Abstract
Emerging evidence suggests that infection and persistent inflammation are key players in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD). Although it is well established that cigarette smoke (CS) promotes atherosclerotic CVD, very little is known about the potential impact of the collective effects of CS and intermittent or chronic subclinical infection on atherosclerosis. Our previous studies demonstrated that mast cell-derived histamine and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) synergistically enhance endothelial cell inflammatory response. We further noted that the synergy between histamine and LPS was due to reciprocal upregulation of histamine receptor and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expression and functions. These results suggest that the combined and persistent effects of mast cell mediators and bacterial agents on the vasculature are risk factors of CVD. Our recent data demonstrated that CS extract enhances histamine- and LPS-induced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in endothelial cells, suggesting that CS and mast cell mediators may collectively amplify inflammatory response in the vessel wall. We hypothesize that CS enhances histamine-mediated upregulation of TLR2/TLR4 signaling in the endothelium and promotes progression of atherosclerosis. This article presents our perspective on the modulatory effects of CS and nicotine on the “histamine-TLR-COX-2 axis.”
Keywords: cigarette smoking, infection, atherosclerosis, mast cells, lipopolysaccharide, histamine, cyclooxygenase-2, toll-like receptors 2 and 4
Introduction
Atherosclerosis (AS) is the underlying cause of several cardiovascular disease (CVD)-associated complications, including myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure, and stroke. Early stages of atherogenesis involve endothelial cell activation, persistent inflammatory response, and altered vascular homeostasis. The fact that the ever-changing milieu of endothelial cells alters cytokine profile, prostanoid homeostasis, and oxidative stress and attracts proinflammatory cells strengthens the notion that AS is an inflammatory disease.
It is recognized that both innate and adaptive immune systems contribute to the inflammatory processes in AS. In this respect, the role of T-lymphocytes, B-cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and neutrophils has been extensively studied. Furthermore, the presence of increased number of mast cells (1–4) and their influence in modulating toll-like receptors (TLRs) appear to be key contributors to the atherosclerotic process (5, 6). The mechanisms by which mast cell-mediated upregulation of innate immune system promote progression of AS remain obscure.
Toll-like receptors are expressed in a variety of cell types including endothelial cells (5). The presence of TLR2 and TLR4 in endothelial cells and their link to the COX-2 pathway add to the interaction between the innate immune system and AS. Our laboratory was the first to report the synergy between histamine and TLR2/TLR4 signaling that leads to overexpression of COX-2 and IL-6 in human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs) (5–7). We demonstrated that the synergy between histamine and bacterial agents is due to reciprocal upregulation of the expression of histamine H1 receptor (H1R), TLR2, and TLR4. These findings strongly suggest that histamine can amplify endothelial inflammatory responses initiated by both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial products.
Cigarette smoke (CS) is a major lifestyle-related risk factor for CVD. However, the impact of CS on intermittent or chronic subclinical infection-induced vascular inflammation and atherogenic pathobiology is unclear. It is well recognized that cigarette smoking increases the risk of microbial infection (8), and CS induces histamine release from mast cells (9). Thus, it is reasonable to postulate that cross-communication between CS, histamine, and bacterial products may lead to amplified inflammatory response. Here, we present a novel paradigm that CS promotes atherogenesis by modulating mast cell-mediated innate immune upregulation and by enhancing persistent vascular inflammation.
Endothelial Cells and Early Events in Atherosclerosis
Endothelial cells constitute the initial site of vascular changes that evolve into life-threatening occlusive lesions. The endothelium covers the tunica intima of the vessel wall and is directly exposed to the circulating milieu and pathogens. Further into the wall, the tunica media contains most of the resident smooth muscle cells and the adventitia on the outside contains mast cells, nerve endings, and microvessels. Endothelial cell activation by blood-borne proinflammatory agents shifts the vascular tone and local vascular homeostasis which, in turn, increase the risk of accelerated development of atherosclerotic lesions (10).
Activation of endothelial cells also increases the expression of adhesion molecules (VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and E-selectin) (11) that recruit monocytes, T-cells, B-cells, dendritic cells, mast cell precursors, and neutrophils into the vascular wall where low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-laden monocytes mature into foam cells. Altered vessel wall environment promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation and causes their migration from the media to the intima where they synthesize matrix proteins including collagen, elastin, and proteoglycans. Immune cells in the developing plaque between endothelial cells and the adventitia release proinflammatory cytokines, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), and reactive oxidants, which ultimately lead to plaque rupture and occlusive event (12).
Cardiovascular disease risk factors including cigarette smoking, hypercholesterolemia, and oxidative stress cause early endothelial dysfunction leading to atherosclerotic changes. Endothelial dysfunction is indicated by decreased production of vasodilatory and homeostatic molecules such as nitric oxide (NO) and prostacyclin (prostaglandin I2, PGI2) or increased production of vasoconstrictive molecules such as endothelin-1 (ET-1) and thromboxane A2 (TXA2). Early endothelial dysfunction promotes the transformation of quiescent endothelial cells toward an active phenotype that involves host defense response (13).
Role of Cyclooxygenase-2 and Prostanoids in Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis
The COX isozymes in concert with specific isomerases modulate cellular homeostasis and vascular tone through the production of several prostanoids. COX-1 is constitutively expressed in most cells, whereas COX-2 expression is induced at sites of inflammation. COX-2 expression is upregulated in activated macrophages and endothelial cells, which makes it a target for the regulation of atherogenesis (7, 14). Although COX-2 expression is transient in acute inflammation, it can be prolonged or persistent in immune disorders (15).
Biological effects of COX products depend on their relative concentrations and receptor densities as well as the cell types and microenvironment. Among the prostanoids, PGI2 and TXA2 have received considerable attention because of their opposing effects in the vasculature (16). Specific threshold levels of their concentrations in systemic circulation and vascular tissues are prerequisite for vascular homeostasis (17). PGI2 functions as a potent vasodilator and inhibitor of leukocyte adhesion and platelet aggregation. Early depletion of PGI2 from endothelium promotes AS by enhancing lipid deposition in smooth muscle cells (18). In contrast, TXA2 is a potent inducer of vasoconstriction, platelet activation, and platelet adhesion. Therefore, a shift in the PGI2/TXA2 equilibrium may dictate the vascular tone.
Our previous work focused on the interaction between histamine and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) with regard to COX-2 expression in endothelial cells (6, 7). The preferential effect of histamine on the induction of COX-2 expression with resultant production of PGE2 and PGI2 and its lack of influence on COX-1 expression or TXA2 production support the concept of a distinct coupling of COX-2 with PGE2 and PGI2 synthases and that of COX-1 with TXA2 synthase. It is intriguing that, despite the coexistence of both COX-1 and COX-2 in HCAEC, histamine is able to segregate its influence on COX-2/PGE2/PGI2 pathway and not on COX-1/TXA2 pathway. The ability of histamine to synergize LPS-induced COX-2 expression and prostanoid production underscores the potential role of this mast cell mediator to amplify infection-associated inflammatory responses. Since a physiological balance in the production of PGI2 and TXA2 by endothelial cells is critical for maintaining vascular integrity and controlling thrombosis, the histamine-induced shift of prostanoid equilibrium in favor of PGI2 production is noteworthy and supports its well-recognized vasodilatory and vasoprotective functions.
Role of Mast Cells in Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis
Mast cells alter the tissue microenvironment and modulate vascular inflammation, progression of AS, cardiac ischemia, and CVD (19). Mast cell progenitors reach the tissue through a chemokine-mediated mechanism and differentiate into mucosal or connective tissue phenotypes. Mucosal mast cells are characterized by the presence of only tryptase and chondroitin sulfate (proteoglycan), whereas connective tissue mast cells contain tryptase as well as chymase and heparin (proteoglycan) (20). Mast cells release vasoactive and angiogenic compounds and proinflammatory mediators, such as arachidonic acid metabolites (prostaglandin D2, leukotrienes), histamine, cytokines (e.g., IL-6 and IFNγ) and chemokines (e.g., eotaxin, MCP-1, and RANTES), platelet-activating factor (PAF), heparin, and proteolytic enzymes (21). These effector molecules are packaged in electron-dense secretory granules (mast cell granules, MCG). Endothelial cells can endocytose MCG in vitro (22) and in vivo (23). MCG can also promote human microvascular endothelial cell proliferation (24), LDL uptake by macrophages, and foam cell formation (21, 25).
Risk factors such as hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, proinflammatory cytokines, oxidized LDL, reactive oxygen species, complement 5a, substance P, endothelin-1, and thrombin can activate mast cells (25). Mast cells express proangiogenic cytokine βFGF and participate in neovascularization and release histamine that increases vascular permeability and proinflammatory effects on endothelial cells (26–28). Clinical significance of mast cells is evident by their accumulation in the human arterial intima and adventitia where they contribute to atherosclerotic plaque development as well as its destabilization through their secretory products (21, 22, 29). Increased number of mast cells is noted in coronary arteries during spasm and in the rupture-prone shoulders of coronary atheromas (2). Although these findings implicate mast cells in vascular homeostasis, the mechanism by which they promote atherogenesis and CVD is not well understood.
The direct role of mast cells in AS is evident from studies by us and others, showing attenuation of AS progression in ApoE−/−/KitW-sh/W-sh or LDLr−/−/KitW-sh/W-sh mice (30–33). These mouse models are generated by crossing AS-prone ApoE−/− or LDLr−/− mice with mast cell-deficient KitW-sh/W-sh mice. Using ApoE−/−/KitW-sh/W-sh mice, we demonstrated that mast cell deficiency attenuates AS progression in ApoE−/− mice. Interestingly, the reduction in atheroma development in ApoE−/−/KitW-sh/W-sh mice was associated with marked decreases in hepatic steatosis, reduced serum levels of cholesterol, LDL, and HDL, and decreased number of T-lymphocytes and macrophages in atheromas. Furthermore, ApoE−/−/KitW-sh/W-sh mice presented significantly lower serum IL-6 and IL-10, with no changes in the levels of IL-2, IL-4, IL-17, IFNγ, and TNFα. Mast cell deficiency did not reduce serum levels of IFNγ in the ApoE−/− mice, suggesting that mast cell-derived IFNγ may not play a role in this mouse model of AS as opposed to the LDLr−/− mouse model (31, 34). Mast cell deficiency did not alter systemic production of TXA2 in ApoE−/− mice but led to significant reduction in the production of PGI2. Significantly lower expression of COX-2 mRNA in the aortic tissues of ApoE−/−KitW-sh/W-sh mice compared with that of ApoE−/− mice suggests that mast cells regulate COX-2 expression. In this regard, the ability of histamine to induce COX-2 expression and PGI2 production in human endothelial cells and the markedly reduced expression of COX-2 mRNA in the aorta of histidine decarboxylase-null mouse (7) emphasize the importance of histamine in prostanoid homeostasis. Taken together, the marked reduction of hypercholesterolemia and vascular inflammation due to mast cell deficiency may attenuate AS progression in ApoE−/−/KitW-sh/W-sh mice.
Role of Histamine and H1 Receptor in Endothelial Cell Inflammatory Response
Histamine is a major secretory product of the mast cell that regulates vasodilation and bronchoconstriction (33, 35) and acts in combination with proteases to destabilize the plaque (35). Histamine induces smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation (36) and regulates intimal thickening (37). Histamine also regulates functions of monocytes and macrophages and eosinophils (38, 39), T-cells (40), neutrophils, and endothelial cells (41, 42). Histamine acts through a family of four distinct G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCR), namely, H1R, H2R, H3R, and H4R (43–45). Endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells highly express H1R, which facilitates histamine-mediated inflammatory and hypersensitivity responses (5–7, 33, 35, 36).
The role of histamine in AS and myocardial damage began to emerge only recently (46–48). Coronary arteries of patients with ischemic heart disease contain more mast cells and histamine than normal vessels (46), and patients with variant angina have elevated levels of histamine in their coronary circulation (49). Increased H1R mRNA expression has been reported in smooth muscle cells of intima/media in the atheroma (50). We found that histamine acting through H1R stimulates the expression of IL-6 and COX-2, with increased production of PGI2 by human endothelial cells. Interestingly, these effects are synergistically enhanced by LPS which suggests that mast cell products and bacterial agents act in concert to enhance vascular inflammation.
Infection, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis
Current literature strongly suggests a key role for infection-related immune activation in AS. Chlamydia pneumoniae, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Helicobacter pylori, and cytomegalovirus have been shown to be present in plaques and to promote AS in animals (51–56). LPS, a cell wall glycolipid of Gram-negative bacteria, induces the production of proinflammatory cytokines and the expression of adhesion molecules on endothelial cells. Gram-positive bacterial cell wall components, peptidoglycan (PGN) and lipoteichoic acid (LTA), also induce endothelial cell activation (5, 6). LPS is detectable in apparently healthy individuals with subclinical or chronic infections such as periodontitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, or diverticulitis. Persistent LPS levels as low as 50 pg/mL may be a strong risk factor for AS, particularly among smokers. Our studies demonstrated that bacterial toxins and histamine synergistically enhance endothelial inflammatory response through overexpression of TLR2 and TLR4 (5–7).
Activation of endothelial cells by pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and/or molecules from damaged host tissues induce the expression of inflammatory cytokines and cell adhesion molecules (57–60). TLRs are innate immune receptors that recognize PAMPs (61). TLR4 is the signaling receptor for LPS or heat shock protein-60 (human and chlamydial) (62, 63). TLR2 recognizes Gram-positive bacterial, mycobacterial, and fungal cell wall components (64, 65).
Increasing evidence suggests that TLR2 and TLR4 modulate vascular inflammation and atherosclerotic disease (66, 67). Endothelial layers of atherosclerotic lesions express higher levels of TLR2 and TLR4 mRNA, and patients with loss-of-function TLR4 polymorphism have reduced risk of CVD (68). Mutations in TLR4 have been linked with a lower incidence of AS and other CVDs (69). Furthermore, TLR4 gene deletion reduces vascular inflammation and atherogenesis in ApoE−/− mouse (70). Anecdotally, it is believed that viral or bacterial infection increases the chances for “acute coronary syndrome.” Despite putative significance of TLR2 and TLR4 in AS (67–70), an association between their expression in the plaque and severity of atherosclerotic disease is not established. Our preliminary clinical study showed an association between overexpression of TLR2, TLR4, and COX-2 in the carotid artery plaque and the severity of widespread AS including the presence of peripheral artery disease (71). These observations underscore the clinical significance of an overactive TLR2/TLR4/COX-2 axis in CVD.
The Synergy Between Mast Cell Histamine and Bacterial Toxins
The TLR-mediated endothelial response to bacterial pathogens may be modulated by mast cell mediators. Our studies show that histamine acting through H1R stimulates the expression of TLR2, TLR4, IL-6, COX-2, PGI2S, and PGE2S genes, leading to enhanced production of IL-6, PGE2, and PGI2 by HCAECs (5–7). We recently showed that LPS upregulates H1R gene and protein expression in HCAECs. We also noted that LPS-exposed HCAECs expressed threefold higher H1R than quiescent cells as assessed by H1R ligand binding. Furthermore, these cells were hyperresponsive to histamine as indicated by increased production of PGI2, PGE2, and IL-6. The LPS-induced hyperresponsiveness to histamine challenge was found to be mediated via H1R since it was abrogated by H1R antagonists (5–7, 72, 73). Thus, convergence of reciprocally upregulated H1R and TLR2/TLR4 functions was evident by the enhanced translocation of NF-κB and inflammatory response in endothelial cells treated with histamine in the presence of TLR ligands (74).
Cigarette Smoke, Innate Immune System, and Atherosclerosis
Cigarette smoke is a major cause of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality (75, 76). CS predisposes the individual to aortic and peripheral AS leading to clinical atherosclerotic syndromes, including stable angina, acute coronary syndromes, sudden death, and stroke (75). CS impacts all phases of AS from endothelial dysfunction to acute clinical events, the latter being largely thrombotic (77–84).
TLR recognition is not restricted to exogenous microbial patterns. Putative endogenous ligands include fibronectin extra domain A fragment, heat shock proteins, and hyaluronan fragments. Endogenous ligands may be released during tissue damage and drive inflammation in the absence of infection. Therefore, a risk factor like CS can potentially promote inflammation via these ligands. Indeed, gaseous and particulate constituents of CS increase TLR2, 4, and 6 expression by gingival epithelial cells (85). It is worth mentioning that CS may deliver bioactive LPS to smokers which may contribute to bronchitis in smokers. However, these investigators did not detect differences in the circulating levels of LPS between non-smokers and smokers (86).
Cigarette smoke upregulates both TLR4 expression and the release of IL-8 and LTB4 in alveolar macrophages (87). CS also induces TLR4 and MMP4 expression in human small airway epithelial (SAE) cells and lung tissue (88). Furthermore, CS has been shown to activate mast cells to release preformed mediators such as histamine and to inhibit prostaglandin production (34).
It is noteworthy that CS not only induces COX-2 expression and its enzyme activity but also increases PGE2 and TXA2 release (89, 90). CS extract (CSE) and sera from smokers increase COX-2 expression in endothelial cells (91), and this change is associated with augmented angiogenesis in the atherosclerotic plaque. CS may exert proinflammatory effects in a PGE2-dependent manner while TXA2 may mediate its proatherogenic effect via platelet activation, vasoconstriction, and angiogenesis (91).
The “H1R–TLR–COX2 Axis” – An Integrated Approach to Study the Immunomodulatory Effects of CS and Infection on Atherogenesis
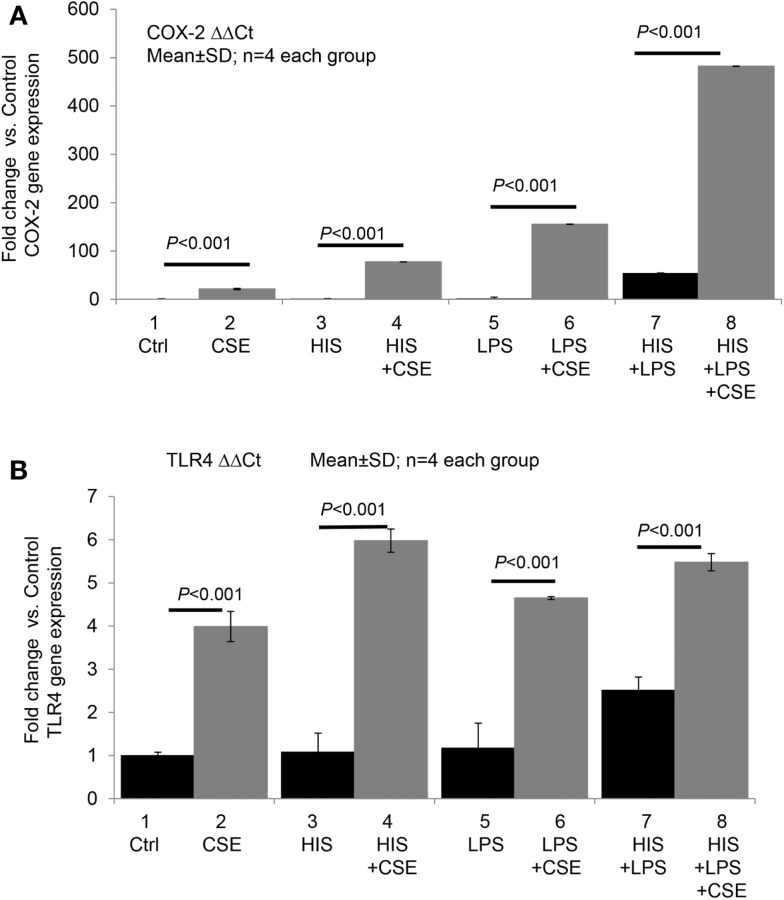
We recently conducted a pilot study to test whether CSE directly or synergistically modulates the effect of histamine or LPS on COX-2 and TLR4 expression in endothelial cells. Briefly, human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were incubated with medium (control), histamine, or LPS alone and in combination with CSE for 24 h (see Figure 1). As shown in Figure 1A, CSE significantly increased the basal as well as histamine- and LPS-induced COX-2 gene expression with varying magnitudes of synergy. Similarly, CSE significantly enhanced the expression of TLR4 mRNA in quiescent and in histamine- and LPS-treated cells (Figure 1B). These results indicate that CS can upregulate COX-2 and TLR4 pathways.
Figure 1.
Cigarette smoke extract directly and synergistically with histamine or LPS enhances the expression of COX-2 and TLR4 in human endothelial cells. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were grown to confluence and incubated with (1) medium (control), (2) cigarette smoke extract (CSE) (final concentration equivalent to 100 nM nicotine), (3) histamine (HIS, 10 μM), (4) HIS + CSE, (5) LPS, 100 ng/mL, (6) LPS + CSE, (7) HIS + LPS, and (8) HIS + LPS + CSE for 24 h. After the incubation, total RNA was extracted and used for RT-qPCR analyses of gene expressions of COX-2 (A) and TLR4 (B). Data presented are mean ± SD of quadruplicate experiments. CS increased COX2 gene expression significantly compared to control, HIS, LPS, or HIS + LPS groups (P < 0.001). HIS + LPS (6) increased COX2 expression compared to control, HIS, or LPS groups (P < 0.001). CS increased TLR4 gene expression significantly compared to control, HIS, LPS, or HIS + LPS groups (P < 0.001). HIS + LPS (6) increased TLR4 expression compared to control, HIS, or LPS groups (P < 0.001).
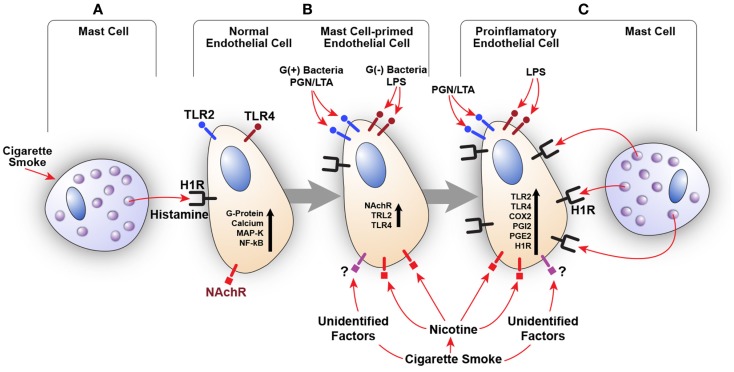
We also examined the effect of histamine on the expression of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α1 (NAChRα1) mRNA in HUVECs. Histamine upregulated NAChRα1 gene expression, which was enhanced by LPS (data not shown). These findings suggest that histamine increases endothelial cell sensitivity to nicotine and CS through overexpression of NAChRα1. The involvement of other nicotinic acetylcholine receptors as well as receptors that recognize unidentified factors in CSE remains to be determined. Based on these preliminary results, our published work (5–7, 72–75, 77–83) and a recent clinical study correlating TLR2, TLR4, and COX-2 overexpression in carotid artery plaques with the severity of disease (71), we postulate that constituents of CS, acting in concert with bacterial toxins and mast cell products, may amplify inflammatory response by engaging the H1R-TLR2/TLR4-COX2 axis (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Amplification of endothelial inflammatory response by cigarette smoke (CS) and bacterial products via innate immune upregulation. (A) Histamine secreted by the mast cell stimulates H1R on endothelial cells. CS may also increase histamine release. (B) H1R-mediated endothelial cell activation leads to increased expression of TLR2/TLR4 and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (NAChR). This cross talk programs endothelial cells to become hyperresponsive to the TLR2/TLR4 ligands (PGN, LTA, and LPS) and CS leading to enhanced inflammatory response. (C) Increased TLR2/TLR4 signaling also increases H1R expression. Collective stimulation of newly expressed TLR2/TLR4 and H1R leads to robust proinflammatory changes in the endothelium and persistent vascular inflammation.
Conclusion
Mast cells and TLRs are constituents of the innate immune system, and they synergistically enhance proatherogenic inflammatory response in endothelial cells. Our published work shows that histamine acting via H1R, and in conjunction with TLR2 or TLR4 ligands, synergistically amplifies the expression of COX-2 and IL-6 in endothelial cells with resultant overproduction of PGI2, PGE2, and IL-6. Preliminary data also show that CS extract enhances histamine- and LPS-induced endothelial expression of COX-2 and TLR4 in a synergistic manner, and histamine induces NAChRα1 expression. We propose that whole CS as well as its constituents such as nicotine modulate innate immune system and amplify infection-mediated proatherogenic inflammatory responses to promote the onset and progression of AS.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the position or policy of the Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States Government. All authors have reviewed and approved the manuscript. All authors have read the journal’s policy on conflicts of interest. None of the authors have any conflict of interest to declare regarding the contents of this paper.
Acknowledgments
The work summarized here was supported by NIH grants R01-HL070101 and 3R01-HL070101-04S1, Joseph and Elizabeth Carey Arthritis Fund and Audrey E. Smith Medical Research Fund from KU Endowment Association, and the Department of Internal Medicine Research Office at the University of Kansas Medical Center. The authors also thank the Kansas City VA Medical Center and the Midwest Biomedical Research Foundation, Kansas City, MO, USA, for their support. Authors wish to sincerely thank Dr. Jianping Zhou, Dr. Alok De, Ms. Maohui Chen and Mr. Siddharth Sharma for the data incorporated in Figure 1.
References
- 1.Davies MJ. The composition of coronary-artery plaques. N Engl J Med (1997) 336(18):1312–4. 10.1056/NEJM199705013361809 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ross R. Atherosclerosis – an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med (1999) 340(2):115–26. 10.1056/NEJM199901143400207 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Glass CK, Witztum JL. Atherosclerosis. The road ahead. Cell (2001) 104(4):503–16. 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00238-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hansson GK, Libby P, Schonbeck U, Yan ZQ. Innate and adaptive immunity in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Circ Res (2002) 91(4):281–91. 10.1161/01.RES.0000029784.15893.10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Talreja J, Kabir MH, B Filla M, Stechschulte DJ, Dileepan KN. Histamine induces toll-like receptor 2 and 4 expression in endothelial cells and enhances sensitivity to Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial cell wall components. Immunology (2004) 113(2):224–33. 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01946.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Raveendran VV, Tan X, Sweeney ME, Levant B, Slusser J, Stechschulte DJ, et al. Lipopolysaccharide induces H1 receptor expression and enhances histamine responsiveness in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Immunology (2011) 132(4):578–88. 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03403.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tan X, Essengue S, Talreja J, Reese J, Stechschulte DJ, Dileepan KN. Histamine directly and synergistically with lipopolysaccharide stimulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin I(2) and E(2) production in human coronary artery endothelial cells. J Immunol (2007) 179(11):7899–906. 10.4049/jimmunol.179.11.7899 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Brian D, Carter BD, Abnet CC, Feskanich D, Freedman ND, Hartge P, et al. Smoking and mortality – beyond established causes. N Engl J Med (2015) 372(7):631–40. 10.1056/NEJMsa1407211 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Thomas PS, Schreck RE, Lazarus SC. Tobacco smoke releases performed mediators from canine mast cells and modulates prostaglandin production. Am J Physiol (1992) 263(1 Pt 1):L67–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stoll LL, Denning GM, Weintraub NL. Potential role of endotoxin as a proinflammatory mediator of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol (2004) 24(12):2227–36. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000147534.69062.dc [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ling S, Nheu L, Komesaroff PA. Cell adhesion molecules as pharmaceutical target in atherosclerosis. Mini Rev Med Chem (2012) 12(2):175–83. 10.2174/138955712798995057 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature (2011) 473:317–25. 10.1038/nature10146 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Liao JK. Linking endothelial dysfunction with endothelial cell activation. J Clin Invest (2013) 123(2):540–1. 10.1172/JCI66843 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Smith DD, Tan X, Tawfik O, Milne G, Stechschulte DJ, Dileepan KN. Increased aortic atherosclerotic plaque development in female apolipoprotein E-null mice is associated with elevated thromboxane A2 and decreased prostacyclin production. J Physiol Pharmacol (2010) 61(3):309–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vane J, Corin RE. Prostacyclin: a vascular mediator. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg (2003) 26(6):571–8. 10.1016/S1078-5884(03)00385-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Dubois RN, Abramson SB, Crofford L, Gupta RA, Simon LS, Van De Putte LB, et al. Cyclooxygenase in biology and disease. FASEB J (1998) 12(12):1063–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kobayashi T, Tahara Y, Matsumoto M, Iguchi M, Sano H, Murayama T, et al. Roles of thromboxane A(2) and prostacyclin in the development of atherosclerosis in apoE-deficient mice. J Clin Invest (2004) 114(6):784–94. 10.1172/JCI200421446 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gryglewski RJ, Dembinska-Kiec A, Korbut R. A possible role of thromboxane A2 (TXA2) and prostacyclin (PGI2) in circulation. Acta Biol Med Ger (1978) 37(5–6):715–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Constantinides P. Mast cells and susceptibility to experimental atherosclerosis. Science (1953) 117(3045):505–6. 10.1126/science.117.3045.505 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kaartinen M, Penttilä A, Kovanen PT. Mast cells of two types differing in neutral protease composition in the human aortic intima. Demonstration of tryptase and tryptase/chymase-containing mast cells in normal intimas, fatty streaks, and the shoulder region of atheromas. Arterioscler Thromb (1994) 14(6):966–72. 10.1161/01.ATV.14.6.966 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bot I, Shi GP, Kovanen PT. Mast cells as effectors in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol (2015) 35(2):265–71. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303570 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Krishnaswamy G, Ajitawi O, Chi DS. The human mast cell: an overview. Methods Mol Biol (2006) 315:13–34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Spinas E, Kritas SK, Saggini A, Mobili A, Caraffa A, Antinolfi P, et al. Role of mast cells in atherosclerosis: a classical inflammatory disease. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol (2014) 27(4):517–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Marks RM, Roche WR, Czerniecki M, Penny R, Nelson DS. Mast cell granules cause proliferation of human microvascular endothelial cells. Lab Invest (1986) 55(3):289–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xu J, Shi GP. Vascular wall extracellular matrix proteins and vascular diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta (2014) 1842(11):2106–19. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.07.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kamat BR, Galli SJ, Barger AC, Lainey L, Silverman KJL. Neovascularization and coronary atherosclerotic plaque: cinematographic localization and quantitative histologic analysis. Hum Pathol (1987) 18(10):1036–42. 10.1016/S0046-8177(87)80220-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kaartinen M, Pentillä A, Kovanen PT. Mast cells accompany microvessels in human coronary atheromas: implications for intimal neovascularization and hemorrhage. Atherosclerosis (1996) 123(1–2):123–31. 10.1016/0021-9150(95)05794-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lappalainen H, Laine P, Pentikäinen MO, Sajantila A, Kovanen PT. Mast cells in neovascularized human coronary plaques store and secrete basic fibroblast growth factor, a potent angiogenic mediator. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol (2004) 24(10):1880–5. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000140820.51174.8d [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Theoharides TC, Sismanopoulos N, Delivanis DA, Zhang B, Hatziagelaki EE, Kalogeromitros D. Mast cells squeeze the heart and stretch the gird: their role in atherosclerosis and obesity. Trends Pharmacol Sci (2011) 32(9):534–42. 10.1016/j.tips.2011.05.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jeziorska M, McCollum C, Woolley DE. Mast cell distribution, activation, and phenotype in atherosclerotic lesions of human carotid arteries. J Pathol (1997) 182(1):115–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Heikkila HM, Trosien J, Metso J, Jauhiainen M, Pentikainen MO, Kovanen PT, et al. Mast cells promote atherosclerosis by inducing both an atherogenic lipid profile and vascular inflammation. J Cell Biochem (2010) 109(3):615–23. 10.1002/jcb.22443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Smith DD, Tan X, Raveendran VV, Tawfik O, Stechschulte DJ, Dileepan KN. Mast cell deficiency attenuates progression of atherosclerosis and hepatic steatosis in apolipoprotein E-null mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol (2012) 302(12):H2612–21. 10.1152/ajpheart.00879.2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hill SJ. Multiple histamine receptors: properties and functional characteristics. Biochem Soc Trans (1992) 20(1):122–5. 10.1042/bst0200122 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sun J, Sukhova GK, Wolters PJ, Yang M, Kitamoto S, Libby P, et al. Mast cells promote atherosclerosis by releasing proinflammatory cytokines. Nat Med (2007) 13(6):719–24. 10.1038/nm1601 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ozben B, Erdogan O. The role of inflammation and allergy in acute coronary syndromes. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets (2008) 7(3):136–44. 10.2174/187152808785748128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bottaro D, Shepro D, Peterson S, Hechtman HB. Serotonin, histamine, and norepinephrine mediation of endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cell movement. Am J Physiol (1985) 248(3 Pt 1):C252–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Miyazawa N, Watanabe S, Matsuda A, Kondo K, Hashimoto H, Umemura K, et al. Role of histamine H1 and H2 receptor antagonists in the prevention of intimal thickening. Eur J Pharmacol (1998) 362(1):53–9. 10.1016/S0014-2999(98)00716-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Elenkov IJ, Webster E, Papanicolaou DA, Fleisher TA, Chrousos GP, Wilder RL. Histamine potently suppresses human IL-12 and stimulates IL-10 production via H2 receptors. J Immunol (1998) 161(5):2586–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dileepan KN, Lorsbach RB, Stechschulte DJ. Mast cell granules inhibit macrophage-mediated lysis of mastocytoma cells (P815) and nitric oxide production. J Leukoc Biol (1993) 53(4):446–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Beer DJ, Matloff SM, Rocklin RE. The influence of histamine on immune and inflammatory responses. Adv Immunol (1984) 35:209–68. 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60577-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jeannin P, Delneste Y, Gosset P, Molet S, Lassalle P, Hamid Q, et al. Histamine induces interleukin-8 secretion by endothelial cells. Blood (1994) 84(7):2229–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Li Y, Chi L, Stechschulte DJ, Dileepan KN. Histamine-induced production of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 by human coronary artery endothelial cells is enhanced by endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Microvasc Res (2001) 61(3):253–62. 10.1006/mvre.2001.2304 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Bakker RA, Timmerman H, Leurs R. Histamine receptors: specific ligands, receptor biochemistry, and signal transduction. Clin Allergy Immunol (2002) 17:27–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hill SJ, Ganellin CR, Timmerman H, Schwartz JC, Shankley NP, Young JM, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XIII. Classification of histamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev (1997) 49(3):253–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Leurs R, Watanabe T, Timmerman H. Histamine receptors are finally ‘coming out’. Trends Pharmacol Sci (2001) 22:337–9. 10.1016/S0165-6147(00)01691-6 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kalsner S, Richards R. Coronary arteries of cardiac patients are hyperreactive and contain stores of amines: a mechanism for coronary spasm. Science (1984) 223(4643):1435–7. 10.1126/science.6701530 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Cabanié M, Godfraind T. The role of histamine in the cardiovascular system. Drugs Exp Clin Res (1988) 14(2–3):141–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Schneider E, Rolli-Derkinderen M, Arock M, Dy M. Trends in histamine research: new functions during immune responses and hematopoiesis. Trends Immunol (2002) 23(5):255–63. 10.1016/S1471-4906(02)02215-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sakata Y, Komamura K, Hirayama A, Nanto S, Kitakaze M, Hori M, et al. Elevation of the plasma histamine concentration in the coronary circulation in patients with variant angina. Am J Cardiol (1996) 77(12):1121–6. 10.1016/S0002-9149(96)00147-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Takagishi T, Sasaguri Y, Nakano R, Arima N, Tanimoto A, Fukui H, et al. Expression of the histamine H1 receptor gene in relation to atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol (1995) 46(4):981–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Armingohar Z, Jorgensen JJ, Kristoffersen AK, Abesha-Belay E, Olsen I. Bacteria and bacterial DNA in atherosclerotic plaque and aneurysmal wall biopsies from patients with and without periodontitis. J Oral Microbiol (2014) 6. 10.3402/jom.v6.23408 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kozarov EV, Dorn BR, Shelburne CE, Dunn WA, Jr, Progulske-Fox A. Human atherosclerotic plaque contains viable invasive Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas gingivalis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol (2005) 25:e17–8. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000155018.67835.1a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Velsko IM, Chukkapalli SS, Rivera MF, Lee JY, Chen H, Zheng D, et al. Active invasion of oral and aortic tissues by Porphyromonas gingivalis in mice causally links periodontitis and atherosclerosis. PLoS One (2014) 9:e97811. 10.1371/journal.pone.0097811 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Thomas GS, Wann LS, Allam AH, Thompson RC, Michalik DE, Sutherland ML, et al. Why did ancient people have atherosclerosis?: from autopsies to computed tomography to potential causes. Glob Heart (2014) 9(2):229–37. 10.1016/j.gheart.2014.04.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hussain M, Stover CM, Dupont A. P. gingivalis in periodontal disease and atherosclerosis – scenes of action for antimicrobial peptides and complement. Front Immunol (2015) 6:45. 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00045 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hettne KM, Weeber M, Laine ML, ten Cate H, Boyer S, Kors JA, et al. Automatic mining of the literature to generate new hypotheses for the possible link between periodontitis and atherosclerosis: lipopolysaccharide as a case study. J Clin Periodontol (2007) 34(12):1016–24. 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2007.01152.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Pober JS, Cotran RS. Cytokines and endothelial cell biology. Physiol Rev (1990) 70(2):427–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Pober JS, Cotran RS. The role of endothelial cells in inflammation. Transplantation (1990) 50(4):537–44. 10.1097/00007890-199010000-00001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Mantovani A, Bussolino F, Dejana E. Cytokine regulation of endothelial cell function. FASEB J (1992) 6(8):2591–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Morrison DC, Lei MG, Chen TY, Flebbe LM, Halling J, Field S. Identification and characterization of mammalian cell membrane receptors for LPS-endotoxin. Adv Exp Med Biol (1992) 319:23–9. 10.1007/978-1-4615-3434-1_3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Cybulsky MI, Chan MK, Movat HZ. Acute inflammation and microthrombosis induced by endotoxin, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor and their implication in gram-negative infection. Lab Invest (1988) 58(4):365–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Medzhitov R, Janeway CA, Jr. Decoding the patterns of self and nonself by the innate immune system. Science (2002) 296(5566):298–300. 10.1126/science.1068883 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Hoshino K, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Ogawa T, Takeda Y, et al. Cutting edge: toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to lipopolysaccharide: evidence for TLR4 as the Lps gene product. J Immunol (1999) 162(7):3749–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science (1998) 282(5396):2085–8. 10.1126/science.282.5396.2085 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Takeuchi O, Hoshino K, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Takada H, Ogawa T, et al. Differential roles of TLR2 and TLR4 in recognition of gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial cell wall components. Immunity (1999) 11(4):443–51. 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80119-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Lehner MD, Morath S, Michelsen KS, Schumann RR, Hartung T. Induction of cross-tolerance by lipopolysaccharide and highly purified lipoteichoic acid via different toll-like receptors independent of paracrine mediators. J Immunol (2001) 166(8):5161–7. 10.4049/jimmunol.166.8.5161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Pasterkamp G, Van Keulen JK, De Kleijn DP. Role of toll-like receptor 4 in the initiation and progression of atherosclerotic disease. Eur J Clin Invest (2004) 34(5):328–34. 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2004.01338.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Ding Y, Subramanian S, Montes VN, Goodspeed L, Wang S, Han C, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 deficiency decreases atherosclerosis but does not protect against inflammation in obese low-density lipoprotein receptor-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol (2012) 32(7):1596–604. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.249847 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Kiechl S, Lorenz E, Reindl M, Wiedermann CJ, Oberhollenzer F, Bonora E, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms and atherogenesis. N Engl J Med (2002) 347(3):185–92. 10.1056/NEJMoa012673 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Michelsen KS, Wong MH, Shah PK, Zhang W, Yano J, Doherty TM, et al. Lack of toll-like receptor 4 or myeloid differentiation factor 88 reduces atherosclerosis and alters plaque phenotype in mice deficient in apolipoprotein E. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2004) 101(29):10679–84. 10.1073/pnas.0403249101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Cherian G, Tan X, Cherian R, Dileepan KN. Overexpression of toll-like receptor-2 in human carotid artery plaques reflects clinical severity of atherosclerotic disease. FASEB J (2013) 27:Abstract 735.2. [Google Scholar]
- 72.Li Y, Stechschulte AC, Smith DD, Lindsley HB, Stechschulte DJ, Dileepan KN. Mast cell granules potentiate endotoxin-induced interleukin-6 production by endothelial cells. J Leukoc Biol (1997) 62(2):211–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Jehle AB, Li Y, Stechschulte AC, Stechschulte DJ, Dileepan KN. Endotoxin and mast cell granule proteases synergistically activate human coronary artery endothelial cells to generate interleukin-6 and interleukin-8. J Interferon Cytokine Res (2000) 20(4):361–8. 10.1089/107999000312298 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Chi L, Stehno-Bittel L, Smirnova I, Stechschulte DJ, Dileepan KN. Signal transduction pathways in mast cell granule-mediated endothelial cell activation. Mediators Inflamm (2003) 12(2):79–87. 10.1080/0962935031000097682 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Ambrose JA, Barua RS. The pathophysiology of smoking and cardiovascular disease: an update. (State of the art paper). J Am Coll Cardiol (2004) 43:1731–7. 10.1016/j.jacc.2003.12.047 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Barnett PG, Hamlett-Berry K, Sung HY, Max W. Health care expenditures attributable to smoking in military veterans. Nicotine Tob Res (2015) 17(5):586–91. 10.1093/ntr/ntu187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Barua RS, Ambrose JA, Eales-Reynolds LJ, DeVoe MC, Zervas JG, Saha DC. Dysfunctional endothelial nitric oxide biosynthesis in healthy smokers with impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilatation. Circulation (2001) 104(16):1905–10. 10.1161/hc4101.097525 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Barua RS, Ambrose JA, Eales-Reynolds LJ, DeVoe MC, Zervas JG, Saha DC. Heavy and light cigarette smokers have similar dysfunction of endothelial vasoregulatory activity: an in vivo and in vitro correlation. J Am Coll Cardiol (2002) 39(11):1758–63. 10.1016/S0735-1097(02)01859-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Barua RS, Ambrose JA, Saha DC, Eales-Reynolds LJ. Smoking is associated with altered endothelial-derived fibrinolytic and anti-thrombotic factors: an in vitro demonstration. Circulation (2002) 106(8):905–8. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000029091.61707.6B [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Barua RS, Ambrose JA, Srivastava S, DeVoe MC, Eales-Reynolds LJ. Reactive oxygen species are involved in smoking-induced dysfunction of nitric oxide biosynthesis and upregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Circulation (2003) 107(18):2342–7. 10.1161/01.CIR.0000066691.52789.BE [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Barua RS, Sy F, Srikanth S, Huang G, Javed U, Buhari C, et al. Effects of cigarette smoke exposure on clot dynamics and fibrin structure. An ex-vivo investigation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol (2010) 30(1):75–9. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.195024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Barua RS, Sy F, Srikanth S, Huang G, Javed U, Buhari C, et al. Acute cigarette smoke exposure reduces clot lysis – association between altered fibrin architecture and the response to t-PA. Thromb Res (2010) 126(5):426–30. 10.1016/j.thromres.2010.07.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Barua RS, Ambrose JA. Mechanisms of coronary thrombosis in cigarette smoke exposure. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol (2013) 33(7):1460–7. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300154 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Messner B, Bernhard D. Smoking and cardiovascular disease: mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction and early atherogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol (2014) 34(3):509–15. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.300156 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Semlali A, Witoled C, Alanazi M, Rouabhia M. Whole cigarette smoke increased the expression of TLRs, HBDs, and proinflammatory cytokines by human gingival epithelial cells through different signaling pathways. PLoS One (2012) 7(12):e52614. 10.1371/journal.pone.0052614 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Hasday JD, Bascom R, Costa JJ, Fitzgerald T, Dubin W. Bacterial endotoxin is an active component of cigarette smoke. Chest (1999) 115(3):829–35. 10.1378/chest.115.3.829 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Yin Y, Hou G, Li E, Wang Q, Kang J. PPARγ agonists regulate tobacco smoke-induced toll like receptor 4 expression in alveolar macrophages. Respir Res (2014) 11(15):28. 10.1186/1465-9921-15-28 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Geraghty P, Dabo AJ, D’Armiento J. TLR4 protein contributes to cigarette smoke-induced matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) expression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Biol Chem (2011) 286(34):30211–8. 10.1074/jbc.M111.238824 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.McAdam BF, Byrne D, Morrow JD, Oates JA. Contribution of cyclooxygenase-2 to elevated biosynthesis of thromboxane A2 and prostacyclin in cigarette smokers. Circulation (2005) 112(7):1024–9. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.542696 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Huang WC, Chai CY, Chen WC, Hou MF, Wang YS, Chiu YC, et al. Histamine regulates cyclooxygenase 2 gene activation through Orai1-mediated NFκB activation in lung cancer cells. Cell Calcium (2011) 50(1):27–35. 10.1016/j.ceca.2011.04.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Barbieri SS, Zacchi E, Amadio P, Gianellini S, Mussoni L, Weksler BB, et al. Cytokines present in smokers’ serum interact with smoke components to enhance endothelial dysfunction. Cardiovasc Res (2011) 90(3):475–83. 10.1093/cvr/cvr032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]