Abstract
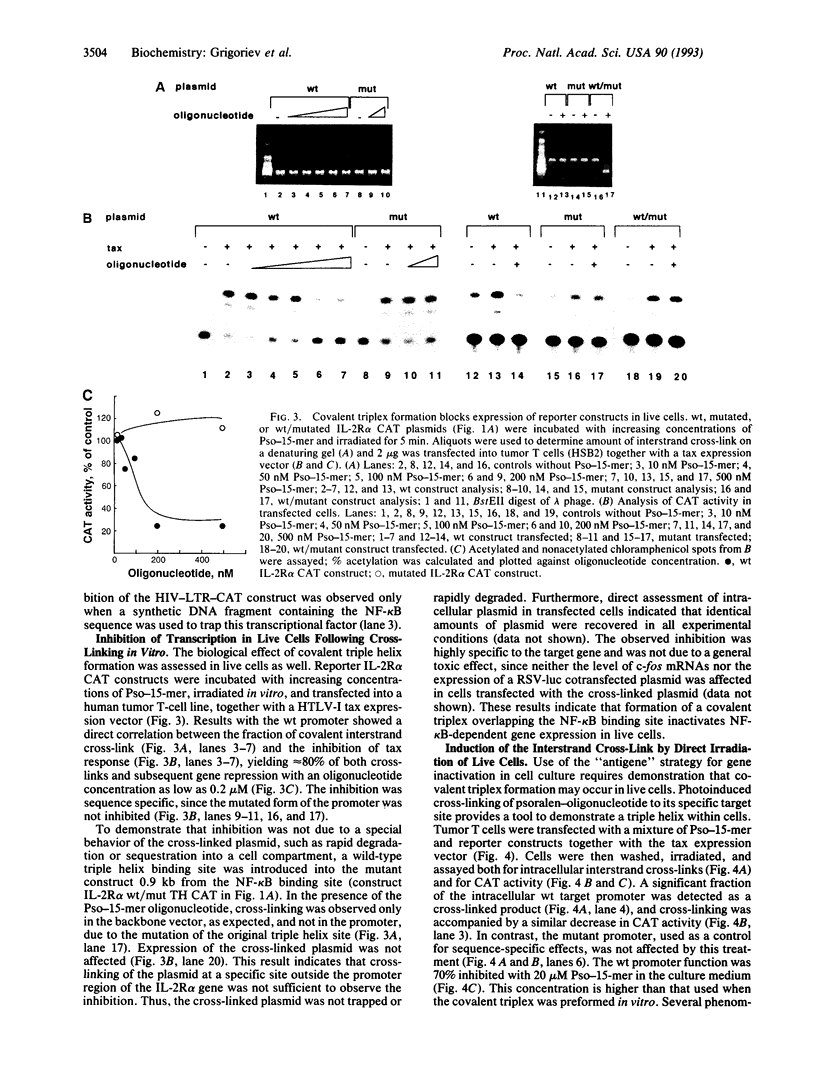
Synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides represent promising tools for gene inhibition in live systems. Triple helix-forming oligonucleotides, which bind to double-stranded DNA, are of special interest since they are targeted to the gene itself rather than to its mRNA product, as in the antisense strategy. Triple helix-forming oligonucleotides can be coupled to DNA-modifying agents and used to introduce modifications in the DNA target in a highly sequence-specific manner. We have recently designed psoralen-oligonucleotide conjugates, which, upon binding to double-stranded DNA sequences via triple helix formation, may be cross-linked in vitro to both strands of the DNA following UV irradiation. A psoralen-oligonucleotide conjugate was targeted to the promoter of the alpha subunit of the interleukin 2 receptor (IL-2R alpha) gene. The triple helix site overlaps the binding site for the transcription factor NF-kappa B, which activates transcription from the IL-2R alpha promoter. After UV irradiation, the oligonucleotide conjugate becomes cross-linked to the target site and inhibits transcription of reporter plasmids transfected in live cells. Inhibition is observed when UV-induced cross-linking occurs both in vitro (before transfection) and in vivo (after transfection). We directly demonstrate that this inhibitory effect is due to triple helix formation at the target site, since a mutant of the promoter, to which oligonucleotide binding was inhibited, was not affected by the psoralen-oligonucleotide conjugate after UV irradiation. In addition, we demonstrate that site-specific cross-linking upstream of the promoter has no effect on transcription.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bielinska A., Shivdasani R. A., Zhang L. Q., Nabel G. J. Regulation of gene expression with double-stranded phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):997–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.2237444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Siekevitz M., Ballard D. W., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. The same inducible nuclear proteins regulates mitogen activation of both the interleukin-2 receptor-alpha gene and type 1 HIV. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimino G. D., Shi Y. B., Hearst J. E. Wavelength dependence for the photoreversal of a psoralen-DNA cross-link. Biochemistry. 1986 May 20;25(10):3013–3020. doi: 10.1021/bi00358a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney M., Czernuszewicz G., Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Hogan M. E. Site-specific oligonucleotide binding represses transcription of the human c-myc gene in vitro. Science. 1988 Jul 22;241(4864):456–459. doi: 10.1126/science.3293213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Halden N. F., Lenardo M. J., Leonard W. J. Functionally distinct NF-kappa B binding sites in the immunoglobulin kappa and IL-2 receptor alpha chain genes. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):466–469. doi: 10.1126/science.2497520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duval-Valentin G., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Specific inhibition of transcription by triple helix-forming oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):504–508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frebourg T., Brison O. Plasmid vectors with multiple cloning sites and cat-reporter gene for promoter cloning and analysis in animal cells. Gene. 1988 May 30;65(2):315–318. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90468-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannangéli C., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Oligodeoxynucleotide-directed photo-induced cross-linking of HIV proviral DNA via triple-helix formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4275–4281. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriev M., Praseuth D., Robin P., Hemar A., Saison-Behmoaras T., Dautry-Varsat A., Thuong N. T., Hélène C., Harel-Bellan A. A triple helix-forming oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugate acts as a transcriptional repressor via inhibition of NF kappa B binding to interleukin-2 receptor alpha-regulatory sequence. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3389–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Brini A. T., Ferris D. K., Robin P., Farrar W. L. In situ detection of a heat-shock regulatory element binding protein using a soluble synthetic enhancer sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 12;17(11):4077–4087. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.11.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C., Toulmé J. J. Specific regulation of gene expression by antisense, sense and antigene nucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 21;1049(2):99–125. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90031-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Woodsworth M. L., Latimer L. J., Morgan A. R. Poly(pyrimidine) . poly(purine) synthetic DNAs containing 5-methylcytosine form stable triplexes at neutral pH. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6603–6614. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonetti J. P., Mechti N., Degols G., Gagnor C., Lebleu B. Intracellular distribution of microinjected antisense oligonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2702–2706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K., Nabel G. J. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):776–778. doi: 10.1038/333776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Wold B., Dervan P. B. Inhibition of DNA binding proteins by oligonucleotide-directed triple helix formation. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):725–730. doi: 10.1126/science.2549631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orson F. M., Thomas D. W., McShan W. M., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Oligonucleotide inhibition of IL2R alpha mRNA transcription by promoter region collinear triplex formation in lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3435–3441. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel E. H., Flint S. J., Kessler D. J., Hogan M. E. Evidence that a triplex-forming oligodeoxyribonucleotide binds to the c-myc promoter in HeLa cells, thereby reducing c-myc mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8227–8231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. S., François J. C., Montenay-Garestier T., Saison-Behmoaras T., Roig V., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific intercalating agents: intercalation at specific sequences on duplex DNA via major groove recognition by oligonucleotide-intercalator conjugates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9198–9202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi M., Guendouz A., Chassignol M., Decout J. L., Lhomme J., Thuong N. T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific photo-induced cross-linking of the two strands of double-helical DNA by a psoralen covalently linked to a triple helix-forming oligonucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5602–5606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trouche D., Robin P., Robillard O., Sassone-Corsi P., Harel-Bellan A. c-fos transcriptional activation by IL-2 in mouse CTL-L2 cells is mediated through two distinct signal transduction pathways converging on the same enhancer element. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2398–2403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trung Le Doan, Perrouault L., Chassignol M., Nguyen T. T., Hélène C. Sequence-targeted chemical modifications of nucleic acids by complementary oligonucleotides covalently linked to porphyrins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8643–8659. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. M., Felber B. K., Paskalis H., Pavlakis G. N. Expression and characterization of the trans-activator of HTLV-III/LAV virus. Science. 1986 Nov 21;234(4779):988–992. doi: 10.1126/science.3490693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]