Abstract
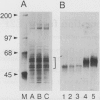
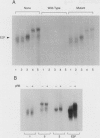
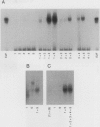
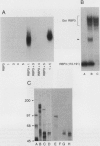
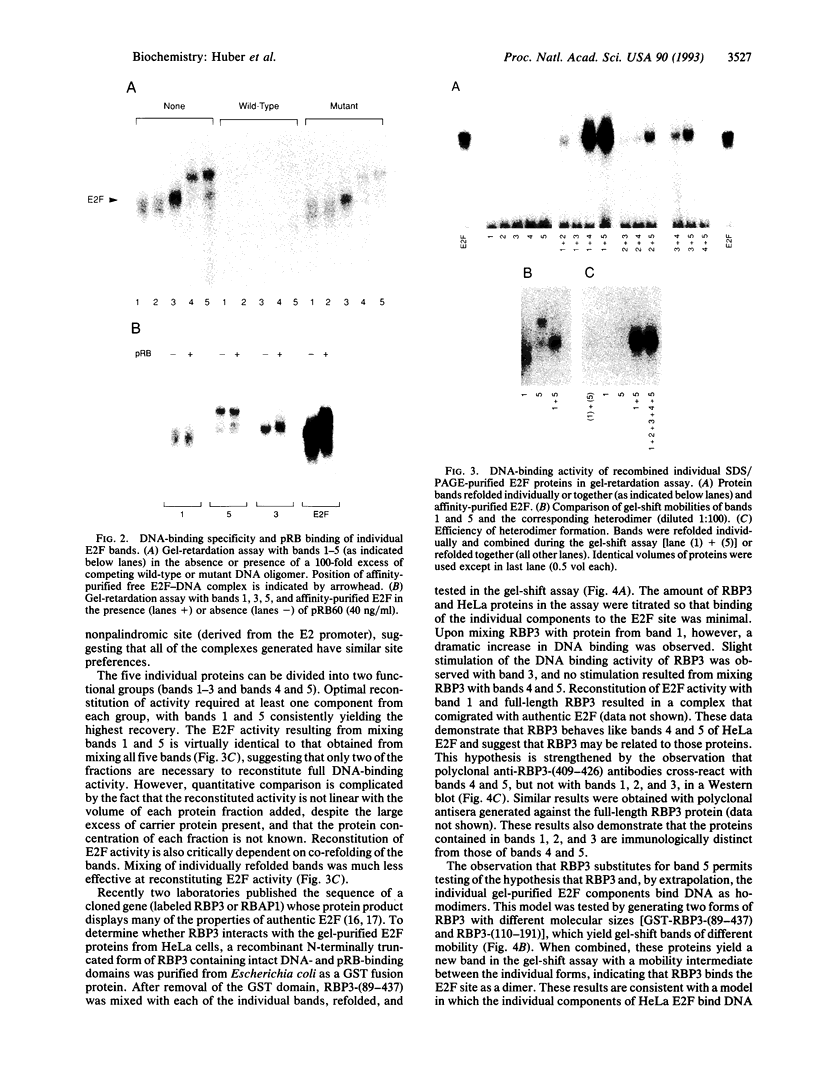
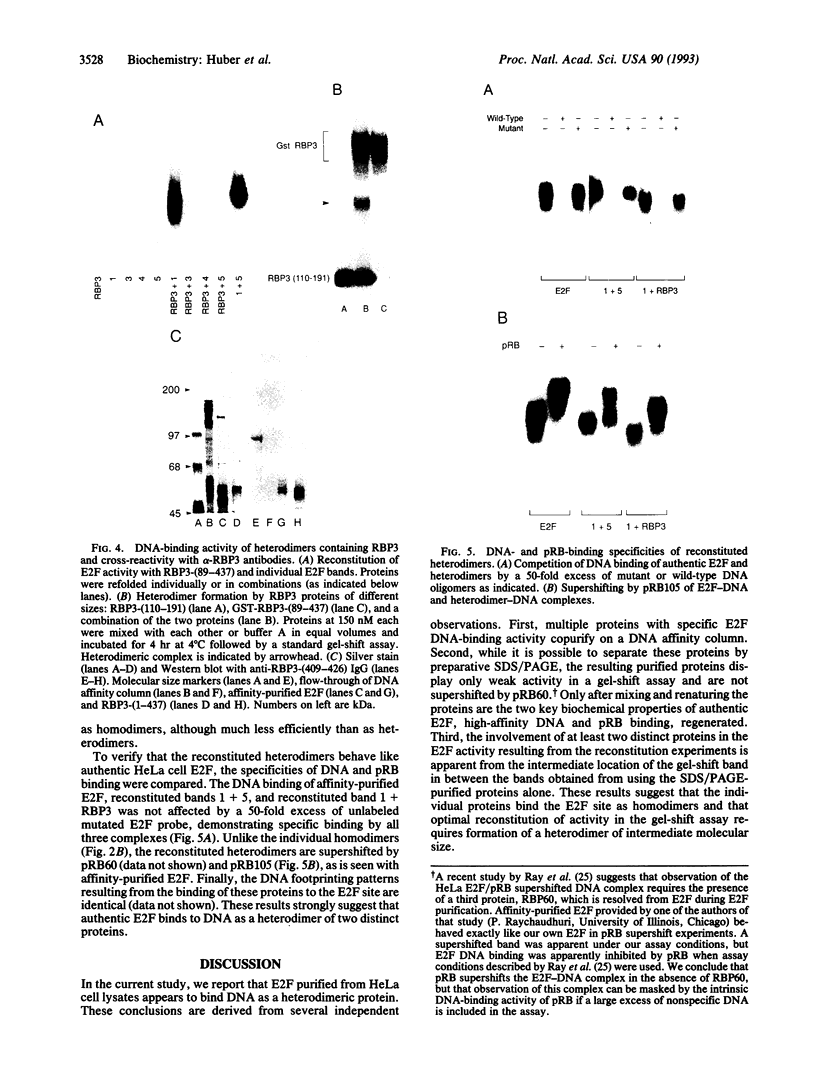
E2F is a mammalian transcription factor that appears to play an important role in cell cycle control. DNA affinity column-purified E2F from HeLa cells reproducibly exhibits multiple protein bands when analyzed by SDS/PAGE. After electrophoretic purification, electroelution, and refolding of the individual protein components, the E2F DNA binding activity of the individual proteins was poor. However, upon mixing the individual components together, a dramatic (100- to 1000-fold) increase in specific DNA binding activity was observed. The five protein bands isolated can be separated into two groups based on apparent molecular mass. Optimal reconstitution of activity requires one of the two proteins found in the group of larger molecular mass (approximately 60 kDa) and one of the three proteins in the smaller-sized group (approximately 50 kDa). The reconstituted heterodimer is identical to authentic affinity-purified E2F by three criteria: DNA-binding specificity, DNA pattern, and binding to the retinoblastoma gene product. A recently cloned protein with E2F-like activity, RBP3/E2F-1, is related to the protein components of the group of larger molecular mass, as determined by Western blot analysis and reconstitution experiments. These data suggest that E2F, like many other transcription factors, binds DNA as an oligomeric complex composed of at least two distinct proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchi S., Weinmann R., Raychaudhuri P. The retinoblastoma protein copurifies with E2F-I, an E1A-regulated inhibitor of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90558-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., La Thangue N. B. Cyclin A and the retinoblastoma gene product complex with a common transcription factor. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):249–251. doi: 10.1038/352249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. C., Azizkhan J. C. Transcription factor E2F is required for efficient expression of the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4994–5002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S. P., Hiebert S., Mudryj M., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90557-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr The T/E1A-binding domain of the retinoblastoma product can interact selectively with a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1073–1082. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90559-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Furukawa Y., Ajchenbaum F., Griffin J. D., Livingston D. M. The retinoblastoma-susceptibility gene product becomes phosphorylated in multiple stages during cell cycle entry and progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1795–1798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G. M., Huber H. E., DeFeo-Jones D., Vuocolo G., Goodhart P. J., Maigetter R. Z., Sanyal G., Oliff A., Heimbrook D. C. Purification and characterization of a functionally homogeneous 60-kDa species of the retinoblastoma gene product. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):7971–7974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Lees J. A., Vidal M., Dyson N., Harlow E., Fattaey A. A cDNA encoding a pRB-binding protein with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90107-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang P. S., Patrick D. R., Edwards G., Goodhart P. J., Huber H. E., Miles L., Garsky V. M., Oliff A., Heimbrook D. C. Protein domains governing interactions between E2F, the retinoblastoma gene product, and human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):953–960. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. Transcriptional regulation by dimerization: two sides to an incestuous relationship. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90207-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marton M. J., Baim S. B., Ornelles D. A., Shenk T. The adenovirus E4 17-kilodalton protein complexes with the cellular transcription factor E2F, altering its DNA-binding properties and stimulating E1A-independent accumulation of E2 mRNA. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2345–2359. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2345-2359.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Devoto S. H., Hiebert S. W., Hunter T., Pines J., Nevins J. R. Cell cycle regulation of the E2F transcription factor involves an interaction with cyclin A. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1243–1253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90019-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Hiebert S. W., Nevins J. R. A role for the adenovirus inducible E2F transcription factor in a proliferation dependent signal transduction pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2179–2184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Control of cellular and viral transcription during adenovirus infection. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;19(4):307–322. doi: 10.3109/10409238609082543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Transcriptional regulation. A closer look at E2F. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):375–376. doi: 10.1038/358375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette M. M., Chen J., Wright W. E., Shay J. W. Complexes containing the retinoblastoma gene product recognize different DNA motifs related to the E2F binding site. Oncogene. 1992 Jun;7(6):1075–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray S. K., Arroyo M., Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P. Identification of a 60-kilodalton Rb-binding protein, RBP60, that allows the Rb-E2F complex to bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4327–4333. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri P., Rooney R., Nevins J. R. Identification of an E1A-inducible cellular factor that interacts with regulatory sequences within the adenovirus E4 promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4073–4081. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02753.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichel R., Neill S. D., Kovesdi I., Simon M. C., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. The adenovirus E4 gene, in addition to the E1A gene, is important for trans-activation of E2 transcription and for E2F activation. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3643–3650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3643-3650.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodkar S., Ewen M., DeCaprio J. A., Morgan J., Livingston D. M., Chittenden T. The transcription factor E2F interacts with the retinoblastoma product and a p107-cyclin A complex in a cell cycle-regulated manner. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stammers D. K., Tisdale M., Court S., Parmar V., Bradley C., Ross C. K. Rapid purification and characterisation of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and RNaseH engineered to incorporate a C-terminal tripeptide alpha-tubulin epitope. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 3;283(2):298–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80613-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Prater C. A., Dean D. C. Retinoblastoma protein switches the E2F site from positive to negative element. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):259–261. doi: 10.1038/358259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee A. S., Raychaudhuri P., Jakoi L., Nevins J. R. The adenovirus-inducible factor E2F stimulates transcription after specific DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):578–585. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]