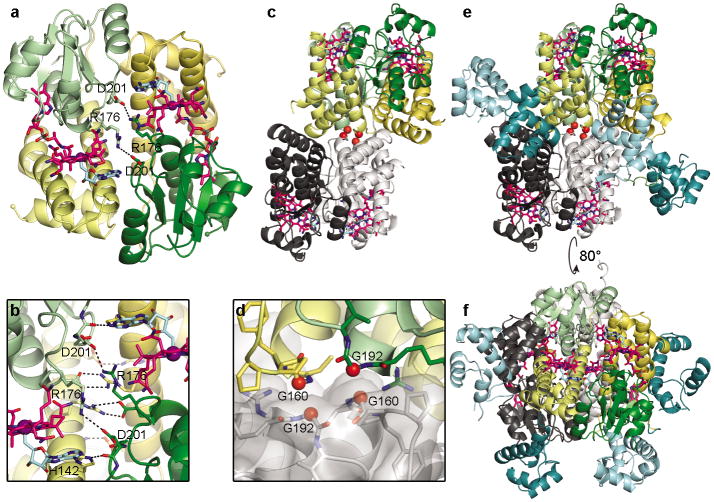
Figure 3.
CarH oligomerization. (a) CarH protomers arranged in a head-to-tail dimer, colored by domain (helix bundle: yellow; Cbl-binding domain: green) with left protomer shown in lighter colors. AdoCbl shown as in Fig. 2a. DNA-binding domains hidden for clarity. (b) Close-up of selected residues at dimer interface. (c) Core of CarH tetramer, assembled from two head-to-tail dimers. Top dimer is colored as in (a) and bottom dimer is colored in black and gray. Gly160 and Gly192 at the dimer-dimer interface are shown as red spheres. Structure is from a sample of CarH that degraded during crystallization and lacks the DNA-binding domains (crystal form 2, see methods). (d) Close-up of Gly160 and Gly192 (red spheres) from two protomers at the dimer-dimer interface. (e) Tetramer of full-length CarH including DNA-binding domains (crystal form 3), colored as in (c). DNA-binding domains of colored dimer are shown in dark cyan, those of gray dimer are shown in light cyan. (f) Additional view of CarH tetramer, revealing how DNA-binding domains are positioned on the protein surface.