Abstract
We (N.L. and L.D.T.) have introduced a human heavy-chain minilocus into mice transgenically. Constructs contain 2 heavy-chain variable (VH; psi VH3-105 and VH5-251), 10 diversity (D), 6 heavy-chain joining (JH), and either constant (C)mu or C mu and C gamma gene segments. Several founder lines were established and studied before immunization. Seventy heavy-chain transcripts were cloned and sequenced from murine splenic B lymphocytes, and gene-segment use was assessed before and after class-switching. In general, the repertoire was "fetal" in appearance with little evidence of somatic mutation in any gene segment. The two VH gene segments were found rearranged to mu- and gamma-chain C segments, with a preference of VH5-251. We observed a preponderance of the most-J-proximal D gene (DHQ52) segments among the mu transcripts (44%). The JH gene-segment use mimics most patterns seen in human antibodies. Diversification in CDR3 was extensive and included clear examples of D inversions and D-D fusions. These data suggest that a human immunoglobulin minilocus can undergo recombinatorial processes in a manner analogous to that seen in the human fetal/preimmune repertoire. This model, in addition to providing a potential source of human monoclonal antibodies, is ideal for the study of further questions concerning immunoglobulin gene-segment recombination.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman J. E., Humphries C. G., Barth J., Alt F. W., Tucker P. W. Structure and expression of human germline VH transcripts. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1529–1535. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann M., Caskey H. M., Teale C., Waldmann H., Williams G. T., Surani M. A., Neuberger M. S. A repertoire of monoclonal antibodies with human heavy chains from transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6709–6713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann M., Spicer C., Buluwela L., Rosewell I., Barton S., Surani M. A., Rabbitts T. H. Human antibody production in transgenic mice: expression from 100 kb of the human IgH locus. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1323–1326. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dersimonian H., McAdam K. P., Mackworth-Young C., Stollar B. D. The recurrent expression of variable region segments in human IgM anti-DNA autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):4027–4033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeney A. J. Lack of N regions in fetal and neonatal mouse immunoglobulin V-D-J junctional sequences. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1377–1390. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guigou V., Guilbert B., Moinier D., Tonnelle C., Boubli L., Avrameas S., Fougereau M., Fumoux F. Ig repertoire of human polyspecific antibodies and B cell ontogeny. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1368–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C., Stewart A. K., Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D. Immunoglobulin heavy chain gene expression in peripheral blood B lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1331–1343. doi: 10.1172/JCI115719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel M., Berry J. K., Dunnick W. Switch region content of hybridomas: the two spleen cell Igh loci tend to rearrange to the same isotype. J Immunol. 1987 May 15;138(10):3539–3548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries C. G., Shen A., Kuziel W. A., Capra J. D., Blattner F. R., Tucker P. W. A new human immunoglobulin VH family preferentially rearranged in immature B-cell tumours. Nature. 1988 Feb 4;331(6155):446–449. doi: 10.1038/331446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara Y., Abe M., Yasui H., Matsuoka H., Kurosawa Y. At least five DH genes of human immunoglobulin heavy chains are encoded in 9-kilobase DNA fragments. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):649–652. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara Y., Matsuoka H., Kurosawa Y. Organization of human immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity gene loci. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4141–4150. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03309.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutzker S., Alt F. W. Structure and expression of germ line immunoglobulin gamma 2b transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1849–1852. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutzker S., Rothman P., Pollock R., Coffman R., Alt F. W. Mitogen- and IL-4-regulated expression of germ-line Ig gamma 2b transcripts: evidence for directed heavy chain class switching. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90379-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek K. D., Hasemann C. A., Capra J. D. Novel rearrangements at the immunoglobulin D locus. Inversions and fusions add to IgH somatic diversity. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):39–57. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
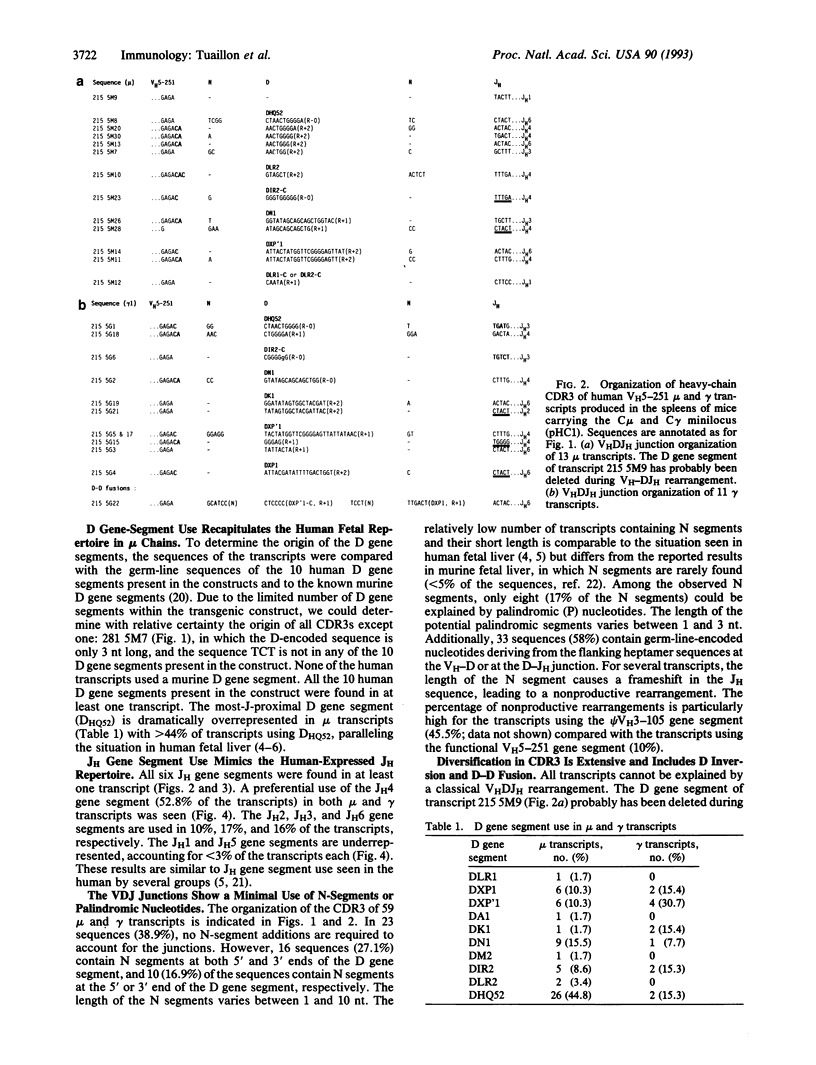
- Nickerson K. G., Berman J., Glickman E., Chess L., Alt F. W. Early human IgH gene assembly in Epstein-Barr virus-transformed fetal B cell lines. Preferential utilization of the most JH-proximal D segment (DQ52) and two unusual VH-related rearrangements. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1391–1403. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascual V., Capra J. D. Human immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable region genes: organization, polymorphism, and expression. Adv Immunol. 1991;49:1–74. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60774-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radbruch A., Müller W., Rajewsky K. Class switch recombination is IgG1 specific on active and inactive IgH loci of IgG1-secreting B-cell blasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3954–3957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz I., Casali P., Thomas J. W., Notkins A. L., Capra J. D. Nucleotide sequences of eight human natural autoantibody VH regions reveals apparent restricted use of VH families. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):4054–4061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz I. Multiple mechanisms participate in the generation of diversity of human H chain CDR3 regions. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1720–1729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Jr, Hillson J. L., Perlmutter R. M. Early restriction of the human antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):791–793. doi: 10.1126/science.3118465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. W., Jr, Wang J. Y. Preferential utilization of conserved immunoglobulin heavy chain variable gene segments during human fetal life. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6146–6150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen A., Humphries C., Tucker P., Blattner F. Human heavy-chain variable region gene family nonrandomly rearranged in familial chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8563–8567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Honjo T. Immunoglobulin class switching. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):801–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Nussenzweig M. C., Han H., Sanchez M., Honjo T. Trans-splicing as a possible molecular mechanism for the multiple isotype expression of the immunoglobulin gene. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1385–1393. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Ravetch J. V., Korsmeyer S., Waldmann T., Leder P. Human immunoglobulin D segments encoded in tandem multigenic families. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):631–635. doi: 10.1038/294631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor L. D., Carmack C. E., Schramm S. R., Mashayekh R., Higgins K. M., Kuo C. C., Woodhouse C., Kay R. M., Lonberg N. A transgenic mouse that expresses a diversity of human sequence heavy and light chain immunoglobulins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6287–6295. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter E., Krawinkel U., Radbruch A. Directed Ig class switch recombination in activated murine B cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1663–1671. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Wasserman R., Reichard B. A., Shane S., Caton A. J., Rovera G. Preferential utilization of specific immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity and joining segments in adult human peripheral blood B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):395–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaoita Y., Honjo T. Deletion of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes from expressed allelic chromosome. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):850–853. doi: 10.1038/286850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijden R. W., Bunschoten H., Pascual V., Uytdehaag F. G., Osterhaus D. M., Capra J. D. Nucleotide sequence of a human monoclonal anti-idiotypic antibody specific for a rabies virus-neutralizing monoclonal idiotypic antibody reveals extensive somatic variability suggestive of an antigen-driven immune response. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2835–2839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]