Abstract
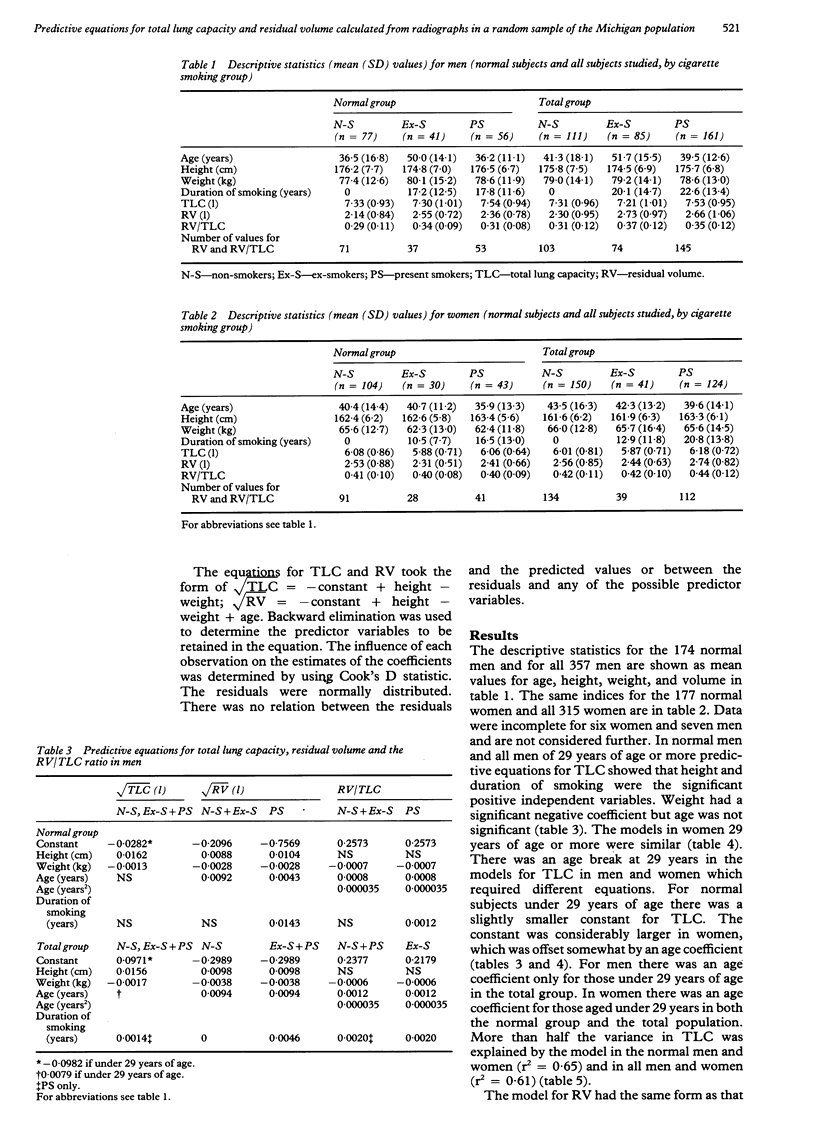
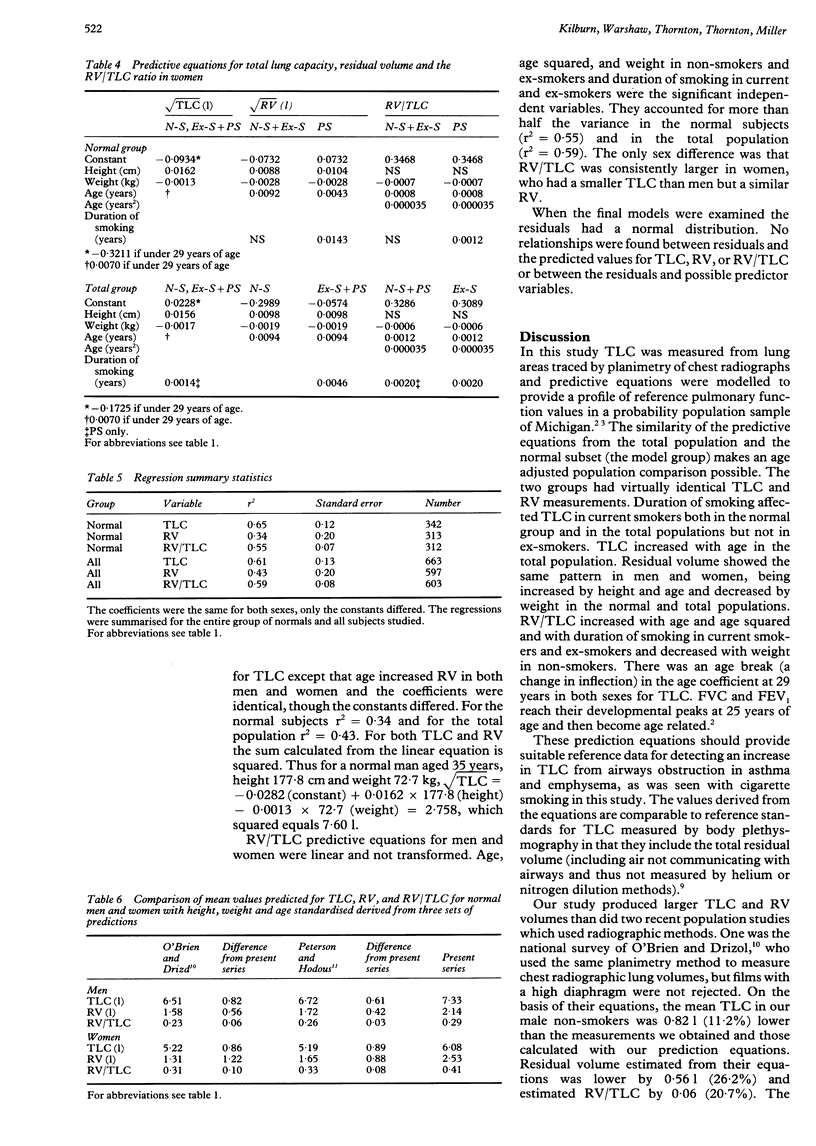
BACKGROUND: Published predicted values for total lung capacity and residual volume are often based on a small number of subjects and derive from different populations from predicted spirometric values. Equations from the only two large studies gave smaller predicted values for total lung capacity than the smaller studies. A large number of subjects have been studied from a population which has already provided predicted values for spirometry and transfer factor for carbon monoxide. METHODS: Total lung capacity was measured from standard posteroanterior and lateral chest radiographs and forced vital capacity by spirometry in a population sample of 771 subjects. Prediction equations were developed for total lung capacity (TLC), residual volume (RV) and RV/TLC in two groups--normal and total. Subjects with signs or symptoms of cardiopulmonary disease were combined with the normal subjects and equations for all subjects were also modelled. RESULTS: Prediction equations for TLC and RV in non-smoking normal men and women were square root transformations which included height and weight but not age. They included a coefficient for duration of smoking in current smokers. The predictive equation for RV/TLC included weight, age, age and duration of smoking for current smokers and ex-smokers of both sexes. For the total population the equations took the same form but the height coefficients and constants were slightly different. CONCLUSION: These population based prediction equations for TLC, RV and RV/TLC provide reference standards in a population that has provided reference standards for spirometry and single breath transfer factor for carbon monoxide.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNHARD H. J., PIERCE J. A., JOYCE J. W., BATES J. H. Roentgenographic determination of total lung capacity. A new method evaluated in health, emphysema and congestive heart failure. Am J Med. 1960 Jan;28:51–60. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90222-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugman T. M., Morris J. F., Temple W. P. Comparison of lung volume measurements by single breath helium and multiple breath nitrogen equilibration methods in normal subjects and COPD patients. Respiration. 1986;49(1):52–60. doi: 10.1159/000194859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. R., Pratt P. C., Kilburn K. H. Total lung capacity measured by roentgenograms. Am J Med. 1971 Jun;50(6):756–763. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilburn K. H., Lilis R., Anderson H. A., Miller A., Warshaw R. H. Interaction of asbestos, age, and cigarette smoking in producing radiographic evidence of diffuse pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Med. 1986 Mar;80(3):377–381. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90709-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Thornton J. C., Warshaw R., Anderson H., Teirstein A. S., Selikoff I. J. Single breath diffusing capacity in a representative sample of the population of Michigan, a large industrial state. Predicted values, lower limits of normal, and frequencies of abnormality by smoking history. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Mar;127(3):270–277. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.3.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Thornton J. C., Warshaw R., Bernstein J., Selikoff I. J., Teirstein A. S. Mean and instantaneous expiratory flows, FVC and FEV1: prediction equations from a probability sample of Michigan, a large industrial state. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1986 Nov-Dec;22(6):589–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. J., Drizd T. A. Roentgenographic determination of total lung capacity: normal values from a National Population Survey. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Nov;128(5):949–952. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.5.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen M. R., Hodous T. K. Lung volume reference values for blue collar workers not exposed to occupational respiratory hazards. J Occup Med. 1988 Aug;30(8):626–632. doi: 10.1097/00043764-198808000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The determination of static lung volumes. Report of the section on respiratory pathophysiology. Chest. 1984 Sep;86(3):471–474. doi: 10.1378/chest.86.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


