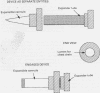
Abstract
The insertion of a chest drain into the pleural space is a common procedure used by many specialties. The commonly used device is a prepacked, sterile plastic tube with its own central metal trocar. Complications may arise during its insertion, with the occasional penetration of intrathoracic and upper abdominal organs. As most chest drains are inserted by junior and relatively inexperienced doctors, it is therefore imperative that a simple, safe, and effective technique of insertion is found. A device has been developed that consists of a 5 cm conical length of an expansible cannula, made from rolled metal foil, which when inserted into the chest reaches only a few millimetres within the pleura. When an expander tube, 10 mm in diameter, is passed through the device from its proximal end the conical tube is distended into a hollow cylindrical one, through which a standard Portex chest catheter is passed. The whole appliance is then removed over the end of the tube, leaving the drain in situ. The efficacy of this unique device has been tested in a pilot study in 22 patients. There have been no complications.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. W., Jr, Jung A. L., Lester P. D. Effectiveness of chest tube evacuation of pneumothorax in neonates. J Pediatr. 1981 Oct;99(4):629–634. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80278-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristol J. B., Harvey J. E. Safer insertion of pleural drains. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Jan 29;286(6362):348–349. doi: 10.1136/bmj.286.6362.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney M., Ravin C. E. Intercostal artery laceration during thoracocentesis: increased risk in elderly patients. Chest. 1979 Apr;75(4):520–522. doi: 10.1378/chest.75.4.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy A. C., Luna G. K., Copass M. Empyema thoracis in patients undergoing emergent closed tube thoracostomy for thoracic trauma. Am J Surg. 1989 May;157(5):494–497. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(89)90643-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firmin R. K., Tolhurst-Cleaver C. Safe intrapleural drainage. Anaesthesia. 1980 Jan;35(1):79–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1980.tb03751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R. S. Lung perforation complicating tube thoracostomy: pathologic description of three cases. Hum Pathol. 1988 May;19(5):518–523. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung A. L., Minton S. D., Roan Y. Pulmonary hemorrhage secondary to chest tube placement for pneumothorax in neonates. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1980 Sep;19(9):624–627. doi: 10.1177/000992288001900910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden P. M., Jones J. W. Tube thoracostomy: anatomical considerations, overview of complications, and a proposed technique to avoid complications. Mil Med. 1985 Dec;150(12):681–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. S., Sahn S. A. Chest tubes. Indications, technique, management and complications. Chest. 1987 Feb;91(2):258–264. doi: 10.1378/chest.91.2.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millikan J. S., Moore E. E., Steiner E., Aragon G. E., Van Way C. W., 3rd Complications of tube thoracostomy for acute trauma. Am J Surg. 1980 Dec;140(6):738–741. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moessinger A. C., Driscoll J. M., Jr, Wigger H. J. High incidence of lung perforation by chest tube in neonatal pneumothorax. J Pediatr. 1978 Apr;92(4):635–637. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80311-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmar J. M. How to insert a chest drain. Br J Hosp Med. 1989 Sep;42(3):231–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pingleton S. K., Jeter J. Necrotizing fasciitis as a complication of tube thoracostomy. Chest. 1983 Jun;83(6):925–926. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.6.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark D. D., Federle M. P., Goodman P. C. CT and radiographic assessment of tube thoracostomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983 Aug;141(2):253–258. doi: 10.2214/ajr.141.2.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walesby R. K. How to insert a chest drain and aspirate a pleural effusion. Br J Hosp Med. 1981 Feb;25(2):198–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. J., Krous H. F. Lung perforation during chest tube placement in the stiff lung syndrome. J Pediatr Surg. 1974 Apr;9(2):213–216. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(74)80124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]