Abstract
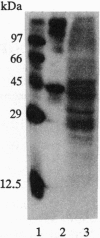
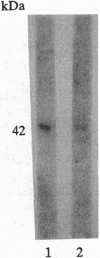
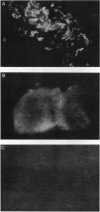
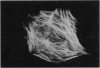
An angiogenin binding protein isolated previously from endothelial cells has been shown to be a member of the actin family. Calf pulmonary artery endothelial (CPAE) cells were investigated for the presence of surface actin by immunoblotting of isolated surface proteins and by immunofluorescence. CPAE cell surface proteins were isolated by selective apical biotinylation and recovery of biotinylated proteins by avidin affinity chromatography. Immunoblotting with a specific smooth muscle alpha-actin antibody detected the presence of this type of actin among the isolated cell surface proteins. Immunofluorescence confirmed that smooth muscle alpha-actin is localized at the surface of nonpermeabilized CPAE cells. Exposure of CPAE cells to angiogenin prior to cell surface immunostaining diminished the signal. When CPAE and rat aortic smooth muscle cells were made permeable before staining, stress fibers could be recognized by the antibody in smooth muscle cells but not CPAE cells. The results indicate that a smooth muscle type of alpha-actin is localized specifically on the surface of cultured CPAE cells where it might interact with angiogenin and other actin binding proteins present in the extracellular environment.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Accinni L., Natali P. G., Silvestrini M., De Martino C. Actin in the extracellular matrix of smooth muscle cells. An immunoelectron microscopic study. Connect Tissue Res. 1983;11(1):69–78. doi: 10.3109/03008208309015012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amberger A., Bauer H., Tontsch U., Gabbiani G., Kocher O., Bauer H. C. Reversible expression of sm alpha-actin protein and sm alpha-actin mRNA in cloned cerebral endothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 5;287(1-2):223–225. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach P. R., Bentley J. P. Structural glycoprotein, fact or artefact. Connect Tissue Res. 1980;7(3):185–196. doi: 10.3109/03008208009152110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak L. S., Yocum R. R., Nothnagel E. A., Webb W. W. Fluorescence staining of the actin cytoskeleton in living cells with 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole-phallacidin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):980–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch G., Hoder D., Reutter W., Tauber R. Selective isolation of individual cell surface proteins from tissue culture cells by a cleavable biotin label. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;50(2):257–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamley J. H., Gröschel-Stewart U., Campbell G. R., Burnstock G. Distinction between smooth muscle, fibroblasts and endothelial cells in culture by the use of fluoresceinated antibodies against smooth muscle actin. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Feb 14;177(4):445–457. doi: 10.1007/BF00220606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Murray A., Segal R. A., Bushnell A., Walsh M. L. Studies on intercellular LETS glycoprotein matrices. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):377–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. W., Meyer D. I. Centractin is an actin homologue associated with the centrosome. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):246–250. doi: 10.1038/359246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeNofrio D., Hoock T. C., Herman I. M. Functional sorting of actin isoforms in microvascular pericytes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):191–202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett J. W., Strydom D. J., Lobb R. R., Alderman E. M., Bethune J. L., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Isolation and characterization of angiogenin, an angiogenic protein from human carcinoma cells. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5480–5486. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett J. W., Strydom D. J., Lobb R. R., Alderman E. M., Bethune J. L., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Isolation and characterization of angiogenin, an angiogenic protein from human carcinoma cells. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5480–5486. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels to a positively charged membrane filter. Anal Biochem. 1982 Aug;124(2):396–405. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Vogel A. M., Gordon D., Lu P. L. A smooth muscle-specific monoclonal antibody recognizes smooth muscle actin isozymes. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):807–813. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallahan T. W., Shapiro R., Vallee B. L. Dual site model for the organogenic activity of angiogenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2222–2226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman I. M., D'Amore P. A. Microvascular pericytes contain muscle and nonmuscle actins. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):43–52. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoock T. C., Newcomb P. M., Herman I. M. Beta actin and its mRNA are localized at the plasma membrane and the regions of moving cytoplasm during the cellular response to injury. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):653–664. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu G. F., Chang S. I., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. An angiogenin-binding protein from endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2227–2231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu G. F., Strydom D. J., Fett J. W., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Actin is a binding protein for angiogenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1217–1221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., Scott-Burden T., Gevers W. Glycoprotein, elastin, and collagen secretion by rat smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):353–357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keski-Oja J., Sen A., Todaro G. J. Direct association of fibronectin and actin molecules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):527–533. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocher O., Gabbiani G. Analysis of alpha-smooth-muscle actin mRNA expression in rat aortic smooth-muscle cells using a specific cDNA probe. Differentiation. 1987;34(3):201–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1987.tb00067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocher O., Madri J. A. Modulation of actin mRNAs in cultured vascular cells by matrix components and TGF-beta 1. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1989 May;25(5):424–434. doi: 10.1007/BF02624627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koteliansky V. E., Glukhova M. A., Morozkin A. D., Musatov A. P., Shirinsky V. P., Tskhovrebova L. A., Smirnov V. N. A study of actin-fibronectin interaction. FEBS Lett. 1981 Oct 12;133(1):31–35. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80464-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bivic A., Real F. X., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Vectorial targeting of apical and basolateral plasma membrane proteins in a human adenocarcinoma epithelial cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9313–9317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees-Miller J. P., Helfman D. M., Schroer T. A. A vertebrate actin-related protein is a component of a multisubunit complex involved in microtubule-based vesicle motility. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):244–246. doi: 10.1038/359244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg U., Eriksson S. Purification from crude extract by affinity chromatography of the inhibitor of deoxyribonucleae I. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Feb;18(4):474–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Caras I. W., Davitz M. A., Rodriguez-Boulan E. A glycophospholipid membrane anchor acts as an apical targeting signal in polarized epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2145–2156. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maes P., Damart D., Rommens C., Montreuil J., Spik G., Tartar A. The complete amino acid sequence of bovine milk angiogenin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maione T. E., Gray G. S., Petro J., Hunt A. J., Donner A. L., Bauer S. I., Carson H. F., Sharpe R. J. Inhibition of angiogenesis by recombinant human platelet factor-4 and related peptides. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.1688470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore F., Riordan J. F. Angiogenin activates phospholipase C and elicits a rapid incorporation of fatty acid into cholesterol esters in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):228–233. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., Auger J., Barber B. H., Edwards A. J., Walsh F. S., Crumpton M. J. Actin may be present on the lymphocyte surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4484–4488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Nowlin D. M., Choi T. B., Yang J., Calaycay J., Shively J. E. Brain capillary 46,000 dalton protein is cytoplasmic actin and is localized to endothelial plasma membrane. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1989 Oct;9(5):675–680. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1989.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders S. K., Craig S. W. A lymphocyte cell surface molecule that is antigenically related to actin. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):370–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargiacomo M., Lisanti M., Graeve L., Le Bivic A., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Integral and peripheral protein composition of the apical and basolateral membrane domains in MDCK cells. J Membr Biol. 1989 Mar;107(3):277–286. doi: 10.1007/BF01871942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Strydom D. J., Olson K. A., Vallee B. L. Isolation of angiogenin from normal human plasma. Biochemistry. 1987 Aug 11;26(16):5141–5146. doi: 10.1021/bi00390a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R., Vallee B. L. Site-directed mutagenesis of histidine-13 and histidine-114 of human angiogenin. Alanine derivatives inhibit angiogenin-induced angiogenesis. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 5;28(18):7401–7408. doi: 10.1021/bi00444a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Ropraz P., Trzeciak A., Benzonana G., Gillessen D., Gabbiani G. A monoclonal antibody against alpha-smooth muscle actin: a new probe for smooth muscle differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2787–2796. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalli O., Vandekerckhove J., Gabbiani G. Actin-isoform pattern as a marker of normal or pathological smooth-muscle and fibroblastic tissues. Differentiation. 1987;33(3):232–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1987.tb01562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soncin F. Angiogenin supports endothelial and fibroblast cell adhesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2232–2236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S., Folkman J. Protamine is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):307–312. doi: 10.1038/297307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]