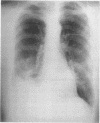
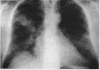
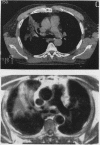
Abstract
A case of exogenous lipoid pneumonia was documented by computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Although strongly suggesting the presence of fat on T1 weighted images, magnetic resonance does not produce images specific for this condition. Computed tomography is the best imaging modality for its diagnosis.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carrillon Y., Tixier E., Revel D., Cordier J. F. MR diagnosis of lipoid pneumonia. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1988 Sep-Oct;12(5):876–877. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198809010-00031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi R. R., Cholankeril J. V. Computed tomography in lipoid pneumonia. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1985 Jan-Feb;9(1):211–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER J. C., ADLER D. I., FULLER D. N. Foreign body granulomata of the lungs due to liquid paraffin. Thorax. 1955 Jun;10(2):157–170. doi: 10.1136/thx.10.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler P. S., Stitik F. P., Hutchins G. M., Klinefelter H. F., Siegelman S. S. Diagnosis of lipoid pneumonia by computed tomography. JAMA. 1981 Jan 2;245(1):65–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]