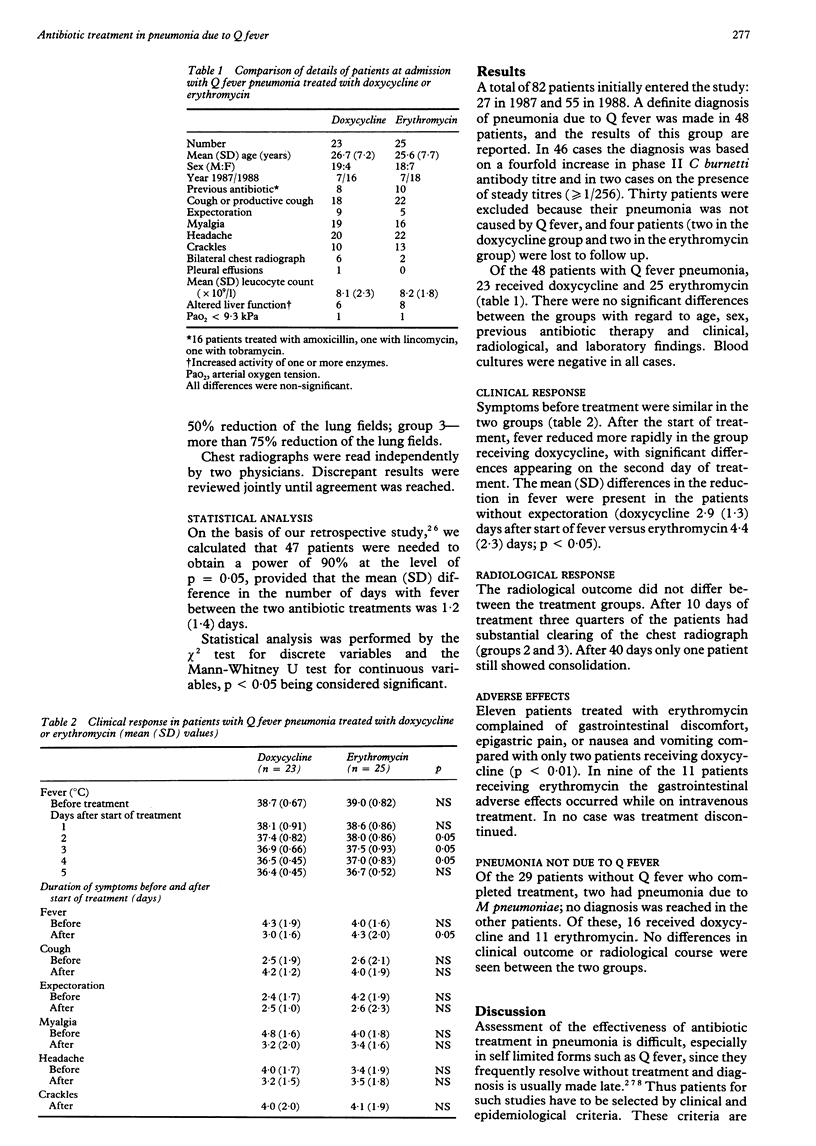
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Whether Q fever responds better to doxycycline or erythromycin is unknown. METHODS: The efficacy of doxycycline and erythromycin in the treatment of pneumonia due to Q fever was assessed in a prospective, randomised, double blind study of 82 patients with a diagnosis of pneumonia and features suggestive of Q fever infection; 48 proved to have Q fever. Of the 48, 23 received doxycycline 100 mg twice a day and 25 patients received erythromycin 500 mg six hourly, both for 10 days. RESULTS: Both treatment groups had similar demographic characteristics. Fever showed a more rapid reduction in the doxycycline group (3(1.6) days versus 4.3(2) days). Side effects were observed in two patients receiving doxycycline compared with 11 patients receiving erythromycin (p less than 0.01). No differences were observed in other clinical or radiological measures. By day 40 the chest radiograph was normal in 47 of 48 patients. CONCLUSION: The results demonstrate the self limiting and benign nature of most cases of pneumonia due to Q fever. Doxycycline was more effective than erythromycin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berntsson E., Blomberg J., Lagergård T., Trollfors B. Etiology of community-acquired pneumonia in patients requiring hospitalization. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;4(3):268–272. doi: 10.1007/BF02013650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK W. H., LENNETTE E. H., MEIKLEJOHN G. Q fever in California. III. Aureomycin in the therapy of Q fever. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1951 Feb;87(2):204–217. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1951.03810020026004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carné X., Moreno V., Porta Serra M., Velilla E. El cálculo del número de pacientes necesarios en la planificación de un estudio clínico. Med Clin (Barc) 1989 Jan 21;92(2):72–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow J. W., Yu V. L. Antibiotic studies in pneumonia. Pitfalls in interpretation and suggested soluions. Chest. 1989 Sep;96(3):453–456. doi: 10.1378/chest.96.3.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Angelo L. J., Hetherington R. Q fever treated with erythromycin. Br Med J. 1979 Aug 4;2(6185):305–306. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6185.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis M. E., Dunbar E. M. In vivo response of acute Q fever to erythromycin. Thorax. 1982 Nov;37(11):867–868. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.11.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macklin J., Barden R., Coles S. Comparison of two oral forms of erythromycin in the treatment of acute respiratory tract infections. A multicentre general practice study. J Int Med Res. 1989 May-Jun;17(3):287–294. doi: 10.1177/030006058901700312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrie T. J., Haldane E. V., Faulkner R. S., Kwan C., Grant B., Cook F. The importance of Coxiella burnetii as a cause of pneumonia in Nova Scotia. Can J Public Health. 1985 Jul-Aug;76(4):233–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL O. W., KENNEDY K. P., McIVER M., SILVERSTONE H. Tetracycline in the treatment of "Q" fever. Australas Ann Med. 1962 Aug;11:184–188. doi: 10.1111/imj.1962.11.3.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer L. A., Fishbein D. B., McDade J. E. Q fever: current concepts. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Sep-Oct;9(5):935–946. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.5.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobradillo V., Ansola P., Baranda F., Corral C. Q fever pneumonia: a review of 164 community-acquired cases in the Basque country. Eur Respir J. 1989 Mar;2(3):263–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelman D. W. Q fever: a study of 111 consecutive cases. Med J Aust. 1982 Jun 26;1(13):547-8, 551, 553. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1982.tb124169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


