Abstract
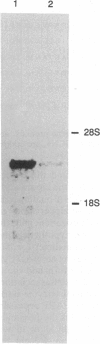
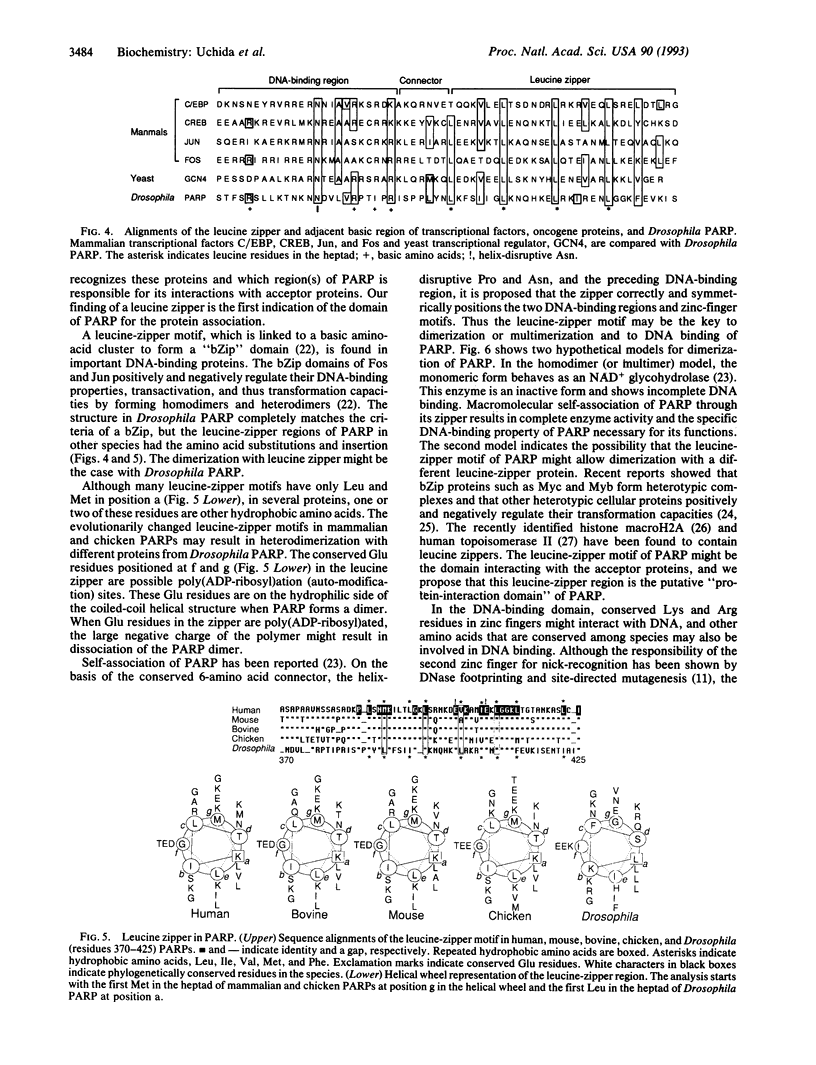
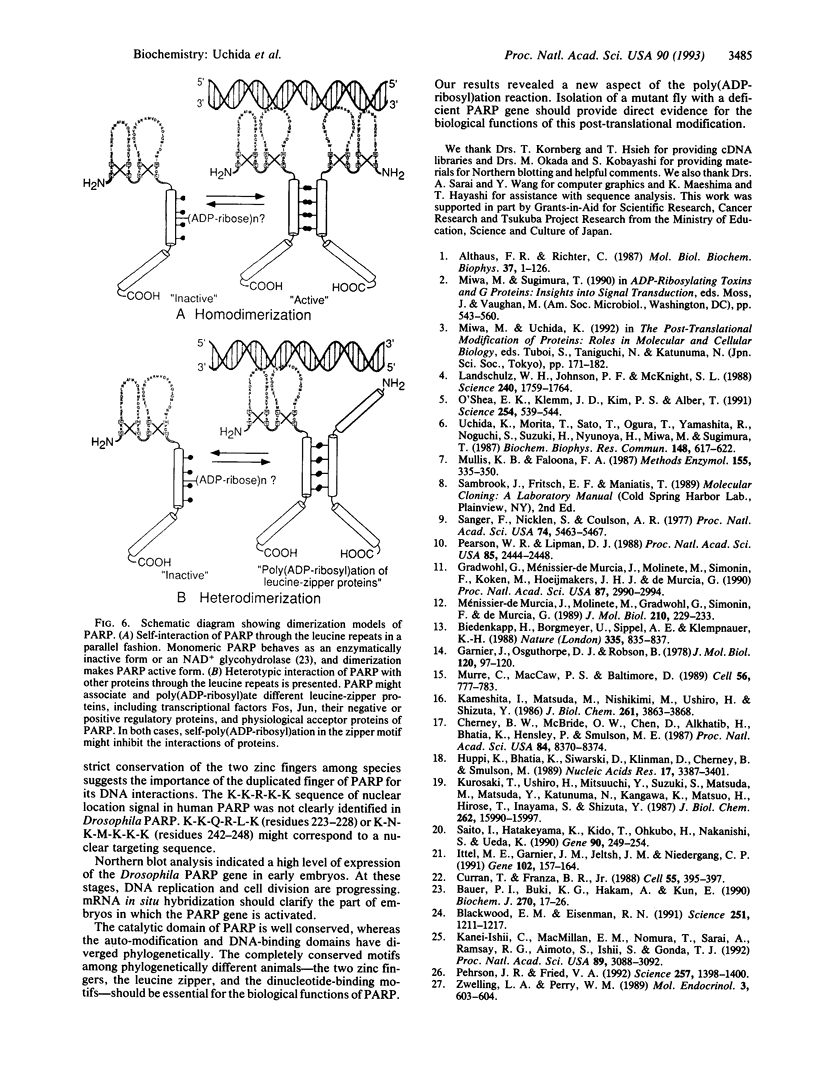
We have isolated cDNA clones for a Drosophila poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP; EC 2.4.2.30) by screening a lambda gt11 cDNA library with a Drosophila partial cDNA fragment. The Drosophila PARP probe was obtained by the polymerase chain reaction with heterologous primers deduced from conserved amino acids in the mammalian, chicken, amphibian, and fish sequences. The Drosophila PARP mRNA is 3.2 kb in length and is expressed in the early stages of development. The PARP protein of 994 amino acids contains two zinc-finger motifs and an NAD-binding motif, which are conserved among different species. Interestingly, the heptad leucine repeat in an alpha-helix was found in Drosophila PARP. Alignments of the auto-modification domains of various species showed the repeated hydrophobic amino acids on the same face of the helix that make the coiled-coil configuration in the mammalian and chicken sequences. The presence of a leucine-zipper motif in the auto-modification domain suggests that this motif might be responsible for protein-protein interaction between PARP and physiological acceptors. PARP may have novel functions, possibly involving its homo- and/or heterodimerization with other nuclear leucine-zipper proteins and its regulation by ADP-ribosylation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Althaus F. R., Richter C. ADP-ribosylation of proteins. Enzymology and biological significance. Mol Biol Biochem Biophys. 1987;37:1–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer P. I., Buki K. G., Hakam A., Kun E. Macromolecular association of ADP-ribosyltransferase and its correlation with enzymic activity. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):17–26. doi: 10.1042/bj2700017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherney B. W., McBride O. W., Chen D. F., Alkhatib H., Bhatia K., Hensley P., Smulson M. E. cDNA sequence, protein structure, and chromosomal location of the human gene for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8370–8374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Franza B. R., Jr Fos and Jun: the AP-1 connection. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradwohl G., Ménissier de Murcia J. M., Molinete M., Simonin F., Koken M., Hoeijmakers J. H., de Murcia G. The second zinc-finger domain of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase determines specificity for single-stranded breaks in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2990–2994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huppi K., Bhatia K., Siwarski D., Klinman D., Cherney B., Smulson M. Sequence and organization of the mouse poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3387–3401. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ittel M. E., Garnier J. M., Jeltsch J. M., Niedergang C. P. Chicken poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase: complete deduced amino acid sequence and comparison with mammalian enzyme sequences. Gene. 1991 Jun 30;102(2):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameshita I., Matsuda M., Nishikimi M., Ushiro H., Shizuta Y. Reconstitution and poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of proteolytically fragmented poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3863–3868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanei-Ishii C., MacMillan E. M., Nomura T., Sarai A., Ramsay R. G., Aimoto S., Ishii S., Gonda T. J. Transactivation and transformation by Myb are negatively regulated by a leucine-zipper structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3088–3092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosaki T., Ushiro H., Mitsuuchi Y., Suzuki S., Matsuda M., Matsuda Y., Katunuma N., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Hirose T. Primary structure of human poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase as deduced from cDNA sequence. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15990–15997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménissier-de Murcia J., Molinete M., Gradwohl G., Simonin F., de Murcia G. Zinc-binding domain of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase participates in the recognition of single strand breaks on DNA. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):229–233. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Klemm J. D., Kim P. S., Alber T. X-ray structure of the GCN4 leucine zipper, a two-stranded, parallel coiled coil. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):539–544. doi: 10.1126/science.1948029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pehrson J. R., Fried V. A. MacroH2A, a core histone containing a large nonhistone region. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1398–1400. doi: 10.1126/science.1529340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Hatakeyama K., Kido T., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S., Ueda K. Cloning of a full-length cDNA encoding bovine thymus poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase: evolutionarily conserved segments and their potential functions. Gene. 1990 Jun 15;90(2):249–254. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90187-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida K., Morita T., Sato T., Ogura T., Yamashita R., Noguchi S., Suzuki H., Nyunoya H., Miwa M., Sugimura T. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA for human fibroblast poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):617–622. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90921-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwelling L. A., Perry W. M. Leucine zipper in human DNA topoisomerase II. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Mar;3(3):603–604. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-3-603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]