Abstract
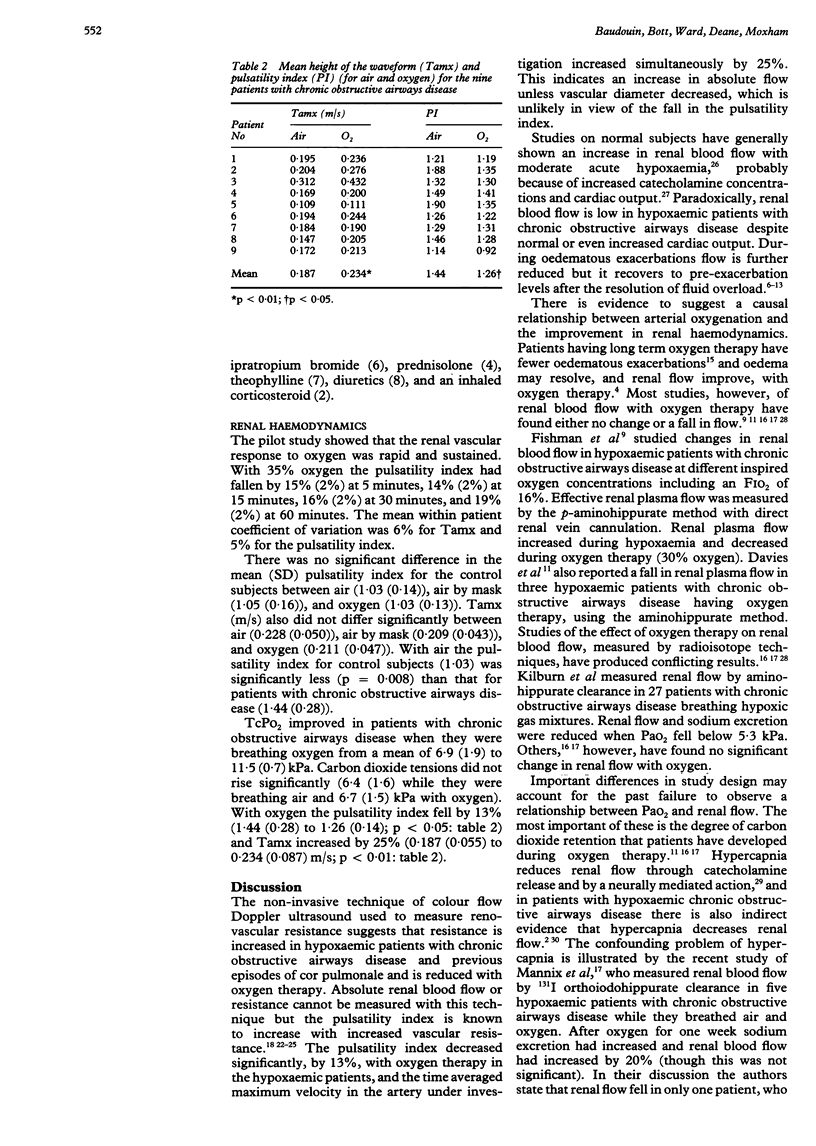
BACKGROUND: Oxygen therapy is effective in the prevention and treatment of oedematous exacerbations of cor pulmonale. As renal blood flow is reduced in cor pulmonale a study was designed to investigate whether one of the beneficial effects of oxygen was to increase renal blood flow. The effect of oxygen therapy on renal haemodynamics measured noninvasively was examined in patients with chronic obstructive airways disease and previous episodes of oedema. METHODS: Renal blood flow waveforms were recorded in a single vessel by colour flow Doppler ultrasound in nine hypoxaemic patients (PaO2) (arterial oxygen tension < 8 kPa while they were breathing air) with chronic obstructive airways disease and previous oedema and eight age matched normoxaemic volunteers (arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) 97% or more when breathing air) while they were breathing air and oxygen. SaO2 and transcutaneous PaO2 (TcPO2) and PaCO2 (TcPCO2) were monitored. Five renal velocity profile recordings were made from the same segmental vessel with the patient breathing room air for one hour followed by oxygen titrated to achieve an oxygen saturation of 95% or more without a rise in TcPCO2 for 15 minutes. Control subjects breathed 35% oxygen. RESULTS: No significant change in the pulsatility index (a measure of distal vascular resistance) or mean height of the waveform (Tamx, a measure of renal blood flow) occurred in the control subjects while they were breathing air or oxygen. The pulsatility index of the patients with chronic obstructive airways disease was significantly greater than that in the control subjects breathing air (1.44 (SD 0.28) v 1.03 (0.14). Breathing oxygen was associated with an increase in TcPO2 in the patients (from 6.9 (1.9) to 11.5 (0.7) kPa), a fall in pulsatility index (from 1.44 (0.28) to 1.26 (0.14) and an increase in Tamx (from 0.187 (0.055) to 0.234 (0.087) m/s). CONCLUSIONS: The results suggest that renal vascular resistance is increased in patients with chronic obstructive airways disease and hypoxaemia and that short term oxygen therapy reduces renal vascular resistance and increases blood flow. Some of the benefits of oxygen therapy in cor pulmonale may be due to improvements in renal haemodynamics.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABER G. M., BISHOP J. M. SERIAL CHANGES IN RENAL FUNCTION, ARTERIAL GAS TENSIONS AND THE ACID-BASE STATE IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC BRONCHITIS AND OEDEMA. Clin Sci. 1965 Jun;28:511–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avasthi P. S., Greene E. R., Voyles W. F., Eldridge M. W. A comparison of echo-Doppler and electromagnetic renal blood flow measurements. J Ultrasound Med. 1984 May;3(5):213–218. doi: 10.7863/jum.1984.3.5.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon P. J. The kidney in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jan 6;296(1):26–32. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197701062960108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES C. E. The effect of treatment on the renal circulation in heart-failure. Lancet. 1951 Dec 8;2(6693):1052–1057. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(51)92974-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN A. P., MAXWELL M. H., CROWDER C. H., MORALES P. Kidney function in cor pulmonale; particular consideration of changes in renal hemodynamics and sodium excretion during variation in level of oxygenation. Circulation. 1951 May;3(5):703–721. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.3.5.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber M. O., Bright T. P., Strawbridge R. A., Robertson G. L., Manfredi F. Impaired water handling in chronic obstructive lung disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Jan;85(1):41–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber M. O., Roberts L. R., Weinberger M. H., Robertson G. L., Fineberg N. S., Manfredi F. Abnormalities of sodium and H2O handling in chronic obstructive lung disease. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Jul;142(7):1326–1330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber M. O., Weinberger M. H., Robertson G. L., Fineberg N. S., Manfredi F. Hormonal abnormalities affecting sodium and water balance in acute respiratory failure due to chronic obstructive lung disease. Chest. 1984 Jan;85(1):49–54. doi: 10.1378/chest.85.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber M. O., Weinberger M. H., Robertson G. L., Fineberg N. S. The effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition on sodium handling in patients with advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Oct;136(4):862–866. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.4.862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMMOND J. D., MACKINNON J., SMITH W. D., STUART-HARRIS C. H. The renal circulation in chronic pulmonary disease and pulmonary heart failure. Q J Med. 1956 Jul;25(99):389–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. E. Regulation of renal hemodynamics. Int Rev Physiol. 1982;26:243–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard P. Hypoxia, almitrine, and peripheral neuropathy. Thorax. 1989 Apr;44(4):247–250. doi: 10.1136/thx.44.4.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. M., Copland J., McDonald C. F., Barter C. E., Rochford P. D., Pierce R. J. Cardiopulmonary response to oxygen therapy in hypoxaemic chronic airflow obstruction. Thorax. 1989 Nov;44(11):930–936. doi: 10.1136/thx.44.11.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilburn K. H., Dowell A. R. Renal function in respiratory failure. Effects of hypoxia, hyperoxia, and hypercapnia. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Apr;127(4):754–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanigan C., Ponte J., Moxham J. Performance of transcutaneous PO2 and PCO2 dual electrodes in adults. Br J Anaesth. 1988 May;60(6):736–742. doi: 10.1093/bja/60.6.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannix E. T., Dowdeswell I., Carlone S., Palange P., Aronoff G. R., Farber M. O. The effect of oxygen on sodium excretion in hypoxemic patients with chronic obstructive lung disease. Chest. 1990 Apr;97(4):840–844. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.4.840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt C. R. Doppler color flow imaging. J Clin Ultrasound. 1987 Nov-Dec;15(9):591–597. doi: 10.1002/jcu.1870150904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris C. S., Barnes R. W. Renal artery flow velocity analysis: a sensitive measure of experimental and clinical renovascular resistance. J Surg Res. 1984 Mar;36(3):230–236. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(84)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver R. M., Peacock A. J., Fleming J. S., Waller D. G. Renal and pulmonary effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition in chronic hypoxic lung disease. Thorax. 1989 Jun;44(6):513–515. doi: 10.1136/thx.44.6.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLATTS M. M., HAMMOND J. D., STUART-HARRIS C. H. A study of cor pulmonale in patients with chronic bronchitis. Q J Med. 1960 Oct;29:559–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff H., Levy S. A. Renin-angiotensin II-aldosterone and ACTH-cortisol control during acute hypoxemia and exercise in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Mar;133(3):396–399. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reihman D. H., Farber M. O., Weinberger M. H., Henry D. P., Fineberg N. S., Dowdeswell I. R., Burt R. W., Manfredi F. Effect of hypoxemia on sodium and water excretion in chronic obstructive lung disease. Am J Med. 1985 Jan;78(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90467-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richens J. M., Howard P. Oedema in cor pulmonale. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 Mar;62(3):255–259. doi: 10.1042/cs0620255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens P. E., Bolsin S., Gwyther S. J., Hanson M. E., Boultbee J. E., Kox W. Practical use of duplex Doppler analysis of the renal vasculature in critically ill patients. Lancet. 1989 Feb 4;1(8632):240–242. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91257-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K. J., Burns P. N., Woodcock J. P., Wells P. N. Blood flow in deep abdominal and pelvic vessels: ultrasonic pulsed-Doppler analysis. Radiology. 1985 Feb;154(2):487–493. doi: 10.1148/radiology.154.2.3880913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. J., Davidson A. C., Treacher D., Rudd R. M., Anderson J. V., Meleagros L., Bloom S. R. Atrial natriuretic peptide concentrations in hypoxic secondary pulmonary hypertension: relation to haemodynamic and blood gas variables and response to supplemental oxygen. Thorax. 1989 Jan;44(1):58–62. doi: 10.1136/thx.44.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



