Abstract
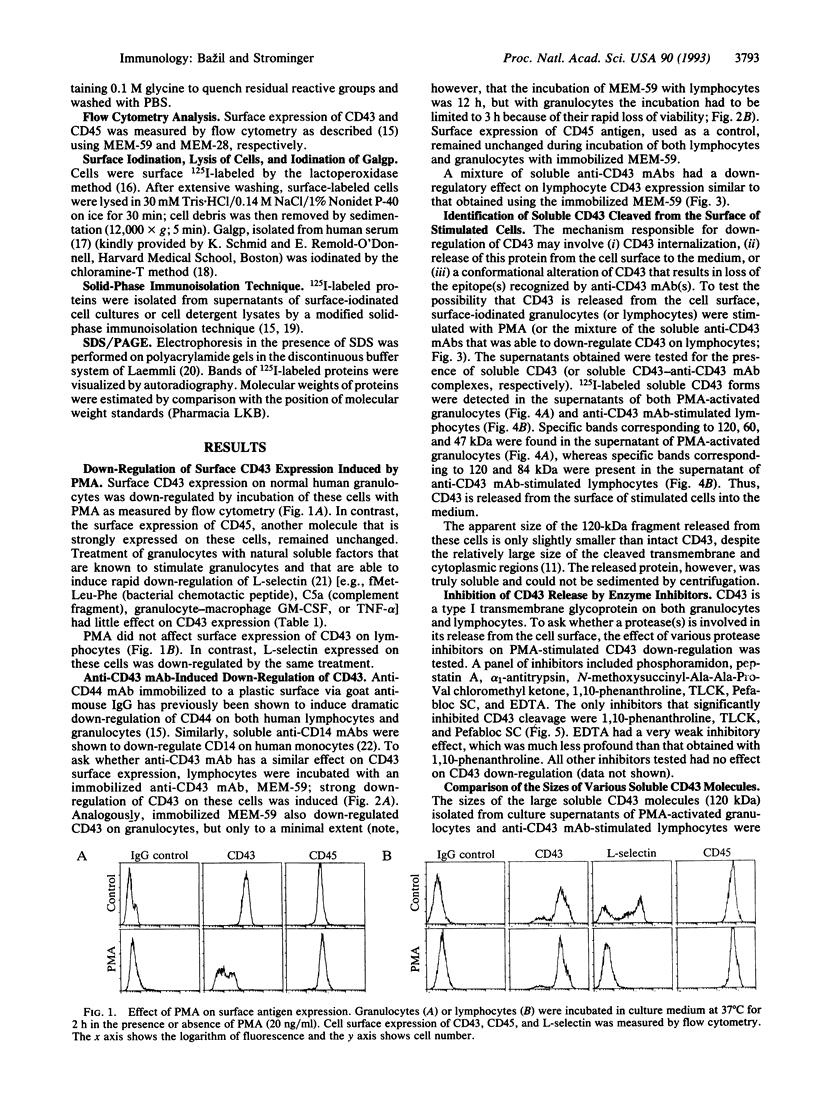
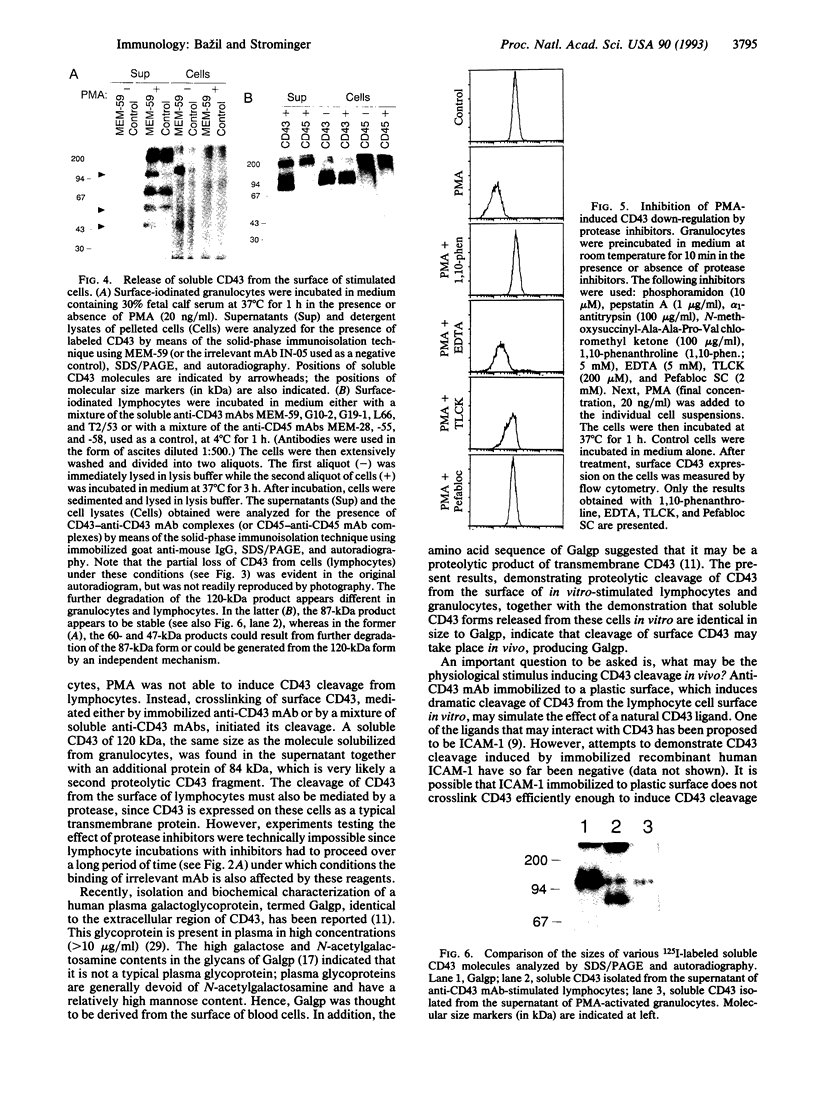
CD43, the major sialoglycoprotein of human leukocytes, whose expression is defective in patients with the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, was down-regulated by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) on granulocytes but not on lymphocytes. However, CD43 expressed on both of these leukocyte subpopulations was down-regulated after crosslinking by anti-CD43 monoclonal antibodies, a stimulation that may simulate the effect of a natural CD43 ligand. Soluble, labeled CD43 molecules were isolated from culture supernatants of both surface-iodinated granulocytes activated by PMA and lymphocytes stimulated with anti-CD43 antibodies. Thus, in this case down-regulation represents release from the cell surface into the culture medium, rather than internalization. The apparent molecular masses of the released molecules and of soluble CD43 isolated from human serum were identical. Importantly, PMA-induced down-regulation of CD43 on granulocytes was markedly blocked both by the metalloprotease inhibitor 1,10-phenanthroline and by the serine protease inhibitors N alpha-(p-tosyl)-L-lysine chloromethyl ketone and Pefabloc SC, which inhibit two different classes of proteases, thus indicating that the release is proteolytic.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelsson B., Hammarström S., Finne J., Perlmann P. The large sialoglycoprotein of human lymphocytes. II. Biochemical features. Eur J Immunol. 1985 May;15(5):427–433. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazil V., Strominger J. L. Shedding as a mechanism of down-modulation of CD14 on stimulated human monocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1567–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker J. C., Dummer R., Hartmann A. A., Burg G., Schmidt R. E. Shedding of ICAM-1 from human melanoma cell lines induced by IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Functional consequences on cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4398–4401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campanero M. R., Pulido R., Alonso J. L., Pivel J. P., Pimentel-Muiños F. X., Fresno M., Sánchez-Madrid F. Down-regulation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha of neutrophil cell surface expression of the sialophorin CD43 and the hyaluronate receptor CD44 through a proteolytic mechanism. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Dec;21(12):3045–3048. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson S. R., Fukuda M. Isolation and characterization of leukosialin, a major sialoglycoprotein on human leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12779–12786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Botran R. Soluble cytokine receptors: their role in immunoregulation. FASEB J. 1991 Aug;5(11):2567–2574. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.11.1868981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey E. A., Miller D. S., Jahr T. G., Sundan A., Bazil V., Espevik T., Finlay B. B., Wright S. D. Soluble CD14 participates in the response of cells to lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1665–1671. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. D., Spertini O., Ernst T. J., Belvin M. P., Levine H. B., Kanakura Y., Tedder T. F. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and other cytokines regulate surface expression of the leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 on human neutrophils, monocytes, and their precursors. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):576–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy G. R., Gordon J. Coordinated action of IgE and a B-cell-stimulatory factor on the CD23 receptor molecule up-regulates B-lymphocyte growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6239–6243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison D., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Involvement of a metalloprotease in spontaneous and phorbol ester-induced release of natural killer cell-associated Fc gamma RIII (CD16-II). J Immunol. 1991 Nov 15;147(10):3459–3465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horejsí V., Angelisová P., Bazil V., Kristofová H., Stoyanov S., Stefanová I., Hausner P., Vosecký M., Hilgert I. Monoclonal antibodies against human leucocyte antigens. II. Antibodies against CD45 (T200), CD3 (T3), CD43, CD10 (CALLA), transferrin receptor (T9), a novel broadly expressed 18-kDa antigen (MEM-43) and a novel antigen of restricted expression (MEM-74). Folia Biol (Praha) 1988;34(1):23–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horejsí V., Hilgert I., Kristofová H., Satayalai O. Murine hybridoma monoclonal antibodies against insulin: cross-reactivity with insulins of three species and blocking of insulin binding to its receptor. Immunol Lett. 1984;8(5):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(84)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizinga T. W., van der Schoot C. E., Jost C., Klaassen R., Kleijer M., von dem Borne A. E., Roos D., Tetteroo P. A. The PI-linked receptor FcRIII is released on stimulation of neutrophils. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):667–669. doi: 10.1038/333667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung T. M., Dailey M. O. Rapid modulation of homing receptors (gp90MEL-14) induced by activators of protein kinase C. Receptor shedding due to accelerated proteolytic cleavage at the cell surface. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3130–3136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., Jutila M. A., Berg E. L., Butcher E. C. Neutrophil Mac-1 and MEL-14 adhesion proteins inversely regulated by chemotactic factors. Science. 1989 Sep 15;245(4923):1238–1241. doi: 10.1126/science.2551036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers T. W., Hoogerwerf M., Kuijpers K. C., Schwartz B. R., Harlan J. M. Cross-linking of sialophorin (CD43) induces neutrophil aggregation in a CD18-dependent and a CD18-independent way. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 1;149(3):998–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., De Vries E., Gravestein L. A., Hintzen R. Q., Van Lier R. A., Borst J. The CD27 membrane receptor, a lymphocyte-specific member of the nerve growth factor receptor family, gives rise to a soluble form by protein processing that does not involve receptor endocytosis. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Feb;22(2):447–455. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentzer S. J., Remold-O'Donnell E., Crimmins M. A., Bierer B. E., Rosen F. S., Burakoff S. J. Sialophorin, a surface sialoglycoprotein defective in the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, is involved in human T lymphocyte proliferation. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1383–1392. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mookhtiar K. A., Van Wart H. E. Purification to homogeneity of latent and active 58-kilodalton forms of human neutrophil collagenase. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10620–10627. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison M. Lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination as a tool for investigation of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):214–220. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nong Y. H., Remold-O'Donnell E., LeBien T. W., Remold H. G. A monoclonal antibody to sialophorin (CD43) induces homotypic adhesion and activation of human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):259–267. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palecanda A., Walcheck B., Bishop D. K., Jutila M. A. Rapid activation-independent shedding of leukocyte L-selectin induced by cross-linking of the surface antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1992 May;22(5):1279–1286. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkman R., Remold-O'Donnell E., Kenney D. M., Perrine S., Rosen F. S. Surface protein abnormalities in lymphocytes and platelets from patients with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Lancet. 1981 Dec 19;2(8260-61):1387–1389. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92802-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porteu F., Nathan C. Shedding of tumor necrosis factor receptors by activated human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):599–607. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Davis A. E., 3rd, Kenney D., Bhaskar K. R., Rosen F. S. Purification and chemical composition of gpL115, the human lymphocyte surface sialoglycoprotein that is defective in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 5;261(16):7526–7530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Kenney D. M., Parkman R., Cairns L., Savage B., Rosen F. S. Characterization of a human lymphocyte surface sialoglycoprotein that is defective in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1705–1723. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold-O'Donnell E., Rosen F. S. Sialophorin (CD43) and the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Immunodefic Rev. 1990;2(2):151–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieu P., Porteu F., Bessou G., Lesavre P., Halbwachs-Mecarelli L. Human neutrophils release their major membrane sialoprotein, leukosialin (CD43), during cell activation. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Nov;22(11):3021–3026. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstein Y., Park J. K., Hahn W. C., Rosen F. S., Bierer B. E., Burakoff S. J. CD43, a molecule defective in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, binds ICAM-1. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):233–235. doi: 10.1038/354233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid K., Hediger M. A., Brossmer R., Collins J. H., Haupt H., Marti T., Offner G. D., Schaller J., Takagaki K., Walsh M. T. Amino acid sequence of human plasma galactoglycoprotein: identity with the extracellular region of CD43 (sialophorin). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):663–667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid K., Mao S. K., Kimura A., Hayashi S., Binette J. P. Isolation and characterization of a serine-threonine-rich galactoglycoprotein from normal human plasma. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3221–3226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. Purification and biologic characterization of a specific tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11966–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Fliszar C. J., Shapiro S. D., Goldberg G. I., Welgus H. G. Human 92- and 72-kilodalton type IV collagenases are elastases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7870–7875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricklin G. P., Jeffrey J. J., Roswit W. T., Eisen A. Z. Human skin fibroblast procollagenase: mechanisms of activation by organomercurials and trypsin. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):61–68. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sármay G., Rozsnyay Z., Szabó I., Biró A., Gergely J. Modulation of type II Fc gamma receptor expression on activated human B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Mar;21(3):541–549. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura G. S., Dailey M. O., Gallatin W. M., McGrath M. S., Weissman I. L., Pillemer E. A. Isolation of molecules recognized by monoclonal antibodies and antisera: the solid phase immunoisolation technique. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;136(2):458–464. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90244-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





