Abstract
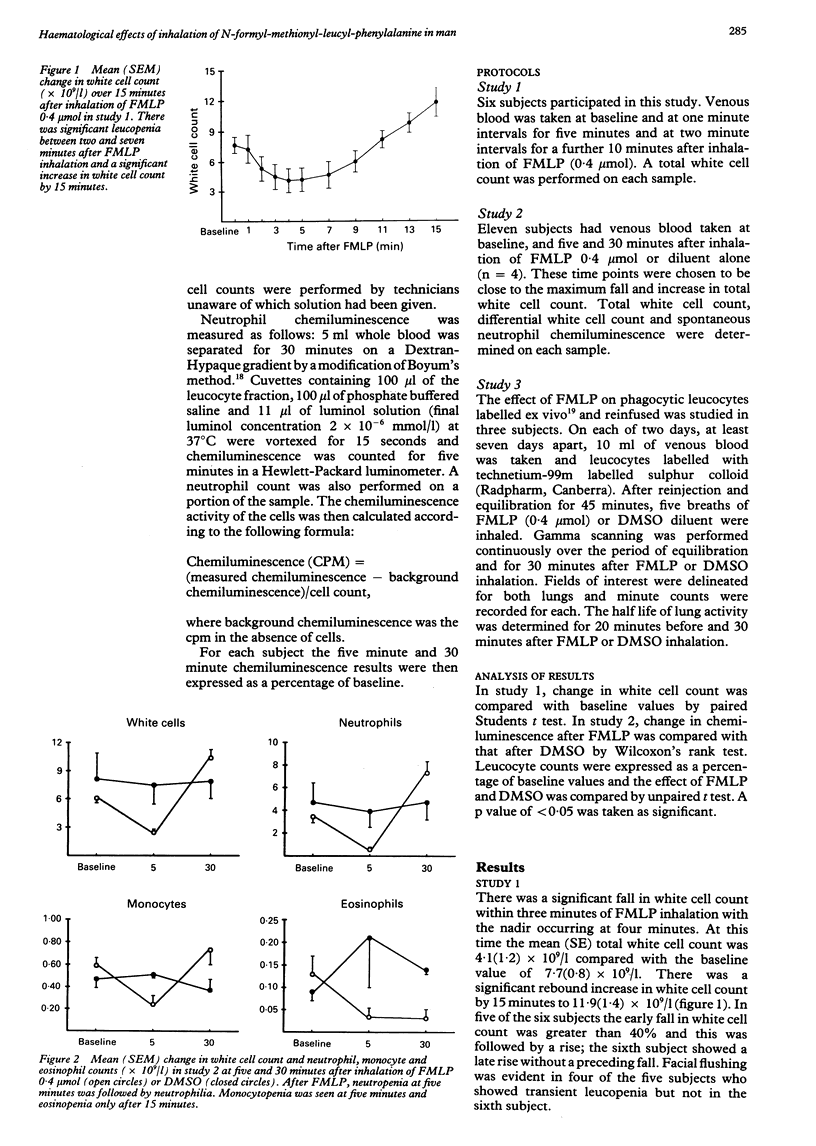
BACKGROUND: N-Formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP) is a bacterial oligopeptide which stimulates neutrophil chemotaxis, degranulation and superoxide generation. Inhalation of FMLP produces bronchoconstriction in man; in the rabbit this is in part neutrophil dependent. The effects of inhalation of FMLP on peripheral blood leucocytes in normal subjects has been studied. METHODS: This was an open study in non-asthmatic subjects. Change in total peripheral white cell count were studied for 15 minutes after inhalation of 0.4 mumol FMLP in six subjects. Change in total and differential white cell count and spontaneous neutrophil chemiluminescence were then studied five and 30 minutes after inhalation of 0.4 mumol FMLP (n = 7) or diluent (n = 4). Finally, leucocytes from three subjects were labelled ex vivo with technetium-99m labelled sulphur colloid and reinfused. The effect of inhalation of FMLP or diluent on pulmonary neutrophil flux was studied by continuous gamma scanning of a pulmonary window. RESULTS: Leucopenia occurs rapidly after inhalation of FMLP, the nadir of the white cell count (53% of baseline) occurring at four minutes. This was followed by a rebound increase in white cell count evident at 15 minutes (154% of baseline). Five minutes after inhalation of 0.4 mumol FMLP, neutropenia (17% of baseline) and monocytopenia (40% of baseline) were seen followed again by a neutrophilia (213% of baseline at 30 minutes). The eosinophil count was significantly reduced at 30 minutes (24% of baseline). Neutrophil chemiluminescence was elevated (186% of baseline) at the time of the neutropenia. There was no influx of labelled cells to the lung during the period of neutropenia. CONCLUSION: FMLP inhalation activates circulating leucocytes. In vivo production of FMLP in the airway could contribute to bronchial inflammation during bacterial infection.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armour C. L., Black J. L., Johnson P. R., Vincenc K. S., Berend N. Formyl peptide-induced contraction of human airways in vitro. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Jan;60(1):141–146. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass D. A., Gonwa T. A., Szejda P., Cousart M. S., DeChatelet L. R., McCall C. E. Eosinopenia of acute infection: Production of eosinopenia by chemotactic factors of acute inflammation. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1265–1271. doi: 10.1172/JCI109789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L. Rous-Whipple award lecture. The formylpeptide receptor of the neutrophil. A search and conserve operation. Am J Pathol. 1987 Oct;129(1):15–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berend N., Armour C. L., Black J. L. Formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine causes bronchoconstriction in rabbits. Agents Actions. 1986 Mar;17(5-6):466–471. doi: 10.1007/BF01965515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berend N., Peters M. J., Armour C. L., Black J. L., Ward H. E. Effect of inhaled formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine on airway function. Thorax. 1988 Jan;43(1):36–40. doi: 10.1136/thx.43.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beswick P. H., Kay A. B. The effects of an ECF-A and formyl methionyl chemotactic peptides on oxidative metabolism of human eosinophils and neutrophils. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Feb;43(2):399–407. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick V. S., Mellor D. M., Myers D. B., Selden A. C., Keshavarzian A., Broom M. F., Hobson C. H. Production of peptides inducing chemotaxis and lysosomal enzyme release in human neutrophils by intestinal bacteria in vitro and in vivo. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1988 Jan;23(1):121–128. doi: 10.3109/00365528809093861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux S., Linch D. C., Campos Costa D., Spittle M. F., Jelliffe A. M. Transient leucopenia induced by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Lancet. 1987 Dec 26;2(8574):1523–1524. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92654-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M. Leukocyte-endothelial interactions. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):513–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslett C., Worthen G. S., Giclas P. C., Morrison D. C., Henson J. E., Henson P. M. The pulmonary vascular sequestration of neutrophils in endotoxemia is initiated by an effect of endotoxin on the neutrophil in the rabbit. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Jul;136(1):9–18. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkansson L., Carlson M., Stålenheim G., Venge P. Migratory responses of eosinophil and neutrophil granulocytes from patients with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 Apr;85(4):743–750. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(90)90193-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick C. J., Melzner I. Alterations in the biophysical properties of the human endothelial cell plasma membrane induced by a chemotactic tripeptide: correlation with enhanced adherence of granulocytes. J Pathol. 1984 Nov;144(3):201–211. doi: 10.1002/path.1711440307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasco W. A., Fantone J. C., Ward P. A. Spasmogenic activity of chemotactic N-formylated oligopeptides: identity of structure--function relationships for chemotactic and spasmogenic activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7470–7473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Craddock P. R., Jacob H. S. Effect of intravascular complement activation on granulocyte adhesiveness and distribution. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):731–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Showell H. J., Ward P. A. Neutropenia induced by systemic infusion of chemotactic factors. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1586–1589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. F., Jr, Soberman R. J., Yoshimoto T., Sheffer A. L., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Synthesis and release of leukotriene C4 by human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):532–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinckard R. N., Halonen M., Palmer J. D., Butler C., Shaw J. O., Henson P. M. Intravascular aggregation and pulmonary sequestration of platelets during IgE-induced systemic anaphylaxis in the rabbit: abrogation of lethal anaphylactic shock by platelet depletion. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2185–2193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleiffenbaum B., Moser R., Patarroyo M., Fehr J. The cell surface glycoprotein Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) mediates neutrophil adhesion and modulates degranulation independently of its quantitative cell surface expression. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3537–3545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroth H. J., Oberhausen E., Berberich R. Cell labelling with colloidal substances in whole blood. Eur J Nucl Med. 1981;6(10):469–472. doi: 10.1007/BF00252805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. O. Leukocytes in chemotactic-fragment-induced lung inflammation. Vascular emigration and alveolar surface migration. Am J Pathol. 1980 Nov;101(2):283–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonnesen M. G., Smedly L. A., Henson P. M. Neutrophil-endothelial cell interactions. Modulation of neutrophil adhesiveness induced by complement fragments C5a and C5a des arg and formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1581–1592. doi: 10.1172/JCI111574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Lepow I. H., Newman L. J. Bacterial factors chemotactic for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1968 Apr;52(4):725–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. J., Chung K. F., Moqbel R., MacDonald A. J., Hartnell A., McCusker M., Collins J. V., Barnes P. J., Kay A. B. Effects of inhaled PAF in humans on circulating and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid neutrophils. Relationship to bronchoconstriction and changes in airway responsiveness. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Feb;141(2):386–392. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/141.2.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worthen G. S., Schwab B., 3rd, Elson E. L., Downey G. P. Mechanics of stimulated neutrophils: cell stiffening induces retention in capillaries. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):183–186. doi: 10.1126/science.2749255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



