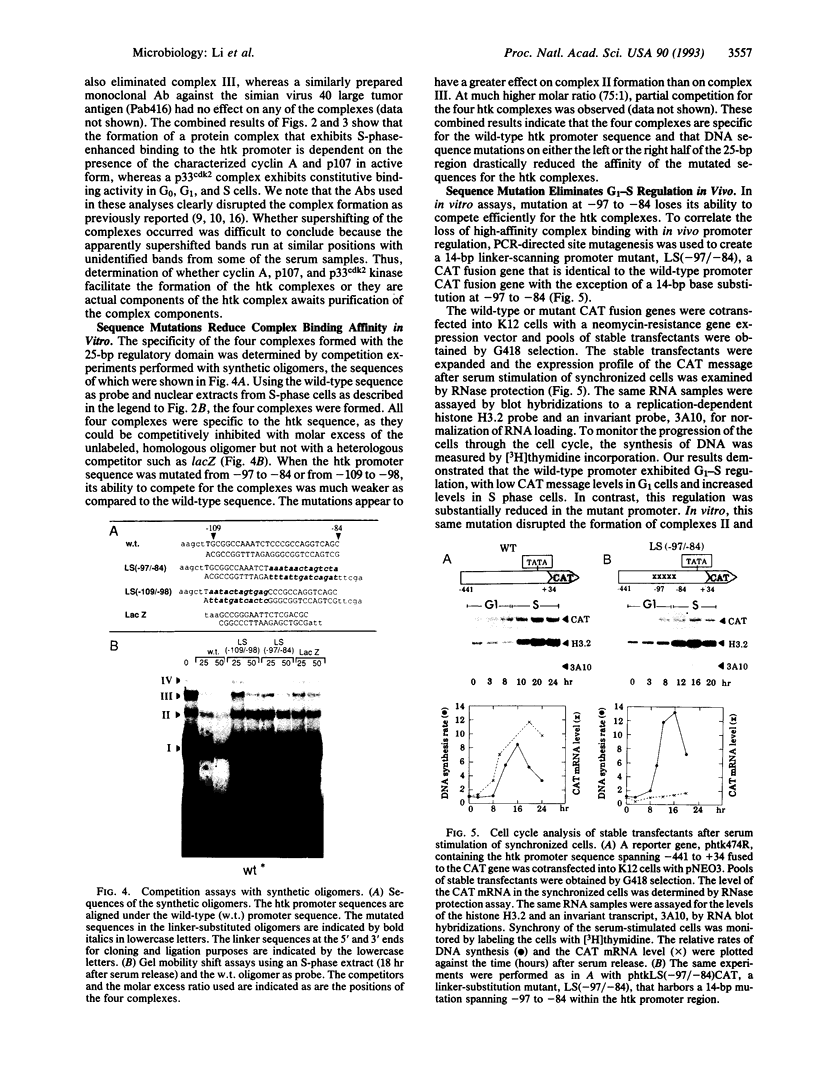
Abstract
The cyclins are an extensive family of proteins whose cell cycle-dependent synthesis is postulated to control multiple events during the cell cycle. The synthesis of A-type cyclins begins at the start of S phase. In mammalian cells, association with the cdc-type kinases suggests that cyclin A complexes are important for DNA replication and regulating other DNA-bound substrates required for S phase. We report here that a 25-bp promoter element previously shown to be important for the G1-S activation of the human thymidine kinase (htk) promoter in growth-stimulated cells is a cellular target of cyclin A and the p33cdk2 complexes. Though the p33cdk2 and other nuclear factor complexes exhibit constitutive binding to the htk G1-S regulatory domain, the binding activity of a cyclin A/p107 protein complex is greatly enhanced when the cells enter S phase, correlating with the increase in the tk mRNA levels and the replication of DNA. The binding activity of the cyclin A complex is maintained throughout S phase. Mutation of the DNA sequences on either half of the 25-bp protein binding site results in the loss of its ability to compete efficiently in vitro for the htk complexes, including that of cyclin A-containing complex. The loss of high-affinity binding for the htk complexes also substantially reduces the S-phase regulation of the htk promoter in vivo. Our results support the hypothesis that a cyclin A complex, in association with the p33cdk2 kinase, mediates the S-phase-regulated transcription of the htk promoter in growth-stimulated cells.
Full text
PDF

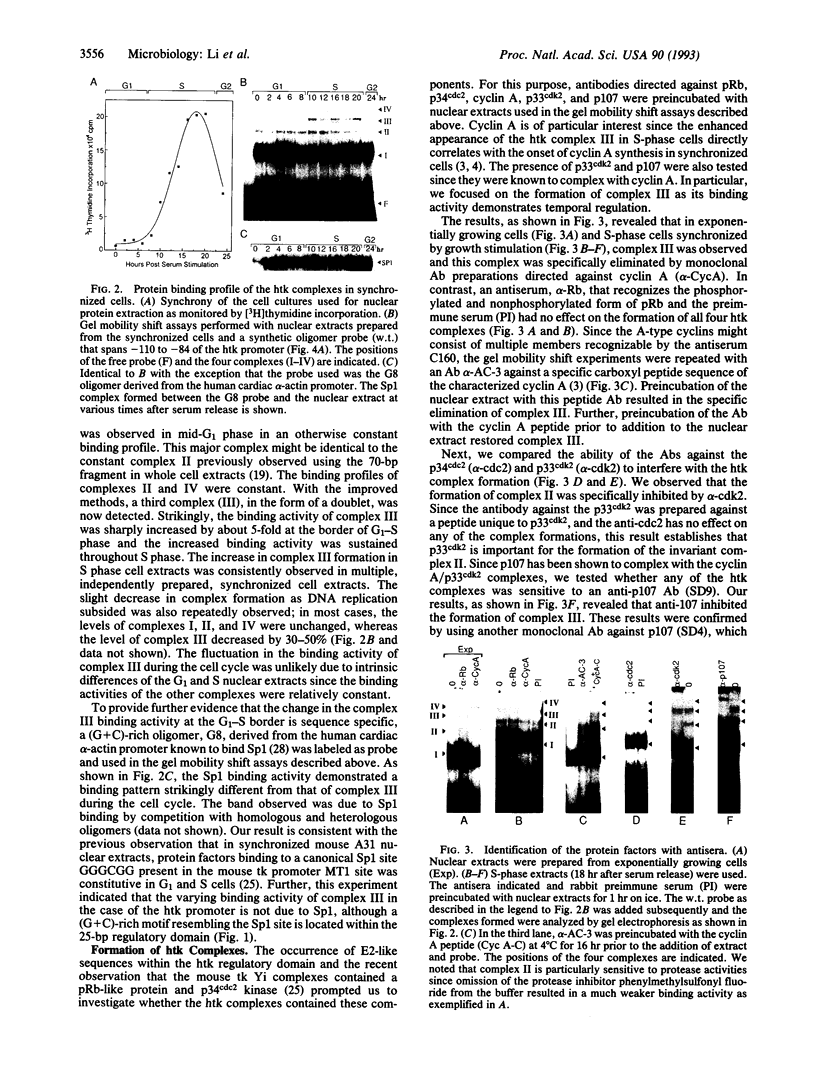

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcot S. S., Flemington E. K., Deininger P. L. The human thymidine kinase gene promoter. Deletion analysis and specific protein binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2343–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artishevsky A., Delegeane A. M., Lee A. S. Use of a cell cycle mutant to delineate the critical period for the control of histone mRNA levels in the mammalian cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2364–2369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artishevsky A., Wooden S., Sharma A., Resendez E., Jr, Lee A. S. Cell-cycle regulatory sequences in a hamster histone promoter and their interactions with cellular factors. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):823–827. doi: 10.1038/328823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L., Faha B., Dembski M., Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Dyson N. Independent binding of the retinoblastoma protein and p107 to the transcription factor E2F. Nature. 1992 Jan 9;355(6356):176–179. doi: 10.1038/355176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. D., Ottavio L., Travali S., Lipson K. E., Baserga R. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3289–3296. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoto S. H., Mudryj M., Pines J., Hunter T., Nevins J. R. A cyclin A-protein kinase complex possesses sequence-specific DNA binding activity: p33cdk2 is a component of the E2F-cyclin A complex. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou Q. P., Fridovich-Keil J. L., Pardee A. B. Inducible proteins binding to the murine thymidine kinase promoter in late G1/S phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1157–1161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou Q. P., Markell P. J., Pardee A. B. Thymidine kinase transcription is regulated at G1/S phase by a complex that contains retinoblastoma-like protein and a cdc2 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3256–3260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G. Cell cycle control in eukaryotes: molecular mechanisms of cdc2 activation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Lees E., Reed S. I. Association of human cyclin E with a periodic G1-S phase protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1958–1961. doi: 10.1126/science.1329201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Sazer S., Tjian R., Schimke R. T. Transcription factor Sp1 recognizes a DNA sequence in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):246–248. doi: 10.1038/319246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Richman R., Hall F. L., Williams R. T., Lodgson N., Harper J. W. CDK2 encodes a 33-kDa cyclin A-associated protein kinase and is expressed before CDC2 in the cell cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2907–2911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich-Keil J. L., Gudas J. M., Dou Q. P., Bouvard I., Pardee A. B. Growth-responsive expression from the murine thymidine kinase promoter: genetic analysis of DNA sequences. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Feb;2(2):67–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard F., Strausfeld U., Fernandez A., Lamb N. J. Cyclin A is required for the onset of DNA replication in mammalian fibroblasts. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1169–1179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90293-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudas J. M., Knight G. B., Pardee A. B. Nuclear posttranscriptional processing of thymidine kinase mRNA at the onset of DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4705–4709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Lipp M., Nevins J. R. E1A-dependent trans-activation of the human MYC promoter is mediated by the E2F factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F. G1 events and the regulation of genes for S-phase enzymes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;4(2):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. K., Lee A. S. Identification of a 70-base-pair cell cycle regulatory unit within the promoter of the human thymidine kinase gene and its interaction with cellular factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2296–2302. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. K., Lee A. S. Identification of a protein-binding site in the promoter of the human thymidine kinase gene required for the G1-S-regulated transcription. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2723–2727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. K., Wells S., Lau Y. F., Lee A. S. Sequences contained within the promoter of the human thymidine kinase gene can direct cell-cycle regulation of heterologous fusion genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5894–5898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Giordano A., Desai D., Yamashita K., Harper J. W., Elledge S., Nishimoto T., Morgan D. O., Franza B. R., Roberts J. M. Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.1388288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson K. E., Chen S. T., Koniecki J., Ku D. H., Baserga R. S-phase-specific regulation by deletion mutants of the human thymidine kinase promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6848–6852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Slansky J. E., McMahon S. L., Knuth M. W., Farnham P. J. The HIP1 binding site is required for growth regulation of the dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1054–1063. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihara K., Cao X. R., Yen A., Chandler S., Driscoll B., Murphree A. L., T'Ang A., Fung Y. K. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of phosphorylation of the human retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1300–1303. doi: 10.1126/science.2588006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Devoto S. H., Hiebert S. W., Hunter T., Pines J., Nevins J. R. Cell cycle regulation of the E2F transcription factor involves an interaction with cyclin A. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1243–1253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90019-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Hiebert S. W., Nevins J. R. A role for the adenovirus inducible E2F transcription factor in a proliferation dependent signal transduction pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2179–2184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeve G. S., Sharma A., Lee A. S. Identification of a 10-base pair protein binding site in the promoter of the hamster H3.2 gene required for the S phase dependent increase in transcription and its interaction with a Jun-like nuclear factor. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Dec;3(12):919–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeve G. S., Sharma A., Lee A. S. Temporal events regulating the early phases of the mammalian cell cycle. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;3(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90150-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Verde F., Ansorge W., Draetta G. Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):961–971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05135.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J. Cell proliferation and control. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;4(2):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehl H. H., Conrad S. E. Identification of a G1-S-phase-regulated region in the human thymidine kinase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3834–3837. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli V., Webster K. A., Kedes L. Muscle-specific expression of the cardiac alpha-actin gene requires MyoD1, CArG-box binding factor, and Sp1. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1811–1822. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodkar S., Ewen M., DeCaprio J. A., Morgan J., Livingston D. M., Chittenden T. The transcription factor E2F interacts with the retinoblastoma product and a p107-cyclin A complex in a cell cycle-regulated manner. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. J., Ito M., Conrad S. E. Evidence for transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of the cellular thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1156–1163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Meyerson M. Isolation of the human cdk2 gene that encodes the cyclin A- and adenovirus E1A-associated p33 kinase. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):174–177. doi: 10.1038/353174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade M., Kowalik T. F., Mudryj M., Huang E. S., Azizkhan J. C. E2F mediates dihydrofolate reductase promoter activation and multiprotein complex formation in human cytomegalovirus infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4364–4374. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]