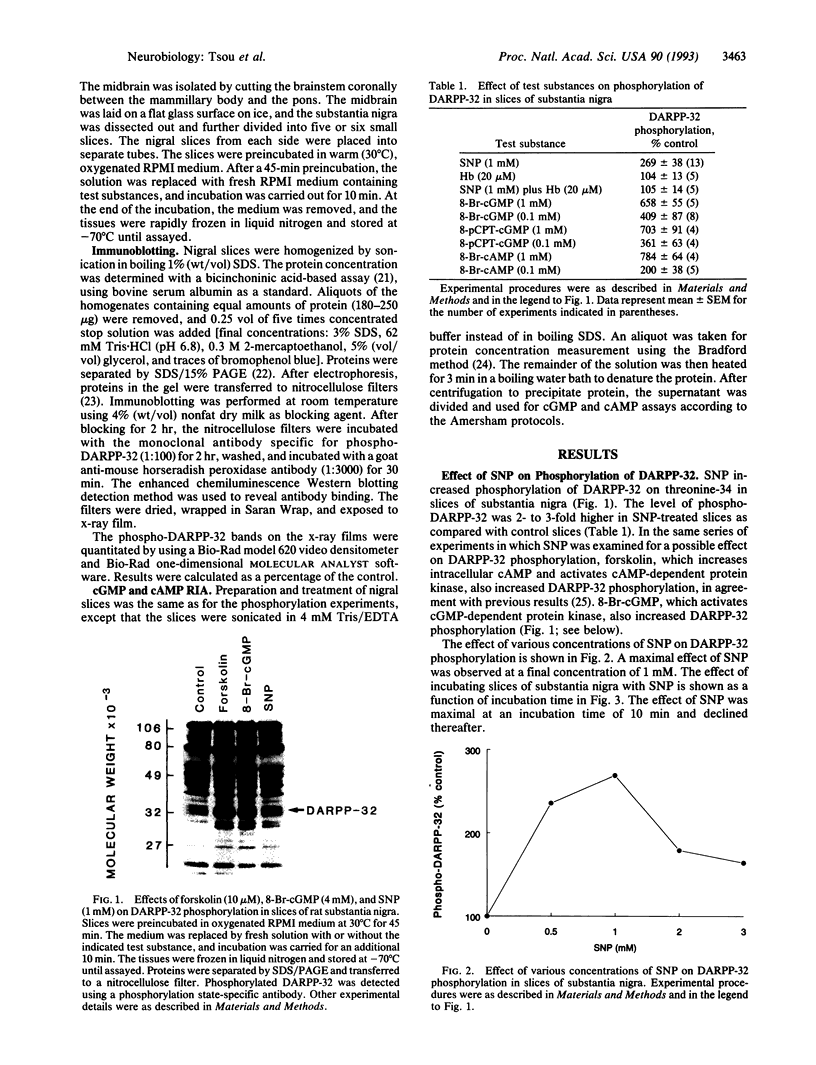
DARPP-32, a dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein of M(r) 32,000, has been shown to be phosphorylated on threonine-34, both in vitro with high efficiency by cAMP-dependent and cGMP-dependent protein kinases and in vivo by dopamine acting through cAMP-dependent protein kinase. In the present study, we investigated the nitric oxide (NO)/cGMP pathway for its ability to regulate the state of phosphorylation of DARPP-32 in slices of rat substantia nigra. DARPP-32 was phosphorylated on threonine-34 in these slices by sodium nitroprusside (SNP), an NO donor. The effect of SNP was abolished by preincubation of the slices with hemoglobin, indicating that the effect of SNP was due to released NO. The same concentration of SNP produced a 4-fold elevation of the cGMP level but did not alter the level of cAMP. The effect of SNP on DARPP-32 phosphorylation was mimicked by low concentrations of 8-bromo-cGMP and 8-(4-chlorophenylthio)-guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate, activators of cGMP-dependent protein kinase, but not by low concentrations of 8-bromo-cAMP, an activator of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. The data indicate a physiological role for the NO/cGMP pathway in the regulation of DARPP-32 phosphorylation in nerve terminals of striatonigral neurons. The results provide further evidence that the state of phosphorylation of DARPP-32 represents an important mechanisms for integration of information arriving at striatonigral neurons via a variety of neuronal pathways.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariano M. A. Distribution of components of the guanosine 3',5'-phosphate system in rat caudate-putamen. Neuroscience. 1983 Nov;10(3):707–723. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90212-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariano M. A., Ufkes S. K. Cyclic nucleotide distribution within rat striatonigral neurons. Neuroscience. 1983 May;9(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90043-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Snyder S. H. Localization of nitric oxide synthase indicating a neural role for nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):768–770. doi: 10.1038/347768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide, a novel neuronal messenger. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90104-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt E., Nolte C., Schulz S., Beltman J., Beavo J. A., Jastorff B., Walter U. Analysis of the functional role of cGMP-dependent protein kinase in intact human platelets using a specific activator 8-para-chlorophenylthio-cGMP. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Jun 23;43(12):2591–2600. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90148-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edley S. M., Graybiel A. M. The afferent and efferent connections of the feline nucleus tegmenti pedunculopontinus, pars compacta. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Jun 20;217(2):187–215. doi: 10.1002/cne.902170207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J., Garthwaite G., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. NMDA receptor activation induces nitric oxide synthesis from arginine in rat brain slices. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct 17;172(4-5):413–416. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J. Glutamate, nitric oxide and cell-cell signalling in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Feb;14(2):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90022-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiger J., Nolte C., Butt E., Sage S. O., Walter U. Role of cGMP and cGMP-dependent protein kinase in nitrovasodilator inhibition of agonist-evoked calcium elevation in human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1031–1035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpain S., Girault J. A., Greengard P. Activation of NMDA receptors induces dephosphorylation of DARPP-32 in rat striatal slices. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):369–372. doi: 10.1038/343369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings H. C., Jr, Greengard P. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein: regional, tissue, and phylogenetic distribution. J Neurosci. 1986 May;6(5):1469–1481. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-05-01469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings H. C., Jr, Greengard P., Tung H. Y., Cohen P. DARPP-32, a dopamine-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein, is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):503–505. doi: 10.1038/310503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings H. C., Jr, Nairn A. C., Greengard P. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein. II. Comparison of the kinetics of phosphorylation of DARPP-32 and phosphatase inhibitor 1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14491–14497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope B. T., Michael G. J., Knigge K. M., Vincent S. R. Neuronal NADPH diaphorase is a nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2811–2814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Palacios M., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Formation of nitric oxide from L-arginine in the central nervous system: a transduction mechanism for stimulation of the soluble guanylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5159–5162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein C. J., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide, a novel biologic messenger. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):705–707. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90301-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maack T. Receptors of atrial natriuretic factor. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:11–27. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.000303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantyh C. R., Kruger L., Brecha N. C., Mantyh P. W. Localization of specific binding sites for atrial natriuretic factor in the central nervous system of rat, guinea pig, cat and human. Brain Res. 1987 Jun 2;412(2):329–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91140-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Villani G. M., Jothianandan D., Furchgott R. F. Selective blockade of endothelium-dependent and glyceryl trinitrate-induced relaxation by hemoglobin and by methylene blue in the rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):708–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouimet C. C., Miller P. E., Hemmings H. C., Jr, Walaas S. I., Greengard P. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. III. Immunocytochemical localization. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):111–124. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00111.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Dalpé M., Dam T. V. Characterization and distribution of receptors for the atrial natriuretic peptides in mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):174–178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renart J., Sandoval I. V. Western blots. Methods Enzymol. 1984;104:455–460. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)04114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh K., Fibiger H. C. Cholinergic neurons of the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus: efferent and afferent connections. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Nov 15;253(3):277–302. doi: 10.1002/cne.902530302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder G. L., Girault J. A., Chen J. Y., Czernik A. J., Kebabian J. W., Nathanson J. A., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of DARPP-32 and protein phosphatase inhibitor-1 in rat choroid plexus: regulation by factors other than dopamine. J Neurosci. 1992 Aug;12(8):3071–3083. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-08-03071.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto T., Hattori T. Organization and efferent projections of nucleus tegmenti pedunculopontinus pars compacta with special reference to its cholinergic aspects. Neuroscience. 1984 Apr;11(4):931–946. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. R., Kimura H. Histochemical mapping of nitric oxide synthase in the rat brain. Neuroscience. 1992;46(4):755–784. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent S. R., Satoh K., Armstrong D. M., Panula P., Vale W., Fibiger H. C. Neuropeptides and NADPH-diaphorase activity in the ascending cholinergic reticular system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1986;17(1):167–182. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Aswad D. W., Greengard P. A dopamine- and cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):69–71. doi: 10.1038/301069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Girault J. A., Greengard P. Localization of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase in rat basal ganglia neurons. J Mol Neurosci. 1989;1(4):243–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Greengard P. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. I. Regional and cellular distribution in the rat brain. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):84–98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00084.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]