Abstract
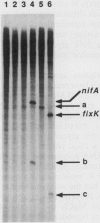
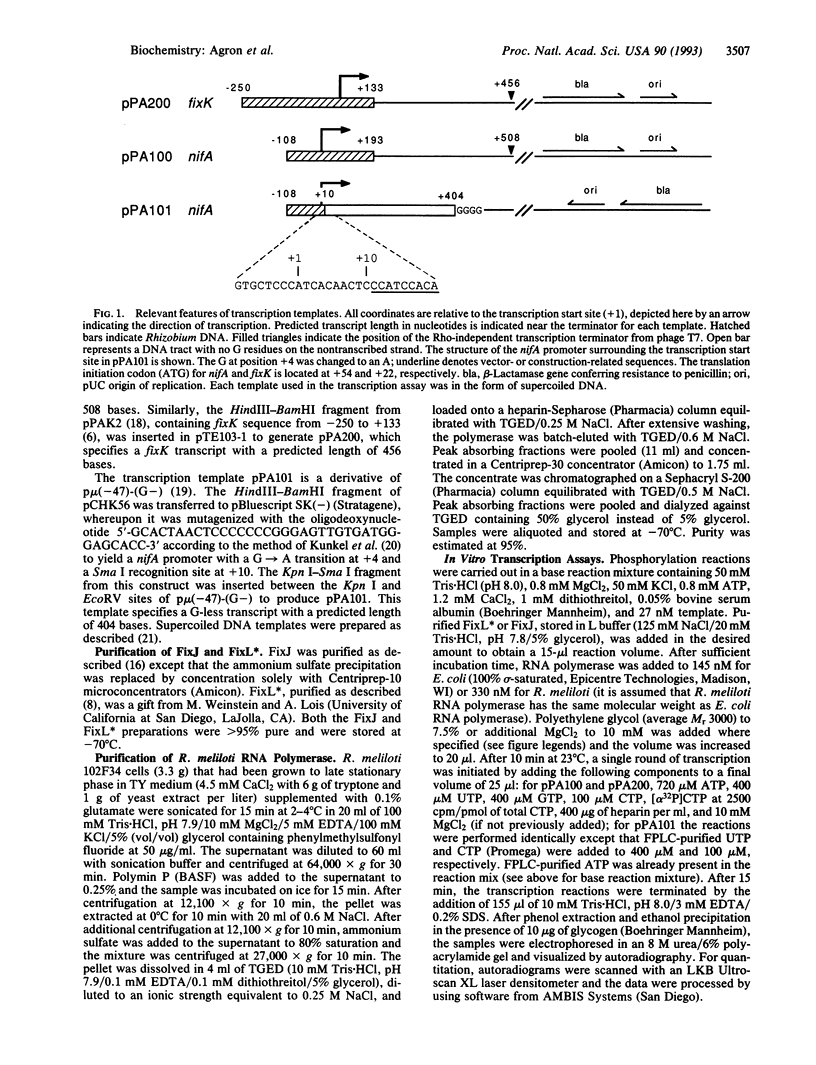
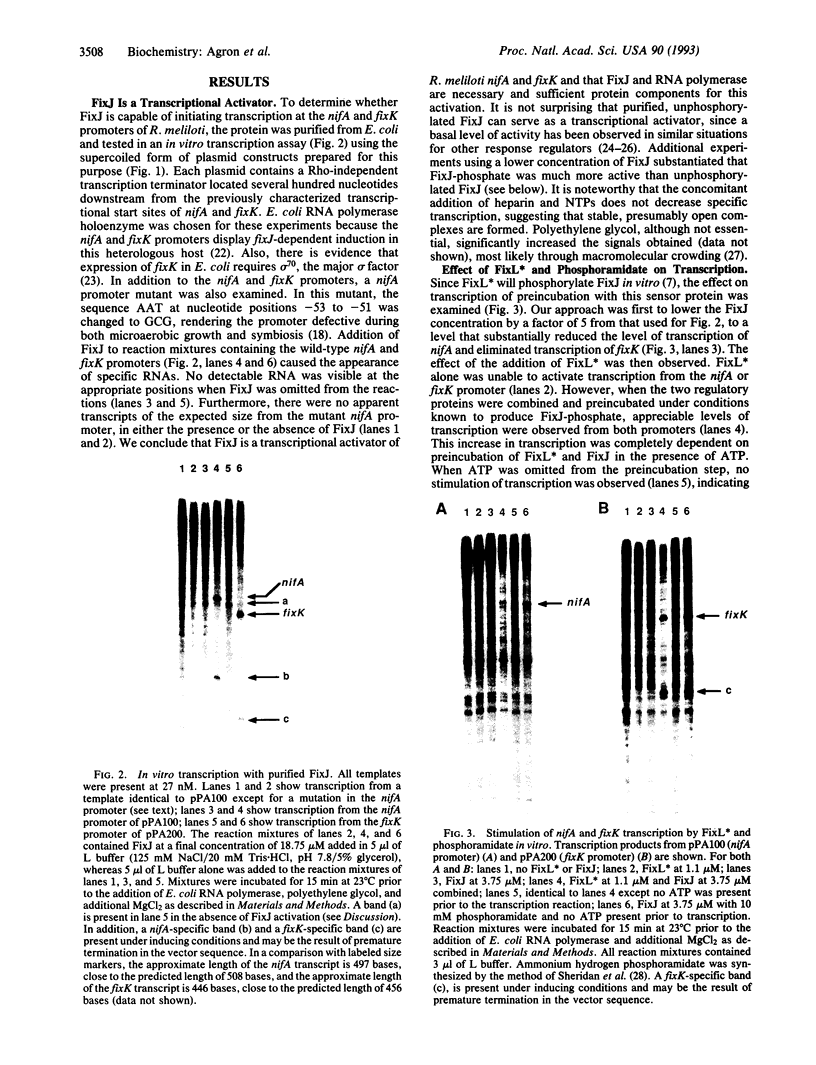
In Rhizobium meliloti, transcription of the key nitrogen-fixation regulatory genes nifA and fixK is induced in response to microaerobiosis through the action of the FixL and FixJ proteins. These two proteins are sensor and regulator homologues, respectively, of a large family of bacterial two-component systems involved in sensing and responding to environmental changes. A soluble, truncated form of the membrane protein FixL, FixL*, has been shown to be a hemoprotein that phosphorylates and dephosphorylates FixJ in response to oxygen tension. Here we use an in vitro transcription system to prove that FixJ is a transcriptional activator of both nifA and fixK and that phosphorylation of FixJ markedly increases its activity. Phosphorylation was achieved either by preincubating FixJ with FixL* and ATP or by exposing FixJ to the inorganic phospho donor ammonium hydrogen phosphoramidate. Both FixJ and FixJ-phosphate formed heparin-resistant complexes under the assay conditions used. Lastly, we were able to show that anaerobiosis, in the presence of FixL* and ATP, greatly stimulates FixJ activity at the nifA promoter with either Escherichia coli or R. meliloti RNA polymerase. This use of atmospheric oxygen to control nifA transcription in vitro represents a reconstitution of a bacterial two-component signal transduction system in its entirety, from effector to ultimate target, by the use of purified components.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agron P. G., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. Mutational analysis of the Rhizobium meliloti nifA promoter. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):4120–4129. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.4120-4129.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthamatten D., Hennecke H. The regulatory status of the fixL- and fixJ-like genes in Bradyrhizobium japonicum may be different from that in Rhizobium meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jan;225(1):38–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00282640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batut J., Daveran-Mingot M. L., David M., Jacobs J., Garnerone A. M., Kahn D. fixK, a gene homologous with fnr and crp from Escherichia coli, regulates nitrogen fixation genes both positively and negatively in Rhizobium meliloti. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batut J., Santero E., Kustu S. In vitro activity of the nitrogen fixation regulatory protein FIXJ from Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5914–5917. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5914-5917.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett L. T., Cannon F., Dean D. R. Nucleotide sequence and mutagenesis of the nifA gene from Azotobacter vinelandii. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):315–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Daveran M. L., Batut J., Dedieu A., Domergue O., Ghai J., Hertig C., Boistard P., Kahn D. Cascade regulation of nif gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):671–683. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Virts E., Palomares A., Kim C. H. The nifA gene of Rhizobium meliloti is oxygen regulated. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3217–3223. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3217-3223.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T., Geiduschek E. P. Defining a bacteriophage T4 late promoter: absence of a "-35" region. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilles-Gonzalez M. A., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. A haemoprotein with kinase activity encoded by the oxygen sensor of Rhizobium meliloti. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):170–172. doi: 10.1038/350170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Regulation of nitrogen fixation genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:567–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertig C., Li R. Y., Louarn A. M., Garnerone A. M., David M., Batut J., Kahn D., Boistard P. Rhizobium meliloti regulatory gene fixJ activates transcription of R. meliloti nifA and fixK genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1736–1738. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1736-1738.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. P., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA by purified Escherichia coli components: core RNA polymerase and the products of glnF, glnG, and glnL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8453–8457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo M. M., Ninfa A. J., Silhavy T. J. A bacterial environmental sensor that functions as a protein kinase and stimulates transcriptional activation. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):598–605. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo M. M., Ninfa A. J., Stock J. B., Silhavy T. J. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of a bacterial transcriptional activator by a transmembrane receptor. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1725–1734. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis T. C., Ring D. M., Daube S. S., von Hippel P. H. "Macromolecular crowding": thermodynamic consequences for protein-protein interactions within the T4 DNA replication complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15160–15167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski P. A., Elmerich C. Involvement of fixLJ in the regulation of nitrogen fixation in Azorhizobium caulinodans. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):665–673. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keener J., Kustu S. Protein kinase and phosphoprotein phosphatase activities of nitrogen regulatory proteins NTRB and NTRC of enteric bacteria: roles of the conserved amino-terminal domain of NTRC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):4976–4980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.4976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipp W., Masepohl B., Pühler A. Identification and mapping of nitrogen fixation genes of Rhodobacter capsulatus: duplication of a nifA-nifB region. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):693–699. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.693-699.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lois A. F., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. The oxygen sensor FixL of Rhizobium meliloti is a membrane protein containing four possible transmembrane segments. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(4):1103–1109. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.4.1103-1109.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lois A. F., Weinstein M., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. Autophosphorylation and phosphatase activities of the oxygen-sensing protein FixL of Rhizobium meliloti are coordinately regulated by oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4370–4375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukat G. S., McCleary W. R., Stock A. M., Stock J. B. Phosphorylation of bacterial response regulator proteins by low molecular weight phospho-donors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):718–722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Shinagawa H., Amemura M., Kimura S., Nakata A., Ishihama A. Regulation of the phosphate regulon of Escherichia coli. Activation of pstS transcription by PhoB protein in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R., Figurski D., Helinski D. R. Physical and genetic studies with restriction endonucleases on the broad host-range plasmid RK2. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Apr 29;152(3):129–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00268809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson E. K., Weinstein M., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. The FixL protein of Rhizobium meliloti can be separated into a heme-binding oxygen-sensing domain and a functional C-terminal kinase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4280–4284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Magasanik B. Covalent modification of the glnG product, NRI, by the glnL product, NRII, regulates the transcription of the glnALG operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5909–5913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa E. G., Stock A., Mowbray S., Stock J. Reconstitution of the bacterial chemotaxis signal transduction system from purified components. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9764–9770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parvin J. D., Sharp P. A. Identification of novel factors which bind specifically to the core promoter of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):22878–22886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D. A., Gillece-Castro B. L., Burlingame A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Phosphorylation site of NtrC, a protein phosphatase whose covalent intermediate activates transcription. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5117–5122. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5117-5122.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokishita S., Yamada H., Aiba H., Mizuno T. Transmembrane signal transduction and osmoregulation in Escherichia coli: II. The osmotic sensor, EnvZ, located in the isolated cytoplasmic membrane displays its phosphorylation and dephosphorylation abilities as to the activator protein, OmpR. J Biochem. 1990 Sep;108(3):488–493. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virts E. L., Stanfield S. W., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. S. Common regulatory elements control symbiotic and microaerobic induction of nifA in Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3062–3065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M., Lois A. F., Monson E. K., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. Isolation of phosphorylation-deficient mutants of the Rhizobium meliloti two-component regulatory protein, FixJ. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Aug;6(15):2041–2049. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]