Abstract
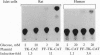
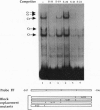
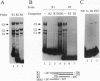
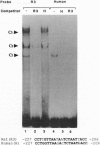
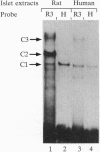
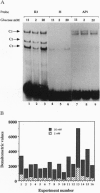
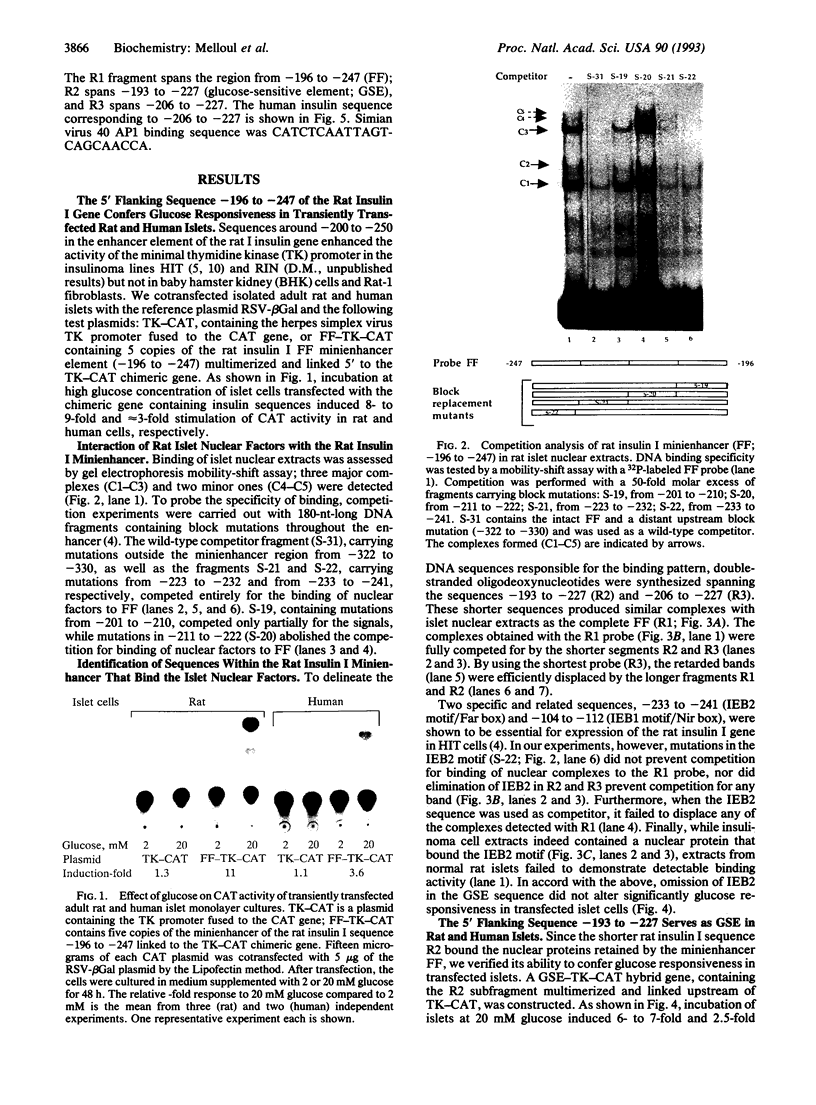
In cultured rat and human pancreatic islets, glucose stimulated transcription of the rat insulin I gene through the mini-enhancer (FF) located between residues -196 and -247. The glucose-sensitive element was delineated to the region -193 to -227. The mini-enhancer bound islet nuclear proteins to form three major complexes (C1-C3). A 22-bp subfragment, spanning the sequence -206 to -227, was sufficient to retain all binding activities of the entire FF. The homologous sequence of the human insulin promoter interacted with rat islet nuclear extracts to form a single complex, corresponding to the C1 complex of the rat insulin I sequence. C1 was present only in insulin-producing cells; it was the major complex detected in isolated human islets with both rat and human insulin sequences. Furthermore, the DNA binding activity of the C1 factor(s) was selectively modulated by extracellular glucose in a dose-dependent manner; a 4.5-fold increase in binding intensity was detected when rat islets were incubated for 1-3 h in the presence of 20 vs. 1-2 mM glucose. We therefore suggest that the factor(s) involved in the C1 complex corresponds to the glucose-sensitive factor and, consequently, may play a determining role in glucose-regulated expression of the insulin gene.
Full text
PDF
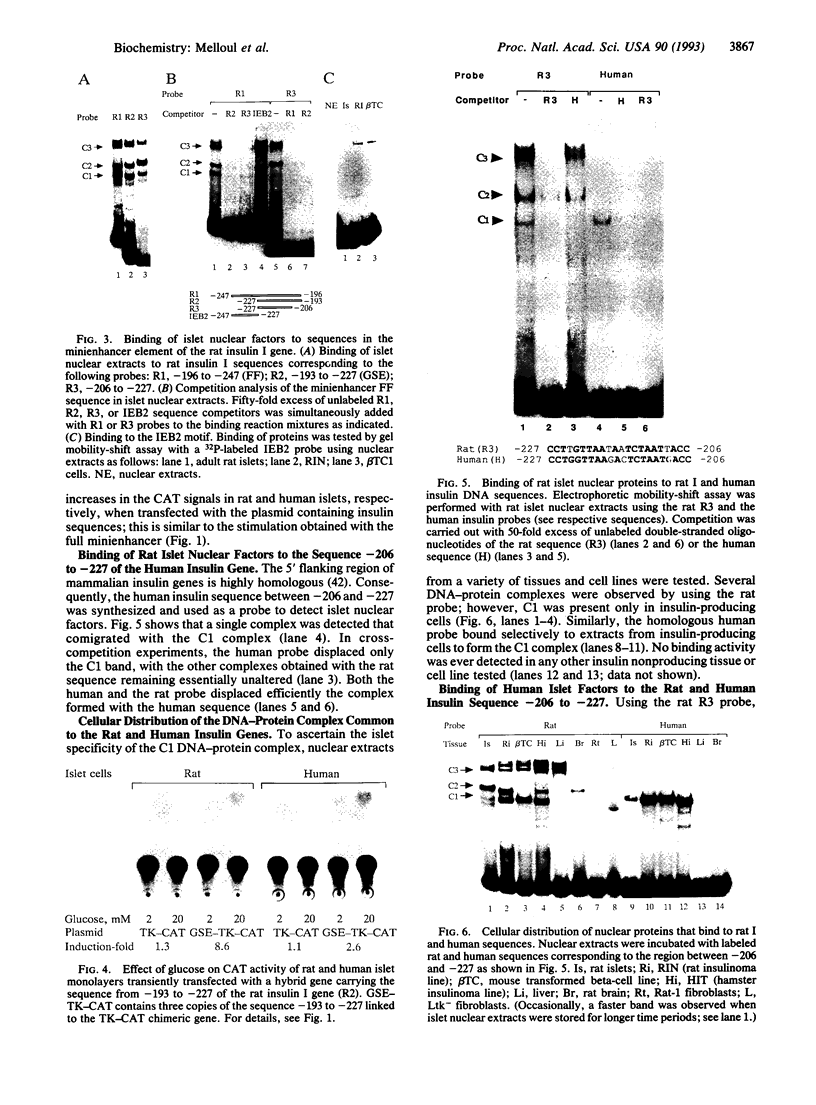
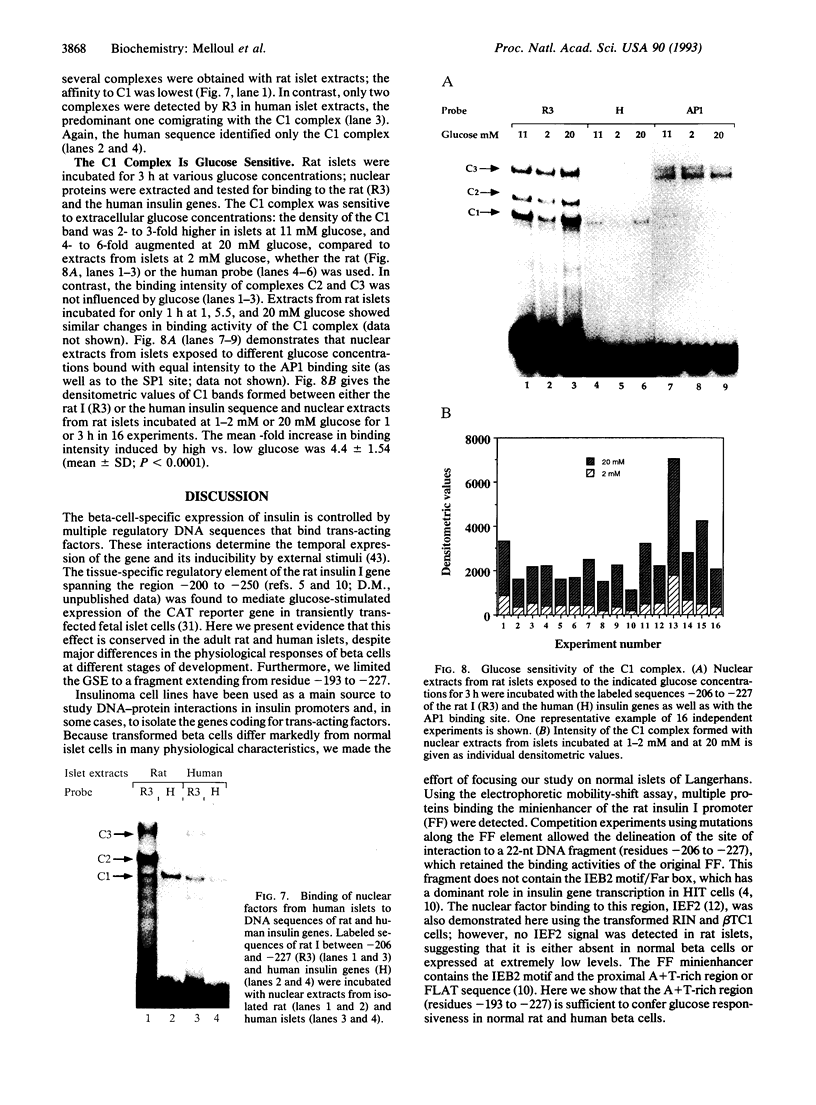

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boam D. S., Clark A. R., Docherty K. Positive and negative regulation of the human insulin gene by multiple trans-acting factors. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8285–8296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boam D. S., Docherty K. A tissue-specific nuclear factor binds to multiple sites in the human insulin-gene enhancer. Biochem J. 1989 Nov 15;264(1):233–239. doi: 10.1042/bj2640233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunstedt J., Chan S. J. Direct effect of glucose on the preproinsulin mRNA level in isolated pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 30;106(4):1383–1389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordle S. R., Henderson E., Masuoka H., Weil P. A., Stein R. Pancreatic beta-cell-type-specific transcription of the insulin gene is mediated by basic helix-loop-helix DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1734–1738. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe D. T., Tsai M. J. Mutagenesis of the rat insulin II 5'-flanking region defines sequences important for expression in HIT cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1784–1789. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong J., Asa S. L., Drucker D. J. Islet cell and extrapancreatic expression of the LIM domain homeobox gene isl-1. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Nov;5(11):1633–1641. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-11-1633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Surana M., Fleischer N. Glucose induces insulin gene transcription in a murine pancreatic beta-cell line. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11141–11143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson J., Thor S., Edlund T., Jessell T. M., Yamada T. Early stages of motor neuron differentiation revealed by expression of homeobox gene Islet-1. Science. 1992 Jun 12;256(5063):1555–1560. doi: 10.1126/science.1350865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M. S., Blanar M. A., Nelson C., Moss L. G., Rutter W. J. Two related helix-loop-helix proteins participate in separate cell-specific complexes that bind the insulin enhancer. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Feb;5(2):292–299. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-2-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M. S., Moss L. G., Rutter W. J. Regulation of insulin gene expression by glucose and calcium in transfected primary islet cultures. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22063–22066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German M. S., Moss L. G., Wang J., Rutter W. J. The insulin and islet amyloid polypeptide genes contain similar cell-specific promoter elements that bind identical beta-cell nuclear complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1777–1788. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Chirgwin J. M., Permutt M. A. Glucose regulated insulin biosynthesis in isolated rat pancreatic islets is accompanied by changes in proinsulin mRNA. Diabetes Res. 1985 Mar;2(2):71–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Chirgwin J., Permutt M. A. Effects of glucose on proinsulin messenger RNA in rats in vivo. Diabetes. 1982 Jul;31(7):624–629. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.7.624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grill V., Asplund K., Hellerström C., Cerasi E. Decreased cyclic AMP and insulin response to glucose in isolated islets of neonatal rats. Diabetes. 1975 Aug;24(8):746–752. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.8.746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds P., Schofield P. N., Ashcroft S. J. Glucose regulates preproinsulin messenger RNA levels in a clonal cell line of simian virus 40-transformed B cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 9;213(1):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81481-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds P., Schofield P. N., Ashcroft S. J., Sutton R., Gray D. W. Regulation and specificity of glucose-stimulated insulin gene expression in human islets of Langerhans. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 19;223(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80523-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Heritable formation of pancreatic beta-cell tumours in transgenic mice expressing recombinant insulin/simian virus 40 oncogenes. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):115–122. doi: 10.1038/315115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwung Y. P., Crowe D. T., Wang L. H., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J. The COUP transcription factor binds to an upstream promoter element of the rat insulin II gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2070–2077. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwung Y. P., Gu Y. Z., Tsai M. J. Cooperativity of sequence elements mediates tissue specificity of the rat insulin II gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1784–1788. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser N., Corcos A. P., Tur-Sinai A., Ariav Y., Cerasi E. Monolayer culture of adult rat pancreatic islets on extracellular matrix: long term maintenance of differentiated B-cell function. Endocrinology. 1988 Aug;123(2):834–840. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-2-834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. Signal transduction from cell surface to nucleus in development and disease. FASEB J. 1992 May;6(8):2581–2590. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.8.1317309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Edlund T., Moss J. B., Rutter W. J., Walker M. D. A mutational analysis of the insulin gene transcription control region: expression in beta cells is dependent on two related sequences within the enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8819–8823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Thor S., Norberg T., Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Insulin gene enhancer binding protein Isl-1 is a member of a novel class of proteins containing both a homeo- and a Cys-His domain. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):879–882. doi: 10.1038/344879a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson O., Walker M. D., Rutter W. J., Edlund T. Individual protein-binding domains of the insulin gene enhancer positively activate beta-cell-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):823–827. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss L. G., Moss J. B., Rutter W. J. Systematic binding analysis of the insulin gene transcription control region: insulin and immunoglobulin enhancers utilize similar transactivators. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2620–2627. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen D. A., Welsh M., Casadaban M. J., Steiner D. F. Control of insulin gene expression in pancreatic beta-cells and in an insulin-producing cell line, RIN-5F cells. I. Effects of glucose and cyclic AMP on the transcription of insulin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13585–13589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Karlsson O., Edlund T. A beta-cell-specific protein binds to the two major regulatory sequences of the insulin gene enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4228–4231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Thor S., Edlund T. Novel insulin promoter- and enhancer-binding proteins that discriminate between pancreatic alpha- and beta-cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;5(7):897–904. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-7-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Permutt M. A., Kipnis D. M. Insulin biosynthesis. I. On the mechanism of glucose stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1194–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki M., Matschinsky F. M. Ca2+, cAMP, and phospholipid-derived messengers in coupling mechanisms of insulin secretion. Physiol Rev. 1987 Oct;67(4):1185–1248. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1987.67.4.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott V., Clark A. R., Hutton J. C., Docherty K. Two proteins act as the IUF1 insulin gene enhancer binding factor. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 23;290(1-2):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81217-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodoyez-Goffaux F., Sodoyez J. C., Foà P. P. Effects of gestational age, birth and feeding on the insulinogenic response to glucose and tolbutamide by fetal and newborn rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1971 Sep;20(9):586–591. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.9.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Park C. W., Rosen A., Aronheim A. A cDNA from a mouse pancreatic beta cell encoding a putative transcription factor of the insulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1159–1166. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M., Nielsen D. A., MacKrell A. J., Steiner D. F. Control of insulin gene expression in pancreatic beta-cells and in an insulin-producing cell line, RIN-5F cells. II. Regulation of insulin mRNA stability. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13590–13594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J., Cordle S. R., Henderson E., Weil P. A., Stein R. Identification of a pancreatic beta-cell insulin gene transcription factor that binds to and appears to activate cell-type-specific expression: its possible relationship to other cellular factors that bind to a common insulin gene sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1564–1572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelan J., Poon D., Weil P. A., Stein R. Pancreatic beta-cell-type-specific expression of the rat insulin II gene is controlled by positive and negative cellular transcriptional elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3253–3259. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]