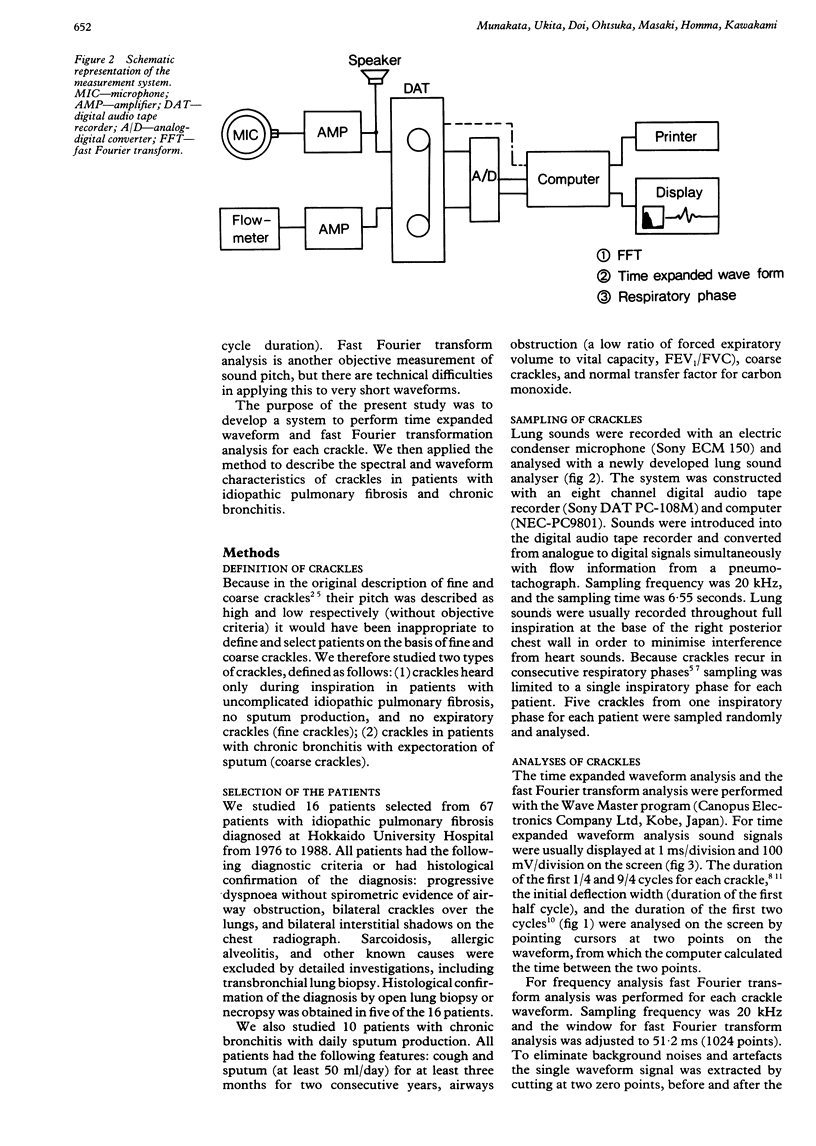
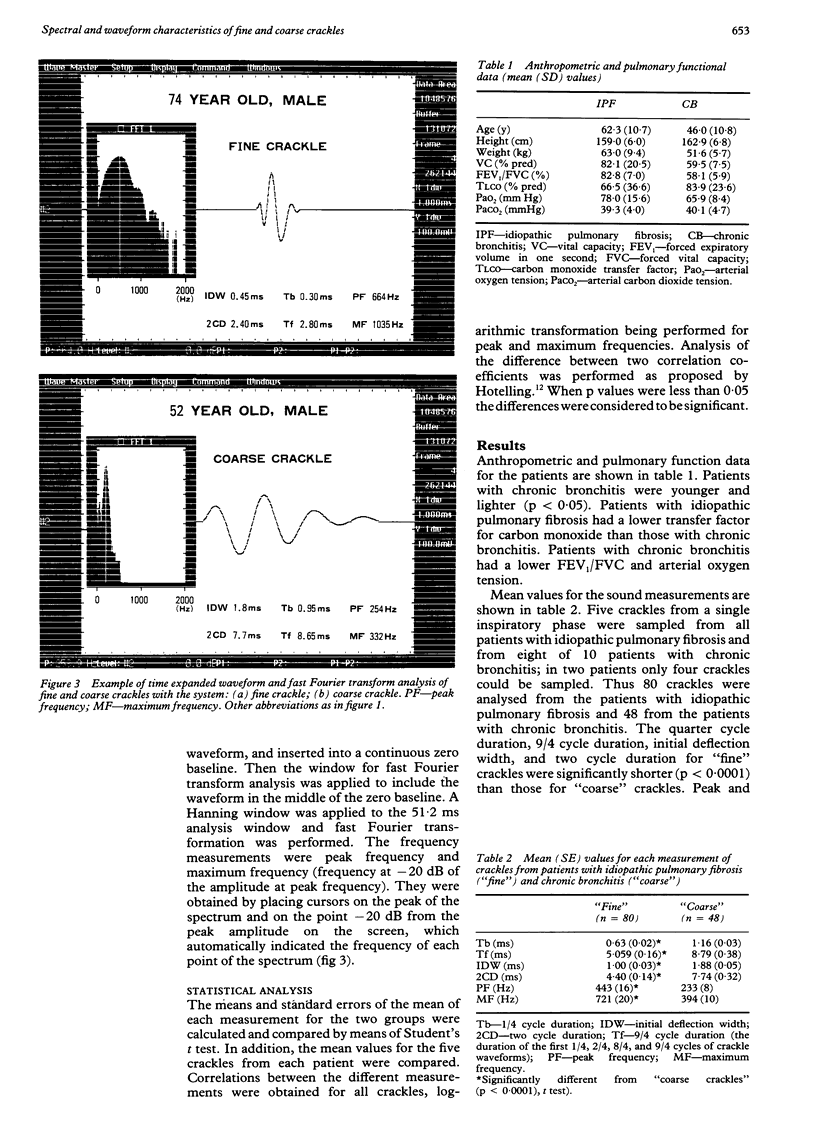
Abstract
Two acoustically different types of lung crackles, fine and coarse, occur in different pathophysiological conditions. To differentiate these crackles from objective characteristics of frequency information, crackles were recorded from 16 patients with pulmonary fibrosis judged clinically to have "fine" crackles and from 10 with chronic bronchitis who had mainly "coarse" crackles. Time expanded waveforms (1/4 cycle duration, initial deflection width, two cycle duration, and 9/4 cycle duration; duration of the first 1/4, 2/4, 8/4, and 9/4 cycles of crackle waveforms) were examined and fast Fourier transform analysis (peak and maximum frequencies) was performed. All waveform measurements for fine crackles were significantly smaller than those for coarse crackles. Peak and maximum frequencies for fine crackles were significantly higher than those for coarse crackles. Although there was some overlap in these values for individual crackles between the two groups when average values of these measurements were calculated for each patient, there was no overlap between fine and coarse crackles and the two groups could be clearly separated. Log peak frequency and log maximum frequency correlated better with 9/4 cycle duration (r = 0.85, 0.84) and two cycle duration (r = 0.87, 0.86) than with 1/4 cycle duration (r = 0.66, 0.77) or initial deflection width (r = 0.67, 0.79). Early and late segments of crackles have different characteristics, probably related to the origin of the sound and the resonance of the lung respectively. These results suggest that spectral and waveform characteristics may help to improve the accuracy of pulmonary auscultation and increase knowledge of how crackles are generated.
Full text
PDF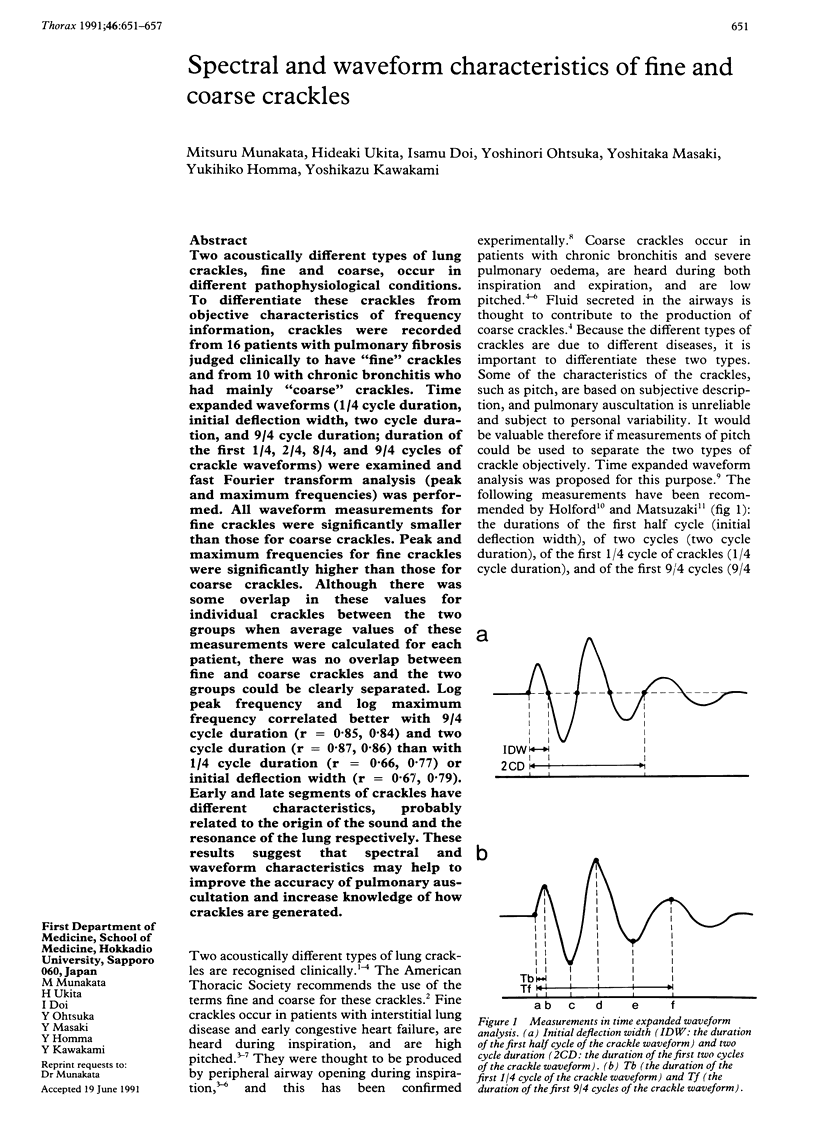
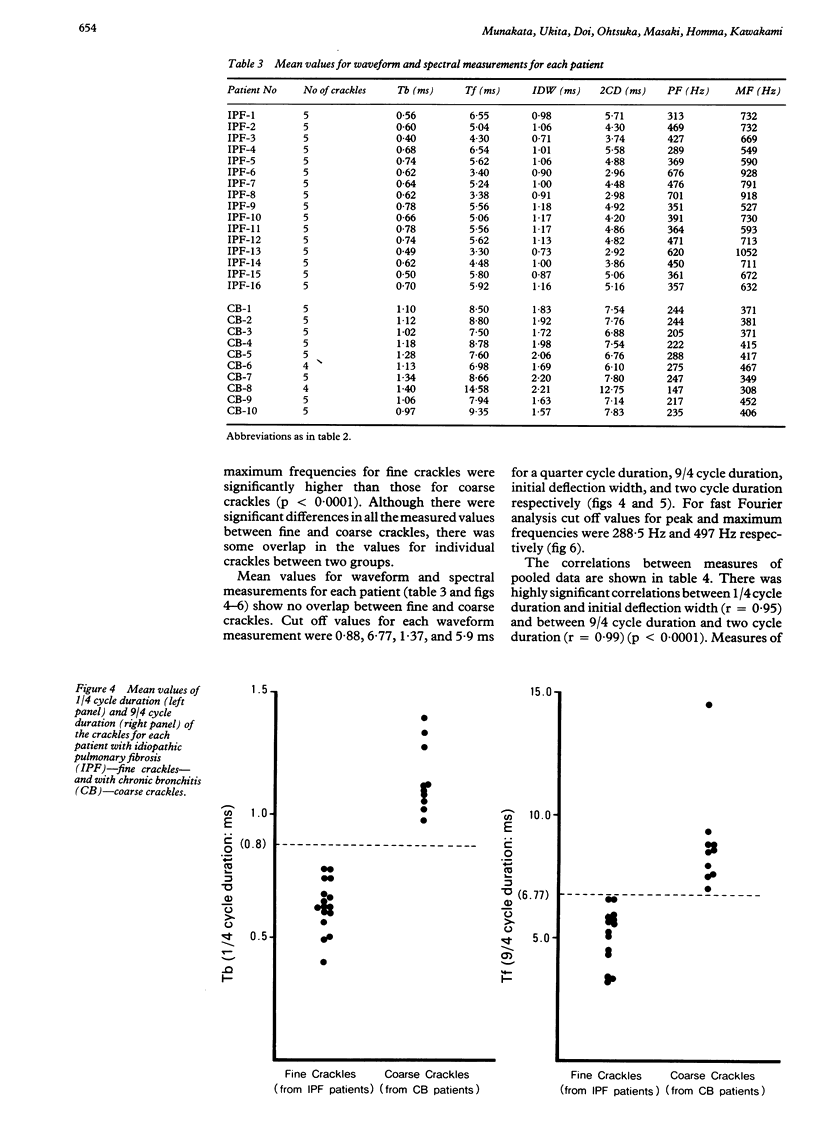
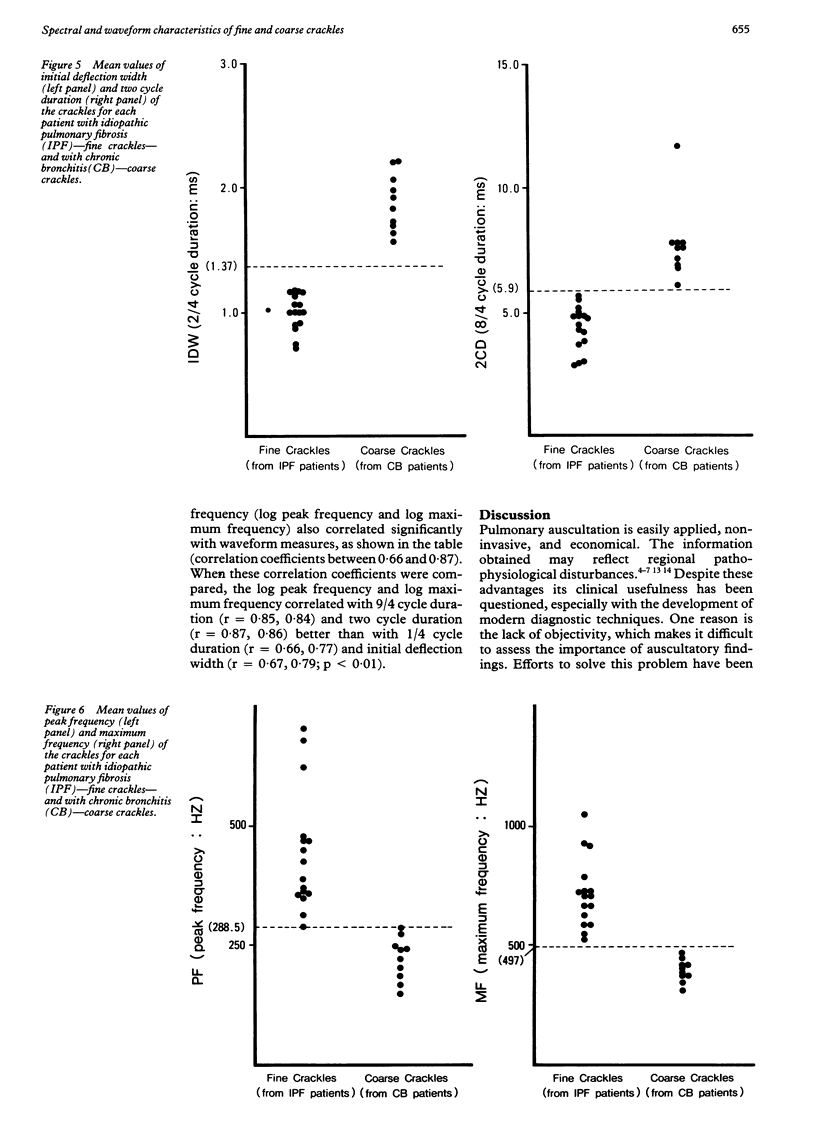


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Forgacs P. Crackles and wheezes. Lancet. 1967 Jul 22;2(7508):203–205. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgacs P. Gravitational stress in lung disease. Br J Dis Chest. 1974 Jan;68(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgacs P. The functional basis of pulmonary sounds. Chest. 1978 Mar;73(3):399–405. doi: 10.1378/chest.73.3.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma Y., Matsuzaki M., Ogasawara H., Munakata M. Phonopneumograph possible for real-time tracing. Comput Biomed Res. 1985 Dec;18(6):502–509. doi: 10.1016/0010-4809(85)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loudon R., Murphy R. L., Jr Lung sounds. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;130(4):663–673. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.4.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loudon R., Murphy R. L., Jr Lung sounds. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;130(4):663–673. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.4.663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzaki M., Homma Y. [A new method for classifying discontinuous adventitious lung sounds]. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1983 Feb;21(2):134–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKUSICK V. A., JENKINS J. T., WEBB G. N. The acoustic basis of the chest examination; studies by means of sound spectrography. Am Rev Tuberc. 1955 Jul;72(1):12–34. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1955.72.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Kinoshita K., Morinari H., Shiraishi T., Koike S., Murao S. Waveform and spectral analysis of crackles. Thorax. 1980 Nov;35(11):843–850. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.11.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munakata M., Homma Y., Matsuzaki M., Ogasawara H., Tanimura K., Kusaka H., Kawakami Y. Production mechanism of crackles in excised normal canine lungs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Sep;61(3):1120–1125. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.61.3.1120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. L. Auscultation of the lung: past lessons, future possibilities. Thorax. 1981 Feb;36(2):99–107. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.2.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. L., Jr, Holford S. K., Knowler W. C. Visual lung-sound characterization by time-expanded wave-form analysis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Apr 28;296(17):968–971. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197704282961704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath A. R., Capel L. H. Inspiratory crackles and mechanical events of breathing. Thorax. 1974 Nov;29(6):695–698. doi: 10.1136/thx.29.6.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walshaw M. J., Nisar M., Pearson M. G., Calverley P. M., Earis J. E. Expiratory lung crackles in patients with fibrosing alveolitis. Chest. 1990 Feb;97(2):407–409. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]