Abstract
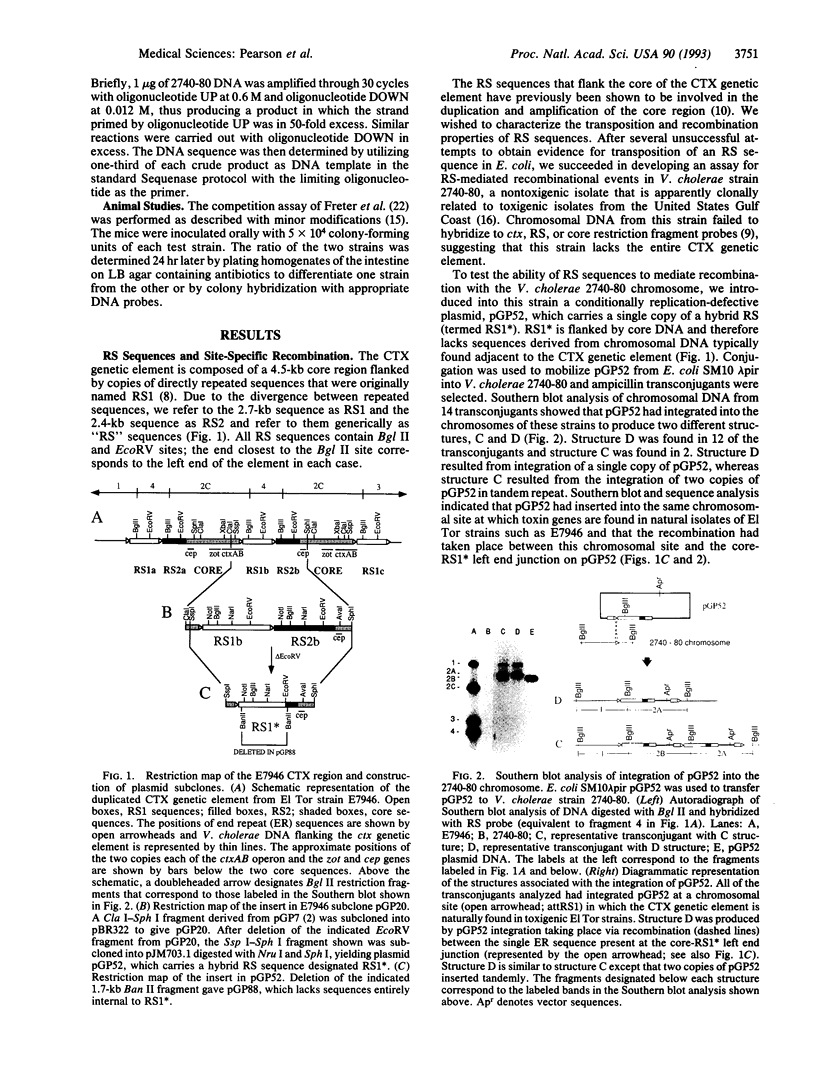
In Vibrio cholerae, the genes encoding cholera toxin (ctxAB) are located on a segment of DNA (termed the "core" region) that is flanked by two or more copies of a repeated sequence called RS1. Together these DNA units comprise the CTX genetic element. Evidence presented here suggests that RS1 sequences encode a site-specific recombination system, which allows integration of a suicide plasmid carrying RS1 into an 18-base-pair sequence (attRS1) located on the chromosome of nontoxigenic V. cholerae strains. Strains of V. cholerae with large deletions removing attRS1 and the entire CTX genetic element no longer undergo site-specific recombination with the RS1 sequence. Additionally, these deletion strains show a defect in intestinal colonization. Recombination experiments localize the gene responsible for enhancing colonization to a portion of the core region of the CTX element. The identified gene encodes a peptide that is highly similar in amino acid sequence to the flexible pilin of Aeromonas hydrophila. These results have important implications in the construction of stable, live attenuated cholera vaccines.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida R. J., Cameron D. N., Cook W. L., Wachsmuth I. K. Vibriophage VcA-3 as an epidemic strain marker for the U.S. Gulf Coast Vibrio cholerae O1 clone. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):300–304. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.300-304.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry B., Fasano A., Ketley J., Kaper J. B. Cloning of a gene (zot) encoding a new toxin produced by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):428–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.428-434.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler M., Galas D. J. Cointegrate formation mediated by Tn9. II. Activity of IS1 is modulated by external DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 15;170(1):61–91. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80227-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A., Parker C. D., Wohlhieter J. A., Baron L. S. Isolation and characterization of the fertility factor P of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):763–771. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.763-771.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J., Mekalanos J. J. Genetic regulation of bacterial virulence. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:455–482. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., O'Brien P. C., Macsai M. S. Role of chemotaxis in the association of motile bacteria with intestinal mucosa: in vivo studies. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):234–240. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.234-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I., Mekalanos J. J. Effect of a recA mutation on cholera toxin gene amplification and deletion events. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):723–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.723-731.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Hall R. H., Losonsky G., Mekalanos J. J., Taylor R. K., Levine M. M. Toxin, toxin-coregulated pili, and the toxR regulon are essential for Vibrio cholerae pathogenesis in humans. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1487–1492. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho A. S., Mietzner T. A., Smith A. J., Schoolnik G. K. The pili of Aeromonas hydrophila: identification of an environmentally regulated "mini pilin". J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):795–806. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho A. S., Sohel I., Schoolnik G. K. Cloning and characterization of fxp, the flexible pilin gene of Aeromonas hydrophila. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2725–2732. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Baldini M. M., Levine M. M. Recombinant nontoxinogenic Vibrio cholerae strains as attenuated cholera vaccine candidates. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):655–658. doi: 10.1038/308655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketley J. M., Kaper J. B., Herrington D. A., Losonsky G., Levine M. M. Diminished immunogenicity of a recombination-deficient derivative of Vibrio cholerae vaccine strain CVD103. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1481–1484. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1481-1484.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krolewski J. J., Murphy E., Novick R. P., Rush M. G. Site-specificity of the chromosomal insertion of Staphylococcus aureus transposon Tn554. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 15;152(1):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Herrington D., Losonsky G., Morris J. G., Clements M. L., Black R. E., Tall B., Hall R. Volunteer studies of deletion mutants of Vibrio cholerae O1 prepared by recombinant techniques. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):161–167. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.161-167.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein C., Brenner S. Site-specific properties of Tn7 transposition into the E. coli chromosome. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(2):380–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00270644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. TnphoA: a transposon probe for protein export signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8129–8133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Swartz D. J., Pearson G. D., Harford N., Groyne F., de Wilde M. Cholera toxin genes: nucleotide sequence, deletion analysis and vaccine development. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):551–557. doi: 10.1038/306551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. A novel suicide vector and its use in construction of insertion mutations: osmoregulation of outer membrane proteins and virulence determinants in Vibrio cholerae requires toxR. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2575–2583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2575-2583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Synthesis of cholera toxin is positively regulated at the transcriptional level by toxR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3471–3475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogg J. E., Timme T. L., Alemohammad M. M. General Transduction in Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):737–741. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.737-741.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. D., DiRita V. J., Goldberg M. B., Boyko S. A., Calderwood S. B., Mekalanos J. J. New attenuated derivatives of Vibrio cholerae. Res Microbiol. 1990 Sep-Oct;141(7-8):893–899. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90127-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Kaper J. B., Mekalanos J. J., Cray W. C., Jr Role of cholera toxin in enteric colonization by Vibrio cholerae O1 in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):813–816. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.813-816.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyamala V., Ames G. F. Amplification of bacterial genomic DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and direct sequencing after asymmetric amplification: application to the study of periplasmic permeases. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1602–1608. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1602-1608.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Miller V. L., Furlong D. B., Mekalanos J. J. Use of phoA gene fusions to identify a pilus colonization factor coordinately regulated with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachsmuth I. K., Bopp C. A., Fields P. I., Carrillo C. Difference between toxigenic Vibrio cholerae O1 from South America and US gulf coast. Lancet. 1991 May 4;337(8749):1097–1098. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91744-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Gojobori T., Yokota T. Evolutionary origin of pathogenic determinants in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae O1. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1352–1357. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1352-1357.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]