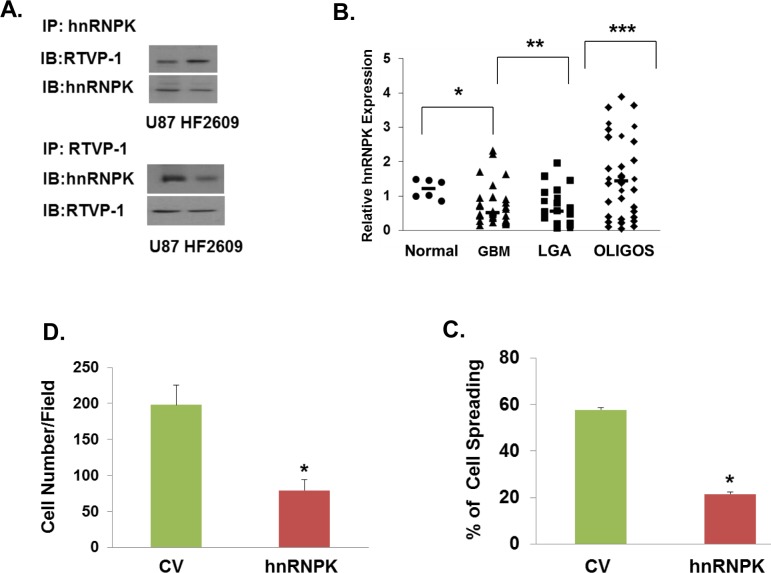
Figure 4. hnRNPK inhibits cell migration and its interaction with RTVP-1 decreases its association with N-WASP.
The association of RTVP-1 and hnRNPK was analyzed in U87 cells using reciprocal co-immunoprecipitation with either anti-N-WASP or RTVP-1 antibodies A. Total RNA was extracted from normal brains (NB) and astrocytic tumor specimens and the expression of hnRNPK was determined using real-time PCR B. Data from individual human tissues are presented with the median and interquartile range noted. Age adjusted t-test, P = 0.001. Results were normalized relative to the levels of S12 mRNA and are presented relative to a reference sample B. A172 cells were transfected with a vector overexpressing hnRNPK, or with a control vector (CV). Cell spreading assays C. and transwell migration assays D. were performed as described in the methods. U87 cells were transfected with hnRNPK siRNA or with a non-specific siRNA as a transfection control. Cell spreading assays E. and transwell migration assays F. were performed. The means ± S.E. from three independent experiments are shown as relative spreading after normalization to that in mock transfected cells. *p < 0.05. hnRNPK, N-WASP and RTVP-1 expression was examined in different subtypes of GBM. The gene expression plot presenting five GBM subtypes of 496 primary GBM specimens from TCGA showing differential hnRNPK gene expression G. ANOVA F-test is presented.