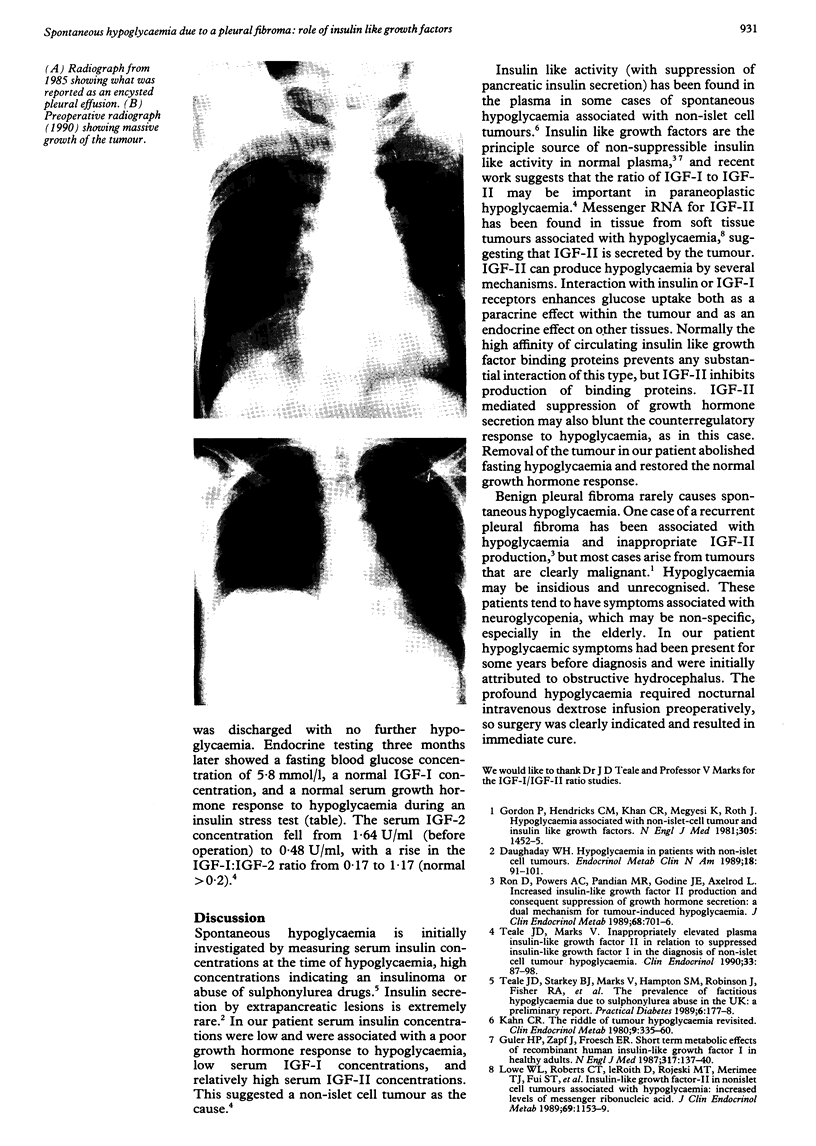
Abstract
A 64 year old woman with a long history of "drop attacks" and dizzy spells was found to have spontaneous hypoglycaemia. A slowly enlarging pleural mass had been present for at least five years. At thoracotomy the mass (weight 1.7 kg) was excised and the hypoglycaemia ceased. Histologically the tumour was a pleural fibroma, with no features of malignancy. Endocrine tests before surgery showed a subnormal growth hormone response to spontaneous hypoglycaemia, a reduced concentration of serum insulin like growth factor I (IGF-I), and an inappropriately high concentration of serum insulin like growth factor II (IGF-II). After resection of the tumour the growth hormone response to insulin induced hypoglycaemia and the IGF-I and IGF-II concentrations were normal. These data suggest that the hypoglycaemia was due to production of IGF-II by the tumour, causing increased glucose utilisation and an impaired growth hormone counterregulatory response to hypoglycaemia.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daughaday W. H. Hypoglycemia in patients with non-islet cell tumors. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1989 Mar;18(1):91–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Hendricks C. M., Kahn C. R., Megyesi K., Roth J. Hypoglycemia associated with non-islet-cell tumor and insulin-like growth factors. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1452–1455. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler H. P., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Short-term metabolic effects of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I in healthy adults. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):137–140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R. The riddle of tumour hypoglycaemia revisited. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jul;9(2):335–360. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(80)80037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe W. L., Jr, Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D., Rojeski M. T., Merimee T. J., Fui S. T., Keen H., Arnold D., Mersey J., Gluzman S. Insulin-like growth factor-II in nonislet cell tumors associated with hypoglycemia: increased levels of messenger ribonucleic acid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Dec;69(6):1153–1159. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-6-1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Powers A. C., Pandian M. R., Godine J. E., Axelrod L. Increased insulin-like growth factor II production and consequent suppression of growth hormone secretion: a dual mechanism for tumor-induced hypoglycemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Apr;68(4):701–706. doi: 10.1210/jcem-68-4-701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teale J. D., Marks V. Inappropriately elevated plasma insulin-like growth factor II in relation to suppressed insulin-like growth factor I in the diagnosis of non-islet cell tumour hypoglycaemia. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1990 Jul;33(1):87–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1990.tb00469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



